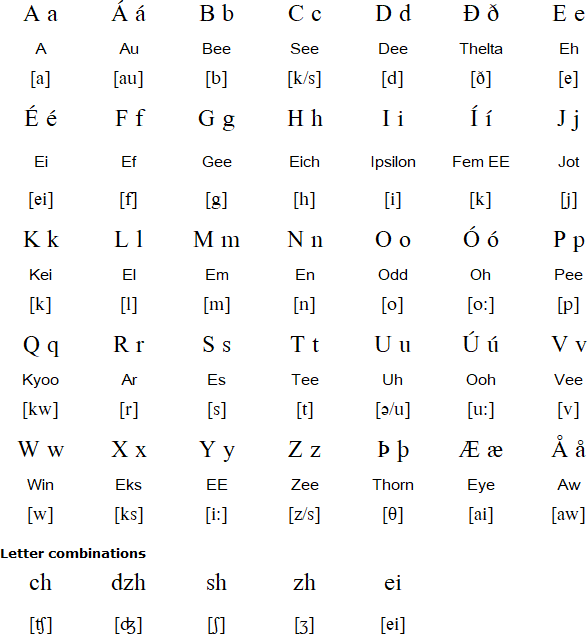
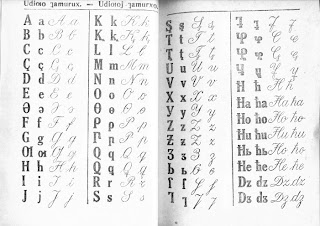
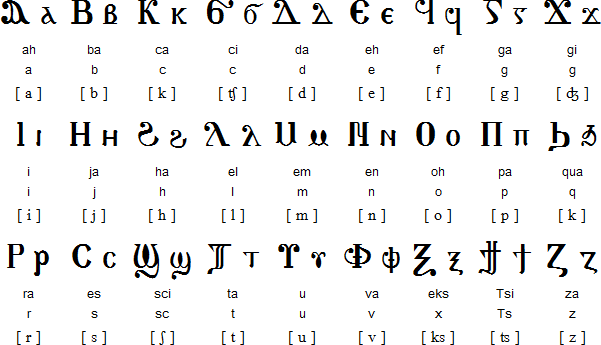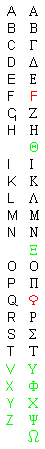Latin Alphabet Is

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
РекламаНайди быстро и удобно выгодное предложение на сервисе сравнения цен - E-katalog
каталог товаров · советы покупателям
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world today. It evolved from the western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, and was initially developed by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language.. During the Middle Ages, it was adapted to the Romance languages, the direct descendants of Latin, as well ...
religion.wikia.org/wiki/Latin_alphabet
Where does the name Latin alphabet come from?
Where does the name Latin alphabet come from?
Latin alphabet is the alphabet most of the West is commonly using. It originates from Roman alphabet, rooting in the Greek alphabet (giving the alphabet its name, from greek Alpha and Beta, the first two letters).
www.quora.com/What-Is-the-Latin-Alphabet
How many letters are in the ancient Latin alphabet?
How many letters are in the ancient Latin alphabet?
The classical Latin alphabet consisted of 23 letters, 21 of which were derived from the Etruscan alphabet. In medieval times the letter I was differentiated into I and J and V into U, V, and W, producing an alphabet equivalent to that of modern English with 26 letters.
www.britannica.com/topic/Latin-alphabet
Is the Roman alphabet the same as the English alphabet?
Is the Roman alphabet the same as the English alphabet?
We use the Latin (Roman) alphabet to write English and very many other modern languages. It is true that in classical times the letters J & W had not developed, and there was little to distinguish between V and U when they were written, but they were different letters.
www.quora.com/What-Is-the-Latin-Alphabet
Which is the most widely used alphabet in the world?
Which is the most widely used alphabet in the world?
Latin alphabet. Written By: Latin alphabet, also called Roman alphabet, most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world, the standard script of the English language and the languages of most of Europe and those areas settled by Europeans.
www.britannica.com/topic/Latin-alphabet
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latin_alphabet
Child systems: Numerous Latin alphabets; …
Parent systems: Egyptian hieroglyphsProto …
Sister systems: Cyrillic, Coptic, Armenian, …
Unicode alias: Latin
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language and its extensions used to write modern languages.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latin_alphabets
Ориентировочное время чтения: 3 мин
Опубликовано: 25.11.2003
Letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet
Alphabets that contain all ISO basic Latin letters
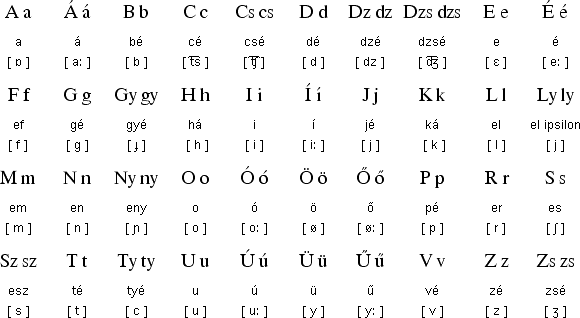
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) includes all 26 letters in their lowercase forms, although g is always single-storey (ɡ) in the IPA and never double-storey ().
Among alphabets for natural languages the Achomi , Afrikaans, Aromanian, Azeri (some dialects) , Basque, , Celtic British, Catalan, Corni…
Alphabets that contain all ISO basic Latin letters
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) includes all 26 letters in their lowercase forms, although g is always single-storey (ɡ) in the IPA and never double-storey ().
Among alphabets for natural languages the Achomi , Afrikaans, Aromanian, Azeri (some dialects) , Basque, , Celtic British, Catalan, Cornish, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Emilian-Romagnol, English, Filipino, Finnish, French, , German, Greenlandic, Hungarian, Indonesian, Javanese, Karakalpak, Kurdish, Modern Latin, Luxembourgish, Malay, Norwegian, Oromo , Papiamento , Polish , Portuguese, Quechua, Rhaeto-Romance, Romanian, Slovak, Spanish, Sundanese, Swedish, Tswana, Tunisian Arabic, Uyghur, Venda, Võro, Walloon, West Frisian, Xhosa, Zhuang, Zulu alphabets include all 26 letters, at least in their largest version.
Among alphabets for constructed languages the Ido, Interglossa, Interlingua, Occidental alphabets include all 26 letters.
Alphabets that do not contain all ISO basic Latin letters
This list is based on official definitions of each alphabet. Still, missing letters might occur in non-integrated loan words and place names.
The I is used in two distinct versions in Turkic languages, dotless (I ı) and dotted (İ i). They are considered different letters, and case conversion must take care to preserve the distinction. Irish traditionally does not write the dot, or tittle, over the small letter i, but the language makes no distinction here if a dot is displayed, so no specific encoding and special case conversion rule is needed like for Turkic alphabets.
Statistics
The chart above lists a variety of alphabets that do not officially contain all 26 letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet. In this list, one letter is used by all of them: A. For each of the 26 basic ISO Latin alphabet letters, the number of alphabets in the list above using it is as follows:
Letters not contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet
Лати́нский алфави́т — восходящая к греческому алфавиту буквенная письменность, возникшая в латинском …
Языки: Первоначально латинский · языки Западной · Центральной и Северной Европы · некоторые языки Азии · мног…
Территория: Первоначально Италия · затем Западная · Центральная и Северная Европа · частично Южная Европа · вся Америка
Период: 700 г. до н. э. по настоящее время
Место возникновения, Дата создания и другое
Текст из Википедии, лицензия CC-BY-SA
https://www.britannica.com/topic/Latin-alphabet
Перевести · 2 дн. назад · Latin alphabet, the most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world, the standard script of the English language and the languages of most of Europe and those areas settled by Europeans. It can be traced through the Etruscan, Greek, and Phoenician scripts to the North Semitic alphabet …
https://www.quora.com/What-Is-the-Latin-Alphabet
Перевести · Latin alphabet is the alphabet most of the West is commonly using. It originates from Roman alphabet, rooting in the Greek alphabet (giving the alphabet its …
Latin alphabet is the alphabet most of the West is commonly using. It originates from Roman alphabet, rooting in the Greek alphabet (giving the alp...
Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is a writing system originally used to write the Latin Language. The Latin alphabet evolved from...
There are two closely related meanings of the term Latin alphabet. 1. The alphabet used to write the Latin language. It was derived from the Greek...
We use the Latin (Roman) alphabet to write English and very many other modern languages. It is true that in classical times the letters J & W had n...
Approximately the same as our modern English alphabet, but they had no J, using I for both sounds. Note that so many languages today use J for the...
Some Vietnamese Historians assumed that ancient Vietnamese might have used something that looks like tadpole script like some other tribes in Pacif...
Short Answer In the XIX century Romanians switched back from the Cyrilic to the Latin alphabet in an effort to: 1.Emphasize the Latin heritage and...
Because they found that this Western-based alphabet actually helped them defeat a Western colonial power, that's why! A quick history lesson: Alexa...
Thanks for asking. An alphabet is actually a set of graphic symbols invented and developed to stand for the sounds in the spoken language. Most lan...
Edit: Apparently, I failed reading comprehension and gave arguments for not replacing the Thai alphabet, instead So here is why it should be replac...
https://mahdi.cheraghchi.info/downloads/latin_for_mountain_men.pdf
21.07.2002 · The Latin Alphabet The Latin alphabet of 23 letters was derived in the 600's BC from the Etruscan alphabet of 26 letters, which was in turn derived from the archaic Greek alphabet, which came from the Phoenician. The letters J, U, and W of the modern alphabet were added in medieval times, and did not appear in the classical alphabet…
https://ru.abcdef.wiki/wiki/Latin_alphabet
This page is based on the copyrighted Wikipedia article "Latin_alphabet" ; it is used under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. You may …
https://www.quora.com/Which-alphabet-is-better-Latin-or-Cyrillic
Перевести · There might be different aspects of what “a good alphabet” means. I can think of the following: * Suitability: If applied to Slavic languages, both are roughly equally good. The differences are the following: * * The Latin …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Latin-script_digraphs
Перевести · In the Ossete Latin alphabet, it is used for /ɡʷ/. gü is used in the Spanish and Catalan orthographies for /ɡw/ before front vowels i e where the digraph gu would …
РекламаНайди быстро и удобно выгодное предложение на сервисе сравнения цен - E-katalog
каталог товаров · советы покупателям
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
This article is about the alphabet used to write the Latin language. For modern alphabets derived from it used in other languages and applications, see Latin script and Latin-script alphabet.
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language and its extensions used to write modern languages.
12 sovereign states and 1 supranational organization
Numerous Latin alphabets; also more divergent derivations such as Osage
This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters.
The term Latin alphabet may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new letters, like the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. Letter shapes have evolved over the centuries, including the development in Medieval Latin of lower-case, forms which did not exist in the Classical period alphabet.
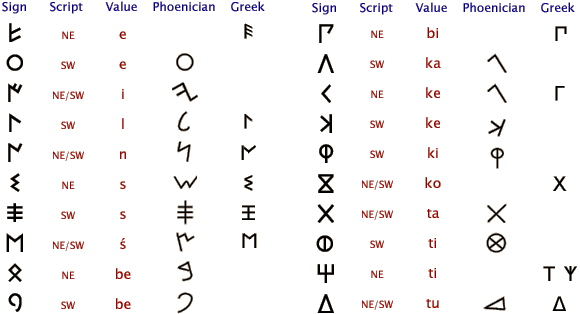
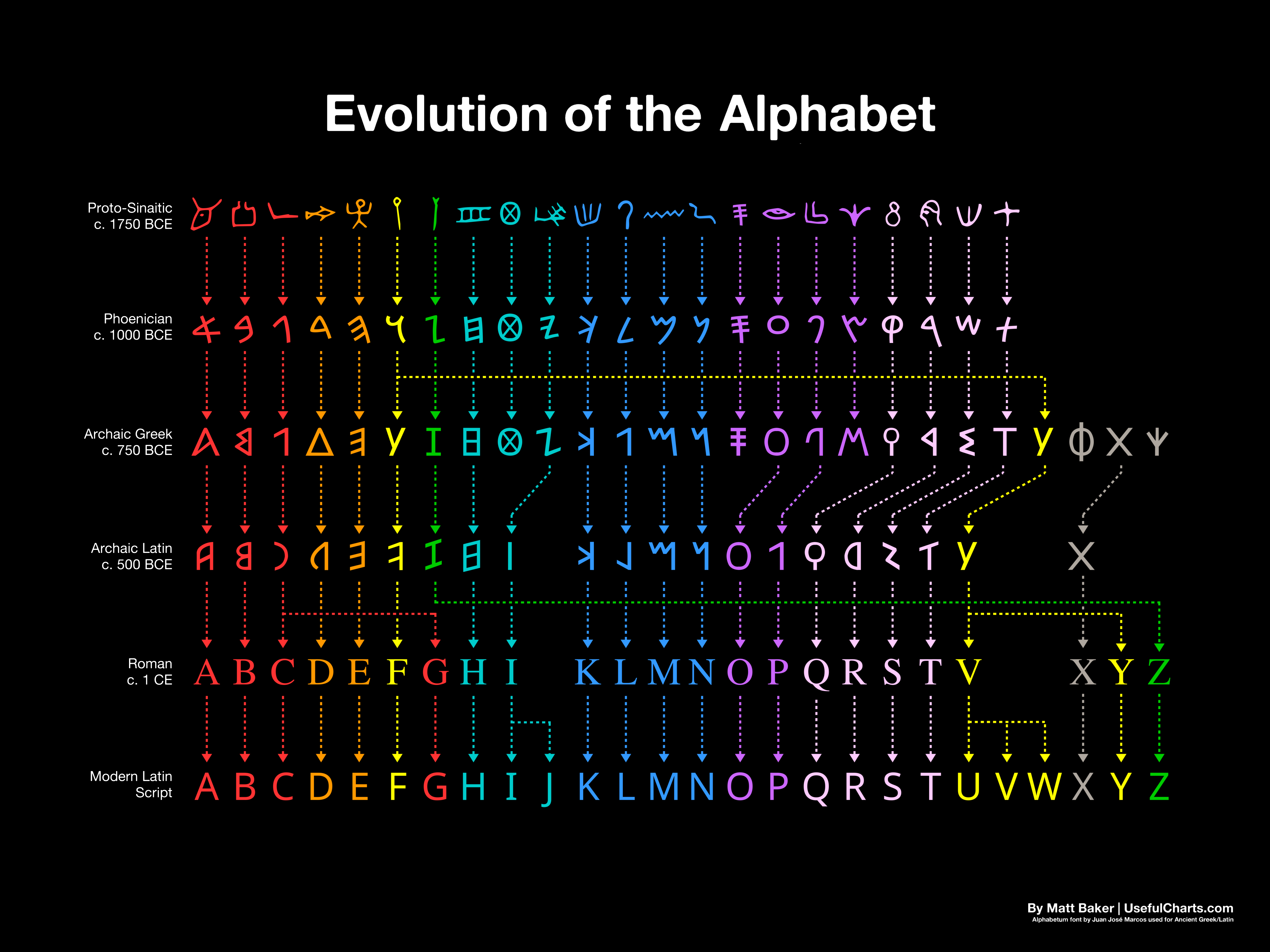
The Latin alphabet evolved from the visually similar Etruscan alphabet, which evolved from the Cumaean Greek version of the Greek alphabet, which was itself descended from the Phoenician alphabet, which in turn derived from Egyptian hieroglyphics.[1] The Etruscans ruled early Rome; their alphabet evolved in Rome over successive centuries to produce the Latin alphabet. During the Middle Ages, the Latin alphabet was used (sometimes with modifications) for writing Romance languages, which are direct descendants of Latin, as well as Celtic, Germanic, Baltic and some Slavic languages. With the age of colonialism and Christian evangelism, the Latin script spread beyond Europe, coming into use for writing indigenous American, Australian, Austronesian, Austroasiatic and African languages. More recently, linguists have also tended to prefer the Latin script or the International Phonetic Alphabet (itself largely based on the Latin script) when transcribing or creating written standards for non-European languages, such as the African reference alphabet.
Although Latin did not use diacritical signs, signs of truncation of words, often placed above the truncated word or at the end of it, were very common. Furthermore, abbreviations or smaller overlapping letters were often used. This was due to the fact that if the text was engraved on the stone, the number of letters to be written was reduced, while if it was written on paper or parchment, it saved precious space. This habit continued even in the Middle Ages. Hundreds of symbols and abbreviations exist, varying from century to century.[2]
It is generally believed that the Latin alphabet used by the Romans was derived from the Old Italic alphabet used by the Etruscans.[citation needed] That alphabet was derived from the Euboean alphabet used by the Cumae, which in turn was derived from the Phoenician alphabet.[citation needed]
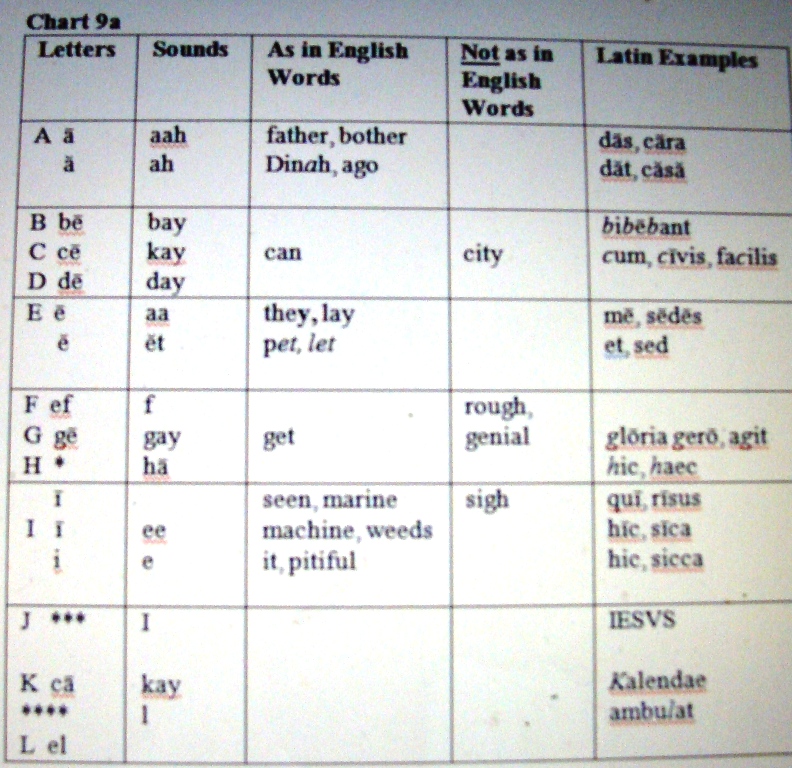
Latin included 21 different characters. The letter ⟨C⟩ was the western form of the Greek gamma, but it was used for the sounds /ɡ/ and /k/ alike, possibly under the influence of Etruscan, which might have lacked any voiced plosives. Later, probably during the 3rd century BC, the letter ⟨Z⟩ – unneeded to write Latin properly – was replaced with the new letter ⟨G⟩, a ⟨C⟩ modified with a small vertical stroke, which took its place in the alphabet. From then on, ⟨G⟩ represented the voiced plosive /ɡ/, while ⟨C⟩ was generally reserved for the voiceless plosive /k/. The letter ⟨K⟩ was used only rarely, in a small number of words such as Kalendae, often interchangeably with ⟨C⟩.
After the Roman conquest of Greece in the 1st century BC, Latin adopted the Greek letters ⟨Y⟩ and ⟨Z⟩ (or readopted, in the latter case) to write Greek loanwords, placing them at the end of the alphabet. An attempt by the emperor Claudius to introduce three additional letters did not last. Thus it was during the classical Latin period that the Latin alphabet contained 23 letters:
The Latin names of some of these letters are disputed; for example, ⟨H⟩ may have been called Latin pronunciation: [ˈaha] or Latin pronunciation: [ˈaka].[3] In general the Romans did not use the traditional (Semitic-derived) names as in Greek: the names of the plosives were formed by adding /eː/ to their sound (except for ⟨K⟩ and ⟨Q⟩, which needed different vowels to be distinguished from ⟨C⟩) and the names of the continuants consisted either of the bare sound, or the sound preceded by /e/.
The letter ⟨Y⟩ when introduced was probably called "hy" /hyː/ as in Greek, the name upsilon not being in use yet, but this was changed to "i Graeca" (Greek i) as Latin speakers had difficulty distinguishing its foreign sound /y/ from /i/. ⟨Z⟩ was given its Greek name, zeta. This scheme has continued to be used by most modern European languages that have adopted the Latin alphabet. For the Latin sounds represented by the various letters see Latin spelling and pronunciation; for the names of the letters in English see English alphabet.
Diacritics were not regularly used, but they did occur sometimes, the most common being the apex used to mark long vowels, which had previously sometimes been written doubled. However, in place of taking an apex, the letter i was written taller: ⟨á é ꟾ ó v́⟩. For example, what is today transcribed Lūciī a fīliī was written ⟨lv́ciꟾ·a·fꟾliꟾ⟩ in the inscription depicted.
The primary mark of punctuation was the interpunct, which was used as a word divider, though it fell out of use after 200 AD.
Old Roman cursive script, also called majuscule cursive and capitalis cursive, was the everyday form of handwriting used for writing letters, by merchants writing business accounts, by schoolchildren learning the Latin alphabet, and even emperors issuing commands. A more formal style of writing was based on Roman square capitals, but cursive was used for quicker, informal writing. It was most commonly used from about the 1st century BC to the 3rd century, but it probably existed earlier than that. It led to Uncial, a majuscule script commonly used from the 3rd to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes.
New Roman cursive script, also known as minuscule cursive, was in use from the 3rd century to the 7th century, and uses letter forms that are more recognizable to modern eyes; ⟨a⟩, ⟨b⟩, ⟨d⟩, and ⟨e⟩ had taken a more familiar shape, and the other letters were proportionate to each other. This script evolved into the medieval scripts known as Merovingian and Carolingian minuscule.
It was not until the Middle Ages that the letter ⟨W⟩ (originally a ligature of two ⟨V⟩s) was added to the Latin alphabet, to represent sounds from the Germanic languages which did not exist in medieval Latin, and only after the Renaissance did the convention of treating ⟨I⟩ and ⟨U⟩ as vowels, and ⟨J⟩ and ⟨V⟩ as consonants, become established. Prior to that, the former had been merely allographs of the latter.[citation needed]
With the fragmentation of political power, the style of writing changed and varied greatly throughout the Middle Ages, even after the invention of the printing press. Early deviations from the classical forms were the uncial script, a development of the Old Roman cursive, and various so-called minuscule scripts that developed from New Roman cursive, of which the insular script developed by Irish literati & derivations of this, such as Carolingian minuscule were the most influential, introducing the lower case forms of the letters, as well as other writing conventions that have since become standard.
The languages that use the Latin script generally use capital letters to begin paragraphs and sentences and proper nouns. The rules for capitalization have changed over time, and different languages have varied in their rules for capitalization. Old English, for example, was rarely written with even proper nouns capitalized, whereas Modern English writers and printers of the 17th and 18th century frequently capitalized most and sometimes all nouns,[4] which is still systematically done in Modern German, e.g. in the preamble and all of the United States Constitution: We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.
The Latin alphabet spread, along with the Latin language, from the Italian Peninsula to the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea with the expansion of the Roman Empire. The eastern half of the Empire, including Greece, Anatolia, the Levant, and Egypt, continued to use Greek as a lingua franca, but Latin was widely spoken in the western half, and as the western Romance languages evolved out of Latin, they continued to use and adapt the Latin alphabet.
With the spread of Western Christianity during the Middle Ages, the script was gradually adopted by the peoples of northern Europe who spoke Celtic languages (displacing the Ogham alphabet) or Germanic languages (displacing earlier Runic alphabets), Baltic languages, as well as by the speakers of several Uralic languages, most notably Hungarian, Finnish and Estonian. The Latin alphabet came into use for writing the West Slavic languages and several South Slavic languages, as the people who spoke them adopted Roman Catholicism.
Later, it was adopted by
Russian Real Anal
Big Pussy Masturbation
Le Wood Anal
Skinny Teen Porno Online
1 8 Sex
Latin alphabet - Wikipedia
List of Latin-script alphabets - Wikipedia
Latin alphabet | Definition, Description, History, & Facts ...
The Latin Alphabet Page 1 of 58 The Latin Alphabet
Латинский алфавит - Latin alphabet - abcdef.wiki
Which alphabet is better, Latin or Cyrillic? - Quora
List of Latin-script digraphs - Wikipedia
Latin Alphabet Is
.svg/9122px-Adyghe_latin_alphabet_(1927).svg.png)