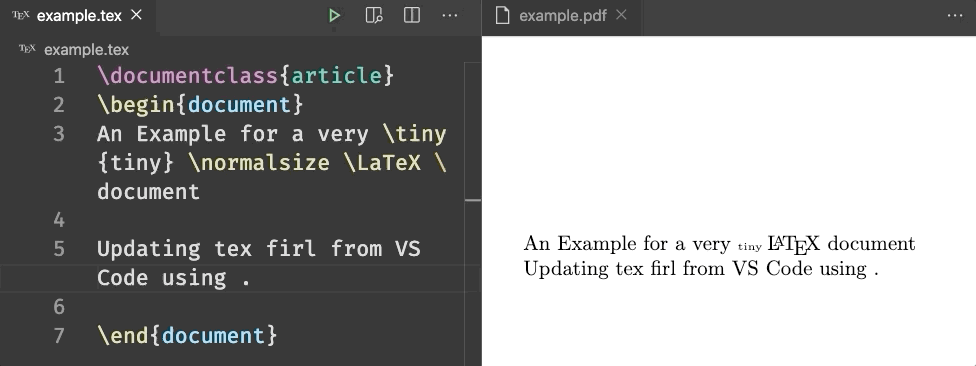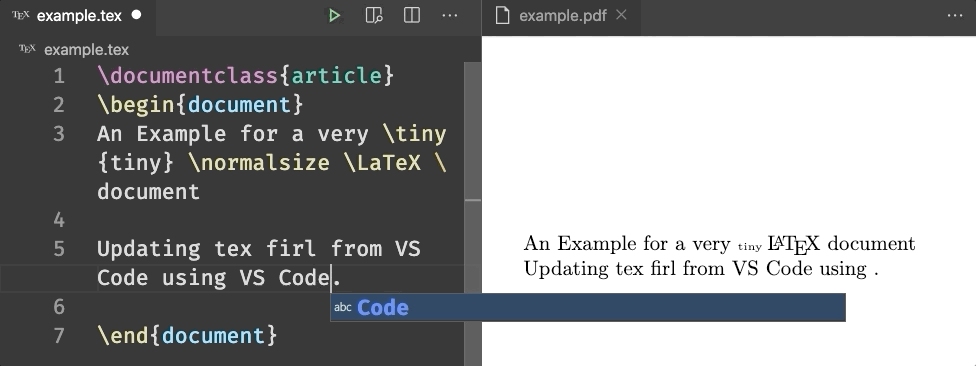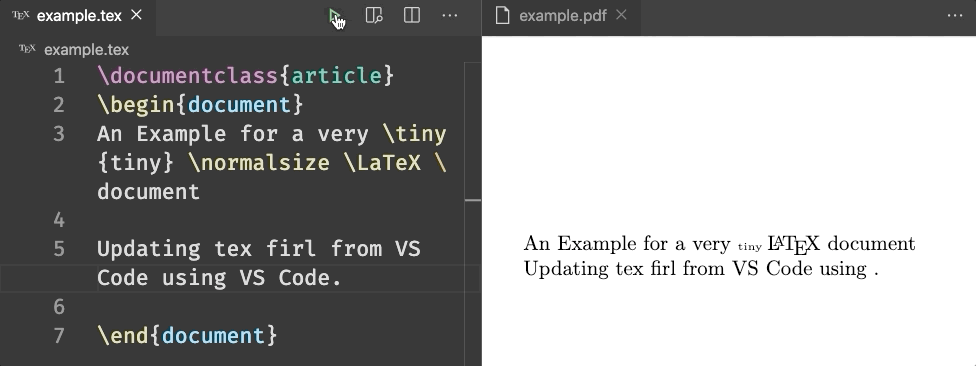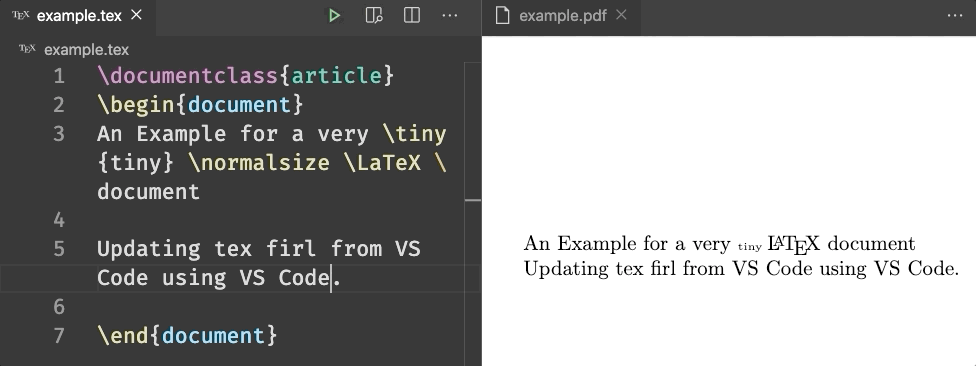
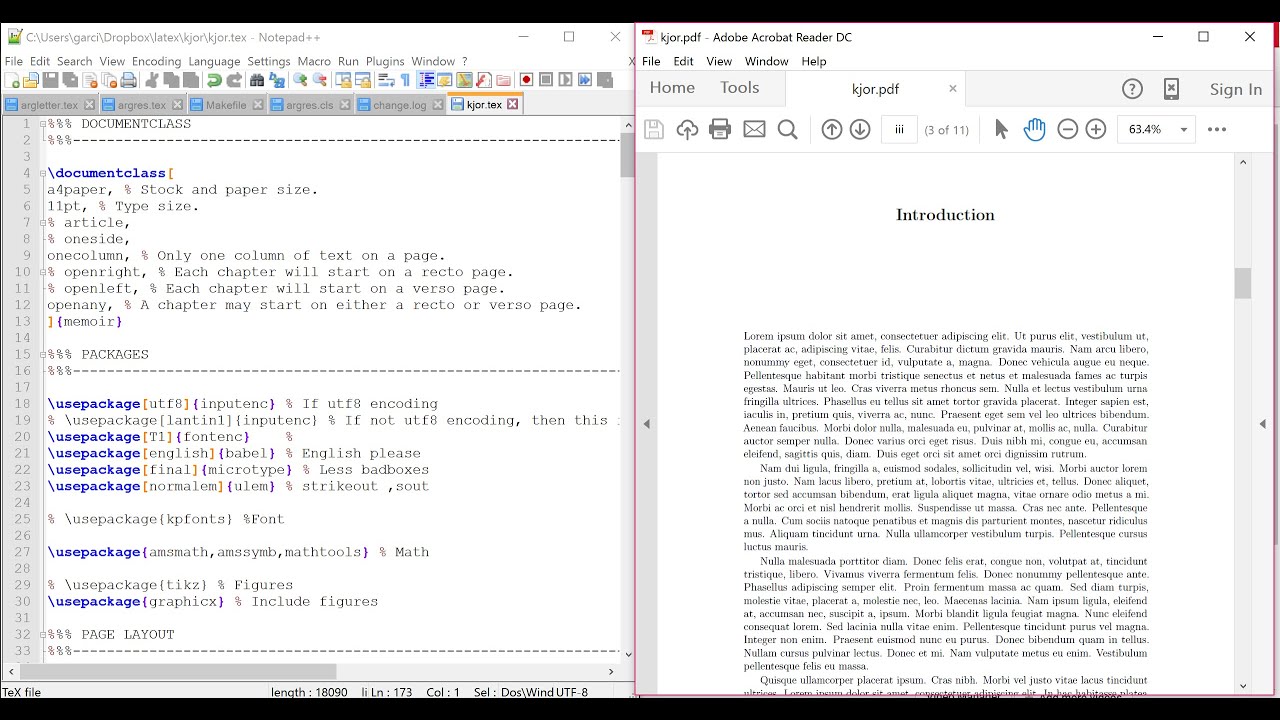
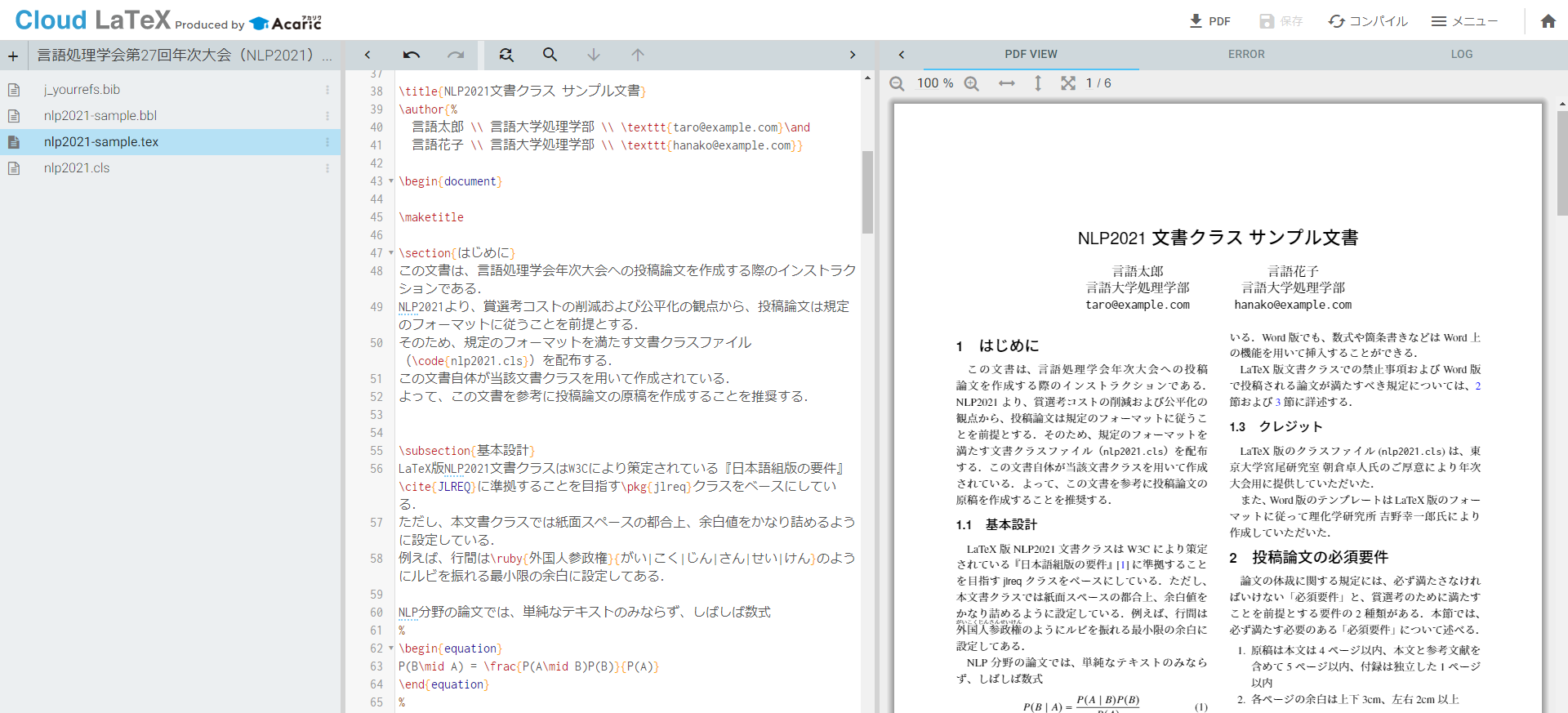
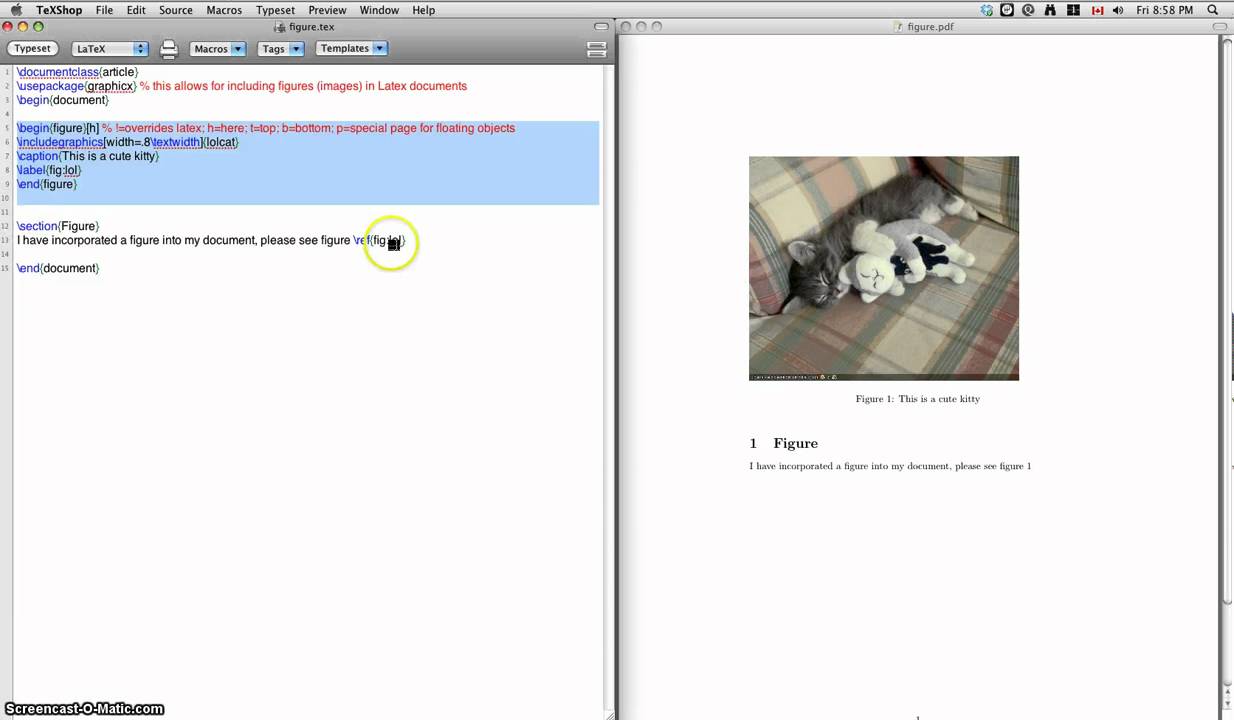
Latex Environment

🛑 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
A LaTeX environment is one of the following:
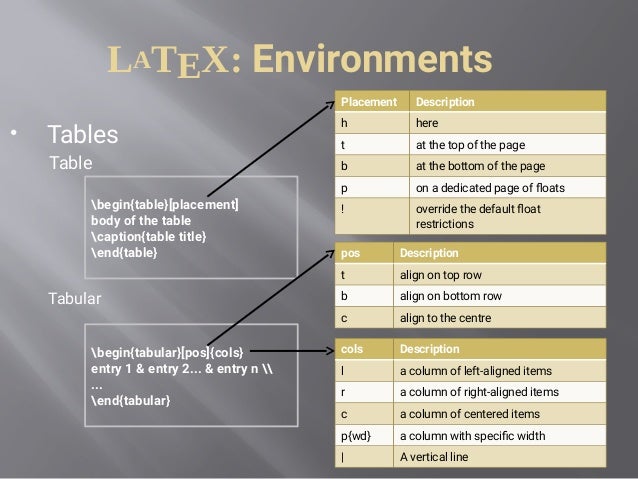
Text inside a float environment is "floated" according to its placement, an optional parameter. The standard report and article classes use the default placement [tbp]. The float environments are figure and table.
\begin{figure}[placement]
% body of the figure
\caption{figure title}
\end{figure}
The table environment has the same characteristics as the figure environment.[improvement needed: elaborate]
The list environments are description, enumerate, itemize, and the generic list, which is seldom used in text, but often in macros. Within a list environment item commands are used to identify the items in the list.
The description environment produces a labeled list.
\begin{description}
\item [label] First item
\item [label] Second item
The enumerate environment produces a numbered list. At least one item is needed. Enumerate lists can be nested inside other enumerate lists, up to four levels deep.
\begin{enumerate}
\item First item
\item Second item
The itemize environment creates an unnumbered, or "bulleted" list.
\begin{itemize}
\item First item
\item Second item
\begin{list}{label}{fmt-params}
\item First item
\item Second item
The math environments are math, displaymath, array, eqnarray, equation, and theorem
The math environment is used within paragraph mode to place mathematical symbols inline with the paragraph's text. The following are all equivalent:
In a wiki, the ... tags create a math environment.
Note: The AMS Short Math Guide recommends against using $$ ... $$ to enter displaymath mode, because it is not documented in the TeX manual, and because it interferes with the proper operation of the fleqn option.
The split environment is used to write multiple lines that are aligned using the ampersand (&) character.
a& =b+c-d\\
& \quad +e-f\\
& =g+h\\
\end{split}
Failed to parse (unknown function "\begin{split}"): {\displaystyle \begin{split} a& =b+c-d\\ & \quad +e-f\\ & =g+h\\ \end{split}}
The array environment is used to make a table of information, with column alignment (left, center, or right) and optional vertical lines separating the columns.
\begin{array}{col1col2…coln}
item11 & item12 … & item1n\\
item21 & item22 … & item2n\\
itemn1 & itemn2 … & itemnn\\
\end{array}
Each of col1, col2, etc. is a single letter,
If a horizontal line is needed in the matrix, \hline can be used.
Within the matrix itself, columns are separated by an &, and each row ends with a double backslash, \\.
\begin{eqnarray}
math formula 1
math formula 2
An equation number is placed on every line unless that line has a \nonumber command. The command \lefteqn is used for splitting long formulas across lines. It typesets its argument in display style flush left in a box of zero width.
The equation environment centers the equation, and places an equation number in the right margin.
\begin{equation}
... math formula
\end{equation}
An asterisk is used for unnumbered equations:
\begin{equation*}
... math formula
\end{equation*}
An equation can be given a label using the \label command, which can later be referenced using the \eqref command.
\begin{equation}\label{xyz}
... math formula
\end{equation}
... using equation \eqref{xyz}, one can derive the following...
The subequations environment affixes letters a, b, c... to the end of the equation number within the environment.
\begin{equation}\label{first}
x=y+z
\end{equation}
some intervening text
\begin{subequations}\label{grp}
\begin{align}
a&=b+c\label{second}\\
d&=e+f+g\label{third}\\
h&=i+j\label{fourth}
\end{align}
\end{subequations}
The multiline environment lets you split equations over multiple lines, aligning the beginning of the equation with the left margin, and the end of it with the right margin. Equations are numbered.
\begin{multline}
a+b+c+d+e+f\\
+i+j+k+l+m+n
\end{multline}
The gather environment gathers and centers equations; each equation is numbered; not available in wiki.
\begin{gather} a_1=b_1+c_1\\
a_2=b_2+c_2-d_2+e_2
\end{gather}
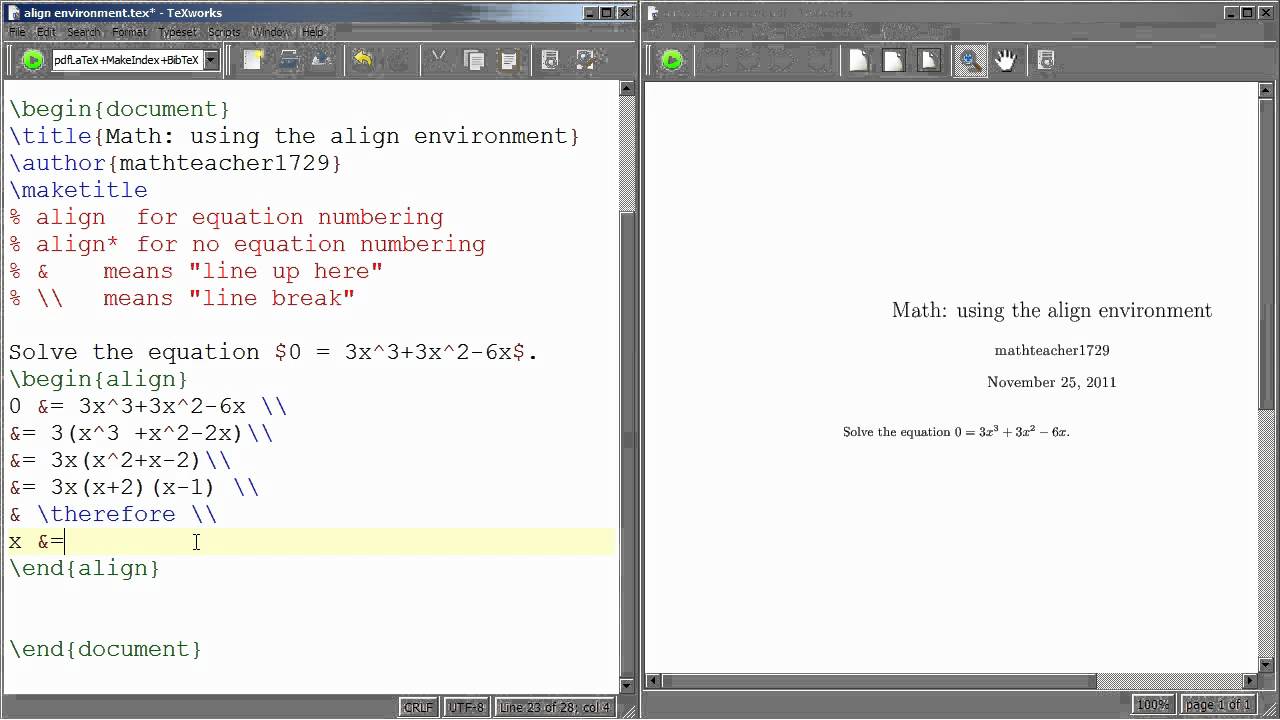
The align environment lets you use the ampersand (&) to align multiple equations; each equation is numbered; not available in wiki.
\begin{align}
a_{11}& =b_{11}&
a_{12}& =b_{12}\\
a_{21}& =b_{21}&
a_{22}& =b_{22}+c_{22} \end{align}
The flalign environment lets you use the ampersand (&) to align multiple equations. The leftmost and rightmost columns are aligned with the margins.
\begin{flalign*}
a_{11}& =b_{11}&
a_{12}& =b_{12}\\
a_{21}& =b_{21}&
a_{22}& =b_{22}+c_{22} \end{flalign*}
The theorem environment produces "Therem x" in bold face, followed by your theorem text. [improvement needed: elaborate - how is theorem name specified?]
\begin{theorem}
... theorem text
\end{theorem}
The matrix environments are matrix, pmatrix, bmatrix, Bmatrix, vmatrix, Vmatrix, and smallmatrix. Each provides a table for expressions, aligned in rows and columns. The main difference between the various types of matrix is the kind of delimeters that surround them.
Each row of a matrix ends with two backslashes (\\). Each column ends with an ampersand (&).
The cases environment is used to left-brace a group of equations or a piecewise-defined function, for example,
f(n) = \begin{cases} n/2 &\mbox{if } n \equiv 0 \\
(3n +1)/2 & \mbox{if } n \equiv 1. \end{cases} \pmod{2}
The align environment can be used to align equations.
\begin{align}
f(x) & = (a+b)^2 \\
& = a^2+2ab+b^2
\end{align}
The alignat environment can be used to align equations, and explicitly specify the number of "equation" columns. An equation column has two parts, separated by the equals-sign. Essentially, this is an array with alternating right-aligned and left-aligned columns. The required parameter of alignat is the maximum number of ampersands in a row plus 1, and then divided by 2. One use of alignat is to explicitly specify the amount of horizontal space between columns by including the required spacing in the first row.
\begin{alignat}{2}
r&l\quad\quad\quad&r&l\\
a& =b &\quad\quad c& =d\\
aaa& =bbb& ccc& =ddd
\end{alignat}
aligning a series of equations, specifying the number of right-left pairs
For some reason, in the wikia wiki, the "align" and "alignat" environments cause errors.
The paragraph environments are center, flushleft, flushright, minipage, quotation, quote, verbatim, and verse. Within a paragraph environment, each line must be terminated with a double backslash, \\.
Related commands are centering, raggedright, raggedleft, parbox, footnote, footnotetext, and verb
The center environment allows you to create a paragraph consisting of lines that are centered within the left and right margins on the current page.
The flushleft environment allows you to create a paragraph consisting of lines that are flushed left, to the left-hand margin.
The flushright environment allows you to create a paragraph consisting of lines that are flushed right, to the right-hand margin.
The minipage environment is similar to the \parbox command. It is not advisable to nest minipage environments, because it messes up footnote positioning.
\begin{minipage}[position]{width}
... text
\end{minipage}
The margins of the quotation environment are indented on the left and the right. The text is justified at both margins and there is paragraph indentation.
The margins of the quotation environment are indented on the left and the right. The text is justified at both margins without paragraph indentation
Uses typewriter (\tt) style, similar to the \verb command.
The verse environment is designed for poetry. The margins are indented on the left and the right. End each lines with \\, and use a blank line to separate the stanzas.
\begin{picture}(width,height)(x offset,y offset)
\begin{tabbing} function \= fact(n : integer) : integer;
The tabular environment uses ampersands (&) to separate columns.
\begin{tabular}[pos]{cols}
column 1 entry & column 2 entry … & column n entry
\begin{tabular*}{width}[pos]{cols}
column 1 entry & column 2 entry … & column n entry
The thebibliography environment is used to print a bibliography. Related commands are bibitem, cite, nocite
\begin{thebibliography}{widest-label}
\bibitem[label]{cite_key}
The titlepage environment is used to print a title page. It has no printed page number or page heading. The following page is numbered page 1. A related commands is maketitle.
Community content is available under CC-BY-SA unless otherwise noted.
What are LaTeX “environments”. While TeX makes direct provision for commands, LaTeX adds a concept of “environment”; environments perform an action on a block (of something or other) rather than than just doing something at one place in your document. A totally trivial environment could change the font in use for a chunk of text, as.
How to define a new environment in latex?
How to define a new environment in latex?
The definition of a new environment can be done by the basic LaTeX command ewenvironment. But I'd like to recommend the package xparse which provides also commands and utilities to define new environments; for instance, it provides a simple test to check if the optional argument is empty or not.
tex.stackexchange.com/questions/60079/c…
How does latex allow arguments to an environment?
How does latex allow arguments to an environment?
LaTeX also allows arguments to an environment: would produce the same effect as the monoblock environment. Environments may also have optional arguments, in much the same way as commands: will observe its optional argument, and behave the same as the monoblock we started with.
What is a float environment in latex?
What is a float environment in latex?
A LaTeX environment is one of the following: Text inside a float environment is "floated" according to its placement, an optional parameter. The standard report and article classes use the default placement [tbp]. The float environments are figure and table.
latex.wikia.org/wiki/List_of_LaTeX_environ…
What is the difference between latex and Tex?
What is the difference between latex and Tex?
While TeX makes direct provision for commands, LaTeX adds a concept of “environment”; environments perform an action on a block (of something or other) rather than than just doing something at one place in your document. A totally trivial environment could change the font in use for a chunk of text, as
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Environments
Introduction
Environments
Overwriting Existing Environments
Reference Guide
Below you can see a very simple example on how to use an environment. In this example all the text inside the centerenvironment is centred. Open an example in Overleaf
https://latex.wikia.org/wiki/List_of_LaTeX_environments
Float Environments
List Environments
Paragraph Environments
Picture Environment
Table Environments
Other Environments
External References
Text inside a float environment is "floated" according to its placement, an optional parameter. The standard report and article classes use the default placement [tbp]. The float environments are figure and table.
Latex Beginners' Course #06 - Advanced Math: Adjusting Brackets, Matrices and Align Environment
Part 1: How to setup the LaTeX Environment
LaTeX Environment Installation in Windows 10 with MikTeX and TeXnicCenter
Easy Setup for Text Editing LaTex Environment
Перевести · What are LaTeX “environments” While TeX makes direct provision for commands, LaTeX adds a concept of “environment”; environments perform an action on a block (of something or other) rather than than just doing something at one place in your document. …
https://sv.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Environments
Перевести · This environment will draw a box around the text within. Right after the \newenvironment, in between braces, you must write the name of the environment, boxed in the example. Below that are two pairs of braces. Inside the first pair of braces is set what your new environment will do before the text within, then inside the second pair of braces declare what your new environment …
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3251076
Перевести · Creating an environment in Latex. Ask Question. Asked 10 years, 6 months ago. Active 10 years, 6 months ago. Viewed 3k times. 2. Hi I'm trying to create an environment in Latex that recreates the …
This works for me: \makeatletter\newenvironment{bc_box}{% \begin{lrbox}{\@tempboxa}\begin{minipage}{\columnwidth}}{\end{minipage}\end{lrbox}%...
Consider this http://kuscsik.blogspot.com/2006/12/how-to-create-new-environment-in-latex.html
Using Donald Arseneau's framed.sty , you can do this, which would also work nicely if you need to span multiple pages. \newenvironment{bashcommand...
https://jupyter-contrib-nbextensions.readthedocs.io/en/latest/nbextensions/latex_envs/...
Перевести · Environments title/numbering can be customized by users in user_envs.json config file. Styles can be customized in the latex_env.css stylesheet Limited autocompletion for $, (, {, [ More environments …
Tex Distributions
CTAN
The Latex Git Repository
Historic Latex
If you’re new to TeX and LaTeX or just want an easy installation, geta full TeX distribution. The TeX Users Group (TUG) has a list of notable distributionsthat are entirely, or least primarily, free software.
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/tex_commands/newenvironment.htm
Перевести · \newenvironment command is used for defining your own environment. \newenvironment must appear (within math delimiters) before it is used. The bracketed # of arguments is omitted when …
https://tex.stackexchange.com/questions/60079
Перевести · The definition of a new environment can be done by the basic LaTeX command \newenvironment. But I'd like to recommend the package xparse which provides also commands …
Add a space before #1 in the environment's definition, and specify \unskip (which will remove the space) as the optional argument's default va...
The definition of a new environment can be done by the basic LaTeX command \newenvironment . But I'd like to recommend the package xparse which...
I would just put in the space if the optional argument is empty (or not used). Also I removed the second \noindent since it can do nothing useful...
www.personal.ceu.hu/tex/environ.htm
Перевести · Latex Standard Environments LaTeX provides a number of different paragraph-making environments. Each environment begins and ends in the same manner. \begin{environment-name} . . . …
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Mistress Latex Slave
Latex Pet Play
Latex Couture
Latex Transformation Girl
Latex Product
Environments - Overleaf, Online LaTeX Editor
List of LaTeX environments | LaTeX Wiki | Fandom
What are LaTeX “environments” | The TeX FAQ
Environments - Overleaf, Online-LaTeX-editor
(some) LaTeX environments for Jupyter notebook — jupyter ...
Get LaTeX - Mac OS, Windows, Linux
\newenvironment - Tex Command - Tutorialspoint
Latex Standard Environments - Personal pages of the CEU
Latex Environment