LEVAMISOLE INDUCED NECROSIS SYNDROME
https://aepiot.com/search.html?q=LEVAMISOLE%20INDUCED%20NECROSIS%20SYNDROMEMultiSearch Tag Explorer
aéPiot
Go
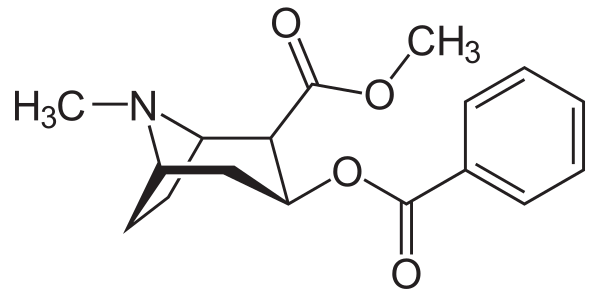
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, Erythroxylum coca and E. novogranatense, which are cultivated almost exclusively in the Andes. Indigenous South Americans have traditionally used coca leaves for over a thousand years. Notably, there is no evidence that habitual coca leaf use causes addiction or withdrawal, unlike cocaine. Medically, cocaine is rarely employed, mainly as a topical medication under controlled settings, due to its high abuse potential and adverse effects. Recreational use is widespread, driven by its euphoric and aphrodisiac properties. Levamisole induced necrosis syndrome (LINES)-a complication of the common cocaine cutting agent levamisole-and prenatal cocaine exposure is particularly harmful. Cocaine is typically snorted, injected, or smoked as crack cocaine, with effects beginning within seconds to minutes and lasting up to 90 minutes depending on the route. Pharmacologically, it is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) that activates the mesolimbic pathway. Intoxication may cause euphoria, psychosis, and physical symptoms like tachycardia and mydriasis. An overdose can lead to stroke, heart attack, or sudden cardiac death. Chronic cocaine use leads to cocaine dependence and can cause nose disorders, commonly referred to as "Cocaine nose", including cocaine-induced midline destructive lesions (CIMDL) when insufflated. Large-scale chemical synthesis of cocaine is unexplored; Instead, 99% of all global cocaine is made by first harvesting coca leaves by cocaleros from their coca plantations in the Andes. These leaves are then extracted into cocaine paste, which is subsequently processed into powdered hydrochloride salt. Both the pharmaceutical supply chain and the illicit supply chain use all these steps, but they operate under very different controls and oversight. For example, legal coca cultivation, which is regulated by governments such as the National Coca Company in Peru, contrasts sharply with illegal cultivation that is targeted by government-led coca eradication efforts. Cocaine is prohibited globally except for restricted medical and scientific uses under treaties like the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. Nevertheless, legal penalties vary by country. Some jurisdictions decriminalize possession of small amounts, leading to inconsistency in the legal status of cocaine worldwide.
In connection with: Cocaine
Description combos: by including to pathway reuptake dopamine habitual cultivated Erythroxylum

Alcohol dependence is a previous (DSM-IV and ICD-10) psychiatric diagnosis in which an individual is physically or psychologically dependent upon alcohol (also chemically known as ethanol). In 2013, it was reclassified as alcohol use disorder in DSM-5, which combined alcohol dependence and alcohol abuse into this diagnosis.
In connection with: Alcohol dependence
Title combos: dependence Alcohol
Description combos: 10 individual in an dependence and this combined use
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, but is named for its appearance. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale (Wickham's striae), commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms. The term lichenoid reaction (lichenoid eruption or lichenoid lesion) refers to a lesion of similar or identical histopathologic and clinical appearance to lichen planus (i.e., an area which resembles lichen planus, both to the naked eye and under a microscope). Sometimes dental materials or certain medications can cause lichenoid reactions. They can also occur in association with graft versus host disease.: 258
In connection with: Lichen planus
Title combos: Lichen planus
Description combos: thought different term is commonly there Lichen the It

Levamisole, sold under the brand name Ergamisol among others, is a medication used to treat parasitic worm infections, specifically ascariasis and hookworm infections. It is taken by mouth. Side effects may include abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, and dizziness. Use is not recommended during breastfeeding or the third trimester of pregnancy. Serious side effects may include an increased risk of infection. It belongs to the anthelmintic class of medications. Levamisole was invented in 1966 in Belgium by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Levamisole is also used as a dewormer for cattle.
In connection with: Levamisole
Description combos: cattle may trimester cattle during taken treat include trimester

Delirium tremens (DTs; lit. 'mental disturbance with shaking') is a rapid onset of confusion usually caused by withdrawal from alcohol. When it occurs, it is often three days into the withdrawal symptoms and lasts for two to three days. Physical effects may include shaking, shivering, irregular heart rate, and sweating. People may also hallucinate. Occasionally, a very high body temperature or seizures (colloquially known as "rum fits") may result in death. Delirium tremens typically occurs only in people with a high intake of alcohol for more than a month, followed by sharply reduced intake. A similar syndrome may occur with benzodiazepine and barbiturate withdrawal. In a person with delirium tremens, it is important to rule out other associated problems such as electrolyte abnormalities, pancreatitis, and alcoholic hepatitis. Prevention is by treating withdrawal symptoms using similarly acting compounds to taper off the use of the precipitating substance in a controlled fashion. If delirium tremens occurs, aggressive treatment improves outcomes. Treatment in a quiet intensive care unit with sufficient light is often recommended. Benzodiazepines are the medication of choice with diazepam, lorazepam, chlordiazepoxide, and oxazepam all commonly used. They should be given until a person is lightly sleeping. Nonbenzodiazepines are often used as adjuncts to manage the sleep disturbance associated with condition. The antipsychotic haloperidol may also be used in order to combat the overactivity and possible excitotoxicity caused by the withdrawal from a GABA-ergic substance. Thiamine (vitamin B1) is recommended to be given intramuscularly, because long-term high alcohol intake and the often attendant nutritional deficit damages the small intestine, leading to a thiamine deficiency, which sometimes cannot be rectified by supplement pills alone. Mortality without treatment is between 15% and 40%. Currently death occurs in about 1% to 4% of cases. About half of people with alcoholism will develop withdrawal symptoms upon reducing their use. Of these, 3% to 5% develop DTs or have seizures. The name delirium tremens was first used in 1813; however, the symptoms were well described since the 1700s. The word "delirium" is Latin for "going off the furrow", a plowing metaphor for disordered thinking. It is also called the shaking frenzy and Saunders-Sutton syndrome. There are numerous nicknames for the condition, including "the DTs" and "seeing pink elephants".
In connection with: Delirium tremens
Title combos: Delirium tremens
Description combos: is however known in rate Sutton haloperidol B1 adjuncts

Marchiafava–Bignami disease (MBD) is a progressive neurological disease of alcohol use disorder or malnutrition, characterized by corpus callosum demyelination and necrosis and subsequent atrophy. The disease was first described in 1903 by the Italian pathologists Amico Bignami and Ettore Marchiafava in an Italian Chianti drinker. In this autopsy, Marchiafava and Bignami noticed that the middle two-thirds of the corpus callosum were necrotic. It presents in three forms: acute, subacute, and chronic. It is very difficult to diagnose and there is no specific treatment. Until 2008 only around 300 cases had been reported. If caught early enough, most patients survive.
In connection with: Marchiafava–Bignami disease
Title combos: Bignami Marchiafava Marchiafava Bignami disease
Description combos: corpus the use were pathologists If MBD of It
Levamisole induced necrosis syndrome
Levamisole induced necrosis syndrome (LINES) is a complication characterized by necrosis resulting from exposure to levamisole, a medication with immunomodulatory properties. While LINES can occur with levamisole use alone, most reported cases are associated with the use of cocaine adulterated with levamisole as a cutting agent. This syndrome is marked by skin necrosis, often affecting areas such as the ears, face, and extremities, and is thought to result from levamisole’s effects on blood vessels and the immune system.
In connection with: Levamisole induced necrosis syndrome
Title combos: syndrome Levamisole induced syndrome Levamisole Levamisole induced necrosis syndrome
Description combos: use ears as levamisole areas skin characterized medication associated
Quick Access
Tag Explorer
Discover Fresh Ideas in the Universe of aéPiot
MultiSearch | Search | Tag Explorer
SHEET MUSIC | DIGITAL DOWNLOADS
© aéPiot - MultiSearch Tag Explorer. All rights reserved.
Hosted by HOSTGATE