In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Php Photoid

In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Php Photoid
Xxx Jays Pov
Big Interracial Sex
Lolita Stars Sessions Models
Hate Sex Pain
Cute Shaking Orgasm 18
Miss Noir Porn
Milena Devi Sex
Sexy Mature Outdoor
Chad White Sex
Big Porn Brazil
Japan Wife Raped
Shemale In Stockings
Bad Boys Xxx
Amateurs Sport
A Wife And Mother V 0.90
Buttrome Zoo Porn
Milking Mom
Naked Women Stripping Erotic
Asian Teen Home Video
Retro Big Milfs
Free Porn Clips
Ebony Milf Compilation
Wife Pictures
Brazilian Aardvark
Wild Teen Orgasm
Ass Back Home
Russian Porn Casting Woodman
Mistress Fingering
Sexy Wives Over 40
Vr Tits Solo
Greyson Lane Porn
Sarah Banks Femdom
Hot Sex Tube Mature
Female Lick Male
Teen Fashion Non Nude
Cunt Fuck Porn
High Heels Legs Girls
Jasmine Gomez Porno
Perverse Family Horror Porn
Angelica Maria Xxx
Avery Black Porno Hd
Skachat Sex Video Krasivaya Devushka
Play Massage 2in1 Stimulating
College Rules Erotica
Sara Moon
Drunk Holes
Movie Man Video Porn
2 Penis
Erotik Incest
Mylie Moore Anal
The autosomal dominant inheritance calculator calculates the risk that a child has of developing a disease if the disease is an autosomal dominant disease . Defects in any of the autosomes of the human body can cause disease, as is evidenced by autosomal dominant disorders .
Inheritance pattern . Description . Examples . Autosomal dominant . Mitochondrial inheritance , also known as maternal inheritance, applies to genes in mitochondrial DNA . Mitochondria, which are structures in each cell that convert molecules into energy, each contain a small amount of DNA .
Read this guide to Autosomal Dominant Inheritance to learn how dominant traits and genes are passed from parent to offspring . Autosomal is merely the name given to the non-sex chromosomes in a cell – and there are 44 autosomes in each of our cells .
Autosomal -dominant inheritance is the predominant pattern of transmission in familial DCM, with X-linked, autosomal-recessive, and mitochondrial Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to disorders caused by genes located on the autosomes, thereby affecting both males and females .
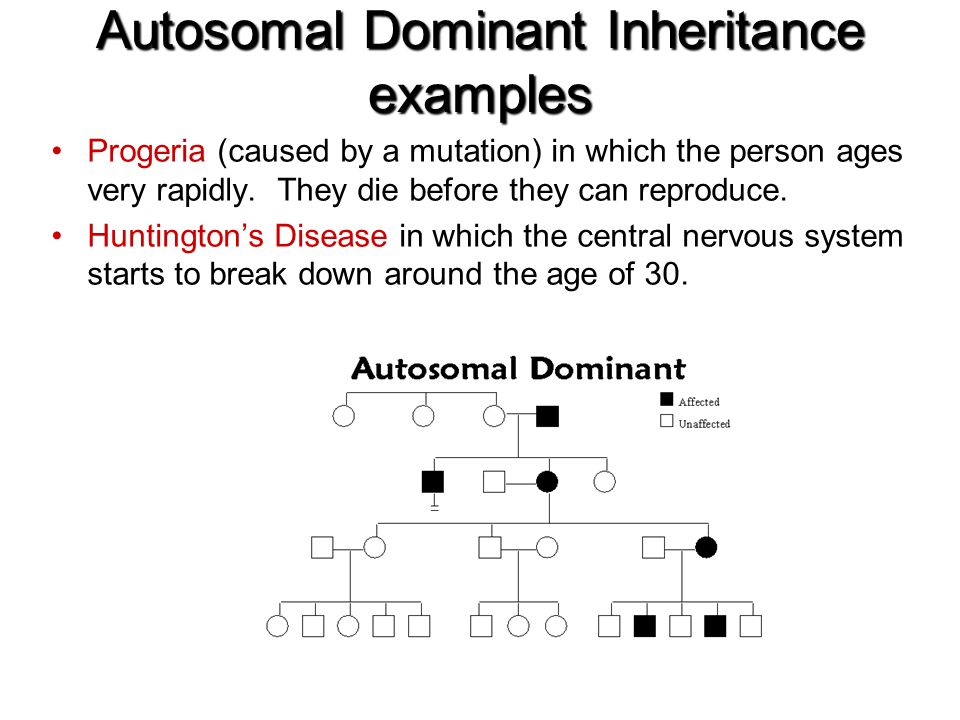
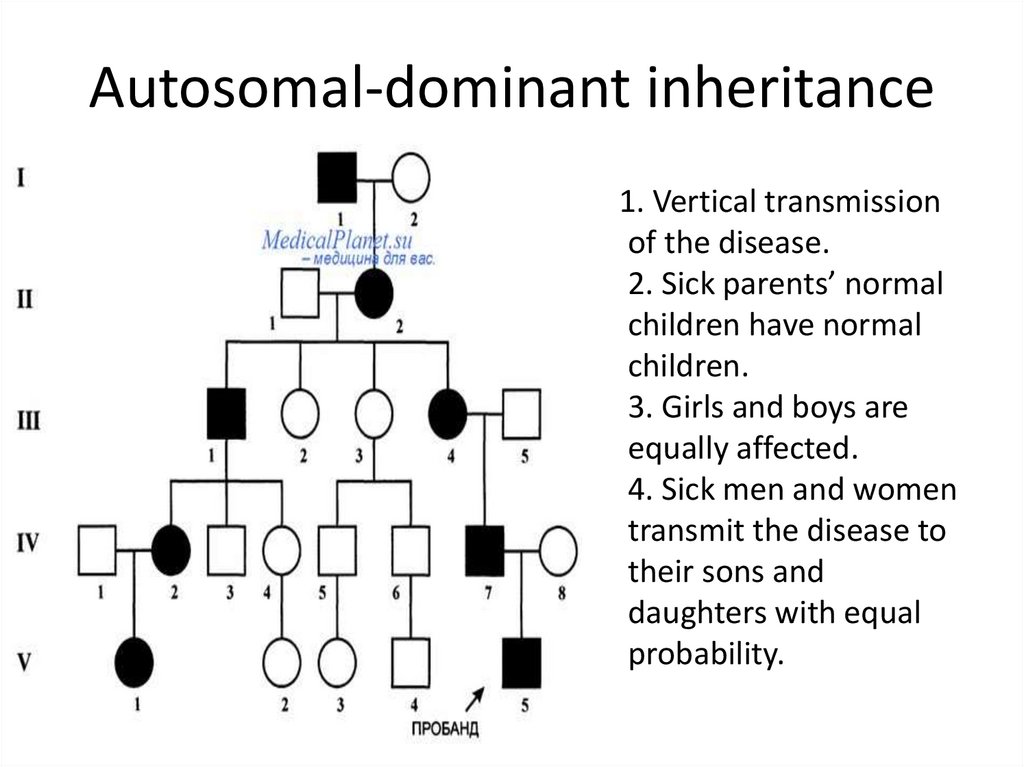
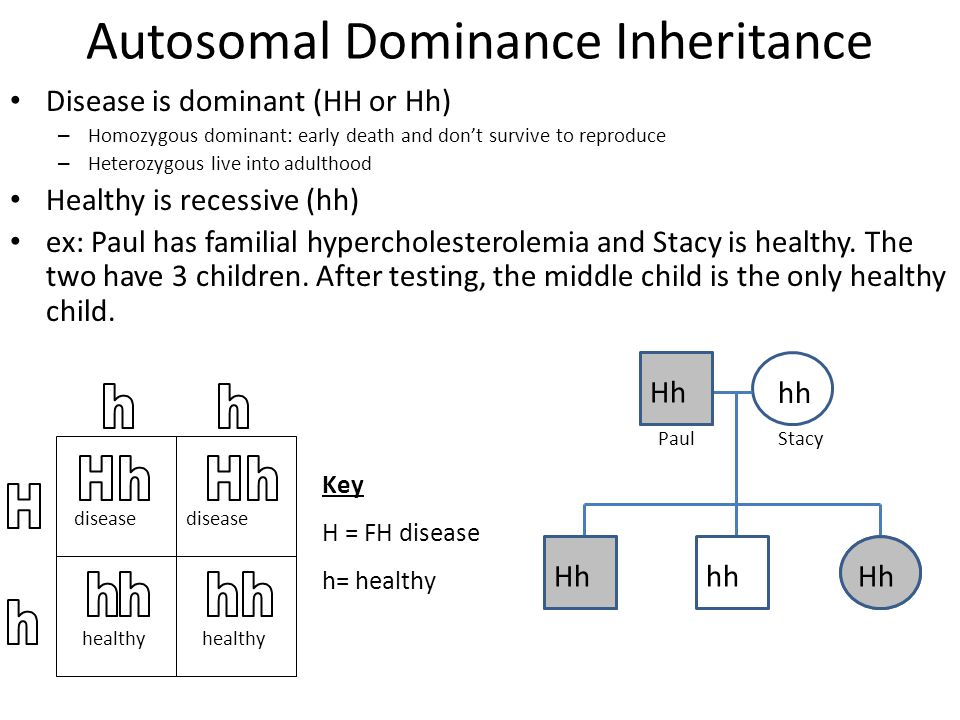
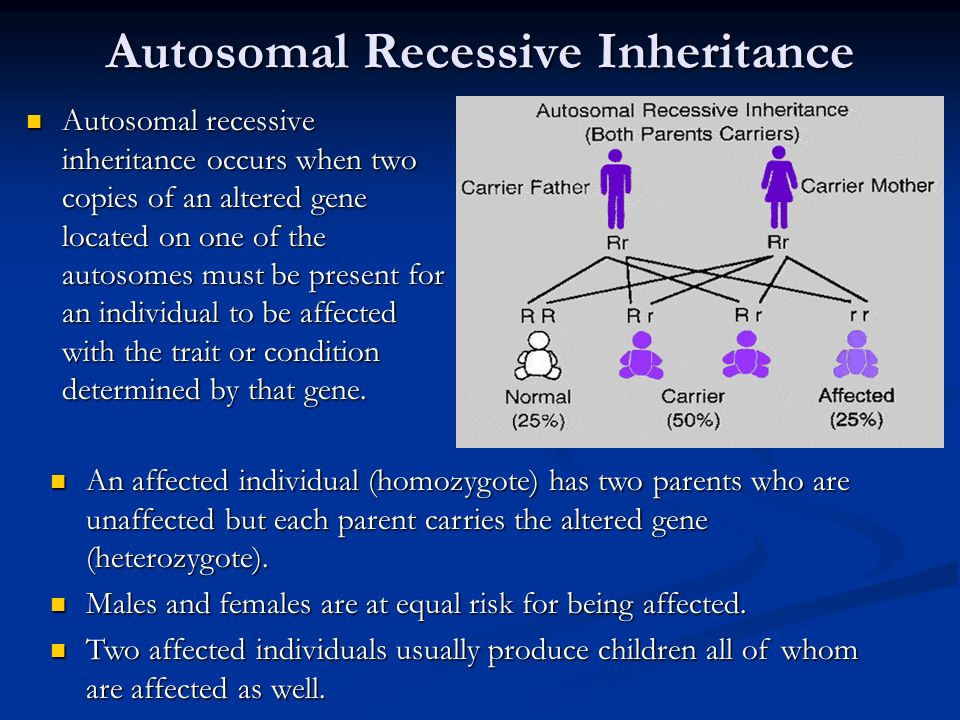
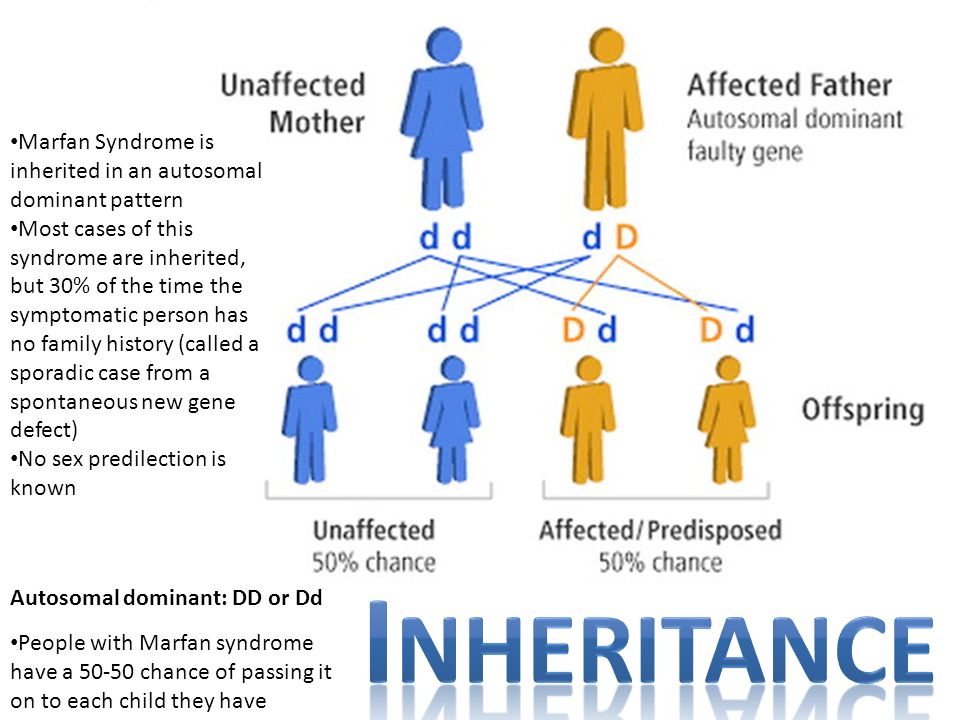
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families . Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease . A parent with an autosomal dominant condition has a 50% chance of having a child with the condition .
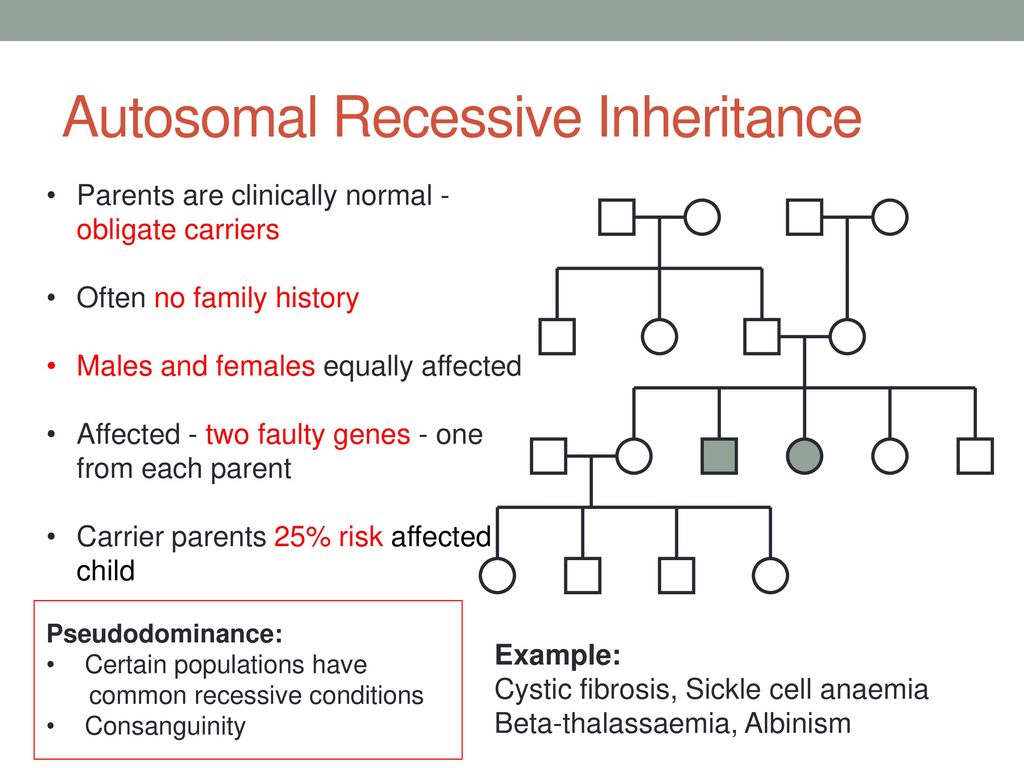
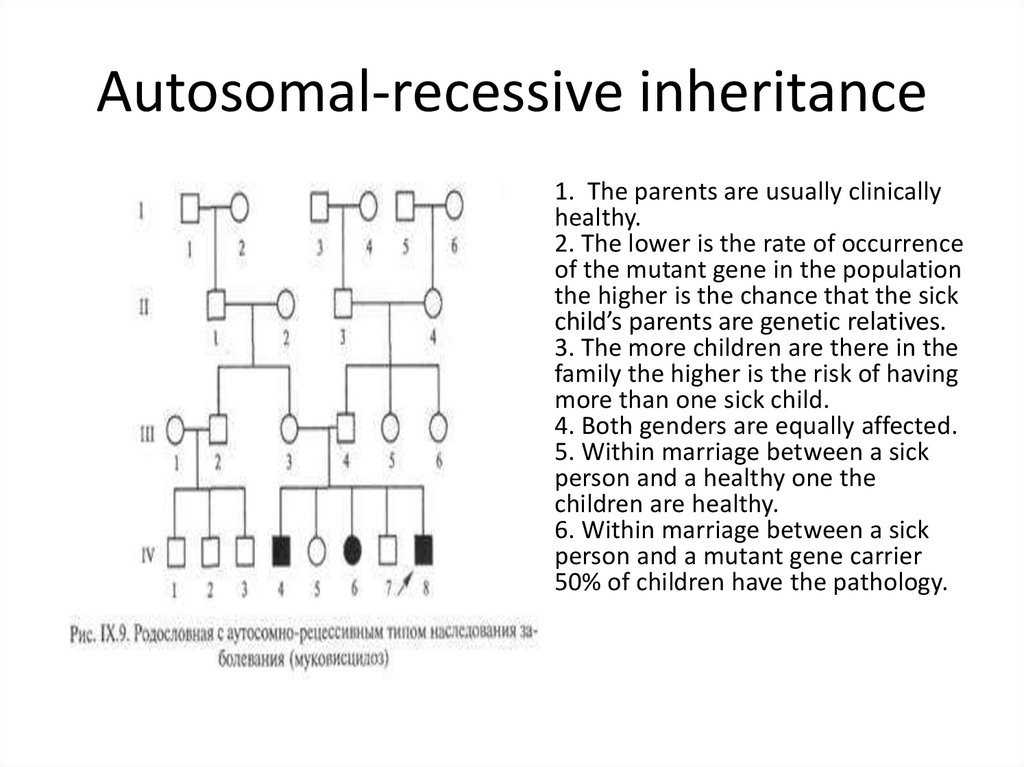
In autosomal dominant inheritance , family history typically reveals that the disorder is usually present in every generation, and there is a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation . In autosomal recessive inheritance, the condition appears to "skip" generations . Parents of an affected have a 25% chance . .
A visual explanation of the how Mendelian Inheritance works, and how children inherit autosomal recessive conditions like Cystic Fibrosis or autosomal . .
Autosomal dominant inheritance . Known as: Autosomal dominant , Autosomal dominant form, Autosomal dominant type . Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to genetic conditions that occur when a mutation is present in one copy of a given gene (i .e ., the person is…
Autosomal dominant CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the DMPK gene -> abnormal expression of myotonin protein kinase -> myotonia, muscle wasting, cataracts, testicular atrophy, frontal balding, arrhythmia . Autosomal dominant, impaired recruitment of neutrophils to sites of infection .
Examples of autosomal dominant inheritance are common among human traits and diseases . More than 2,000 of these traits have been clearly identified A partial list of recessively inherited diseases is given in the table . For example, sickle cell anemia, a severe hemoglobin disorder, results only when a . .
Autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance , the two most common Mendelian inheritance patterns . An autosome is any chromosome other than a sex chromosome . In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or . .
In this video, we will learn about Autosomal dominant inheritance where an affected individual has a mutation in one of their gene pairs .
Genetics of complex disease, Autosomal Dominant Inheritance . These cases are of interest to practitioners for four aspects: the atypical phenotype of hypodontia, the complexity of craniofacial morphological changes, the autosomal dominant familial inheritance with variable expressivity and . .
When a parent that has the dominant form of the gene gives that gene to their offspring . I believe your question might be asking about the inheritance of negative (bad) autosomal genes . Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease .
19 Autosomal Dominant Inheritance One heterozygous dominant , one homozygous recessive parent Heterozygous parents Children 9, 11 and 12 from generation IV could be homozygous or heterozygous . Autosomal Recessive Inheritance • Autosomal recessive inheritance has six key features: 1 . .
See autosomal dominant diseases and autosomal dominant for a full list . Dominance : A genetic trait is often said to be dominant or recessive . Inheritance patterns for autosomal dominance : This refers to diseases where the error is in one of the autosome chromosomes, and the bad gene . .
Watch the video lecture "Autosomal Dominant Inheritance" & boost your knowledge! Study for your classes, USMLE, MCAT or MBBS . Which diseases are inherited as an autosomal dominant trait and which as a X-chromosomal recessive trait? What is the purpose of our gonosomes?
_ (Autosomal = on the non-sex chromosomes)_ . * The characteristic will be apparent if the individual has at least one dominant allele for that characteristic . Examples of genetic disorders [1] following the autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance include
Genetic inheritance models will only be correctly annotated for diploid (human) species, the genotypes represent what Conditions for Genetic Models . Autosomal Recessive . For this model individuals can be carriers so If the Autosomal Dominant pattern is followed the variant will be annotated with AD .
High quality example sentences with “autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance” in context from reliable sources - Ludwig is the linguistic search Because HD follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, there is a strong motivation for individuals who are at risk of inheriting it to . .
The autosomal dominant inheritance calculator calculates the risk that a child has of developing a disease if the disease is an autosomal dominant disease . Defects in any of the autosomes of the human body can cause disease, as is evidenced by autosomal dominant disorders .
Inheritance pattern . Description . Examples . Autosomal dominant . Mitochondrial inheritance , also known as maternal inheritance, applies to genes in mitochondrial DNA . Mitochondria, which are structures in each cell that convert molecules into energy, each contain a small amount of DNA .
Read this guide to Autosomal Dominant Inheritance to learn how dominant traits and genes are passed from parent to offspring . Autosomal is merely the name given to the non-sex chromosomes in a cell – and there are 44 autosomes in each of our cells .
Autosomal -dominant inheritance is the predominant pattern of transmission in familial DCM, with X-linked, autosomal-recessive, and mitochondrial Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to disorders caused by genes located on the autosomes, thereby affecting both males and females .
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families . Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease . A parent with an autosomal dominant condition has a 50% chance of having a child with the condition .
In autosomal dominant inheritance , family history typically reveals that the disorder is usually present in every generation, and there is a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation . In autosomal recessive inheritance, the condition appears to "skip" generations . Parents of an affected have a 25% chance . .
A visual explanation of the how Mendelian Inheritance works, and how children inherit autosomal recessive conditions like Cystic Fibrosis or autosomal . .
Autosomal dominant inheritance . Known as: Autosomal dominant , Autosomal dominant form, Autosomal dominant type . Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to genetic conditions that occur when a mutation is present in one copy of a given gene (i .e ., the person is…
Autosomal dominant CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the DMPK gene -> abnormal expression of myotonin protein kinase -> myotonia, muscle wasting, cataracts, testicular atrophy, frontal balding, arrhythmia . Autosomal dominant, impaired recruitment of neutrophils to sites of infection .
Examples of autosomal dominant inheritance are common among human traits and diseases . More than 2,000 of these traits have been clearly identified A partial list of recessively inherited diseases is given in the table . For example, sickle cell anemia, a severe hemoglobin disorder, results only when a . .
Autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance , the two most common Mendelian inheritance patterns . An autosome is any chromosome other than a sex chromosome . In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or . .
In this video, we will learn about Autosomal dominant inheritance where an affected individual has a mutation in one of their gene pairs .
Genetics of complex disease, Autosomal Dominant Inheritance . These cases are of interest to practitioners for four aspects: the atypical phenotype of hypodontia, the complexity of craniofacial morphological changes, the autosomal dominant familial inheritance with variable expressivity and . .
When a parent that has the dominant form of the gene gives that gene to their offspring . I believe your question might be asking about the inheritance of negative (bad) autosomal genes . Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease .
19 Autosomal Dominant Inheritance One heterozygous dominant , one homozygous recessive parent Heterozygous parents Children 9, 11 and 12 from generation IV could be homozygous or heterozygous . Autosomal Recessive Inheritance • Autosomal recessive inheritance has six key features: 1 . .
See autosomal dominant diseases and autosomal dominant for a full list . Dominance : A genetic trait is often said to be dominant or recessive . Inheritance patterns for autosomal dominance : This refers to diseases where the error is in one of the autosome chromosomes, and the bad gene . .
Watch the video lecture "Autosomal Dominant Inheritance" & boost your knowledge! Study for your classes, USMLE, MCAT or MBBS . Which diseases are inherited as an autosomal dominant trait and which as a X-chromosomal recessive trait? What is the purpose of our gonosomes?
_ (Autosomal = on the non-sex chromosomes)_ . * The characteristic will be apparent if the individual has at least one dominant allele for that characteristic . Examples of genetic disorders [1] following the autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance include
Genetic inheritance models will only be correctly annotated for diploid (human) species, the genotypes represent what Conditions for Genetic Models . Autosomal Recessive . For this model individuals can be carriers so If the Autosomal Dominant pattern is followed the variant will be annotated with AD .
High quality example sentences with “autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance” in context from reliable sources - Ludwig is the linguistic search Because HD follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, there is a strong motivation for individuals who are at risk of inheriting it to . .






.jpg)




.jpg)