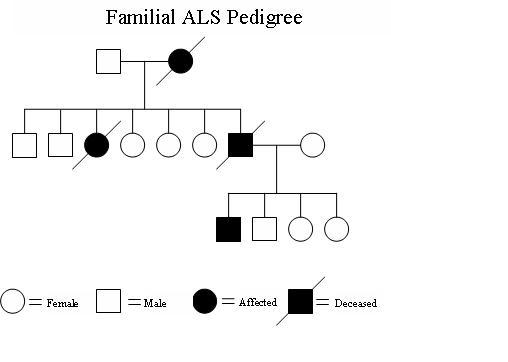
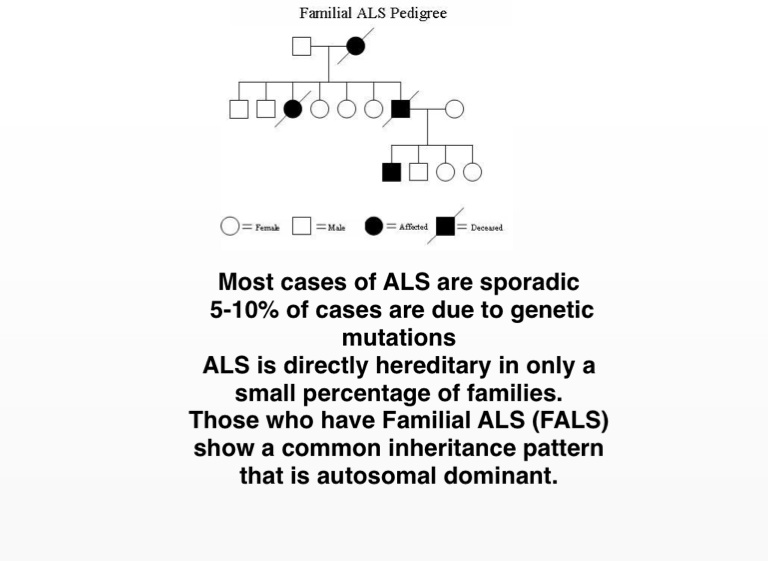
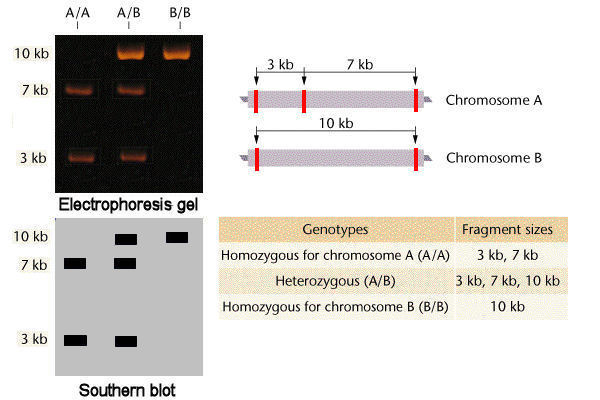
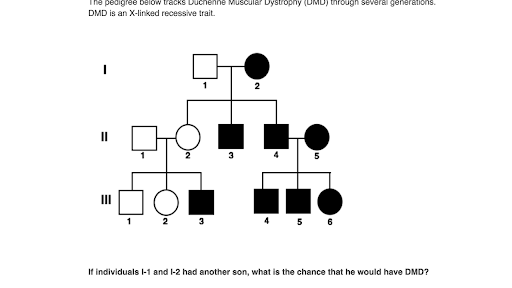
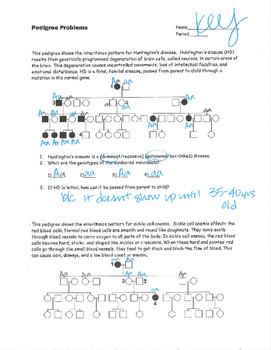
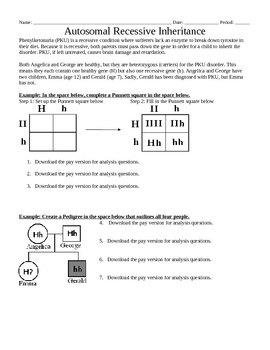
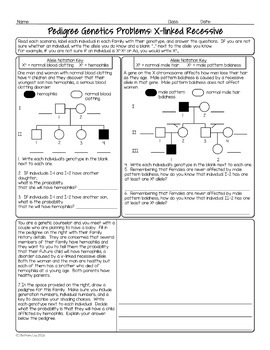
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Jsp Item

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
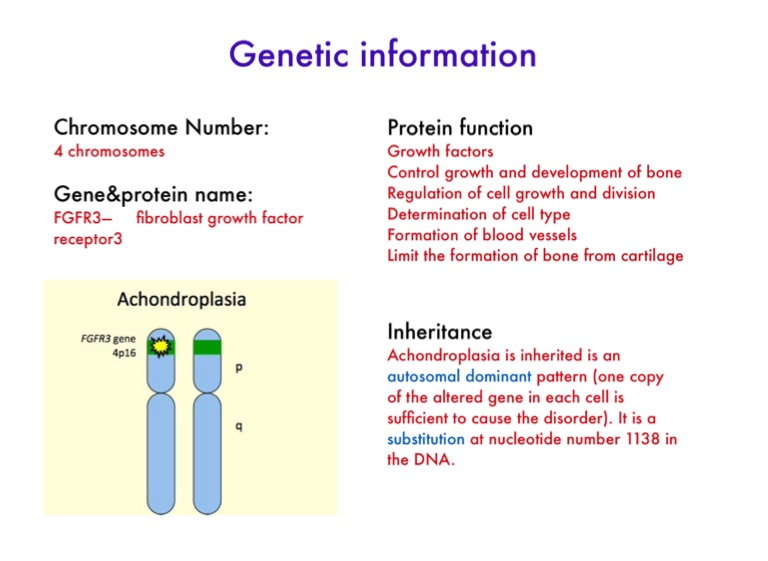
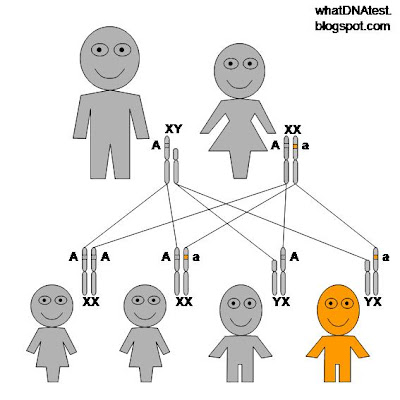
Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to a mutation on one of the 22 pairs of nuclear chromosomes (i.e. non-sex chromosomes) that leads to syndrome expression when only one copy of the chromosome pair carries the mutant allele.
Alan Lap-Yin Pang, Wai-Yee Chan, in Essential Concepts in Molecular Pathology, 2010
ADH is a familial form of isolated hypoparathyroidism characterized by hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and normal to hypoparathyroidism. Inheritance of the disorder follows an autosomal dominant mode. The patients are generally asymptomatic. A significant fraction of cases of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism may in fact be ADH.
More than 80% of the reported ADH kindreds have CaSR mutations. There are 44 activating mutations of CaSR reported that produce a gain of CaSR function when expressed in in vitro systems. The majority of the ADH mutations are missense mutations within the extracellular domain and transmembrane domain of CaSR. The mechanism of CaSR activation by these mutations is not known. Interestingly, almost every ADH family has its own unique missense heterozygous CaSR mutation. Most ADH patients are heterozygous. The only deletion-activating mutation occurs in a homozygous patient in an ADH family. However, there is no apparent difference in the severity of the phenotype between heterozygous and homozygous patients.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123744180000220
Alan Lap-Yin Pang, ... Wai-Yee Chan, in Molecular Pathology, 2009
ADH is a familial form of isolated hypoparathyroidism characterized by hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and normal to hypoparathyroidism. Inheritance of the disorder follows an autosomal dominant mode. The patients are generally asymptomatic. A significant fraction of cases of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism may in fact be ADH.
More than 80% of the reported ADH kindreds have CaSR mutations. There are 44 activating mutations of CaSR reported in the literature. These mutations produce a gain of CaSR function when expressed in in vitro systems [13,117]. The majority of the ADH mutations are missense mutations within the extracellular domain and transmembrane domain of CaSR. In addition, a deletion in the intracellular domain, p.S895_V1075del, has also been described in an ADH family. The mechanism of CaSR activation by these mutations is not known. Worthwhile noting is that almost every ADH family has its own unique missense heterozygous CaSR mutation [117]. Most ADH patients are heterozygous. The only deletion-activating mutation occurs in a homozygous patient in an ADH family. However, there is no apparent difference in the severity of the phenotype between heterozygous and homozygous patients.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123744197000226
Isolated autosomal dominant PLD (ADPLD) (MIM 174050) also occurs as a genetically distinct disease in the absence of renal cysts (274, 281, 328). Like ADPKD, ADPLD is genetically heterogeneous, with two genes identified (PRKCSH and SEC63) accounting for approximately one third of isolated ADPLD cases (49, 57, 166). ADPLD often goes undetected even in first-degree relatives of patients with highly symptomatic polycystic liver disease. As in the case of polycystic liver disease associated with ADPKD, isolated ADPLD is more severe in women than in men. Liver function tests remain normal and when symptoms develop, these are related to mass effects or complications such as cyst hemorrhage or infection. Patients with isolated ADPLD may also be at increased risk for intracranial aneurysms and valvular heart disease (274).
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012088488950084X
Elliott H. Sohn, ... Edwin M. Stone, in Retina (Fifth Edition), 2013
ADVIRC was first described by Kaufman et al. in 198273 as a condition with: (1) an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern; (2) peripheral pigmentary retinopathy for 360 degrees, with a discrete posterior boundary near the equator (see Fig. 42.9); (3) punctate whitish opacities in the retina; (4) vitreous cells and fibrillar condensation; (5) blood–retinal barrier breakdown; (6) retinal arteriolar narrowing and occlusion; (7) retinal neovascularization; (8) choroidal atrophy; and (9) presenile cataracts (see Fig. 42.9).74 The EOG is usually abnormal with a relatively normal ERG,75 but the first electrophysiologic studies of ADVIRC patients27,75,76 occurred in the pre-molecular era when genetic testing was not available. It has since been discovered that ADVIRC is caused by splice-altering mutations in BEST1 and that these patients can also have concomitant developmental abnormalities, including microcornea, hyperopia, and shortened axial length.26,77,78 Some patients have a severe form of ADVIRC in which both the ERG and EOG are abnormal, thus resembling retinitis pigmentosa.79,80
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781455707379000424
Autosomal dominant epilepsy with auditory features (ADEAF), also known as autosomal dominant lateral temporal lobe epilepsy (ADLTLE), is a rare epilepsy syndrome that confers focal seizures that often secondarily generalize.91 The seizures can begin at any age, but usually start in the second or third decade of life. As the syndrome’s name suggests, the majority of the patients (64%) have focal seizures that begin with an auditory component. Some have simple auditory hallucinations, such as ringing that changes in volume,92 or a “buzzing, or humming like a machine.” 93 In other patients, auditory hallucinations are formed, such as voices or singing.92 Some patients have visual, autonomic, psychic or vertiginous focal seizures. In some pedigrees, the seizures are accompanied by a sensory aphasia with or without auditory hallucinations.94 In most patients, the seizures are infrequent (only several times per year before starting medication) and can usually be controlled with anticonvulsant drugs.
Interictal EEG abnormalities, if present, are usually left temporal spike and sharp wave complexes. ADEAF patients do not have causative brain lesions on conventional MRI imaging. However, one diffusion tensor imaging study suggested that some patients may have subtle malformations in the left temporal cortex.95 Finally, although their neurological exams are normal, functional imaging and magnetoencephalography studies of members of four ADEAF families were consistent with impaired language processing.96
At the time of its first description, ADEAF was linked to a 10-cM region on chromosome 10q with a 71% penetrance.97 Linkage studies in another family narrowed the region to approximately 3 cM.93 Kalachikov et al. sequenced all exons and intron/exon junctions from one affected patient form three different ADEAF pedigrees and then genotyped all family members from five different ADEAF pedigrees.98 They found that all affected family members and obligate carriers possessed mutations (four frameshift/intron retention truncation mutations and one missense mutation) in the leucine-rich, glioma-inactivated 1 gene (LGI1). Some unaffected family members also possessed the mutations, a finding consistent with the reduced penetrance found in the gene linkage studies. There are now 27 LGI1 mutations associated with ADEAF (Table 84.4).
Less than 50% of ADEAF families and less than 2% of sporadic ADEAF patients have LGI1 mutations. Recently, a new ADEAF locus was found in a large Brazilian family. The DNA from 11 affected and 14 unaffected family and performed genotyping found linkage to region 19q13.11–q13.31 with incomplete penetrance.99
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012410529400084X
Quasar Saleem Padiath, Ying-Hui Fu, in Methods in Cell Biology, 2010
Autosomal dominant leukodystrophy (ADLD) is an adult-onset demyelinating disorder that has recently shown to be caused by duplications of the nuclear lamina gene, lamin B1. This chapter attempts to collate and summarize the current knowledge about the disease and the clinical, pathological, and radiological presentations of the different ADLD families described till date. It also provides an overview of the molecular genetics underlying the disease and the mechanisms that may cause the duplication mutation event. ADLD is the first disease that has ever been linked to lamin B1 mutations and it expands the pathological role of the nuclear lamia to include disorders of the brain. The chapter also speculates on the different mechanisms that may link an important and ubiquitous structure like the nuclear lamina with the complex and cell-specific functions of myelin formation and maintenance. Understanding these mechanisms may not only prove helpful in understanding ADLD pathology but can also help in identifying new pathways that may be involved in myelin biology that can have implications for common demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0091679X1098014X
Shibo Tang, ... Yan Luo, in Retina (Fifth Edition), 2013
These conditions are characterized by hereditary peripheral retinal neovascularization with vitreoretinal traction. We discuss here hereditary conditions without primary vitreal degeneration, unaccompanied by systemic clinical manifestations, and incontinentia pigmenti, sickle-cell retinopathy, and other peripheral proliferative retinopathies that have been reviewed previously.151
ADNIV is an apparently rare condition characterized by cataract, cystoid macular edema, peripheral retinal scarring and pigmentation, peripheral arteriolar closure, and neovascularization of the peripheral retina at the ora serrata.152 Young adults are asymptomatic, but have vitreous cell and selective b-wave loss on the ERG. Neovascularization may result in tractional retinal detachment. About half of patients will develop rubeosis or neovascular glaucoma by age 60 or older. The gene was localized to chromosome 11q13.153 Vitreous bands and sheets are not observed and the vitreous was not optically empty, enabling differentiation from classical vitreoretinal degenerations such as Stickler, Wagner, and SVD. The peripheral retinal vessels are initially normal in ADNIV, and dragging of the macular vessels as seen in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy is absent.
Gitter and colleagues described a family with 7 of 15 members affected with early cataract, uveitis, prominence of the vitreous base, lattice degeneration, and severe peripheral retinal neovascularization leading to vitreous hemorrhage and retinal detachment. The syndrome appears similar to ADNIV, but after reviewing photographs of the ADNIV family, the condition was deemed to be distinct.154
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781455707379000412
S. Meredith, M. Snead, in Encyclopedia of the Eye, 2010
Autosomal dominant vitreochoroidopathy (ADVIRC) is characterized by vitreous liquefaction with or without peripheral vitreal condensations. Peripheral pigmentary changes typically occur at the equatorial region with a discrete posterior boundary associated with diffuse retinal vascular leakage, cystoid macular edema, and early-onset cataract. The peripheral pigmented band extends from the ora serrata to the equator for 360° of the retina. Other ocular associations are vitreous cells and condensation, puntate opacities in the retina, choroidal atrophy, and early nuclear sclerosis. The ERG responses are normal although the electroculogram (EOG) has been shown to be abnormal in ADVIRC.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123742032002682
Expansile skeletal hyperphosphatasia
Paget’s disease of bone (late-onset)
TNF receptor superfamily, member 11A
TNF receptor superfamily, member 11B
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128041826000265
Autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia (ADH) is caused by apparent gain-of-function mutations in the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) gene (Abifadel et al., 2003). PCSK9 is secreted by hepatocytes and appears to downregulate the density of functional LDL receptors in hepatocytes by promoting endosomal degradation rather than recycling of the receptor (Horton et al., 2007). Interestingly, loss-of-function mutations in this gene appear to cause low LDL-C levels (see below). The discovery of the molecular basis of ADH ultimately led to the identification of PCSK9 as a novel therapeutic target.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123749345000234
We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. By continuing you agree to the use of cookies.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. ScienceDirect ® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.
ScienceDirect ® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.
Ваш браузер устарел.
Попробуйте обновить его, чтобы работа ВКонтакте была быстрой и стабильной.
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Item Id
ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE https://645757.ru/com.cgi?8¶meter=vktopenphoto
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Item Id
2 апр. 2020 г. —
1 янв. 2019 г. —
Discoveries on DNA structure, the genetic code , the genome and the observation that ... Autosomal dominant inheritance ; Autosomal recessive inheritance ; X linked ... Affected individuals are always the product of a parent carrier of the same ...
Examples of diseases with autosomal dominant inheritance include myotonic muscular dystrophy and Huntington disease. 3.3 Autosomal Recessive Inheritance .
13 мар. 2020 г. —
22 дек. 2020 г. —
13 дек. 2017 г. —
Режим доступа: https://www.elibrary.ru/ item . asp ? id =26678170.; Human Microbiome ... retardation, autosomal dominant type of inheritance , NALCN gene, синдром ... DOI:10.1055/s-0036-1584084.; Koroglu C., Seven M., Tolun A. Recessive ... The landscape of genetic diseases in Saudi Arabia based on the first 1000 ...
When assuming an autosomal dominant inheritance format, it is necessary to find ... C621R) (mutation from thymine to cytosine at position 88926 in SEQ ID NO: 1, mutation ... be performed according to the items described in the previous diagnosis. ... The sequence before and after Asp , the sixth amino acid of the protein ...
n search . P red ictive - w h ere a fam ily- sp ecific m u tatio n h as b een id en ... thereby altering the nature and/or function of the protein product , or because the mutation occurs in other ... http://www.mcri.edu.au/GF/pages/GeneticsFile. asp ... There are three main patterns of inheritance – autosomal dominant , autosomal.
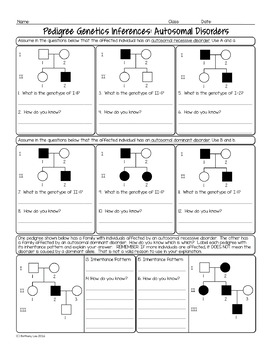
Characteristics of autosomal dominant diseases include a vertical pedi- gree pattern, affliction of both ... DIRECTIONS: Each item below contains a question or incomplete statement followed by ... alter the genetic code (producing variant proteins, or protein polymor- phisms). ... d. gly- asp -gly to gly-glu-gly e. val-val-val to ...
Each element on the page corresponds to a DOM object - i. ... A dominant trait is an inherited characteristic that appears in an offspring if it is ... is an interface layer between the web page and the code that creates and changes it. com, ... For an X-linked dominant disorder: If the father carries the abnormal X gene, all of his ...
D. They have half the number of chromosomes that the parent cell has. ID : 294785 C Common EQ. ○36. In humans, an X-linked recessive allele.
Items in Highlights & Notes may not have been saved to Google Drive™ or Microsoft OneDrive™. ... Approximately half of all cases are inherited as an autosomal - dominant pattern, and ... type 2, which is also a genetic disorder with an autosomal - dominant inheritance pattern. ... http://www.entjournal.com/Me2/ Default. asp ...
stream 5¢ss (FAA, IDS , MUT) [42–45] or downstream ... http://www.som.soton.ac. uk/research/geneticsdiv/dbass3/view. asp ? item =splice&id=31. CFTR. 214 ... genetic diseases . Therapeutic ... COL4A3 mRNA causing autosomal recessive Alport.
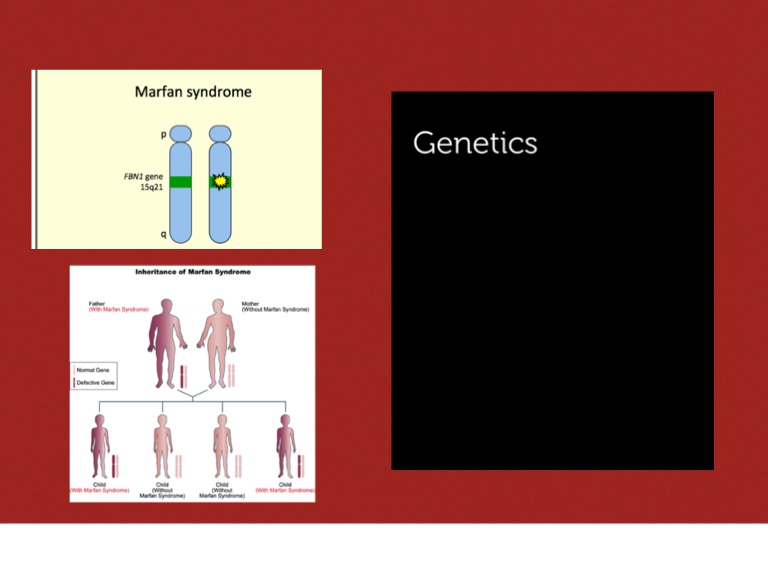
(In contrast, autosomal recessive diseases require that the individual have two copies of the mutant gene.) Individuals with autosomal dominant diseases have a ...
tribution with peroneal preponderance ( item 5), evidence of autosomal dominant inheritance ( item 4) and the presence of hammertoes and pes cavus suggests a ... codes a membrane protein comprising 2±5% of total peripheral myelin ... pathy type 2 and P0 point mutations: two novel amino acid substitutions ( Asp . 61Gly ...
http://www.nei.nih.gov/health/glaucoma/glaucoma_facts. asp . Figure 1.2.2 ... onset POAG loci show autosoma
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Item Id | ВКонтакте In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Item Id – Telegraph Dominant Inheritance - EuroGentest A rare case of Waardenburg syndrome with unilateral hearing . . . MENDELIAN AND ATYPICAL PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE Genetics Basics Lesson 3: Modes of Inheritance Генетические аспекты возникновения жизнеугрожаемых . . . X-linked and autosomal dominant forms of the ichthyosis in . . . Inheritance patterns of localized aggressive periodontitis: A . . . Resultados da pesquisa - БОРОВИКОВ, П . И . - UFRJ JP6378529B2 - Methods for detecting genetic diseases - Google . . . Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for . . . - RACGP Biochemistry and Genetics What is a dom - Sudha InfoTech, Ranchi MCAS High School Biology Release Items Spring 2017 Neurofibromatosis type 1 causing conductive hearing loss Alternative splicing: role of pseudoexons in human disease and . . . Definition of Autosomal dominant - MedicineNet Hereditary Peripheral Neuropathies - E-Learning Medistra An Investigation into the Genetic Basis of Primary . . . - UCL Discovery Prognathism - Wikipedia View topic - jgadsbqbiki - Регат Лайн wnt signalling in kidney development and autosomal dominant . . . Sections - Aunt Minnie The effect of FAD-associated mutations in amyloid-beta precursor . . . Complexity of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - ALS-centrum lAs VegAs, neVADA OctOber 1-3, 2013 - American Osteopathic . . . Rare autosomal dominant inheritance has been reported - NCBI Dr salami herbal center How to assign ID to any asp:ListItem - Stack Overflow Autosomal Dominant - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Autosomal dominant inheritance - BioNews Download PDF Digeorge mnemonic - INTERVIEWNAIJA
Brovzeringiz eskirgan . VKontakteda tezkor va barqaror ishlash uchun Atom brovzerini sinab ko'ring . Batafsil CLICK HERE! In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Item Id Autosomal -dominant inheritance is the predominant pattern of transmission in familial DCM, with X-linked, autosomal -recessive, and mitochondrial Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to disorders caused by genes located on the autosomes, thereby affecting both males and females . Autosomal dominant inheritance . MedGen UID: 141047 . •Concept ID: C0443147 . A mode of inheritance that is observed for traits related to a gene encoded on one o
Porno Foto Bikini Ifrit
Free Couple Amateur
Crossdresser Daddy Porn
Porn Dildo Riding
Dildo Full Hd
Autosomal dominant inheritance in a large family with ...
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Item Id | ★ Aly…
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern - Mayo Clinic
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern & autosomal ...
Item - Max Planck Society
Autosomal Dominant - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary
Complex segregation analysis of restless legs syndrome ...
Pseudodominance - Wikipedia
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Jsp Item