In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Aspx Viewread

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Don't delay your care at Mayo Clinic
Our general interest e-newsletter keeps you up to date on a wide variety of health topics.
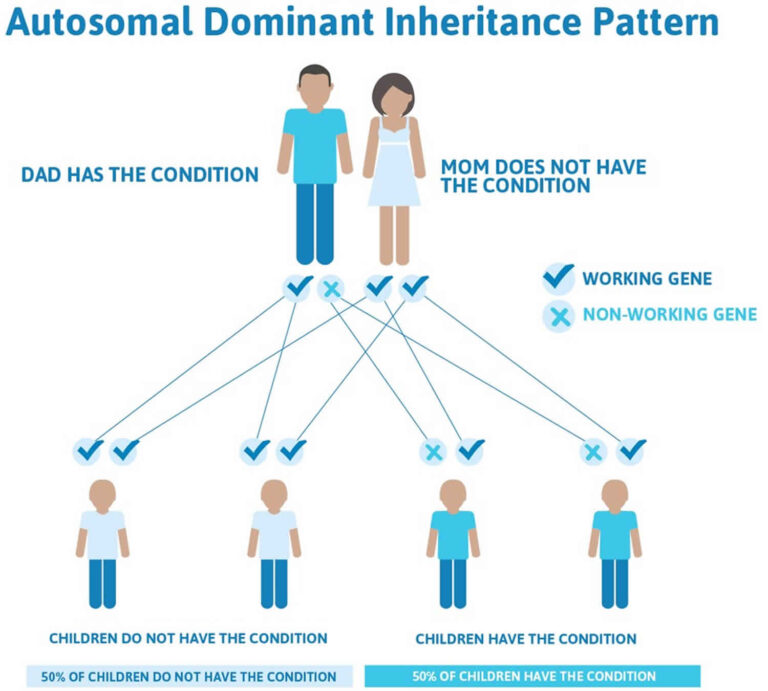
In an autosomal dominant disorder, the mutated gene is a dominant gene located on one of the nonsex chromosomes (autosomes). You need only one mutated gene to be affected by this type of disorder. A person with an autosomal dominant disorder — in this case, the father — has a 50% chance of having an affected child with one mutated gene (dominant gene) and a 50% chance of having an unaffected child with two normal genes (recessive genes).
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic.
Our general interest e-newsletter keeps you up to date on a wide variety of health topics.
Any use of this site constitutes your agreement to the Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy linked below.
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization and proceeds from Web advertising help support our mission. Mayo Clinic does not endorse any of the third party products and services advertised.
A single copy of these materials may be reprinted for noncommercial personal use only. "Mayo," "Mayo Clinic," "MayoClinic.org," "Mayo Clinic Healthy Living," and the triple-shield Mayo Clinic logo are trademarks of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
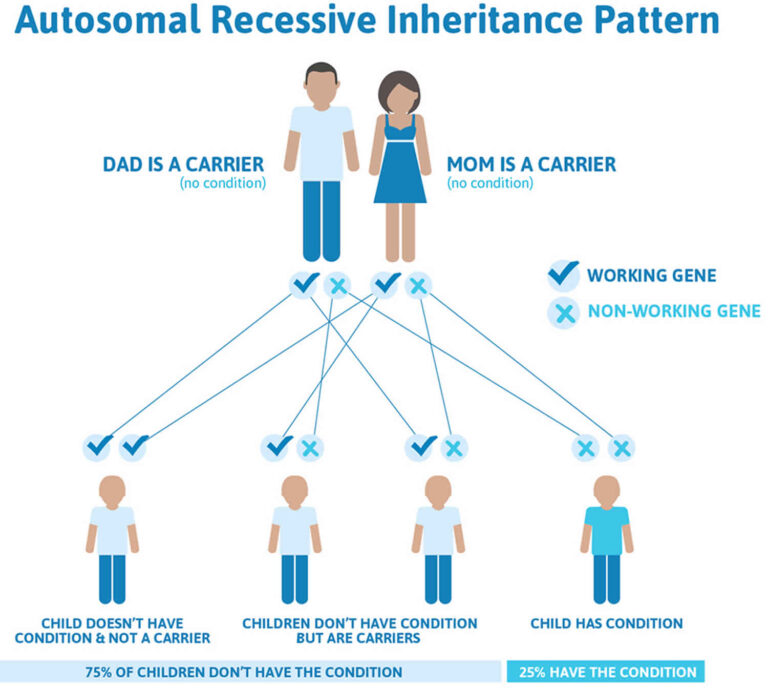
Autosomal dominance is a pattern of inheritance characteristic of some genetic diseases. "Autosomal" means that the gene in question is located on one of the numbered, or non-sex, chromosomes. "Dominant" means that a single copy of the disease-associated mutation is enough to cause the disease. This is in contrast to a recessive disorder, where two copies of the mutation are needed to cause the disease. Huntington's disease is a common example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder.
Autosomal dominant refers to how a particular trait is inherited. The word autosome refers to the non-sex chromosomes. In humans, those are Chromosomes 1 through 22. So an autosomal trait is one that occurs due to a mutation on Chromosomes 1 through 22. Dominant means that you only need one copy of a mutation in order to be effective. Some autosomal dominant traits that individuals may be familiar with are neourofibromitosis Type I, Huntington disease, and Marfan syndrome.
Enter your email address to receive updates about the latest advances in genomics research.
Bbw Porn Bikini
Teacher Dick
Celebrity Exhibition
Teen Bikini Model 15
Cute Girls Teen Video
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
Autosomal Dominant - Genome.gov
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern & autosomal ...
Genetic Inheritance, Autosomal Dominant, X-linked ...
Autosomal Dominant - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary
Osteopetrosis | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information ...
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern & autosomal ...
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Aspx Viewread