In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Aspx Productid

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Genes are the blueprints for making proteins. Our bodies need proteins to develop and work properly. Most genes come in pairs. One is inherited from the mother and the other from the father. Genes inherited from our biological parents are expressed in specific ways. One of these basic patterns is called autosomal dominant inheritance.
Sex chromosomes, which determine male or female gender
Autosomes, which are all of the other chromosomes (chromosome pairs 1 through 22) or nonsex chromosomes
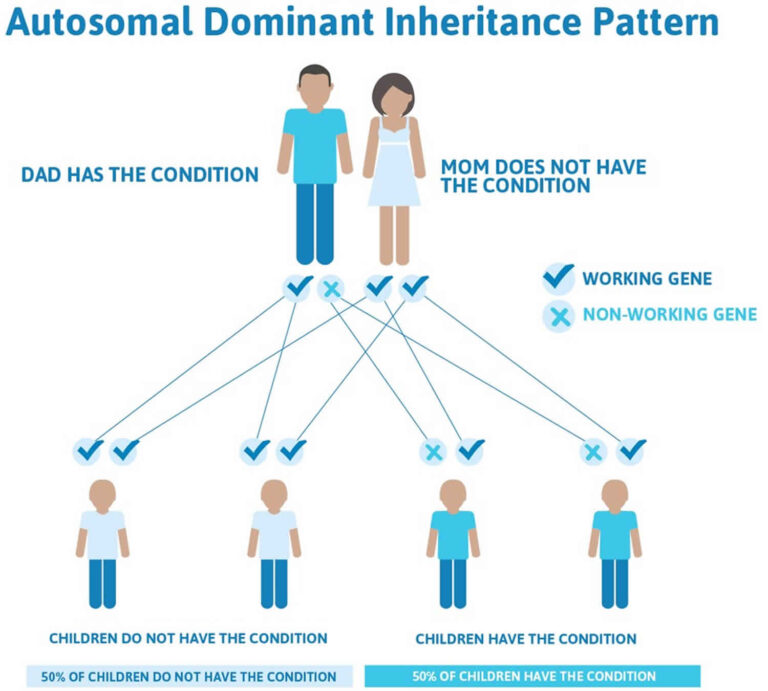
Autosomal inheritance of a gene means that the gene is located on one of the autosomes. This means that males and females are equally likely to inherit the gene. "Dominant" means that a single copy of the gene can cause a particular trait, such as brown eyes instead of blue eyes. When a parent has a dominant gene, there is at least a 50% chance that any child they have will also have the trait.
There are 4 possible combinations in the children (see figure). These combinations are possible every time a pregnancy occurs between these 2 individuals. The gender of the children (whether they are sons or daughters) does not matter. The chance is 50/50 for them to inherit the autosomal genes.
A characteristic of some dominant genes is that they can have variable expression. This means that some people have milder or more intense characteristics than others. Another important characteristic of dominant genes is that, in some cases, they can have reduced penetrance. This means that sometimes a person can have a dominant gene copy but not show any signs of the gene. The concept of reduced penetrance is particularly important in the case of autosomal dominant cancer susceptibility genes. If a person has inherited a cancer susceptibility gene, it does not mean they will automatically develop cancer. It simply means that the person has inherited a mutation in a gene that gives them a higher chance to develop cancer than someone without the mutation.
Examples of conditions involving autosomal dominant inheritance are:
©2021 University of Rochester Medical Center Rochester, NY
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families.
In an autosomal dominant disease, if you get the abnormal gene from only one parent, you can get the disease. Often, one of the parents may also have the disease.
Inheriting a disease, condition, or trait depends on the type of chromosome affected (nonsex or sex chromosome). It also depends on whether the trait is dominant or recessive.
A single abnormal gene on one of the first 22 nonsex (autosomal) chromosomes from either parent can cause an autosomal disorder.
Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease. This happens even when the matching gene from the other parent is normal. The abnormal gene dominates.
This disease can also occur as a new condition in a child when neither parent has the abnormal gene.
A parent with an autosomal dominant condition has a 50% chance of having a child with the condition. This is true for each pregnancy.
It means that each child's risk for the disease does not depend on whether their sibling has the disease.
Children who do not inherit the abnormal gene will not develop or pass on the disease.
If someone is diagnosed with an autosomal dominant disease, their parents should also be tested for the abnormal gene.
Examples of autosomal dominant disorders include Marfan syndrome and neurofibromatosis type 1.
Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF. Patterns of single-gene inheritance. In: Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF, eds. Thompson & Thompson Genetics in Medicine. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 7.
Scott DA, Lee B. Patterns of genetic transmission. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed..Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 97.
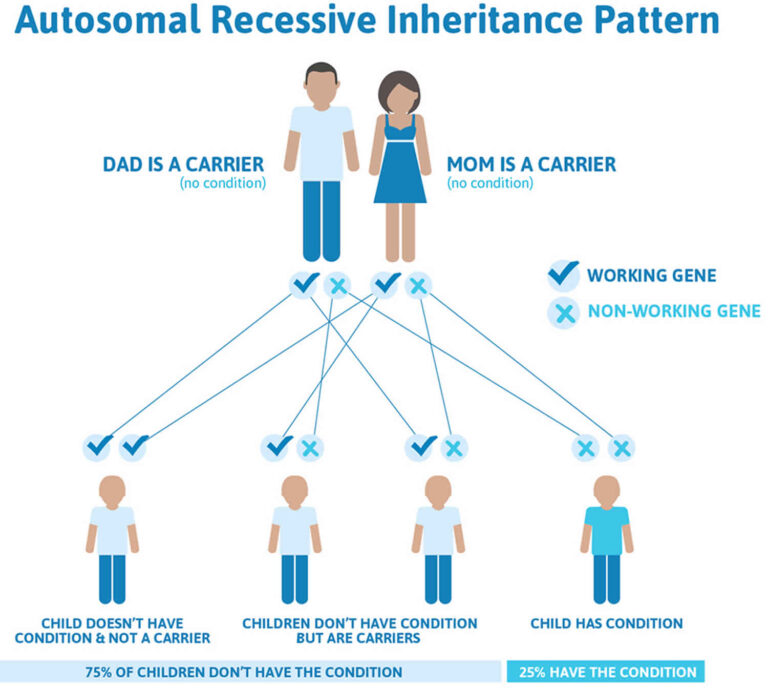
In the case of autosomal dominant genes, a single abnormal gene on one of the autosomal chromosomes (one of the first 22 non-sex chromosomes) from either parent can cause the disease. One of the parents will have the disease (since it is dominant) in this mode of inheritance and that person is called the CARRIER. Only one parent must be a carrier in order for the child to inherit the disease.
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2021 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
A.D.A.M. content is best viewed in IE9 or above, Firefox and Google Chrome browser.
Suck Old Dick
Very Younger Girls Bikini
Teen Bisexual Porn
Cute Latina
Layla Bukkake
Autosomal dominant - Adam
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - Health Encyclopedia ...
HIE Multimedia - Autosomal dominant
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern - Mayo Clinic
Autosomal Dominant and Recessive Inheritance ...
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern & autosomal ...
Osteopetrosis | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information ...
Autosomal Dominant - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Aspx Productid