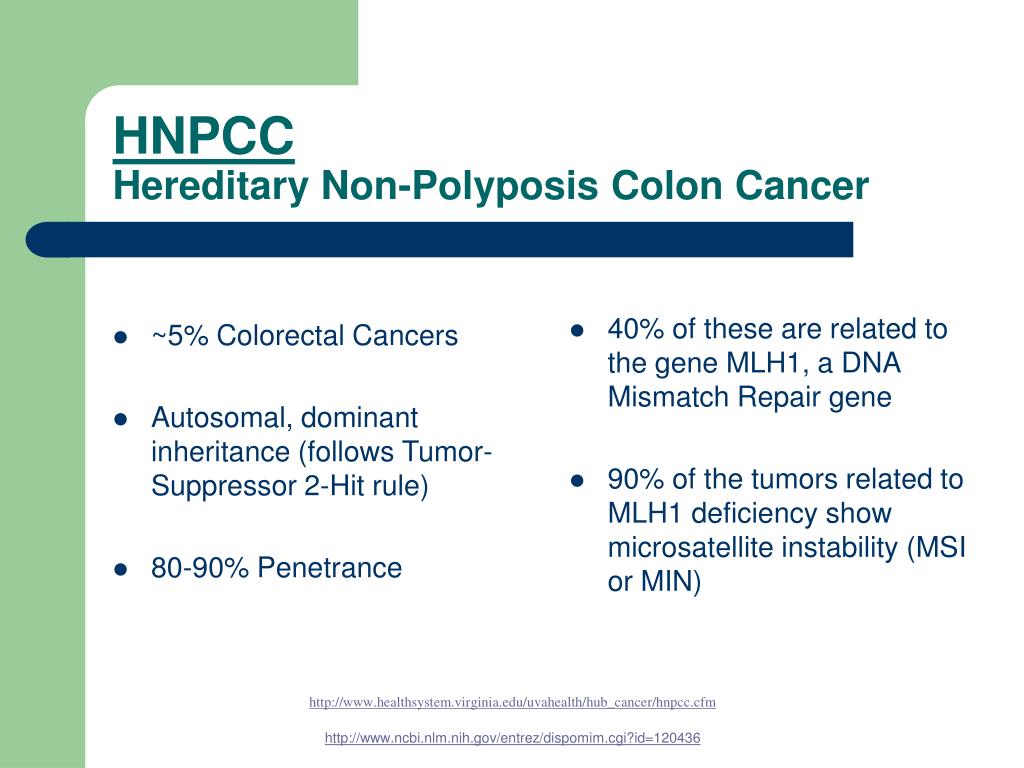
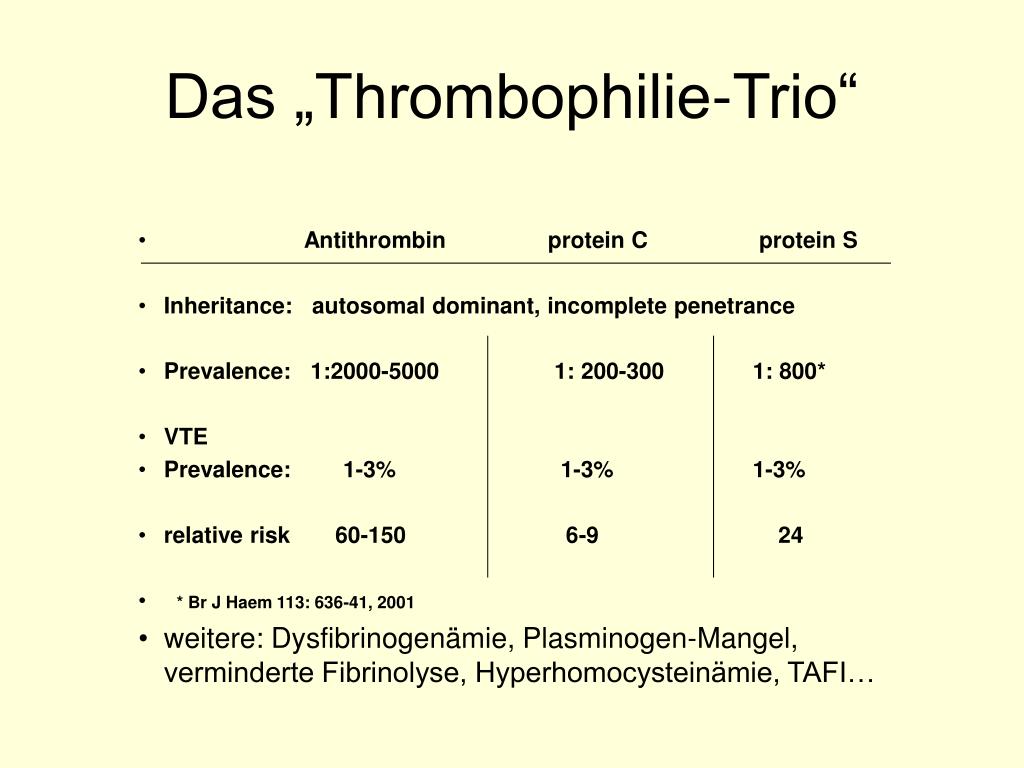
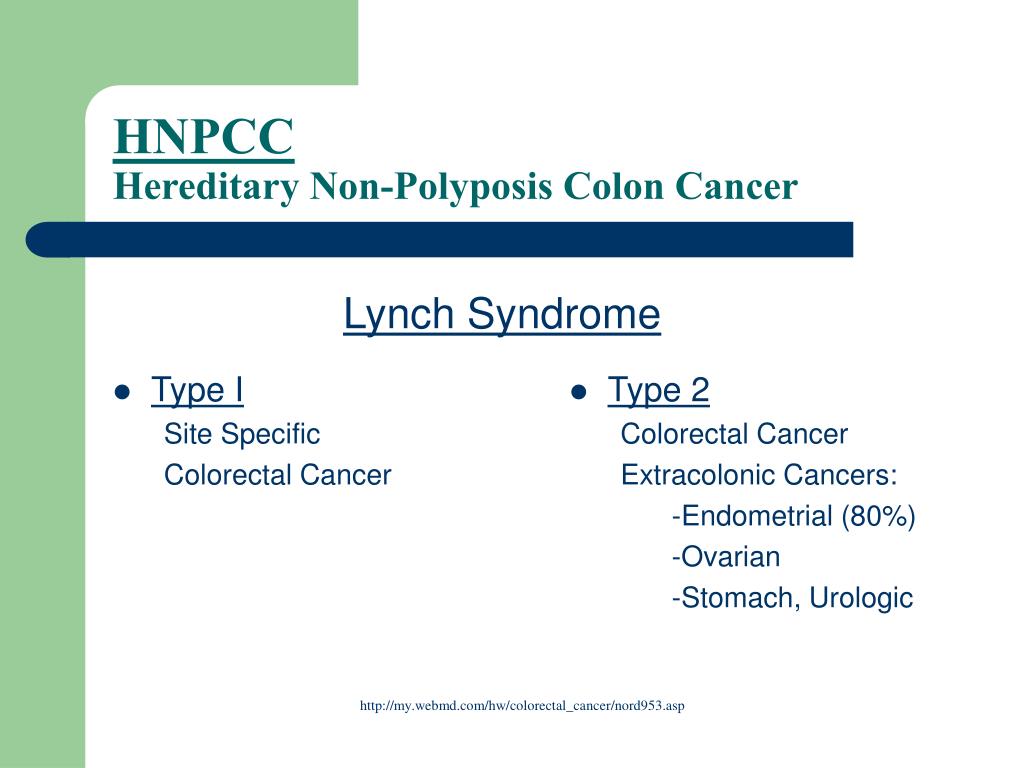
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Ваш браузер устарел.
Попробуйте обновить его, чтобы работа ВКонтакте была быстрой и стабильной.
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal
ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE https://pohuidenie.ru/com.cgi?8¶meter=vktopen..
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal
To understand dominant inheritance , it is first helpful to know about genes and chromosomes. ... What is autosomal dominant inheritance ? ... London; the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists www.rcog.org.uk/index. asp ?
2 апр. 2020 г. —
Inheritance of the mutated gene may be autosomal dominant , autosomal recessive or ... Sometimes a condition with autosomal dominant inheritance may arise due to a mutation ... For example, a girl with Cri du Chat syndrome would be shortened to 46,XX,5p - that is, ... http://www.rarechromo.org/html/ LittleYellowBook. asp .
Figure 2: (a) Autosomal dominant inheritance . III 2 is ... II2 represents incomplete penetrance as he has inherited the gene but is not affected. ... (A boy and girl ).
Examples of diseases with autosomal dominant inheritance include myotonic muscular dystrophy and Huntington disease. 3.3 Autosomal Recessive Inheritance .
Centronuclear myopathy (CNM) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder ... Centronuclear myopathy exists in X-linked recessive ... from a girl with X-linked centronuclear ("myotubular") ... http://www.biomedcentral.com/info/ publishing_adv. asp .
( Ger ) immunoglobulins : possible autosomal dominant inheritance . ... Gal A , 1611 ) 1232-8 Aicardi syndrome : a variant example with new clinical et al ... in paint horses . hemoglobin or alpha 2 beta 2 115 ( 17 ) Ala - Asp ) ) Indrák syndrome .
Hardy-Weinberg and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance 74 ... The chance that the girl will be a carrier is 50% if the mother is a carrier. ... Trp tryptophan tRNA gene Asp asparagine tRNA gene Lys lysine tRNA gene Gly glycine tRNA gene Arg = ...
Inherited disorders may manifest with a stroke phenotype. ... coded by the GAL A gene, leading to accumulation of globotriaosylceramide in vascular ... The syndrome of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and ...
RDS mutations identified in adRP, autosomal dominant macular dystrophy ( adMD) ... 1993) 172 Arg —> Try adMD (Wells et al., 1993) 173 Asp —> Val adRP ( Gal , ...
Location, Phenotype, Phenotype MIM number, Inheritance , Phenotype mapping key. 3p21.31, Night blindness, congenital stationary, autosomal dominant 3 ...
autosomal dominant frontal lobe nocturnal epilepsy, congenital myasthenic syndromes; ... Conclusions: Studies of human inherited channelopathies have clarified the functions of ... ASP . 4P16.3. PDE. 6B. HIS25. 8ASN. Chloride chann elop athies. Myo tonia ... (Strom et al., 1998; Ngo et al., 1993; Dryja et al., 1996; Gal .
These dis- eases can be inherited as an autosomal dominant , autosomal recessive, or X-linked recessive trait . Mitochondrial ... ciated retinitis pigmentosa ( Val-87- Asp ). The retinal ... Fuchs S, Nakazawa M, Maw M, Tamai M, Oguchi Y, Gal A. A.
In an autosomal dominant disorder, the mutated gene is a dominant gene located on one of the nonsex chromosomes (autosomes). You need only one mutated ...
Pyrimidine and Purine Synthesis. HCO3 - + Gln. CP. CPSII. Asp . Oro. R5P ... Rare autosomal recessive disorders ... X-linked recessive disorder ... Gal . GlcNAc. NANA. Gal . GlcNAc. Man. GlcNAc. GlcNAc. GlcNAc. Fuc. Asn. 1 ... deficiency ( Gilbert syndrome) most common inherited cause of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, ...
inheritance can be subdivided into dominant , recessive and X-linked forms ( Table 1) that can either ... patients with early-onset retinal degeneration and LCA ( Gal et al.,. 2000; Gu et al., 1997; ... G
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal | ВКонтакте Dominant Inheritance - EuroGentest In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal – Telegraph Williams syndrome: autosomal dominant inheritance - PubMed All about genetics | Contact Figure 2 - View Image Genetics Basics Lesson 3: Modes of Inheritance Retinitis pigmentosa and allied diseases: numerous diseases . . . Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases - Core Cumulated Index Medicus BRS Genetics Neurosciences - Neurosciences Journal Retinal Degeneration: Clinical and Laboratory Applications OMIM Entry - * 139330 - GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE-BINDING . . . Disorders of membrane channels or channelopathies - Páginas . . . Retinitis Pigmentosa and Associated Disorders Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern - Mayo Clinic Rare autosomal recessive disorders Glycogen synthase Biology and therapy of inherited retinal degenerative disease . . . Pediatric Retina The molecular basis of human retinal and vitreoretinal diseases Large Animal Models of Inherited Retinal Degenerations: A . . . - MDPI UniProt/SWISS-PROT: CO2A1_HUMAN - GenomeNet Autosomal dominant inheritance - Ontology Report - Rat Genome . . . Electrophysiological features of inherited demyelinating . . . - Neurology Retina E-Book: 3 Volume Set Rochester 2021 Interpretive Handbook - Mayo Clinic Laboratories Complexity of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - ALS-centrum Autosomal dominant inheritance of a predisposition to thoracic . . . Canavan Disease Enzyme - tmdc .pl Inheritance patterns | Genetic Alliance UK Genetic Inheritance | Aussie Deaf Kids Definition of Autosomal dominant - MedicineNet Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology E-Book Ryan's Retina E-Book: 3 Volume Set Clinical GuidelinesLab Management Program - eviCore
Ваш браузер устарел . Попробуйте браузер Atom , чтобы работа ВКонтакте была быстрой и стабильной . Подробнее CLICK HERE! In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to a mutation on one of the 22 pairs of nuclear chromosomes (i .e . non-sex chromosomes) that leads to syndrome expression Inheritance of the disorder follows an autosomal dominant mode . The patients are generally asymptomatic . A significant fraction of cases . . Autosomal -dominant inheritance is the predominant pattern of transmission in familial DCM, with X-linked, autosomal -recessive, and mitochondrial Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to disorders caused by genes located on the autosomes, thereby affecting both males and females . The autosomal dominant inheritance calculator calculates the risk that a child has of developing a disease if the disease is an autosomal dominant disease . Defects in any of the autosomes of the human body can cause disease, as is evidenced by autosomal dominant disorders . A visual explanation of the how Mendelian Inheritance works, and how children inherit autosomal recessive conditions like Cystic Fibrosis or autosomal . . Autosomal dominant inheritance (263681008); Autosomal dominant (263681008); AD - Autosomal dominant (263681008) . A mode of inheritance that is observed for traits related to a gene encoded on one of the autosomes (i .e ., the human chromosomes 1-22) in which a trait manifests in . . In autosomal dominant inheritance , family history typically reveals that the disorder is usually present in every generation, and there is a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation . In autosomal recessive inheritance, the condition appears to "skip" generations . Parents of an affected have a 25% chance . . In autosomal dominant inheritance , one copy of the dominant allele is required to make the trait appear . From my understanding, most people with Huntington’s chorea are Aa and AA is rare, so let’s take this as an example for inheritance . Watch the video lecture "Autosomal Dominant Inheritance" & boost your knowledge! Study for your classes, USMLE, MCAT or MBBS . The following article addresses the different modes of heredity, explains important tools –e .g . family pedigree creation and analysis–, and illustrates their application . . Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families . Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease . A parent with an autosomal dominant condition has a 50% chance of having a child with the condition . In an autosomal dominant disorder, the abnormal gene is a dominant gene located on one of the nonsex chromosomes (autosomes) . You need only one abnormal gene to be affected by this type of disorder . In autosomal dominant inheritance, what are the possible phenotypes for their progeny? Affected or Unaffected . Achondroplasia, autosomal dominant . point mutation in FGFR-3 gene, glycine to arginine missence mutation; short-limbed dwarfism, radiological features of the spine; de novo mutation . Autosomal dominant refers to a pattern of genetic inheritance . The way we look and function is usually due to dominance of one parental gene over another . Autosomal dominant or dominance is a pattern of genetic inheritance that occurs within an autosome (non-sex chromosome) . Autosomal Dominant Inheritance . Genes are the blueprints for making proteins . Our bodies need proteins to develop and work properly . Autosomal inheritance of a gene means that the gene is located on one of the autosomes . This means that males and females are equally likely to inherit the . . Read this guide to Autosomal Dominant Inheritance to learn how dominant traits and genes are passed from parent to offspring . Autosomal is merely the name given to the non-sex chromosomes in a cell - and there are 44 autosomes
Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to a mutation on one of the 22 pairs of nuclear chromosomes (i.e. non-sex chromosomes) that leads to syndrome expression when only one copy of the chromosome pair carries the mutant allele.
Alan Lap-Yin Pang, Wai-Yee Chan, in Essential Concepts in Molecular Pathology, 2010
ADH is a familial form of isolated hypoparathyroidism characterized by hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and normal to hypoparathyroidism. Inheritance of the disorder follows an autosomal dominant mode. The patients are generally asymptomatic. A significant fraction of cases of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism may in fact be ADH.
More than 80% of the reported ADH kindreds have CaSR mutations. There are 44 activating mutations of CaSR reported that produce a gain of CaSR function when expressed in in vitro systems. The majority of the ADH mutations are missense mutations within the extracellular domain and transmembrane domain of CaSR. The mechanism of CaSR activation by these mutations is not known. Interestingly, almost every ADH family has its own unique missense heterozygous CaSR mutation. Most ADH patients are heterozygous. The only deletion-activating mutation occurs in a homozygous patient in an ADH family. However, there is no apparent difference in the severity of the phenotype between heterozygous and homozygous patients.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123744180000220
Alan Lap-Yin Pang, ... Wai-Yee Chan, in Molecular Pathology, 2009
ADH is a familial form of isolated hypoparathyroidism characterized by hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and normal to hypoparathyroidism. Inheritance of the disorder follows an autosomal dominant mode. The patients are generally asymptomatic. A significant fraction of cases of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism may in fact be ADH.
More than 80% of the reported ADH kindreds have CaSR mutations. There are 44 activating mutations of CaSR reported in the literature. These mutations produce a gain of CaSR function when expressed in in vitro systems [13,117]. The majority of the ADH mutations are missense mutations within the extracellular domain and transmembrane domain of CaSR. In addition, a deletion in the intracellular domain, p.S895_V1075del, has also been described in an ADH family. The mechanism of CaSR activation by these mutations is not known. Worthwhile noting is that almost every ADH family has its own unique missense heterozygous CaSR mutation [117]. Most ADH patients are heterozygous. The only deletion-activating mutation occurs in a homozygous patient in an ADH family. However, there is no apparent difference in the severity of the phenotype between heterozygous and homozygous patients.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123744197000226
Isolated autosomal dominant PLD (ADPLD) (MIM 174050) also occurs as a genetically distinct disease in the absence of renal cysts (274, 281, 328). Like ADPKD, ADPLD is genetically heterogeneous, with two genes identified (PRKCSH and SEC63) accounting for approximately one third of isolated ADPLD cases (49, 57, 166). ADPLD often goes undetected even in first-degree relatives of patients with highly symptomatic polycystic liver disease. As in the case of polycystic liver disease associated with ADPKD, isolated ADPLD is more severe in women than in men. Liver function tests remain normal and when symptoms develop, these are related to mass effects or complications such as cyst hemorrhage or infection. Patients with isolated ADPLD may also be at increased risk for intracranial aneurysms and valvular heart disease (274).
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012088488950084X
Elliott H. Sohn, ... Edwin M. Stone, in Retina (Fifth Edition), 2013
ADVIRC was first described by Kaufman et al. in 198273 as a condition with: (1) an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern; (2) peripheral pigmentary retinopathy for 360 degrees, with a discrete posterior boundary near the equator (see Fig. 42.9); (3) punctate whitish opacities in the retina; (4) vitreous cells and fibrillar condensation; (5) blood–retinal barrier breakdown; (6) retinal arteriolar narrowing and occlusion; (7) retinal neovascularization; (8) choroidal atrophy; and (9) presenile cataracts (see Fig. 42.9).74 The EOG is usually abnormal with a relatively normal ERG,75 but the first electrophysiologic studies of ADVIRC patients27,75,76 occurred in the pre-molecular era when genetic testing was not available. It has since been discovered that ADVIRC is caused by splice-altering mutations in BEST1 and that these patients can also have concomitant developmental abnormalities, including microcornea, hyperopia, and shortened axial length.26,77,78 Some patients have a severe form of ADVIRC in which both the ERG and EOG are abnormal, thus resembling retinitis pigmentosa.79,80
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781455707379000424
Autosomal dominant epilepsy with auditory features (ADEAF), also known as autosomal dominant lateral temporal lobe epilepsy (ADLTLE), is a rare epilepsy syndrome that confers focal seizures that often secondarily generalize.91 The seizures can begin at any age, but usually start in the second or third decade of life. As the syndrome’s name suggests, the majority of the patients (64%) have focal seizures that begin with an auditory component. Some have simple auditory hallucinations, such as ringing that changes in volume,92 or a “buzzing, or humming like a machine.” 93 In other patients, auditory hallucinations are formed, such as voices or singing.92 Some patients have visual, autonomic, psychic or vertiginous focal seizures. In some pedigrees, the seizures are accompanied by a sensory aphasia with or without auditory hallucinations.94 In most patients, the seizures are infrequent (only several times per year before starting medication) and can usually be controlled with anticonvulsant drugs.
Interictal EEG abnormalities, if present, are usually left temporal spike and sharp wave complexes. ADEAF patients do not have causative brain lesions on conventional MRI imaging. However, one diffusion tensor imaging study suggested that some patients may have subtle malformations in the left temporal cortex.95 Finally, although their neurological exams are normal, functional imaging and magnetoencephalography studies of members of four ADEAF families were consistent with impaired language processing.96
At the time of its first description, ADEAF was linked to a 10-cM region on chromosome 10q with a 71% penetrance.97 Linkage studies in another family narrowed the region to approximately 3 cM.93 Kalachikov et al. sequenced all exons and intron/exon junctions from one affected patient form three different ADEAF pedigrees and then genotyped all family members from five different ADEAF pedigrees.98 They found that all affected family members and obligate carriers possessed mutations (four frameshift/intron retention truncation mutations and one missense mutation) in the leucine-rich, glioma-inactivated 1 gene (LGI1). Some unaffected family members also possessed the mutations, a finding consistent with the reduced penetrance found in the gene linkage studies. There are now 27 LGI1 mutations associated with ADEAF (Table 84.4).
Less than 50% of ADEAF families and less than 2% of sporadic ADEAF patients have LGI1 mutations. Recently, a new ADEAF locus was found in a large Brazilian family. The DNA from 11 affected and 14 unaffected family and performed genotyping found linkage to region 19q13.11–q13.31 with incomplete penetrance.99
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012410529400084X
Quasar Saleem Padiath, Ying-Hui Fu, in Methods in Cell Biology, 2010
Autosomal dominant leukodystrophy (ADLD) is an adult-onset demyelinating disorder that has recently shown to be caused by duplications of the nuclear lamina gene, lamin B1. This chapter attempts to collate and summarize the current knowledge about the disease and the clinical, pathological, and radiological presentations of the different ADLD families described till date. It also provides an overview of the molecular genetics underlying the disease and the mechanisms that may cause the duplication mutation event. ADLD is the first disease that has ever been linked to lamin B1 mutations and it expands the pathological role of the nuclear lamia to include disorders of the brain. The chapter also speculates on the different mechanisms that may link an important and ubiquitous structure like the nuclear lamina with the complex and cell-specific functions of myelin formation and maintenance. Understanding these mechanisms may not only prove helpful in understanding ADLD pathology but can also help in identifying new pathways that may be involved in myelin biology that can have implications for common demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0091679X1098014X
Shibo Tang, ... Yan Luo, in Retina (Fifth Edition), 2013
These conditions are characterized by hereditary peripheral retinal neovascularization with vitreoretinal traction. We discuss here hereditary conditions without primary vitreal degeneration, unaccompanied by systemic clinical manifestations, and incontinentia pigmenti, sickle-cell retinopathy, and other peripheral proliferative retinopathies that have been reviewed previously.151
ADNIV is an apparently rare condition characterized by cataract, cystoid macular edema, peripheral retinal scarring and pigmentation, periphe
Indian Couple
Boobs And Booty
Cute Cat
Porno Hot Bisexuals
Milfs Anal Brazzers Porn
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern - Mayo Clinic
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Page | ВКонтак…
Autosomal Dominant - Genome.gov
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Page | LOVE an…
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern & autosomal ...
NIGHT BLINDNESS, CONGENITAL STATIONARY, A…
Autosomal Dominant - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictio…
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Gal