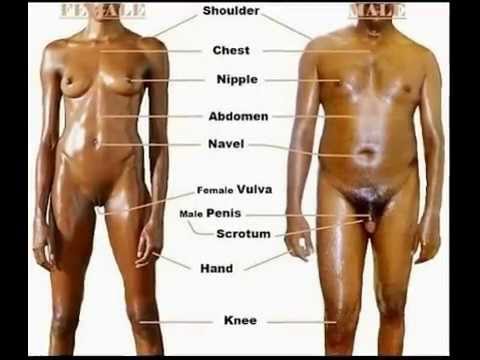
Human Male Female

🛑 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_sex_ratio
Gender imbalance is a disparity between males and females in a population. As stated above, males usually exceed females at birth but subsequently experience different mortality rates due to many possible causes such as differential natural death rates, war casualties, and deliberate gender control.
According to Nicholas Kristof and Shery…
Gender imbalance is a disparity between males and females in a population. As stated above, males usually exceed females at birth but subsequently experience different mortality rates due to many possible causes such as differential natural death rates, war casualties, and deliberate gender control.
According to Nicholas Kristof and Sheryl WuDunn, two Pulitzer Prize-winning reporters for the New York Times, violence against women is causing gender imbalances in many developing countries. They detail sex-selective infanticide in the developing world, particularly in China, India and Pakistan.
Commonly, countries with gender imbalances have three characteristics in common. The first is a rapid decline in fertility, either because of preference for smaller families or to comply with their nation's population control measures. Second, there is pressure for women to give birth to sons, often because of cultural preferences for male heirs. Third, families have widespread access to technology to selectively abort female foetuses.
As a contributing measure to gender imbalance in developing countries, Kristof and WuDunn's best estimate is that a girl in India, from 1 to 5 years of age, dies from discrimination every four minutes (132,000 deaths per year); that 39,000 girls in China die annually, within the first year of life, because parents did not give girls the same medical care and attention that boys received. The authors describe similar gender discrimination and gendercide in Congo, Kenya, Pakistan, Iraq, Bahrain, Thailand and many other developing countries.
Some of the factors suggested as causes of the gender imbalance are warfare (excess of females, notably in the wake of WWI in western Europe, and WWII, particularly in the Soviet Union); sex-selective abortion and infanticide (excess of males, notably in China as a result of the one-child policy, or in India); and large-scale migration, such as that by male labourers unable to bring their families with them (as in Qatar and other Gulf countries ). Gender imbalance may result in the threat of social unrest, especially in the case of an excess of low-status young males unable to find spouses, and being recruited into the service of militaristic political factions. Economic factors such as male-majority industries and activities like the petrochemical, agriculture, engineering, military, and technology also have created a male gender imbalance in some areas dependent on one of these industries.
One study found that the male-to-female sex ratio in the German state of Bavaria fell as low as 0.60 after the end of World War II for the most severely affected age cohort (those between 21 and 23 years old in 1946). This same study found that out-of-wedlock births spiked from approximately 10–15% during the inter-war years up to 22% at the end of the war. This increase in out-of-wedlock births was attributed to a change in the marriage market caused by the decline in the sex ratio.
The Northern Mariana Islands have the highest female ratio with 0.77 males per female. Qatar has the highest male ratio, with 2.87 males/female. For the group aged below 15, Sierra Leone has the highest female ratio with 0.96 males/female, and the Republic of Georgia and the People's Republic of China are tied for the highest male ratio with 1.13 males/female (according to the 2006 CIA World Factbook).
The value for the entire world population is 1.01 males/female, with 1.07 at birth, 1.06 for those under 15, 1.02 for those between 15 and 64, and 0.78 for those over 65.
The "First World" G7 members all have a gender ratio in the range of 0.95–0.98 for the total population, of 1.05–1.07 at birth, of 1.05–1.06 for the group below 15, of 1.00–1.04 for the group aged 15–64, and of 0.70–0.75 for those over 65.
Countries on the Arabian peninsula tend to have a 'natural' ratio of about 1.05 at birth but a very high ratio of males for those over 65 (Saudi Arabia 1.13, Arab Emirates 2.73, Qatar 2.84), indicating either an above-average mortality rate for females or a below-average mortality for males, or, more likely in this case, a large population of aging male guest workers. Conversely, countries of Northern and Eastern Europe (the Baltic states, Belarus, Ukraine, Russia) tend to have a 'normal' ratio at birth but a very low ratio of males among those over 65 (Russia 0.46, Latvia 0.48, Ukraine 0.52); similarly, Armenia has a far above average male ratio at birth (1.17), and a below-average male ratio above 65 (0.67). This effect may be caused by emigration and higher male mortality as result of higher Soviet era deaths; it may also be related to the enormous (by western standards) rate of alcoholism in the former Soviet states. Another possible contributory factor is an aging population, with a higher than normal proportion of relatively elderly people: we recall that due to higher differential mortality rates the ratio of males to females reduces for each year of age.
In the evolutionary biology of sexual reproduction the operational sex ratio (OSR), is the ratio of sexually competing males that are ready to mate to sexually competing females that are ready to mate, or alternatively the local ratio of fertilizable females to sexually active males at any given time. This is different from the physical sex ratio because it does not take into account sexually inactive or non-competitive individuals (individuals that do not compete for mates). On occasion, regions with a high male-low female sex ratio, e.g. Alaska, have shown a correlation with a higher rate of reported rape.
Factors affecting sex ratio in humans
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_differences_in_human_physiology
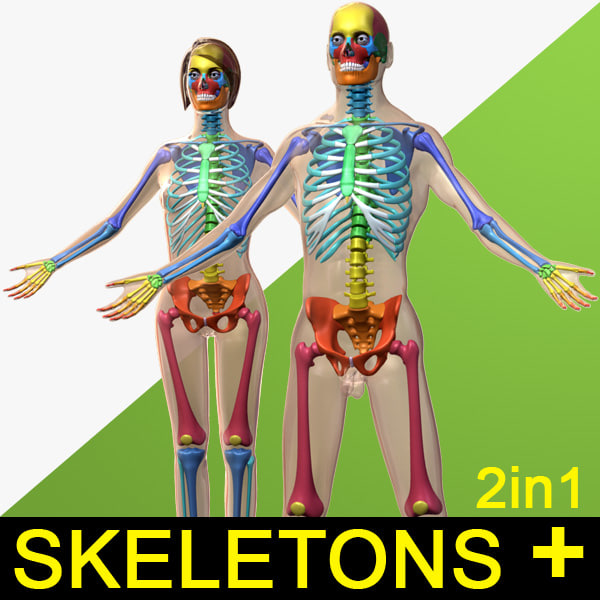
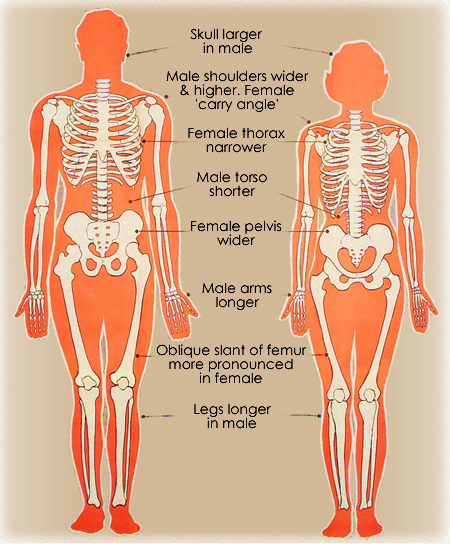
Skeleton
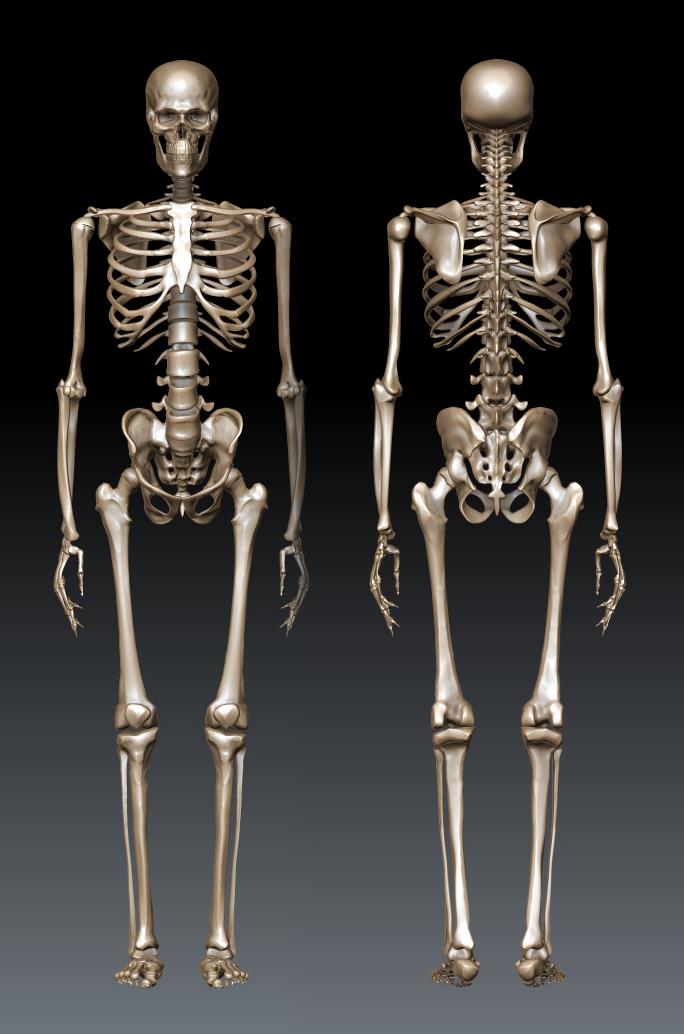
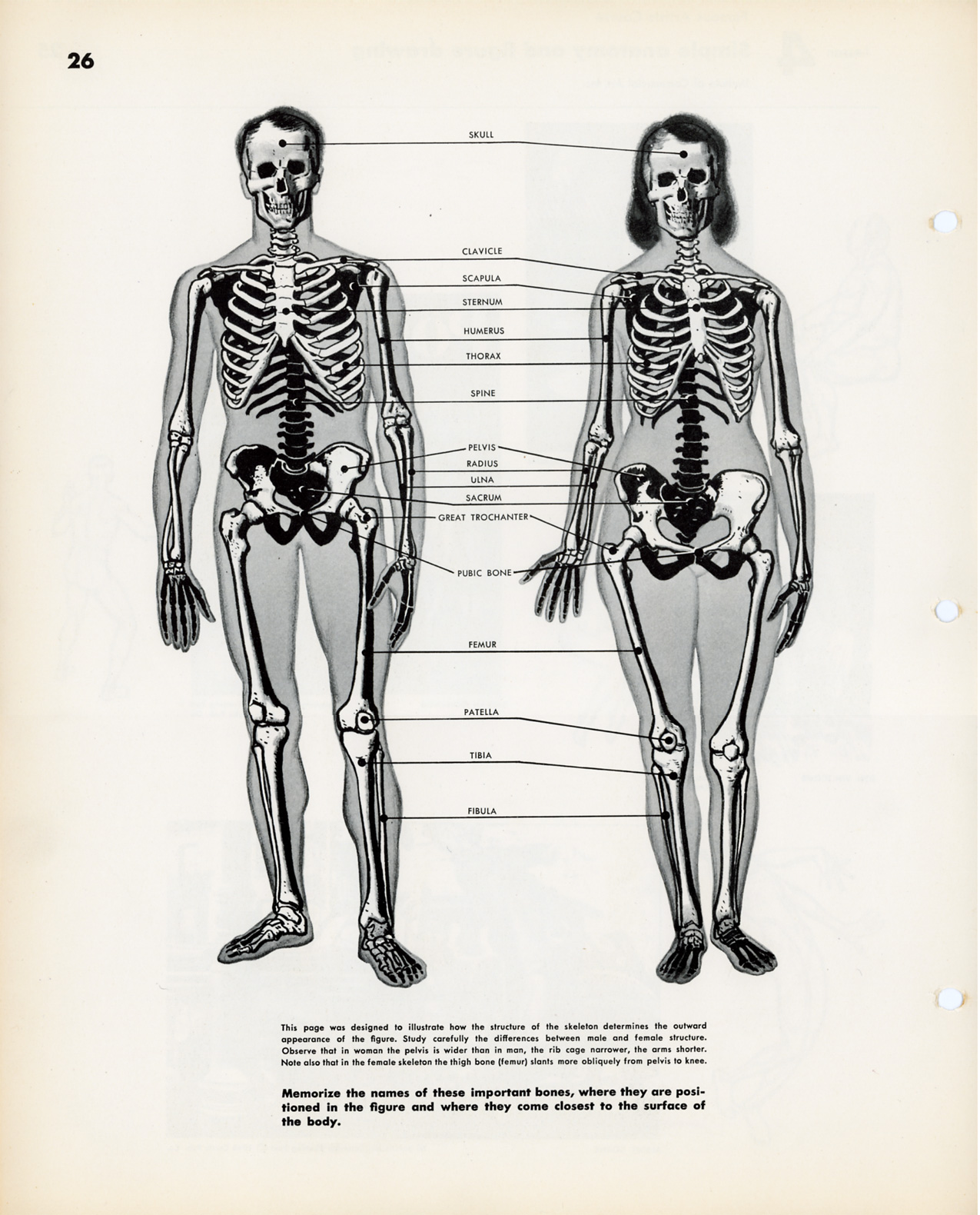
The female skeleton is generally less massive, smoother, and more delicate than the male; its rib cage is more rounded and smaller, its lumbar curve greater, and a generally longer and smaller female waist results from the chest being more narrow at the base, and the pelvis generally not as high.
The
Skeleton
The female skeleton is generally less massive, smoother, and more delicate than the male; its rib cage is more rounded and smaller, its lumbar curve greater, and a generally longer and smaller female waist results from the chest being more narrow at the base, and the pelvis generally not as high.
The pelvis is, in general, different between the human female and male skeleton. It differs both in overall shape and structure. The female pelvis, adapted for gestation and childbirth, is less high, but proportionately wider and more circular than in the male; its sacrum—the triangular bone at the upper posterior of the pelvic cavity, serving as the base of the spine—is also wider. The female pelvis is tilted anteriorly, often resulting in the more sway-backed appearance.
In females, the acetabula, the concave surfaces to which the balls of the femurs attach via ligaments, are located farther apart, which increases the distance between the most outer points of the femurs (their greater trochanters) and thus the width of the hips; female femurs are therefore, more generally angled (laterally, further away from vertical). This greater angle applies a larger portion of the gravitational/vertical load as valgus torque (rotational force against the knee). This, combined with the female's weaker tendons & ligaments and a narrower intercondylar notch, causes increased susceptibility to injury of the ACL in female athletes.
In contrast, the pelvis of the human male appears to be slightly narrower. It is believed that this makes it more optimized for walking and that an even wider female pelvis would have made walking more difficult; yet, more recent research tends to disprove this.
The following further generalizations have been made regarding male-female skeletal differences:
• Males in general have denser, stronger bones, tendons, and ligaments.
• Female skulls and head bones differ in size and shape from the male skull, with the male mandible generally wider, larger, and squarer than the female. In addition, males generally have a more prominent brow, an orbital with rounded border, and more greatly projecting mastoid processes.
• Males have a more pronounced Adam's apple or thyroid cartilage (and deeper voices) due to larger vocal cords.
• In males, the second digit (index finger) tends to be shorter than the fourth digit (ring finger), while in females the second digit tends to be longer than the fourth (see digit ratio).
• Males have slightly larger teeth than females and a greater proportion of the tooth in males is made up of dentine, whereas females have proportionately more enamel.
Finally, contrary to popular belief, males and females do not differ in the number of ribs; both normally have twelve pairs.
Muscle mass and strength
Females in general have lower total muscle mass than males, and also having lower muscle mass in comparison to total body mass; males convert more of their caloric intake into muscle and expendable circulating energy reserves, while females tend to convert more into fat deposits. As a consequence, males are generally physically stronger than females. While individual muscle fibers have similar strength between male and female, males have more fibers as a result of their greater total muscle mass. Males remain stronger than females when adjusting for differences in total body mass, due to the higher male muscle-mass to body-mass ratio. The greater muscle mass is reported to be due to a greater capacity for muscular hypertrophy as a result of higher levels of circulating testosterone in males.
Gross measures of body strength suggest that women are approximately 50-60% as strong as men in the upper body, and 60-70% as strong in the lower body. One study of muscle strength in the elbows and knees—in 45 and older males and females—found the strength of females to range from 42 to 63% of male strength. Another study found men to have significantly higher hand-grip strength than women, even when comparing untrained men with female athletes. Differences in width of arm, thighs and calves appear during puberty.
Sex determination and differentiation
Evolution of sexual dimorphism in human voice pitch
Sexual organs and reproductive systems
https://www.turbosquid.com/3d-models/3d/603879
Перевести · Human Male and Female Complete Anatomy - Body, Muscles, Skeleton, Internal Organs and …
https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/human-male-and-female-pelvis-6e04b899c5204a4eae1d20c4...
Перевести · THESE TWO PELVIS,MALE AND FEMALE,HAS BEEN BUILT FOR COMPARATIVE ANATOMY PROJECT. THE ORIGINAL CT FILES ARE FROM HEALTHY LIVING MEN AND WOMEN.HAS BEEN TRANSFORMED TO STL FILES WITH 3D SLICER(FREE SOFTWARE). - HUMAN MALE AND FEMALE …
HUMAN ANATOMY in ADVANCE- FEMALE & MALE BODY DIFFERENCES
Human #female reproductive system |sexual reproduction| 10th Biology :CBSE | ncert class 10 |Science
How to Draw Human Anatomy Male & Female Part 1 | Figure Drawing Basics | pixreels
Sexual Reproduction - Male and Female Reproductive System, Class 10 Biology
Human Reprodection Male and Female Part 3
Class 12 | Biology | Human Reproduction | Female Reproductive System
https://www.livescience.com/33513-men-vs-women-our-physical-differences-explained.html
Introduction
Breasts vs. Chests
Big Apple vs. Small
Square vs. Heart-Shaped Faces
Hairy vs. Not
Fair vs. Swarthy
Muscular vs. Curvy
\"Sexual dimorphism\" is the scientific term for physical differences between males and females of a species. Many extreme examples exist: Peacocks far outclass peahens, for instance, while female anglerfish both outsize and outwit their tiny, rudimentary, parasitic male counterparts.Unlike those animals, men and women are more physically similar than we are different. Nonetheless, there are a few key distinctions in our ph…
https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Male_human_genitalia
Перевести · 30.07.2020 · See also categories: Female human genitalia and Comparison of female and male genitalia. This is a main category requiring frequent diffusion and maybe maintenance . As many pictures …
What is the difference between male and female organs?
What is the difference between male and female organs?
Males and females have different sex organs. Females have two ovaries that store the eggs, and a uterus which is connected to a vagina. Males have testicles that produce sperm. The testicles are placed in the scrotum behind the penis. The male penis and scrotum are external extremities, whereas the female sex organs are placed "inside" the body.
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_differences_in_…
What is the ratio of males to females?
What is the ratio of males to females?
If there are 108,000 males and 100,000 females the ratio of males to females is 1.080 and the proportion of males is 51.9%. Scientific literature often uses the proportion of males. This article uses the ratio of males to females, unless specified otherwise.
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_sex_ratio
What are the differences between women and men?
What are the differences between women and men?
Tissues and hormones 1 Women generally have a higher body fat percentage than men, [1] whereas men generally have more muscle tissue mass. 2 Women usually have lower blood pressure than men, and women's hearts beat faster, even when they are asleep. 3 Men and women have different levels of certain hormones. ... More items...
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_differences_in_…
What is the difference between male and female hair?
What is the difference between male and female hair?
On average, males have more body hair than females. Males have relatively more of the type of hair called terminal hair, especially on the face, chest, abdomen and back. In contrast, females have more vellus hair. Vellus hairs are smaller and therefore less visible.
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_differences_in_…
https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Female_human_genitalia?uselang=de
Перевести · Siehe auch die Kategorien: Male human genitalia und Comparison of female and male genitalia. Dies ist eine Hauptkategorie, die häufig überfüllt ist. Es sollten so viele Bilder und Mediendateien wie möglich …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Third_gender
Перевести · Inscribed pottery shards from the Middle Kingdom of Egypt (2000–1800 BCE), found near ancient Thebes (now Luxor, Egypt), list three human genders: tai (male), sḫt ("sekhet") and hmt (female). Sḫt is …
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
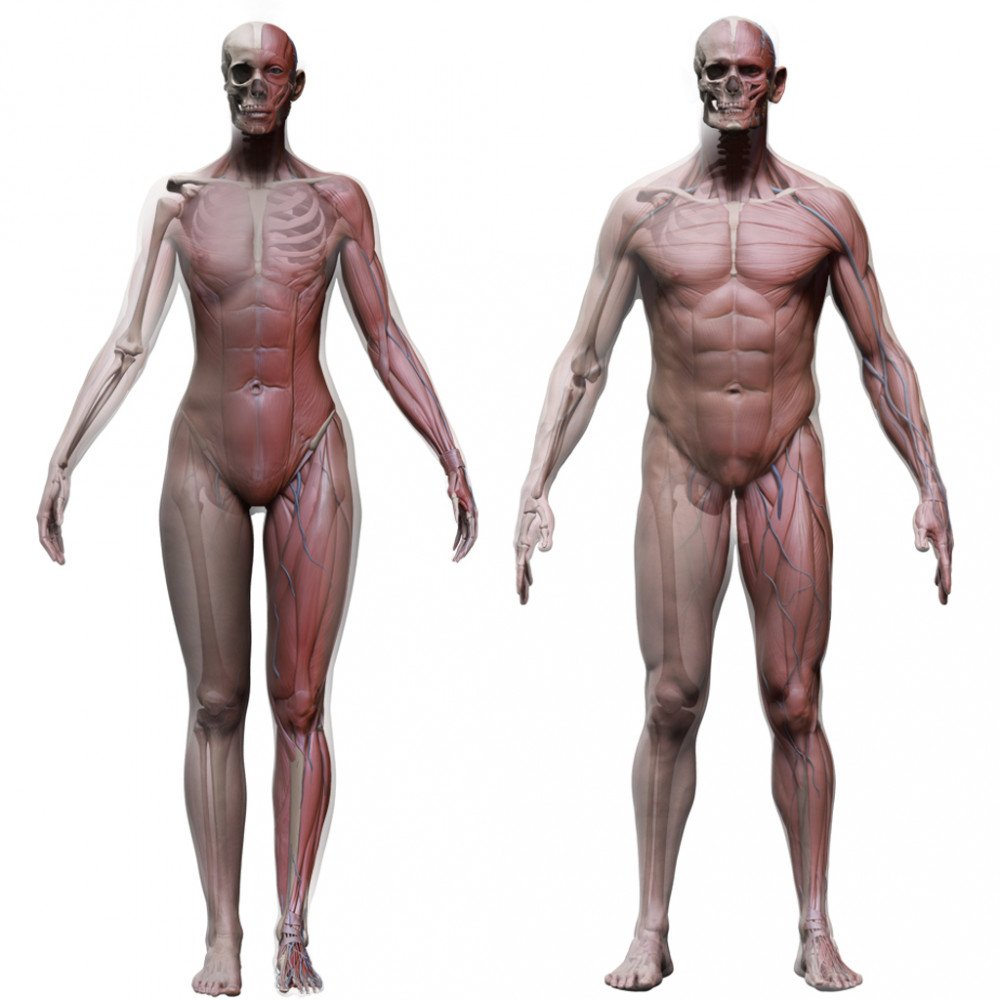
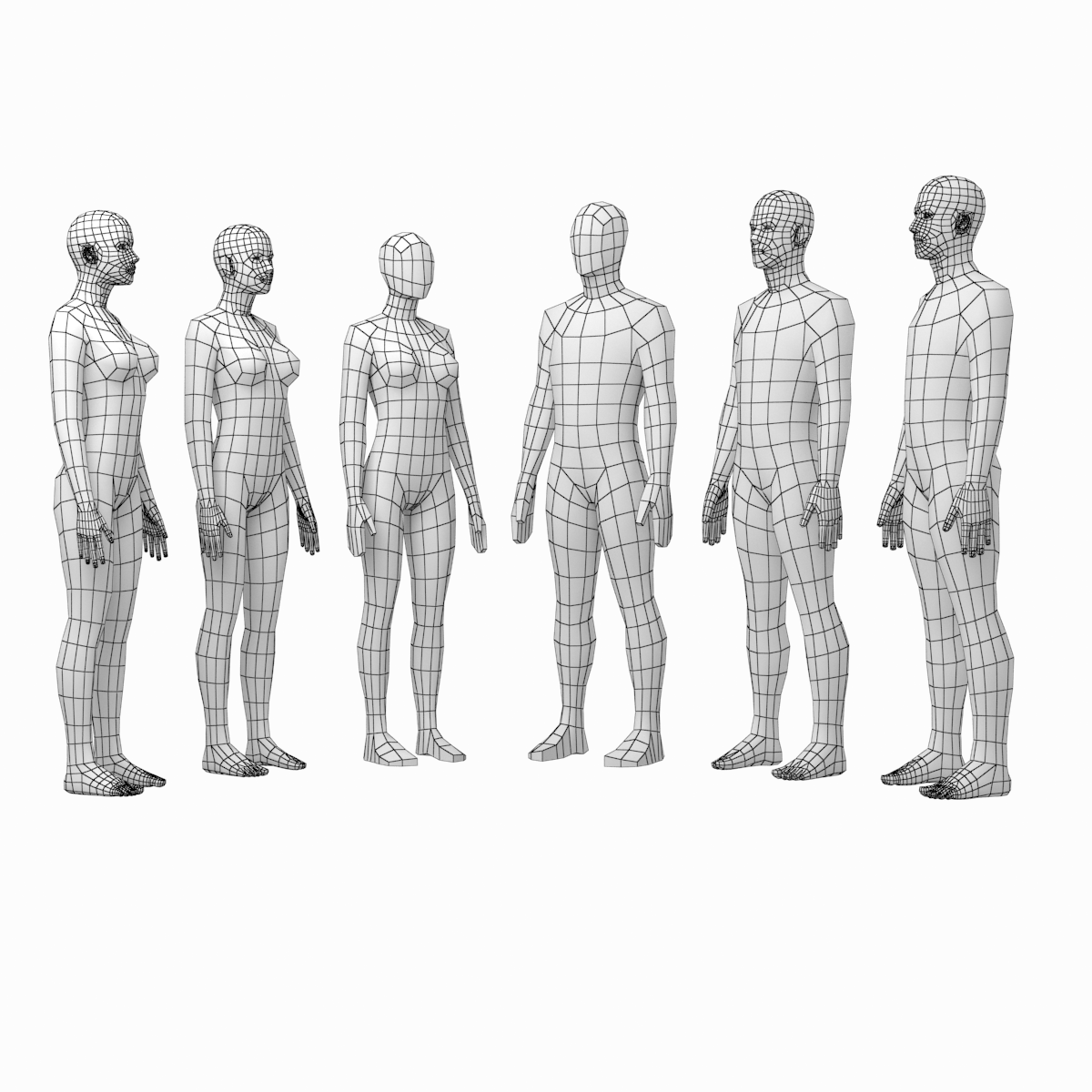
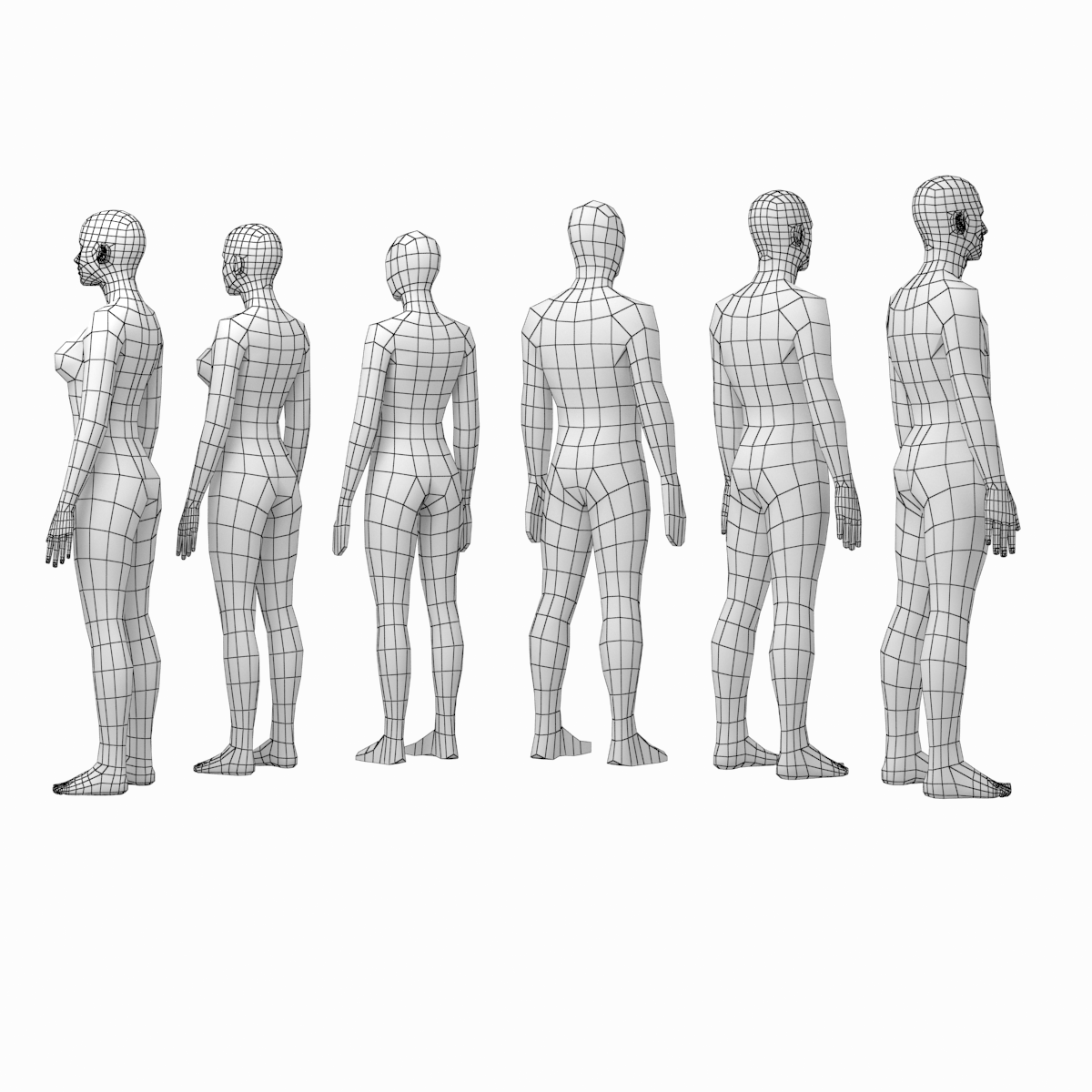
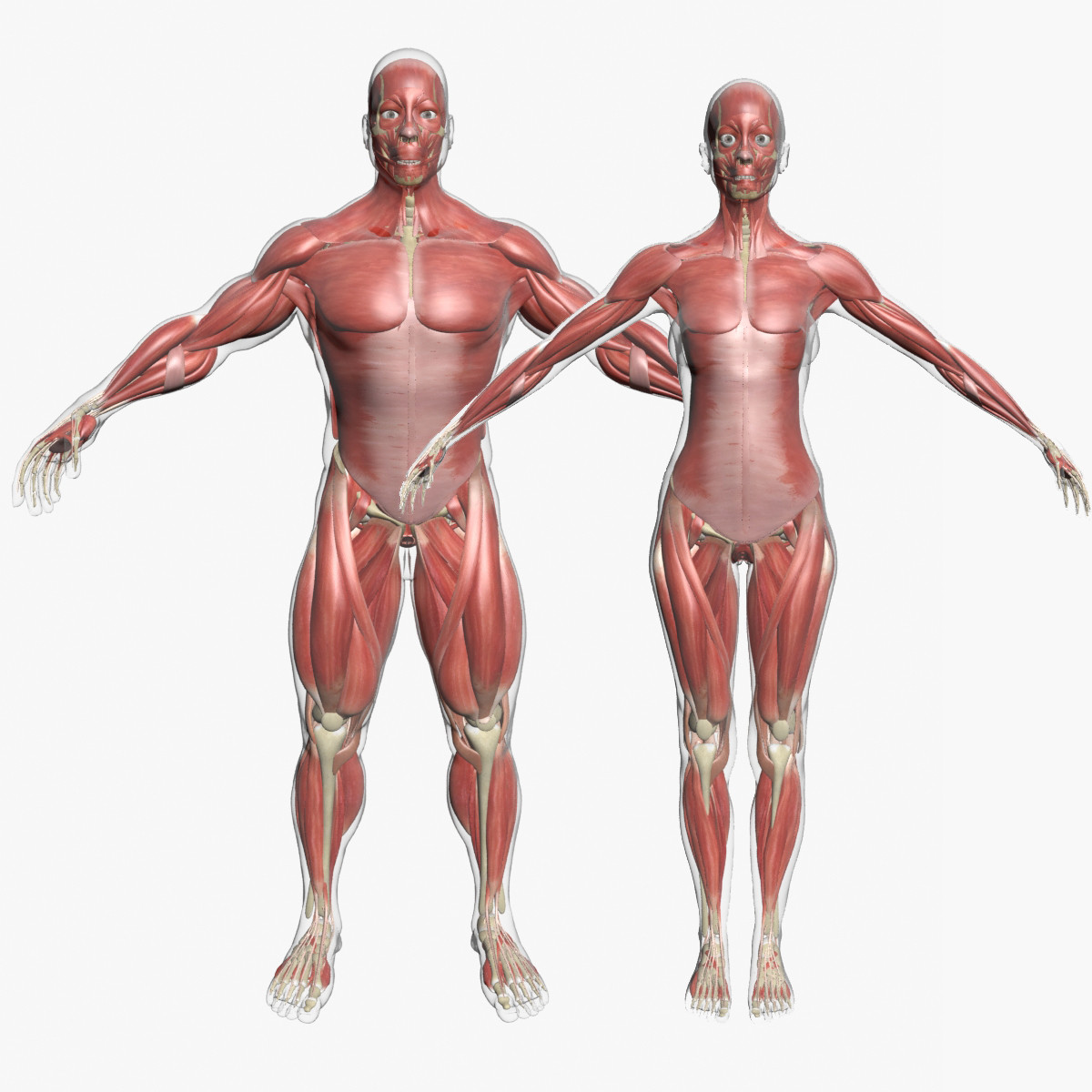
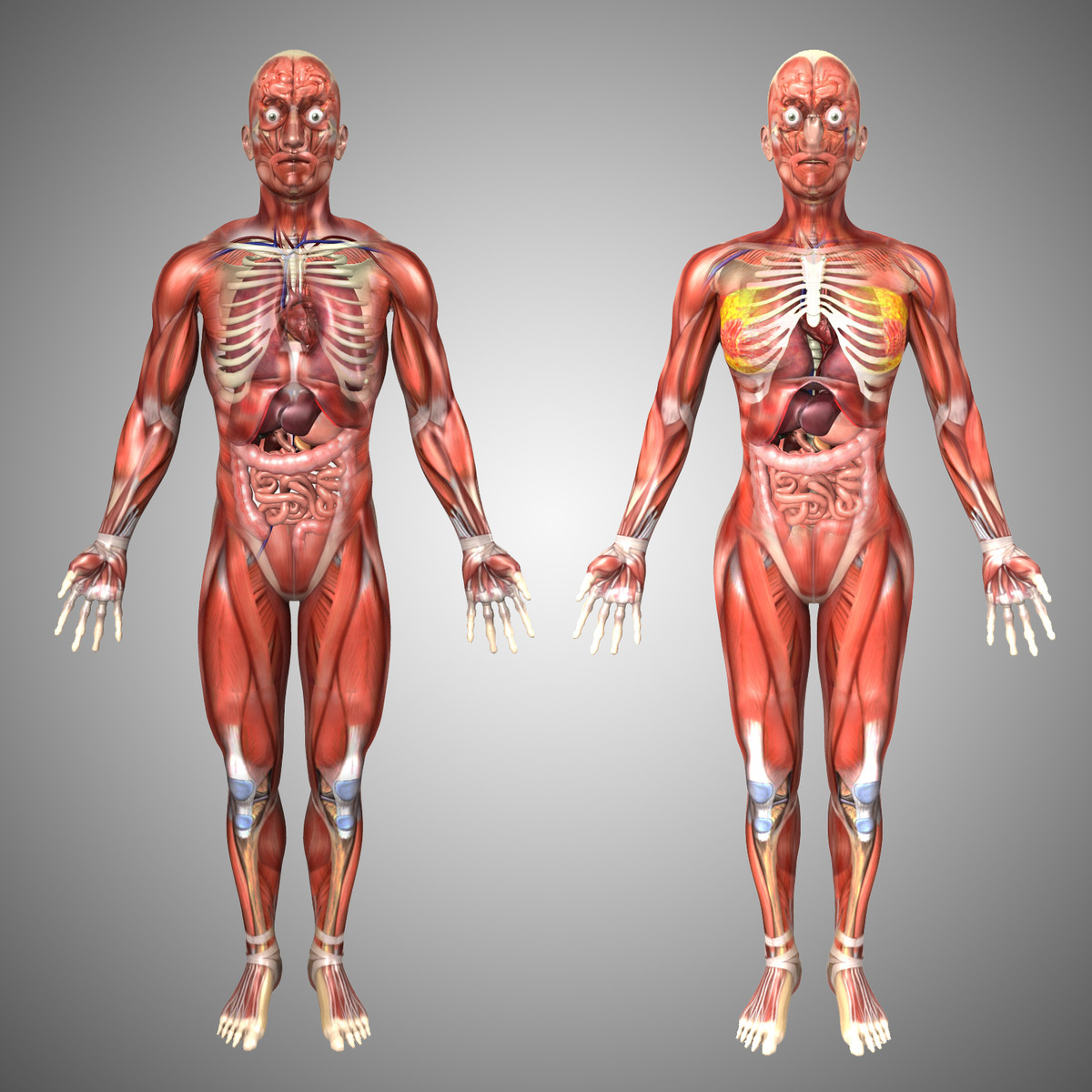
Human Male and Female Complete Anatomy - Body, Muscles, Skeleton, Internal Organs and Lymphatic
Realistic, detailed and anatomically accurate fully textured Human Male and Female Complete Anatomy - Body, Muscles, Skeleton, Internal Organs and Lymphatic.
By purchasing this complete pack you are saving $896.
This product includes ALL the anatomy systems:
- Cardiovascular System
- Circulatory System
- Digestive System
- Endocrine System
- Integumentary System
- Lymphatic System
- Muscular System (including both deep and external)
- Nervous System
- Reproductive System
- Respiratory System
- Skeletal System
- Urinary System
Every system is perfectly fitted with each other and every object and material has been carefully and properly named for easy customization.
These models have been originally created with real world scale dimensions in cm units for every format.
The 3ds max format includes both VRay and Scanline default renderer versions. The final images of the thumbnails have been created with the model, materials and shaders from the VRay version (lighting setup not included).
The base control mesh has been included in every format without being colapsed so you can subdivide the geometry as much as you need in your own 3D software. The accurate details of the model work perfectly for extreme closeups.
Available formats:
- 3ds max 9 and above (.max)
- Cinema 4D 10 and above (.c4d)
- Maya 7 and above (.mb)
- Softimage XSI 5 and above (.xsi)
- Lightwave 6 and above (.lws)
- Luxology Modo (.lxo)
- Blender (.blend)
- Wavefront OBJ (.obj and .mtl)
- Autodesk FBX (.fbx)
- Collada DAE (.dae)
- 3DS (.3ds)
- Direct X (.x)
- DXF (.dxf)
The model has been converted to other formats using exporters and convertion tools and carefully checked in every software. If you have any problem with the format you need to use, don't hesitate to contact with me for assistance.
Keywords:
anatomy human body male female man woman circulatory digestive lymphatic muscular nervous reproductive respiratory skeleton urinary system heart brain muscle zygote internal organ organs medicine head face torso vein artery lung liver stomach cerebellum cerebrum penis bone textured man surgery
Standard Protections (included)
$10,000 in Legal Protection (Indemnification)
Small Business License (+$149.00)
$250,000 in Legal Protection (Indemnification)
Assignable model rights
Enterprise License (+$299.00)
$1,000,000 in Legal Protection (Indemnification)
Waiver from injunctive relief
Assignable model rights
There are currently no models in your cart.
Get this item for $ when you bundle it
with the items in your cart.
You can enter multiple email addresses separated by commas
Thank you for shopping at TurboSquid. If you have any questions about these
items before you purchase, please contact us at
https://support.turbosquid.com/
Products are subject to the TurboSquid, Inc. Term of Use on www.turbosquid.com. Prices are only guaranteed at the time of the creation of this document. Prices do not include additional fees, such as shipping, handling, and taxes.
Natalie Creampie
Short Hair Tits
Cute Models Little Com
Ebony Booty Anal
Huge Natural Boobs
Human sex ratio - Wikipedia
Sex differences in human physiology - Wikipedia
Human Male and Female Complete Anatomy - Body, Mus…
HUMAN MALE AND FEMALE PELVIS. - Download Free 3D m…
Men vs. Women: Our Key Physical Differences Explained ...
Category:Male human genitalia - Wikimedia Commons
Category:Female human genitalia – Wikimedia Commons
Third gender - Wikipedia
Human Male Female