How to intercept traffic using Wireshark
@CyberPentestLab
How to intercept traffic using Wireshark
Protocols are used for data transmission. Unsecured plaintext protocols are protocols where sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords, is transmitted in plaintext. This allows you to intercept traffic using the MITM (Man-in-the-Middle) technique. This attack is also known as "Sniffing".
To intercept traffic, we will use Wireshark. It is a popular tool for capturing and analyzing packets, as well as for detecting problems in local networks.
Wireshark works with most well-known protocols, has an easy-to-understand graphical interface and a filter system. It supports various operating systems, such as Linux, Windows, Solaris, Mac OS X, etc. It is distributed free of charge and is pre-installed in Kali Linux.
To demonstrate traffic interception, we need a stand or three virtual machines that will be located on the same local network.
- Victim — vulnerable Metasploitable 2 machine
- The victim is an Ubuntu distribution (or any other Linux distribution, such as Parrot).
- The attacking machine is Kali Linux.
We will use the vulnerable version of Metasploitable 2 as a victim, as it runs many of the services required for this guide by default. In general, I recommend using Metasploitable for hacking practice.
Let's assume that you have completed the installation of virtual machines. In my case, this is what happened.
Metasploitable2 — 192.168.64.128 (Victim):
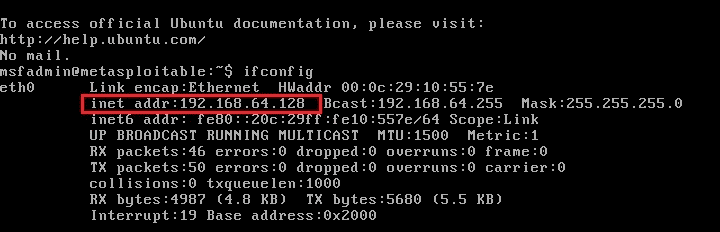
Ubuntu — 192.168.64.132 (Victim):
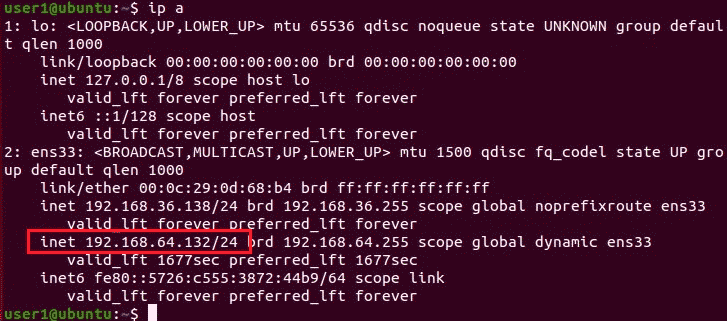
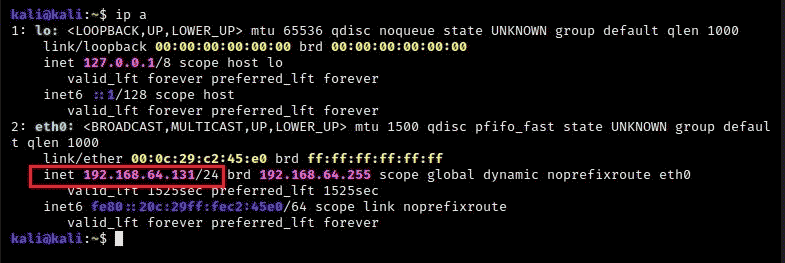
Kali Linux — 192.168.64.132 (Hacker):
Run Wireshark on the attacker's computer (on Kali Linux).
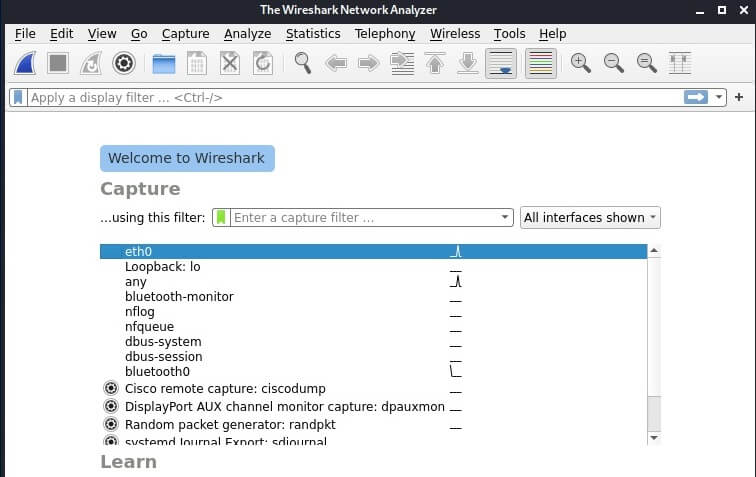
Select the eth0 interface and click on the fin icon to start intercepting traffic.
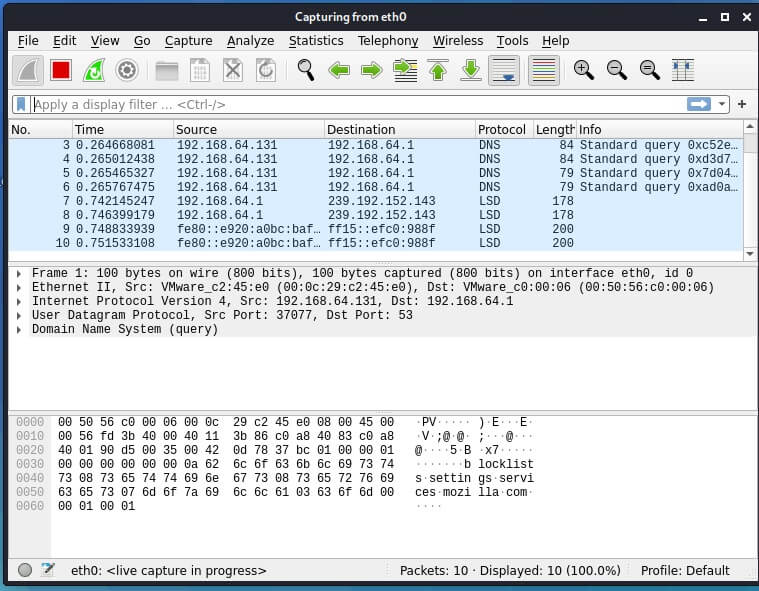
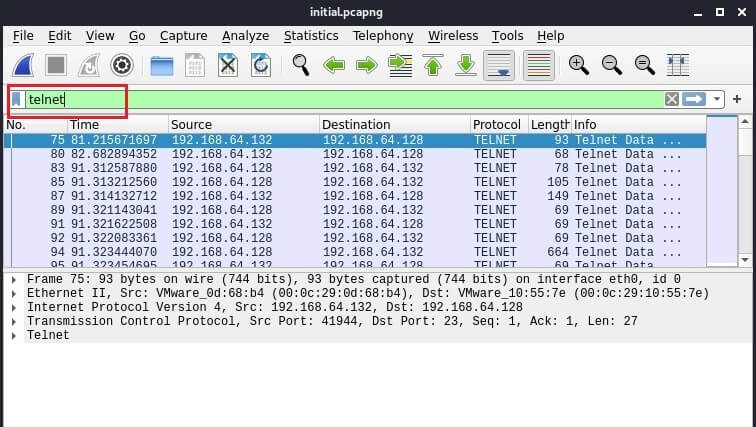
Intercept Telnet traffic using Wireshark
First, let's try to intercept Telnet traffic. The protocol is used for connecting to other computers. On most Linux systems, the Telnet client is installed by default.
So, we open the Ubuntu terminal and try to connect to the Metasploitable 2 machine using the telnet login and password command:
$ telnet 192.168.64.128
- Login — msfadmin
- Password-msfadmin
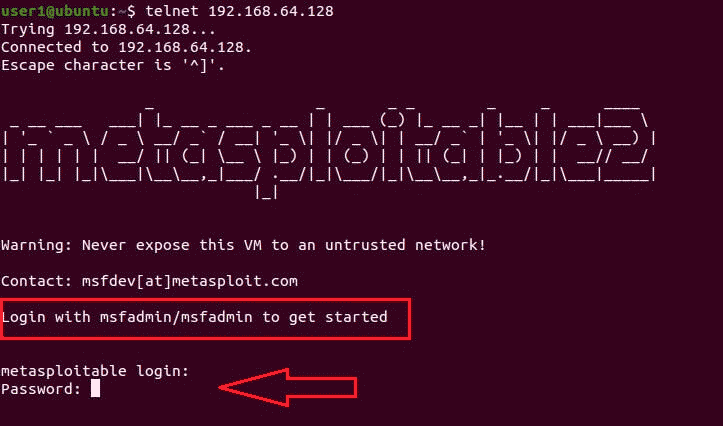
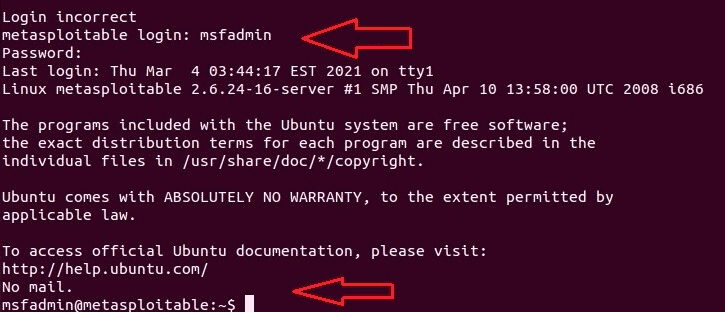
We have established a connection to the vulnerable Metasploitable 2 machine.
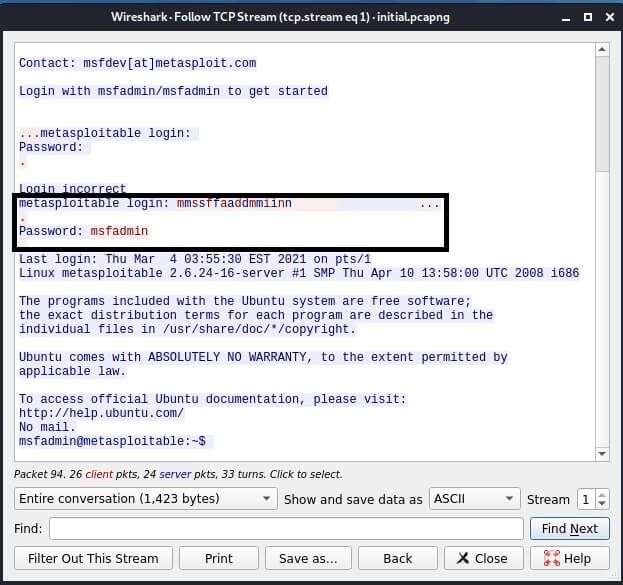
We return to Kali Linux and in Wireshark we see traffic over the Telnet protocol.
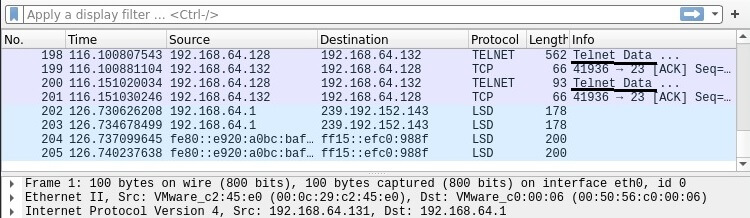
Right - click on the Telnet stream and select "Follow"from the drop-down menu.
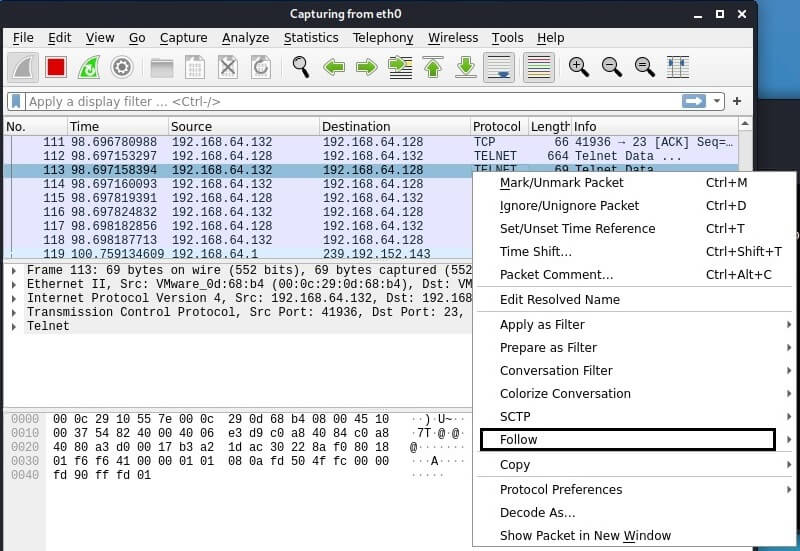
Only the TCP stream will be displayed in the window that opens. In the window, you can see the credentials that we just used to log in to the Metasploitable2 target system.
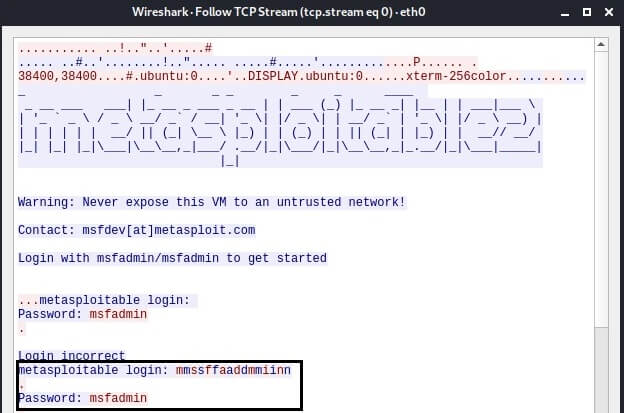
Telnet is a simple text protocol that transmits data in plain text. This makes it easy to intercept traffic and, of course, the credentials themselves.
Because of its lack of security, it has not been used much recently, and Secure Shell (SSH) is used instead. However, there are organizations that cannot opt out of Telnet for compatibility reasons.
Intercept FTP traffic using Wireshark
Consider a different protocol. The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a protocol that is used for file sharing. It also transmits data in plain text.
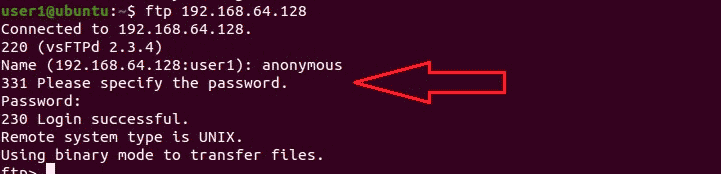
Go to the Ubuntu VM and connect via FTP to the Metasploitable VM.
$ ftp 192.168.64.128
- Username — anonymous
- Password — anonymous
Go to Wireshark and see how data is transferred via FTP.
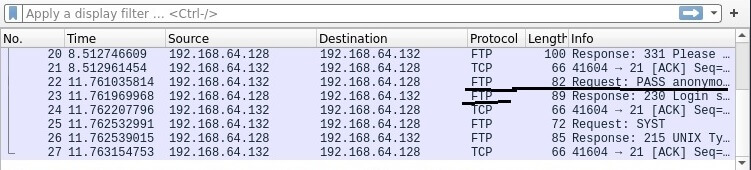
Right-click on the FTP stream and select "Follow"from the drop-down menu.
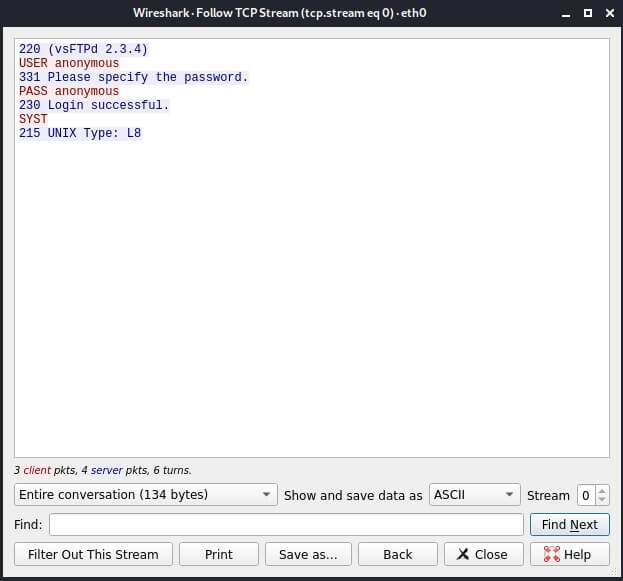
The intercepted FTP traffic will appear in the window, including your username and password.
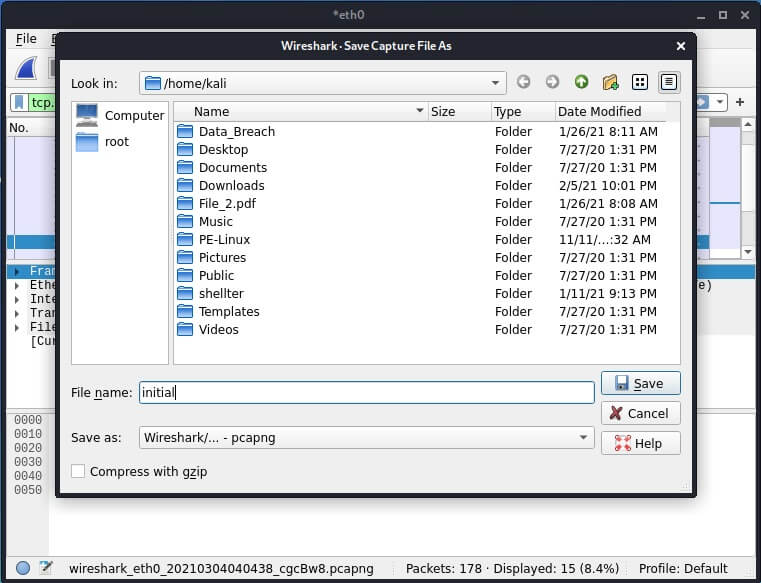
Saving captured traffic to a file
We can save the packet capture file and open it for analysis later. To do this, open the File —> Save Capture File.
To open the report file.
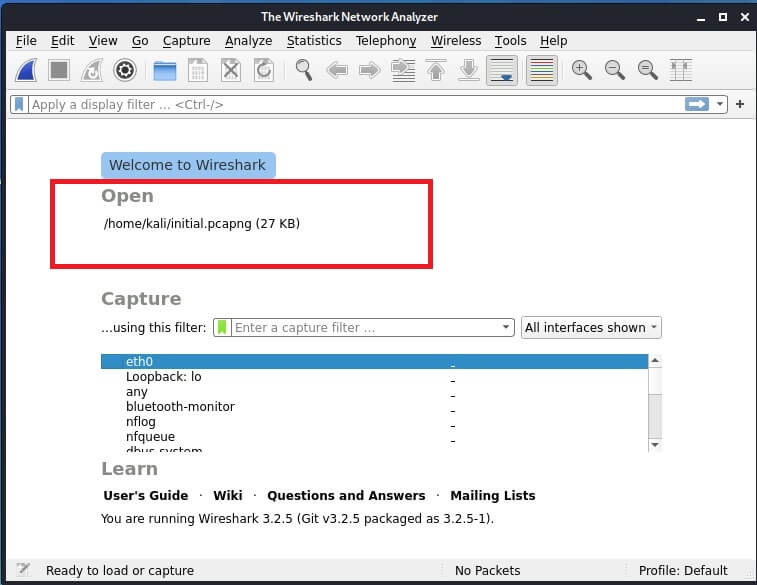
After opening the file, you can filter out the captured packets. To do this, enter the protocol name in the search bar.
Then, following the TCP flow, we get the credentials.
The end!
📺YouTube channel - link