How to Get Singapore Work Visa for Indians: Expert Guide [2025]
Did you know that professionals in Singapore earn an average annual salary of SGD 70,000, with software engineers making up to …These attractive figures, however, aren't the only reason Indians are eyeing Singapore's job market. In fact, the country faces significant skill shortages across IT, hospitality, finance, and manufacturing sectors, making it increasingly open to international talent.
The singapore work visa for indians comes in several forms, with the Employment Pass being the most sought-after option. Starting January 2025, you'll need to earn at least SGD 5,600 monthly (SGD 6,200 for financial services) to qualify.
Additionally, the visa processing typically takes just 10 business days, making it one of the faster options for Indians looking to work abroad.
Ready to start your Singapore journey? Let's break down everything you need to know about getting your work visa approved in 2025.
👉 Apply for singapore work visa for indians!

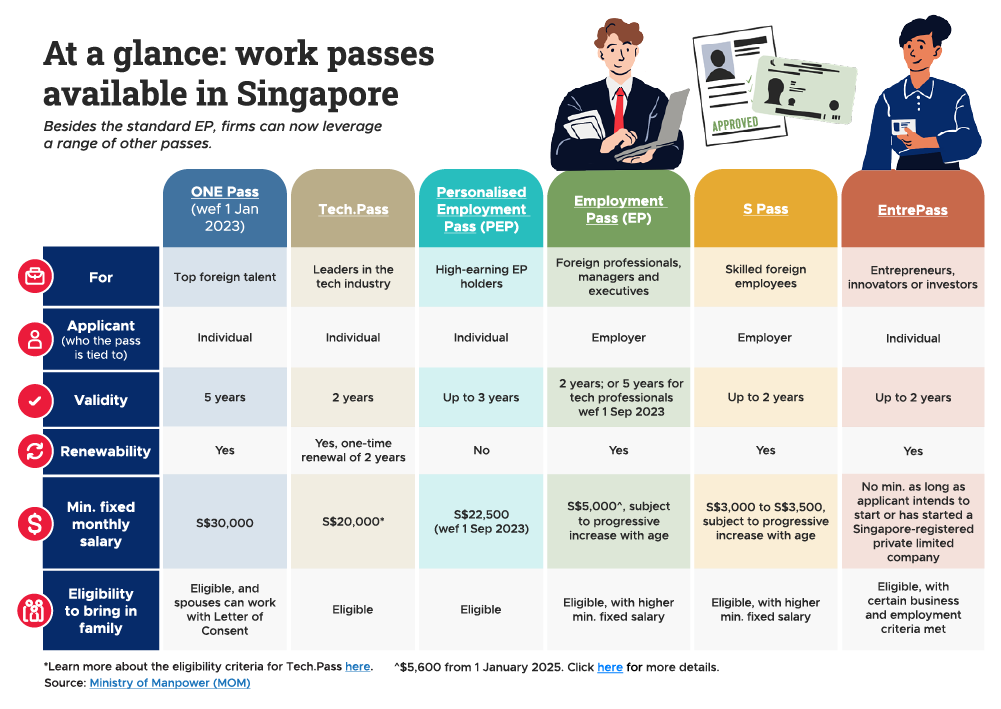
Understanding Singapore Work Visa Types
Singapore's work visa system offers multiple pathways for Indian professionals seeking employment opportunities. The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) has established specific visa categories based on qualification levels and salary thresholds.
Employment Pass Overview
The Employment Pass stands as the premier work visa for highly skilled professionals. Specifically, candidates must earn at least INR 472,530.52 monthly, with financial sector positions requiring INR 523,158.79 or more. Furthermore, the salary threshold increases progressively with age, reaching up to INR 902,870.82 for those aged 45 and above.
Starting September 2023, EP applications must pass through a two-stage eligibility framework. Primarily, candidates need to meet the salary requirements, followed by clearing the Complementarity Assessment Framework (COMPASS) with 40 points.
S Pass Requirements
The S Pass caters to mid-skilled workers with specific salary and qualification requirements. Notably, candidates must earn a minimum monthly salary of INR 265,798.42, which increases with age up to INR 392,369.10 for those 45 and above. For the financial services sector, the threshold starts at INR 307,988.65.
Essential requirements include:
- A job offer from a Singapore employer
- Relevant qualifications or work experience
- Medical insurance coverage
- Compliance with quota requirements
Other Visa Categories
Beyond the EP and S Pass, Singapore offers several specialized work visas:
The Training Employment Pass suits professionals undergoing practical training, requiring a minimum monthly salary of INR 253,141.35. Essentially, the Work Holiday Pass provides opportunities for students and graduates aged 18-25 to work in Singapore for six months.
For tech professionals with specialized skills, a 5-year EP option is available, requiring a minimum salary of INR 902,870.82 for those aged 36 and below. This salary requirement increases to INR 1,204,109.03 for professionals aged 45 and above.
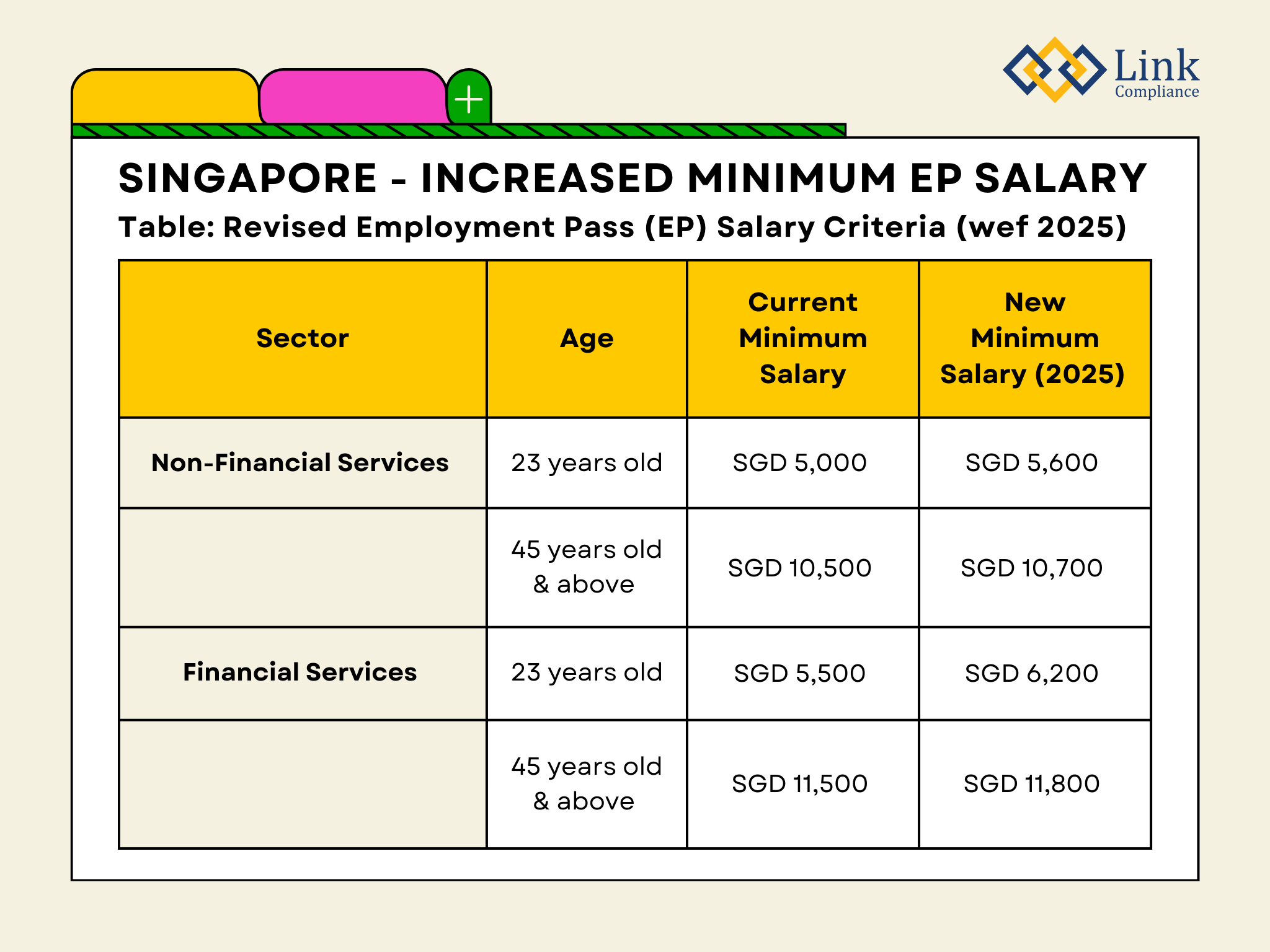
Latest Salary Requirements for 2025
The Ministry of Manpower has announced significant changes to salary requirements for work visas in Singapore, effective January 2025. These updates affect both Employment Pass and S Pass categories across all sectors.
Employment Pass Salary Thresholds
The Employment Pass qualifying salary for new applications starting January 2025 varies by sector. For non-financial services, candidates must earn a minimum monthly salary of INR 472,530.52. Primarily, those in the financial services sector face a higher threshold of INR 523,158.79.
For EP renewals expiring between January to December 2025, the minimum qualifying salaries are:
- Non-financial sectors: INR 421,902.25
- Financial services: INR 464,092.48
Moreover, these requirements will apply to all EP renewals expiring from January 2026 onwards, regardless of when the renewal application is submitted.
Age-based Salary Criteria
The salary requirements increase progressively with age, particularly for experienced professionals. For non-financial sectors:
- Age 23 and below: INR 472,530.52
- Age 35: INR 707,276.94
- Age 45 and above: INR 902,870.82
Subsequently, the financial services sector maintains higher thresholds across age groups:
- Age 23 and below: INR 523,158.79
- Age 35: INR 780,941.07
- Age 45 and above: INR 995,689.32
The S Pass category also sees updates, with new minimum salaries from September 2025:
- Standard sectors: INR 278,455.49 (to be finalized)
- Financial services: INR 320,645.71 (to be finalized)
These revised thresholds align with Singapore's strategy to maintain high-quality foreign workforce standards. The final qualifying salaries will be announced closer to the implementation date, based on prevailing local wages.
COMPASS Points System Explained
The COMPASS framework, implemented in September 2023, introduces a transparent points-based system for evaluating Employment Pass applications. Primarily designed to ensure high-quality foreign professionals complement Singapore's workforce, this system requires candidates to score at least 40 points across multiple criteria.
Scoring Criteria
The framework evaluates applications through four foundational criteria and two bonus categories. Each criterion offers varying point allocations:
CriterionMaximum PointsSalary Benchmark (C1)20Qualifications (C2)20Workforce Diversity (C3)20Local PMET Share (C4)20Skills Bonus (C5)20Strategic Economic Priorities (C6)10
The salary benchmark (C1) compares fixed monthly salary against sector-specific standards. Candidates earning above the 90th percentile receive 20 points, while those between the 65th and 90th percentile earn 10 points.
Meanwhile, qualification points depend on educational background. Degrees from top 100 universities or Singapore's Autonomous Universities earn 20 points, whereas other degree-equivalent qualifications receive 10 points.
How to Calculate Your Points
The calculation process involves assessing individual and company-related factors. For workforce diversity (C3), organizations with fewer than 25 PMETs automatically receive 10 points. Above all, companies with larger workforces earn points based on nationality distribution among their PMET employees.
Local PMET share (C4) evaluates support for local employment:
- 50th percentile and above: 20 points
- 20th to 50th percentile: 10 points
- Below 20th percentile: 0 points
In addition to the foundational criteria, bonus points come from two sources:
- Skills Bonus: Up to 20 points for roles on the Shortage Occupation List, provided the candidate's nationality comprises less than one-third of the company's PMET workforce
- Strategic Economic Priorities: 10 points for companies participating in government-endorsed innovation or internationalization programs
The Self-Assessment Tool (SAT) on the Ministry of Manpower portal helps evaluate potential scores before submission. Nevertheless, actual application outcomes might differ, as the SAT serves as a preliminary guide rather than a guarantee.
The Self-Assessment Tool (SAT) on the Ministry of Manpower portal helps evaluate potential scores before submission. Nevertheless, actual application outcomes might differ, as the SAT serves as a preliminary guide rather than a guarantee.

Step-by-Step Application Process
Securing a singapore work visa for indians begins with obtaining a job offer from a Singapore-based employer. Initially, your employer takes charge of the visa application process, making it crucial to understand each step thoroughly.
Document Preparation
A complete application requires these essential documents:
- Valid passport with minimum six months validity
- Recent passport-size photographs
- Educational certificates and professional qualifications
- Job offer letter from Singapore employer
- Detailed work description
- Past employment testimonials
- Completed visa application form
Primarily, ensure all documents match the information in your passport. Your employer must verify these documents thoroughly, as any discrepancies could lead to application delays or rejection.
Medical Examination Requirements
The medical examination screens for four specific conditions:
- Tuberculosis (chest X-ray)
- HIV
- Syphilis
- Malaria
During the examination, a Singapore-registered doctor evaluates your fitness to work. The screening must be completed within two weeks of arrival in Singapore. First-time applicants can undergo the examination in their home country, though renewal applicants must complete it in Singapore.
Application Submission
The submission process follows a structured timeline:
- Your employer submits the application through the Employment Pass Online Portal
- Upon approval, you receive an In-Principle Approval (IPA) letter
- You can travel to Singapore within six months of IPA issuance
- After arrival, your employer applies for the work pass
- You must register at the Employment Pass Services Center within two weeks
The application fee ranges from INR 2,953.32 to INR 14,766.58, depending on the pass type. Consequently, your employer must pay additional processing fees once you arrive in Singapore.
Processing Timeline
The processing duration varies based on application type and method:
- Employment Pass (online): 10 business days
- S Pass applications: 3 weeks for most cases
- Work Permit applications: 1 week for standard cases
- Manual applications: Up to 3 weeks
Third, if additional information is required, the processing time might extend. Ultimately, once approved, the work pass card typically arrives within four working days after registration.
For Employment Pass applications, your employer can track the status online using the application number. The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) sends updates and requests for additional information through the online portal.
Complete Cost Breakdown
Understanding the financial aspects of a singapore work visa for indians requires careful consideration of both direct and indirect costs. Primarily, the fee structure varies based on visa type and duration.
Application Fees
The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) maintains a two-tier payment system for work visas. The initial application fee stands at INR 8,859.95. Accordingly, upon approval, candidates must pay an issuance fee of INR 18,985.60.
The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) uses a two-tier payment system for work visas:
- Initial application fee: INR 8,859.95
- Issuance fee (upon approval): INR 18,985.60
Fee structure varies by visa type:
- Employment Pass: Application Fee - INR 8,859.95.
- Issuance Fee: INR 18,985.60
- S Pass:Application Fee: INR 8,859.95
- Issuance Fee: INR 18,985.60
- Training Employment Pass:Application Fee: INR 2,531.41
- Issuance Fee: N/A
- ONE Pass:Application Fee: INR 27,517.74
- Issuance Fee: N/A
For short-term work visas (up to 60 days), the fee is lower at INR 2,500.41.
Payment options include GIRO, Visa, Mastercard, or American Express.
Hidden Costs to Consider
Beyond the standard application fees, several additional expenses significantly impact the total cost:
- Multiple Journey Visa (MJV)
- Additional charge of INR 2,531.41
- Required for frequent travel during visa validity
- Medical Examination Expenses
- Mandatory health screening
- Tests for tuberculosis, HIV, syphilis, and malaria
- Costs vary by healthcare provider
- Document Processing
- Translation fees for non-English documents
- Notarization charges
- Authentication costs for educational certificates
- Monthly Levy Requirements The government imposes a monthly levy on employers, varying by:
- Sector of employment
- Skill level of the employee
- Company's foreign worker quota
- Extension Costs
- Short Term Visit Pass (STVP) extension fees
- Must be requested 7-14 days before expiration
- Late extension requests may incur overstaying fines
- Visa Duration Costs For longer durations:
- Up to 6 months: INR 14,007.15
- 6 months to 1 year: INR 23,120.24
- 1 to 5 years: INR 34,427.22
The processing timeline affects cost planning. Standard processing takes 10 business days, but some applications might extend to 8 weeks. Undoubtedly, this duration impacts accommodation and living expenses during the waiting period.
For financial planning purposes, candidates should maintain a buffer of 15-20% above the basic visa fees to cover unexpected expenses. Namely, this includes potential document resubmission fees, medical report translations, or expedited processing charges if required.
Common Rejection Reasons
Navigating the approval process for a singapore work visa for indians requires careful attention to detail, as applications face scrutiny across multiple criteria. Understanding common rejection reasons helps applicants avoid potential pitfalls and increase their chances of success.
Qualification Issues
The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) primarily focuses on educational credentials and professional experience when evaluating applications. Insufficient qualifications stand as one of the most frequent reasons for rejection. For Employment Pass applications, candidates must possess:
- A recognized degree with relevant work experience
- Credentials that align with the job scope
- Qualifications matching industry standards
Primarily, MOM evaluates whether the candidate's background suits the proposed role. Applications face rejection when qualifications do not align with job requirements or industry standards. Therefore, candidates must ensure their experience and educational profile matches the position they're applying for.
Salary Mismatches
Salary-related rejections often stem from discrepancies between offered compensation and candidate credentials. Applications face scrutiny when:
- The proposed salary appears too high for the candidate's qualifications
- Compensation doesn't meet minimum thresholds for visa categories
- Salary increases seem disproportionate compared to previous roles
Indeed, even high salary offers can lead to rejection if they don't align with the candidate's credentials. Yet, offering salaries below category minimums similarly results in automatic rejection.
Experience Level and Salary Consideration:
- Entry Level: Must match qualification standards.
- Mid-Career: Should reflect industry experience.
- Senior Roles: Need to align with market rates.
Even high salary offers can lead to rejection if they don't match the candidate's credentials.
Offering salaries below the category minimums results in automatic rejection.
Documentation Errors
Documentation mistakes present another significant hurdle in visa applications. Common errors include:
- Incomplete Submissions
- Missing employment records
- Incorrect personal information
- Incomplete application forms
- Inconsistent Information
- Discrepancies between documents
- Conflicting employment history
- Mismatched qualification details
Ultimately, even minor documentation errors can delay or derail applications. Hence, applicants should verify all information thoroughly before submission.
Presently, the Ministry of Manpower maintains strict verification processes for all submitted documents. Occasionally, applications receive rejection due to:
- Omission of required certificates
- Failure to disclose complete educational history
- Inconsistencies in employment records
Similarly, prior immigration offenses or visa violations significantly impact future applications. Applications face heightened scrutiny if candidates have:
- Previous visa rejections
- History of overstaying
- Past immigration infractions
For successful applications, candidates should:
- Review all documentation thoroughly
- Ensure salary alignment with qualifications
- Verify credential authenticity
- Address previous rejection reasons
- Submit complete employment history
The appeal process remains available for rejected applications, provided candidates can address the specific issues mentioned in their rejection advisory. Applications must submit appeals within three months of rejection, alternatively, they'll need to file a new application.
Conclusion
Securing a Singapore work visa requires careful attention to detail and thorough preparation. The process might seem complex, but understanding each requirement helps ensure a successful application.
Most importantly, candidates must meet the updated 2025 salary thresholds and score at least 40 points under the COMPASS framework. Additionally, proper documentation and accurate information submission play crucial roles in avoiding common rejection reasons.
The financial investment ranges between INR 8,859.95 and INR 34,427.22, depending on visa type and duration. Therefore, maintaining a buffer of 15-20% above basic visa fees helps cover unexpected expenses during the application process.
Success rates improve significantly when candidates match their qualifications with appropriate job roles and ensure their salary aligns with industry standards. Remember to verify all documentation thoroughly and address any previous visa issues before applying.
Armed with this comprehensive guide, you can now confidently pursue your career opportunities in Singapore while avoiding common pitfalls that lead to rejection.
https://www.bestmigrationconsultant.com/singapore-study-visa/