How Exploratory study of brain waves and corresponding brain can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.
 Beta Brainwaves Frequency Guide
Beta Brainwaves Frequency GuideNot known Details About What Are Beta Brainwaves? Improve Focus and Motivation
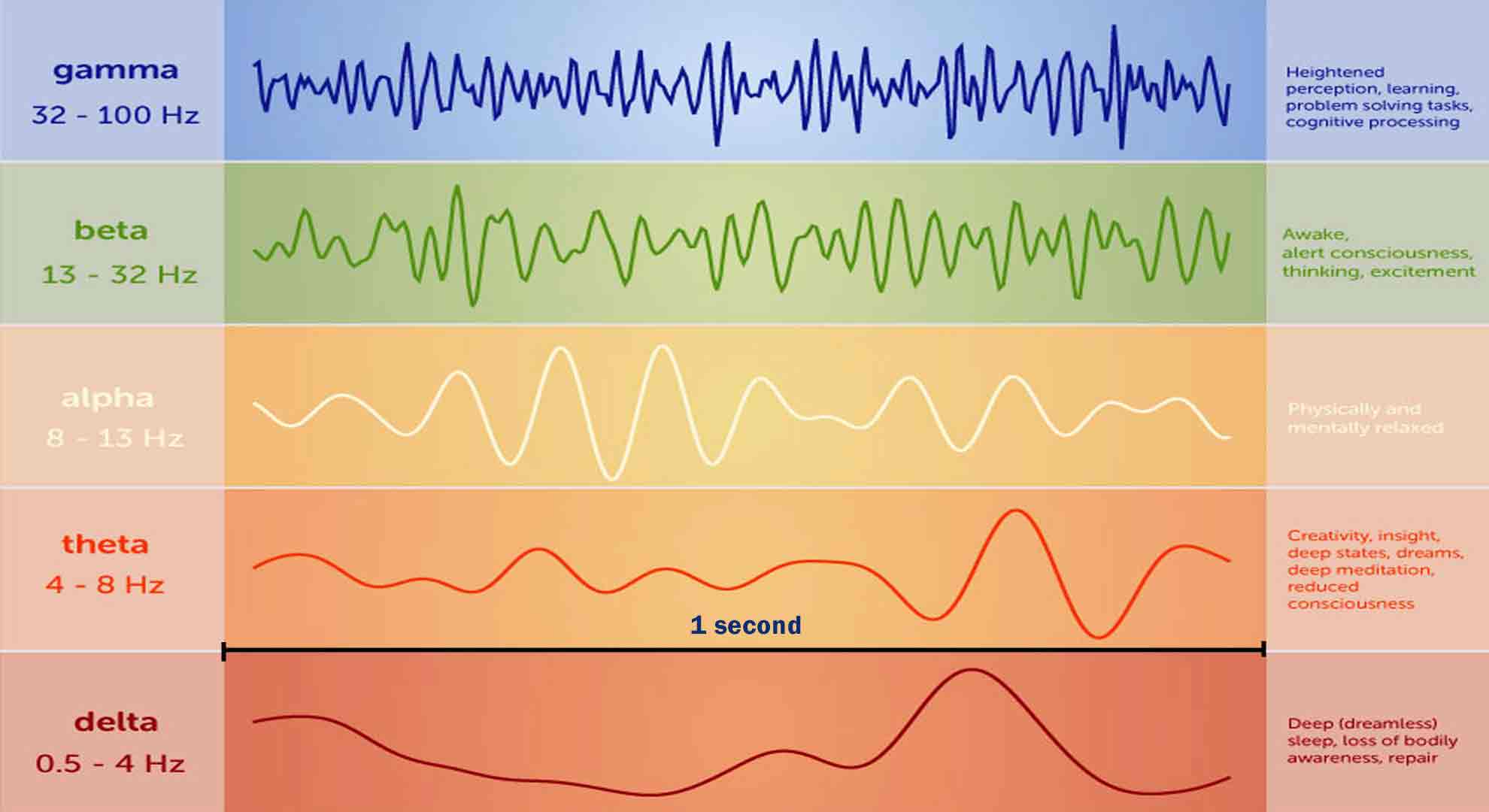
Neural oscillation in the brain with a frequency variety of between 12. 5 and 30 Hz Beta waves, or beta rhythm, are a neural oscillation (brainwave) in the brain with a frequency variety of between 12. 5 and 30 Hz (12. 5 to 30 cycles per 2nd). Beta waves can be divided into three areas: Low Beta Waves (12.

520 Hz, "Beta 2"); and High Beta Waves (20. 528 Hz, "Beta 3"). Full Article are the states related to normal waking awareness. History [edit] Beta waves were found and named by the German psychiatrist Hans Berger, who developed electroencephalography (EEG) in 1924, as an approach of tape-recording electrical brain activity from the human scalp.
 How to Manipulate Brain Waves for a Better Mental State — The Nexus
How to Manipulate Brain Waves for a Better Mental State — The NexusThe smaller sized amplitude, faster frequency waves that changed alpha waves when the subject opened his or her eyes were then called beta waves. Function [modify] Low-amplitude beta waves with several and differing frequencies are typically related to active, hectic or distressed thinking and active concentration. Over the motor cortex, beta waves are connected with the contraction that happen in isotonic motions and are suppressed prior to and during motion modifications.
Beta activity is increased when movement has to be withstood or voluntarily suppressed. The artificial induction of increased beta waves over the motor cortex by a type of electrical stimulation called Transcranial alternating-current stimulation constant with its link to isotonic contraction produces a slowing of motor movements. Investigations of benefit feedback have revealed two unique beta parts; a high beta (low gamma) component, and low beta component.
What are Brainwaves? - Improve Brain Health with for DummiesHowever the low beta element is said to be connected to the omission of gains, when gains are anticipated. Relationship with GABA [modify] Scattered beta waves present together with other frequencies in spontaneous EEG tape-recorded from a 28-month-old child with Dup15q syndrome. Beta waves are often considered a sign of repressive cortical transmission mediated by gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the mammalian worried system.
Spontaneous beta waves are likewise observed diffusely in scalp EEG recordings from children with duplication 15q11. 2-q13. 1 syndrome (Dup15q) who have duplications of GABAA receptor subunit genes,, and. Likewise, kids with Angelman syndrome with deletions of the very same GABAA receptor subunit genes feature decreased beta amplitude.