Homosexuality In Roman Times

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Wiki User
Answered December 03, 2014 1:16AM
Regarding the answer above, when the western part of the Roman Empire fell, it did not evolve into the Holy Roman Empire (HRE). The HRE was created in 962, nearly 500 years after the fall of this part of this empire. When it fell, it was split into the kingdoms of Germanic peoples: Vandals, Sueves, Visigoths, Burgundians, Franks and Alemanni. Christianity changed Roman attitudes towards homosexuality and this occurred with the spread of Christianity around the Roman Empire during the period of the Later Empire. It must not be forgotten that Christianity spread and developed during the Roman days and that it is the Romans who have given us Christianity (both Catholic and Orthodox).
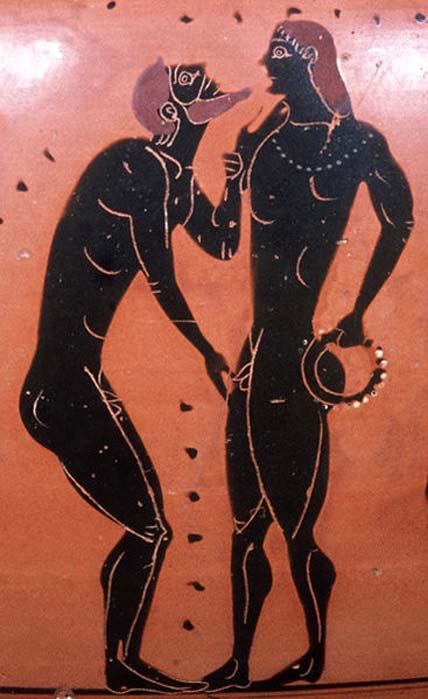
The Romans were not bothered about homosexuality as such. Latin does not even have words which can be precisely translated into heterosexual and homosexual. Homosexual intercourse was all right as long as it did not occur between Roman citizens, because this went against the notion of Romans as virile men. The Romans almost had a cult of virility. Homosexual intercourse with a slave or a non-Roman was fine because this implied that it was the slave or non-Roman who was penetrated. Penetration was considered dominant and masculine. The idea of a Roman citizen being penetrated was abhorrent because it was considered passive, submissive and effeminate. The real dichotomy for the Romans was between dominant/masculine and passive/submissive/effeminate. Sex with prostitutes and entertainers was fine even if they were Roman citizens because they had the inferior social status of infamia (without reputation and esteem).
A man who got penetrated was called with the derogatory term of pathicus. This comes from the verb passus (to undergo, submit to, endure, suffer,) from which the word passive is derived. Cinaedus was a derogatory word for a man who was perceived as a deviant because his mannerisms, sense of dress and use of cosmetics were considered as effeminate and deficient as a man. He was perceived as allowing himself to be penetrated, even if he had sex with them. The puer delicatus or deliciae (delightful boy) was a child slave who was the toy boy of his master.
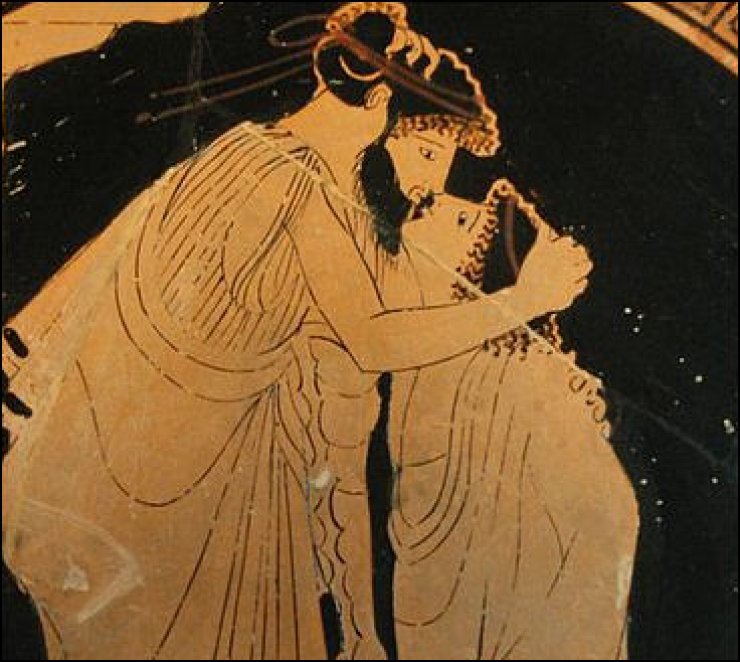
Same sex relations with non-Romans needed not be keep secret. There were important men who had male lovers or concubines. The emperor Hadrian deified Antinous, a Greek who was his lover, when the drowned in the Nile and created a cult devoted to him. Both of these had previously been reserved for members of the imperial family. Healso had a city should be built on the site of his death in his commemoration and called it Antinopolis (city of Antinous).
Sexual intercourse between Roman soldiers was punished harshly as a violation of military discipline as well as being considered socially abhorrent. There was a report of a soldier being clubbed to death for willingly submitting to penetration. A soldier who killed his commanding officer because of sexual assault was acquitted in his trial, escaping the death penalty. He was also given the crown of bravery. He had upheld his right to defend his sexual integrity. Romans soldiers were allowed to obtain sexual gratification from prostitutes of either gender, male slaves and same-sex relations with non-Romans.
Roman female homosexuality is hardly documented. It was the subject of male fantasies, such as women using dildos for penetration or doing it with a huge clitoris, sodomising boys, being masculine looking, drinking and eating like men, being heavily into exercise and the like.
the death of the roman emperor Julius Caesar, he was stabbed 30 sum times by the senators
this was the year the roman empire collapsed
Copyright ©2021 Multiply Media, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The material on this site can not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with prior written permission of Multiply.
From Wikibooks, open books for an open world
Homosexuality in ancient Rome was a large part of society and of sexuality in general. Sex in the ancient world was considered a casual day-to-day practice with no emotional attachment, which is very different from the views of sex in modern day society. Despite its commonality, sex was something that was kept under wraps in ancient Rome and seldom spoken of. The ancient Romans also had a very different understanding of homosexuality than we do in modern society. There was no real concept of homosexuality or of heterosexuality.
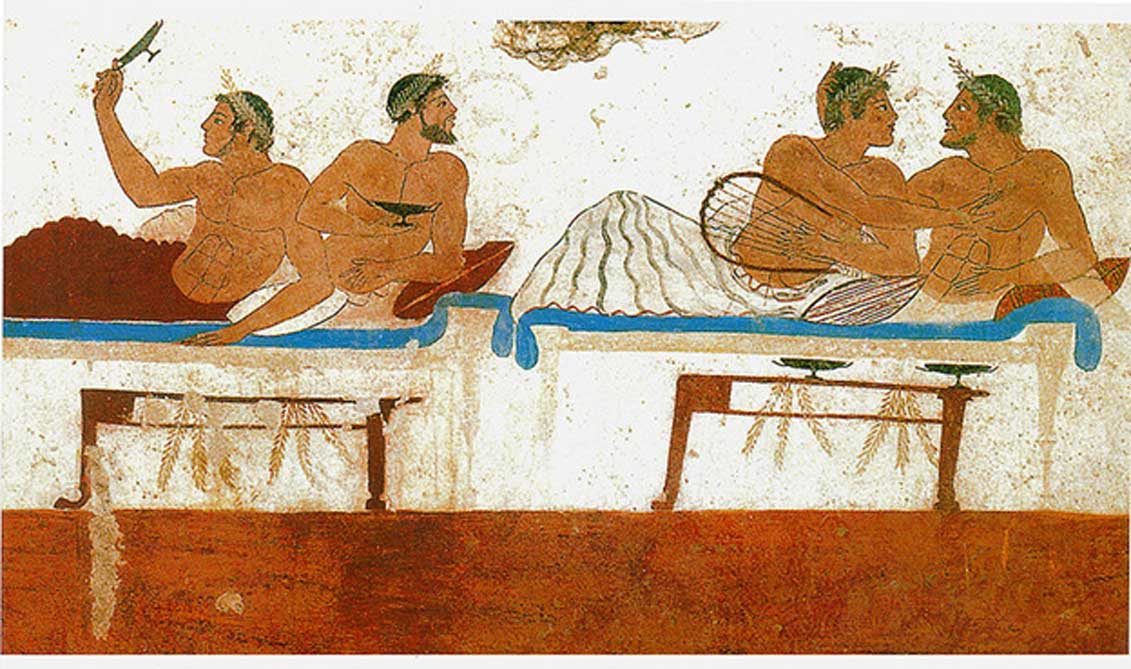
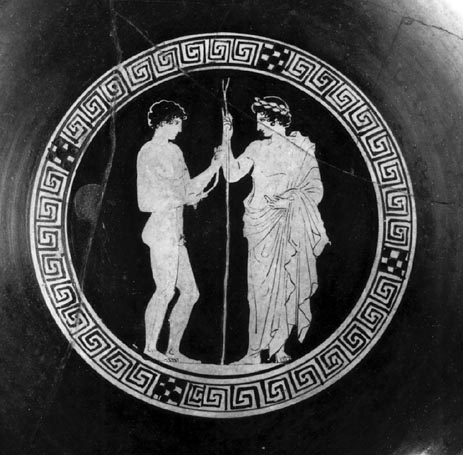
Male with male relations were the most common and prevalent type of homosexuality in ancient Rome. Older men taking a young male lover was very common. For example the emperor Hadrian took a young lover named Antinous despite being married. Most scholars assume they were lovers because when Antinous died tragically Hadrian had a large of amount of deified statues made of him and placed all over the Empire. The emperor Nero also had a male lover who he eventually married. The dynamic between two male lovers was simple. First of all, one was usually of upper class and the other was either a slave or of lower class. The older and richer man was never the receiving party with regards to penetration. This was an unspoken rule among these couples and was in place because if a man was on the receiving end of a sexual relationship he was no longer considered masculine by society’s standards. If a man was the dominant one in a male on male sexual relationship it was just another way for him to assert his place of power in society. A place that was common for random male on male intercourse was the Roman bathhouse. It has been discovered that as a sign that a man was looking for sexual activity a man would scratch his head with one finger to signal that he was sexually available.
The homosexuality of women was viewed in a completely different light then that of men in ancient Rome. First of all, the views of sexuality in ancient Rome were very focused among one figure in the relationship being masculine and deriving pleasure from the activity. This was because it was considered taboo and unheard of for women to have an active role in sexual activity in ancient Rome. As a result of this women who engaged in homosexual activity were usually portrayed as participating in masculine activities such as bodybuilding and drinking and eating excessive amounts. Overall the view of homosexual women was a negative one in the ancient world. It has even been recorded that some husbands would murder their wives for homosexual affairs.
Historians have based a majority of what they know about Roman sexual practices on art and sculpture from the ancient world. One extremely popular example of this type of art is the Warren cup. Edward Perry Warren, for whom it is now named, first owned this cup and it currently resides in the British Museum. There are two main depictions on the Warren cup, both of male on male sexual activity. One side shows a young adult male and boy couple engaging in sexual acts. And the other side portrays a bearded man and a young adult male engaging in similar sexual acts. Historians interpret this cup to show the same lovers in two different times during their affair. This cup has been a valuable resource to historians and is the most valuable of its kind, despite that fact that its validity has been questioned.
Homosexuality in Ancient Rome
What Happend To The Homosexuality In Roman times? - Answers
Roman Culture/Homosexuality - Wikibooks, open books for an open world
Romosexuality – embracing queer sex and love in Ancient times
Roman Law and the Banning of ‘Passive’ Homosexuality | Ancient Origins
Homemade Big Tit Milf
Girls For Mature Tube
Prostate Massage Instruction
Homosexuality In Roman Times





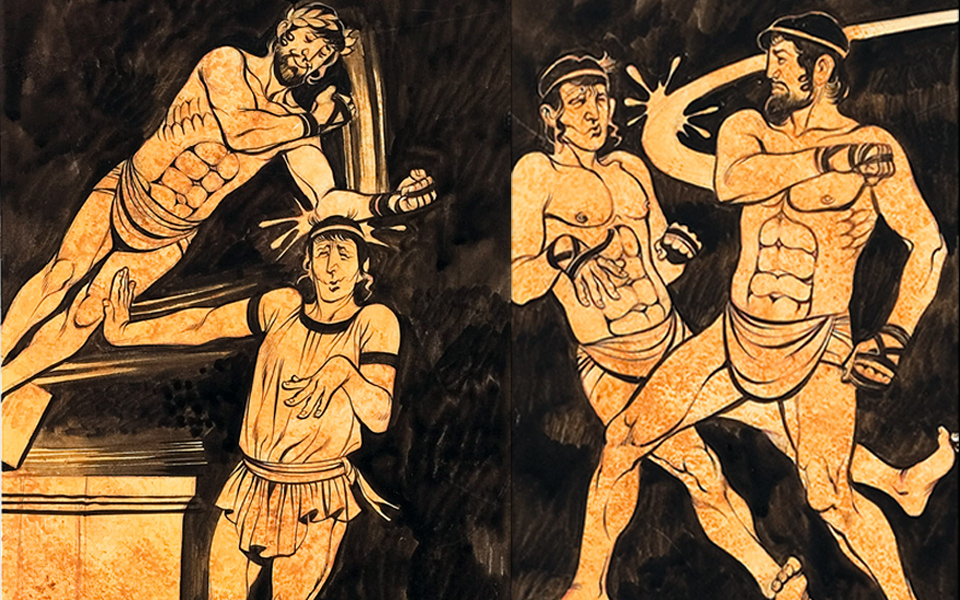
















 630_.jpg" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">
630_.jpg" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">


















 204" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">203" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">200_.jpg" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">
204" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">203" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">200_.jpg" width="550" alt="Homosexuality In Roman Times" title="Homosexuality In Roman Times">