Grasping Nerve Dysfunction: Exploring Nerve Damage
Nerve damage is a concept that covers a variety of disorders defined by damage to the nerves, impacting how the neural system communicates with the rest of the physical body. This detailed network of nerves holds a key role in sending messages between the brain, spine, and various organs, making neuropathy a condition that can cause significant physical and sensory disabilities. Grasping neuropathy is essential, as it can develop from multiple origins and may manifest in diverse modes, depending on the particular nerves are affected.
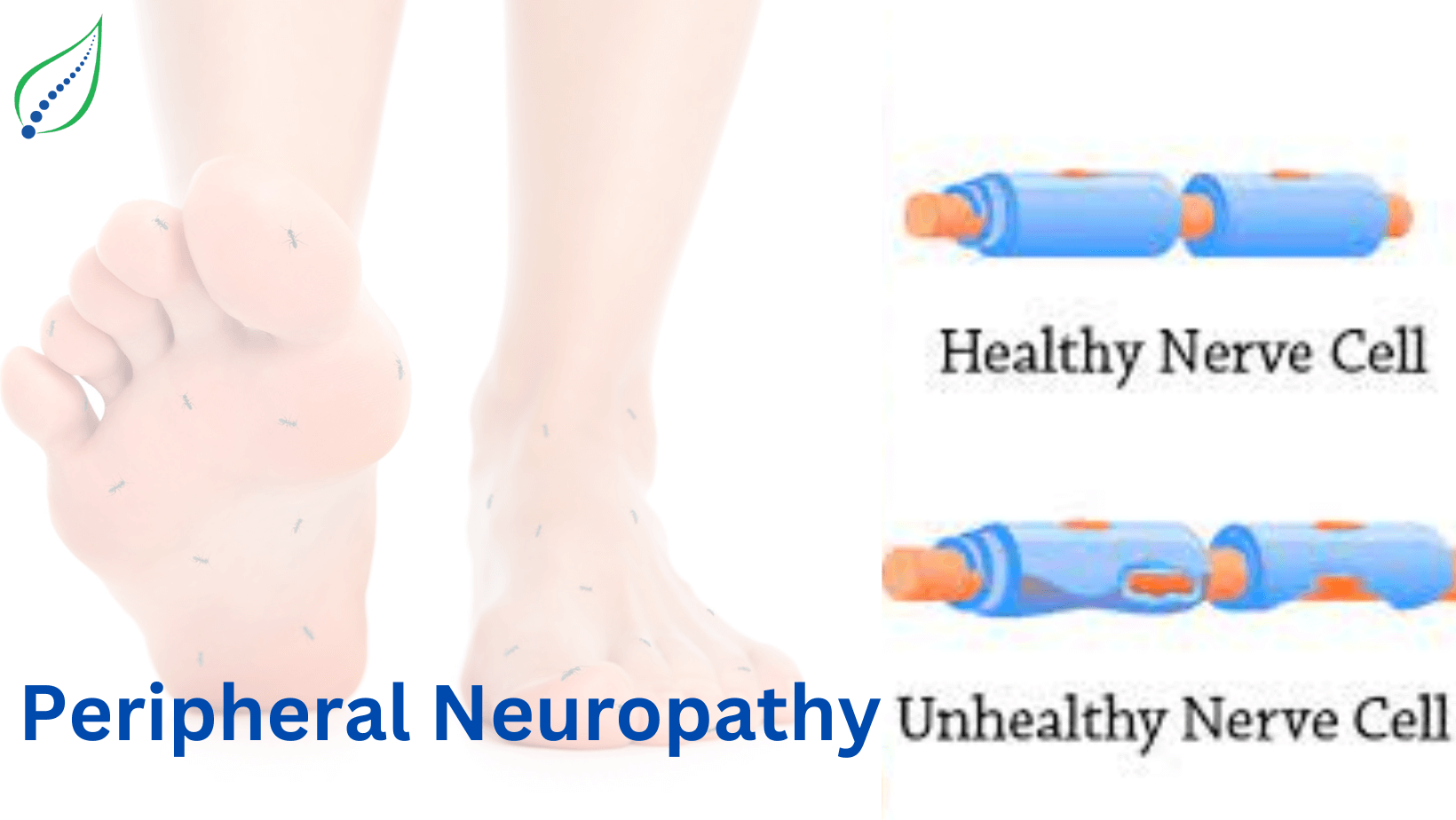
For numerous people, neuropathy shows with symptoms such as tingling, numbness, or discomfort, often in the limbs. The consequence of neuropathy can be significant, shaping everyday tasks and overall quality of life. Although it is often associated with high blood sugar, various causes including bacterial infections, injuries, and chemicals can result in nerve damage. In this write-up, we will delve into the complexities of neuropathy, shedding light on its origins, signs, identification, and treatment options to support those affected by this difficult condition.
Factors of Nerve Damage
Nerve damage can arise from a variety of underlying issues, making its causes varied and complicated. One of the primary factors is diabetes, with diabetic neuropathy affecting a large number of people with this condition. Elevated blood sugar levels over time can injure nerves, particularly in the limbs, leading to weakness, discomfort, and numbness. Keeping in check diabetes is crucial to avoiding and reducing the risk of nerve-related issues.
An additional potential cause of nerve damage is autoimmune diseases, where the body's immune system erroneously attacks its own tissues. Diseases such as rheumatoid conditions, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can lead to nerve damage through inflammatory processes. In these cases, the immune response disrupts normal nerve function, resulting in various symptoms depending on the areas involved.
Along with diabetes and autoimmune conditions, contact with toxins and certain medications can also lead to nerve damage. Chemicals such as toxic metals and chemical solvents, as well as high levels of alcohol consumption, can have neurotoxic effects. Cancer treatment drugs used in cancer treatment are another significant contributor, where the damage to peripheral nerves is a known side effect. Identifying and mitigating exposure to these harmful substances is important for preventing nerve damage.
Symptoms and Evaluation
Neuropathy presents with a variety of symptoms that can differ depending on the type and extent of nerve damage. Typical signs include prickling or numbness, often starting in the hands and toes. Patients may also experience sensitivity to touch, burning sensations, or sharp pain. In some instances, neuropathy can lead to weakness in muscles, coordination issues, and difficulties with balance, which can significantly impact daily functions.
To diagnose neuropathy, healthcare providers conduct a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. They evaluate symptoms, review any underlying issues, and perform neurological tests to assess sensory and motor capability. diabetic neuropathy doctors near me may also be ordered to identify potential contributors of nerve damage, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies. In some cases, nerve conduction studies or electromyography may be used to assess the electrical response of nerves and muscles, providing further insight into the level of nerve impairment.
The correct diagnosis of neuropathy is essential for effective treatment. Identifying the underlying reason enables healthcare providers to tailor management strategies, which might include medications, lifestyle changes, or physical therapy. Timely intervention can help reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent further nerve damage, making awareness of neuropathy symptoms vital for swift evaluation and care.
Treatment and Management
Treating neuropathy often necessitates a comprehensive approach that addresses both the signs and the root causes. Medications such as pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs, and antidepressants are commonly prescribed to help alleviate discomfort. These treatments aim to minimize nerve pain and improve overall well-being for patients affected by neuropathy. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to tailor medication plans to each patient to ensure maximum efficacy while minimizing side effects.
In addition to medication interventions, lifestyle changes can have a significant role in managing neuropathy. Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding toxins such as alcohol can improve nerve function and reduce symptoms. Physical therapy may also be advised to help rebuild strength and function in affected areas. Patients are encouraged to stay proactive in their health management by making changes that support their health.
Complementary therapies can also provide relief for some individuals. Methods such as acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements may help ease symptoms of neuropathy. Patients should consult these options with their healthcare provider to ensure their safety and effectiveness, particularly in conjunction with other treatments. By integrating various strategies, individuals can create a tailored management plan that meets their unique needs and enhances their overall quality of life.