German Weapons Of World War Ii

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
85,390 delivered from 1941 to 1944.[1]
10,450 Astra 600s had been delivered to Germany until German occupation of France ceased.[4] The remainder of the German order, consisting of 28,000 pistols, was intercepted by Allied forces in September 1944.[1]
319,000 manufactured under German occupation. Designated Pistole 640(b) in German service.
Böhmische Waffenfabrik (Czech made under German occupation (after mid-March 1939))
All ČZ 27's Produced for German use were all marked on the slide with "Pistole Modell 27 Kal 7.65" with the addition of "Böhmische Waffenfabrik Prag."
Examples produced for German use included a manual safety, which was absent from the Hungarian-issue version. Designated Pistole 37(u) in German service.
The FN M1910 was produced under the German occupation. Designated "Pistole 621" in German service.
The FN M1922 was mainly produced for the Luftwaffe, Also used by Wehrmacht, SS, Reich Government Officials, but oddly enough was still sold commercially up until 1942.
8200 were produced under German occupation. Designated "Pistole 657" in German service.
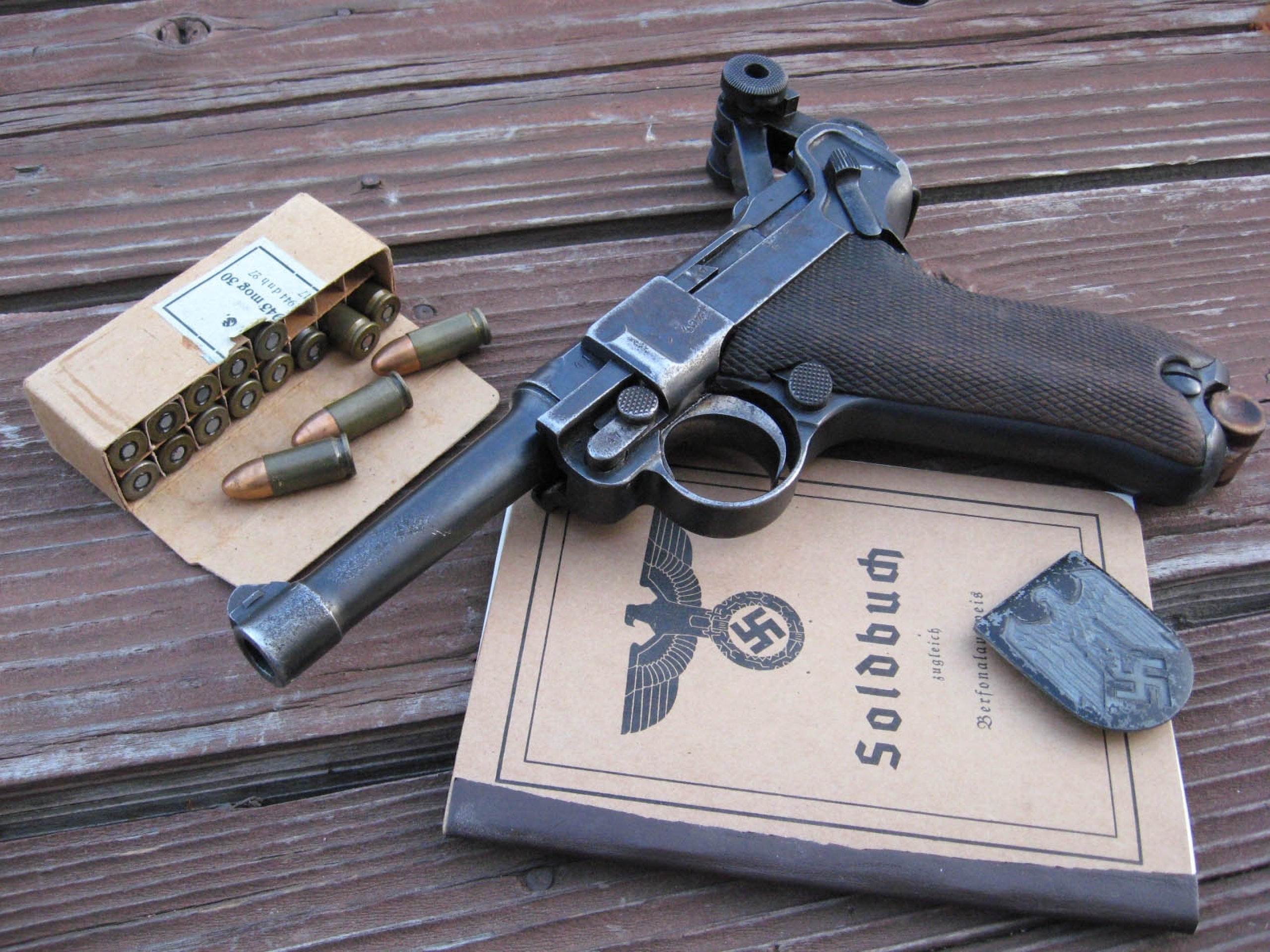
The Luger P08's production was taken over by Mauser after World War I.[8]
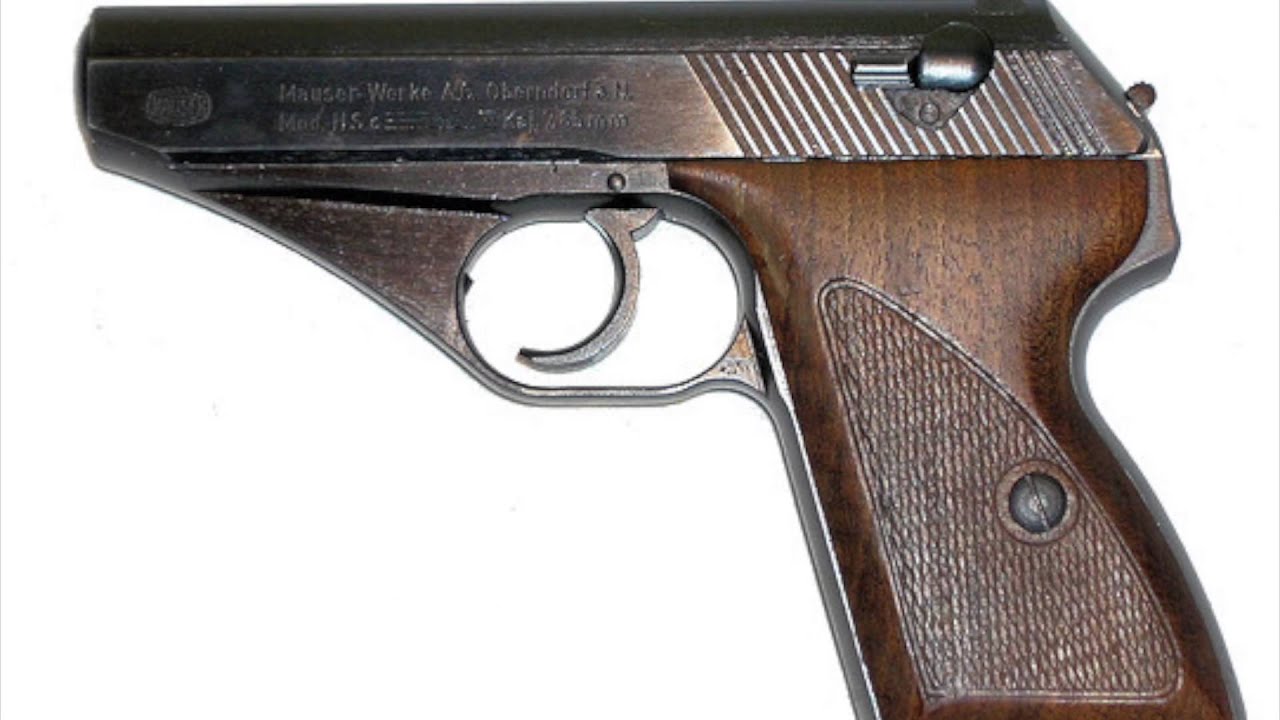
Originally produced as a commercial pistol, The Mauser HSc was fully adopted by the German Navy and Air force.[10]
After German forces occupied France, the MAB Model D was adopted for use by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
Designated Pistole 645(p) in German service.
When the Austrian Army was absorbed, existing Steyr M1912 pisols were rechambered to fire 9mm Parabellum rounds.[13] Designated Pistole 12(ö) in German service.
The manual safety on the Sauer 38H was excluded on pistols produced between 1944 and 1945.[13]
25,000 delivered prior to liberation of France.
An emergency weapon production can be traced to Mauser and Walther but full identification is still uncertain.[16]
480,000 Walther P38s were made by 1945 for the German military.[18]
Approximately 2,000 produced of first variation, 5,000 of second and third variations.
Modification of Czechoslovak vz. 24 rifle to more closely conform with standard-issue Karabiner 98k. 330,050 produced in occupied Czechoslovakia from 1938 to 1943.
Modification of Polish vz. 29 rifle to more closely conform with standard-issue Karabiner 98k. The factory was run by the Austrian firm Steyr.
Adaptation of Czechoslovak vz. 33. 131,503 produced from 1940 to 1942 for German use.
Mauser self-loading rifle design tested in 1941, not accepted for service.
Walther self-loading rifle adopted as standard in 1942 but superseded by improved Gewehr 43.
Modification of Gewehr 41(W) to gas operation, later renamed Karabiner 43.
The Gewehr 88 was the first rifle adopted by Germany that used Smokeless powder.
Standard German infantry rifle of World War I. Saw limited use in World War II, including issue to Adolf Hitler's SS bodyguard unit.
Adaptation of Hungarian 35M rifle to fire 7.92×57mm Mauser ammunition and to mount German bayonets. 138,400 produced from 1941 to 1944.
Adopted as standard German infantry rifle in 1935. Over 14 million produced from 1934 until German surrender.
Accepted after troop trials in 1943, about 8,000 produced. Served as basis for MP 43.
A competitor of the Maschinenkarabiner 42(H) from Walther. About 3,000-5,000 produced.
Issued as survival weapon for Luftwaffe aircrews.
Evolved from MKb 42(H). First series completed in July 43, first combat use in Eastern Front. Initially named Maschinenpistole 43 and then Maschinenpistole 44.
Experimental lightweight selective-fire weapon, with roller-locked blowback system, only prototypes built prior to end of war. Forefunner of the Spanish CETME 58.
Intended as a cheap and mass-produced self-loading, semi-automatic weapon. First series completed in late 1944.
A proposed version of the Gewehr 1-5 that had a firing-selector, and could be switched from fully-automatic and semi-automatic.
Standard machine gun of World War I. Saw limited use in World War II.
The MG 15 was at the beginning of the war mainly used on aircraft of the Luftwaffe. After being replaced by other machine guns many MG 15s were modified for use by ground forces.
Rejected by the Reichswehr but accepted by the Luftwaffe for aircraft use. Later transferred to Wehrmacht ground units.
Czechoslovak ZB vz. 30 produced under German occupation for Waffen-SS use.
Adapted from MG30 and adopted as standard machine gun in 1934. Issued to German troops starting in 1935.
Successor to MG34, adopted in 1942. Over 400,000 produced prior to German surrender.
Proposed MG42 replacement using an unusual delayed blowback operation.
Designated Maschinenpistole 738(i) in German service.
Designated Maschinenpistole 739(i) in German service.
Not officially adopted, but used in small numbers by the Waffen-SS.
Select-fire, removable-magazine version of the Mauser C96 pistol.
Designed by Rheinmetall but produced in Austria by Steyr to evade Treaty of Versailles restrictions. After the Anschluss, produced from 1938 to 1940 for the Waffen-SS. Pre-Anschluss Austrian examples designated Maschinenpistole 34(ö) in German service.
Produced from 1935 to 1944. Used primarily by the Waffen-SS.
The MP40 is an improved version of MP38, utilizing stamped metal parts for easier mass production.
Combined the receiver, operating mechanism, and magazine housing of the MP40 and the stock, trigger and fire selector of the MP28.
Based on British Sten Mk II, designed as an easy to manufacture last-ditch weapon. Approximately 10,000 produced in 1945.
Produced in occupied Czechoslovakia for Waffen-SS use.
Conversion of Panzerbüchse 39 to launch rifle grenades.
Improved version of Panzerbüchse 38.
Disposable recoilless single-shot anti-tank grenade launcher.
Popularly referred to as Panzerschreck. Enlarged version of American M1A1 Bazooka.
Improved version of the Raketenpanzerbüchse 43, adding a blast shield.
Full-automatic version of the Solothurn S-18/1000.
Modification of standard flare guns to launch grenades.
Later succeed by improved Flammenwerfer 41
Cheap produced variant produced for the Volkssturm or the Werwolf movements.
^ a b c d e Walter (2004), pp. 110–111.
^ Hogg & Walter (2004), p. 111.
^ a b Fowler & Stronge (2007), p. 136.
^ Hogg & Walter (2004), p. 355.
^ Walter (2004), p. 105.
^ Hogg & Walter (2004), p. 265.
^ Kokalis, Peter (2005). "Hungarian Small Arms in Germany's Service". Shotgun News. 59 (36): 12–13.
^ McNab (2004), p. 130.
^ Hogg & Weeks (2000), p. 41.
^ Hogg & Weeks (2000), p. 46.
^ a b Fowler & Stronge (2007), p. 160.
^ Bishop, Chris (2006). The Encyclopedia of Small Arms and Artillery. Grange Books. pp. 13–14. ISBN 978-1-84013-910-5.
^ a b Hogg & Weeks (2000), p. 16.
^ Fowler & Stronge (2007), p. 179.
^ McNab (2004), p. 159.
^ Hogg & Walter (2004), p. 148.
^ Hogg & Weeks (2000), p. 47.
^ Hogg & Walter (2004), p. 365.
^ a b c Fowler & Stronge (2007), p. 162.
^ "Mannlicher Gew.98/40 German Infantry Rifle". Manowar's Hungarian Weapons. Archived from the original on September 2, 2012. Retrieved June 10, 2012.
^ Fjestad, S.P. (2009). Blue Book of Gun Values 2009. Blue Book Publications. p. 1318. ISBN 1-886768-87-0.
^ Kokalis, Peter (May 10, 2009). "Luftwaffe drilling: world's most expensive survival arm". Shotgun News: 26–30. Archived from the original on December 9, 2017. Retrieved June 9, 2012.
^ "Modern Firearms - EMP.35 Erma". world.guns.ru. Archived from the original on 2012-06-21. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
^ "Modern Firearms - Zk-383". world.guns.ru. Archived from the original on 2012-06-16. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted.
The following is a list of German military equipment of World War II which includes artillery, vehicles and vessels. World War II was a global war that was under way by 1939 and ended in 1945. Following political instability build-up in Europe from 1930, the Germans, which aimed to dominate Europe, attacked Poland on 1 September 1939, marking the start of World War II. The war in Europe ended 8 May 1945 with the unconditional surrender of Germany to the Allied forces.
The Germans used a number of type designations for their weapons. In some cases the type designation and series number (i.e. FlaK 30) are sufficient to identify a system, but occasionally multiple systems of the same type are developed at the same time and share a partial designation.[1]
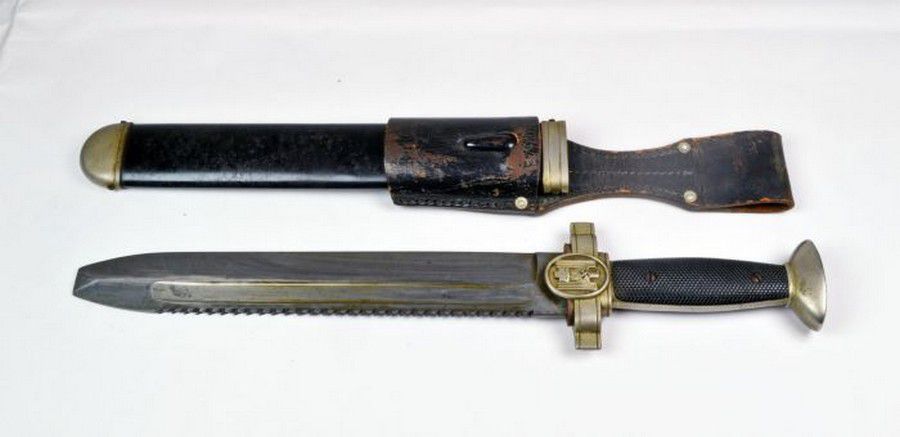
First incorporated into the German army as a bayonet for the Mauser M1898 rifle
Converted to 9mm Parabellum as the P12(Ö)
Also known as Radom wz.35 Vis - occupied Polish production
Off-axis bolt-travel delayed blowback
Main German rifle during World War II
Issued to Luftwaffe aircraft as survival weapon
Upgraded to Karabiner 98k standards, occupied Czech production
Metall- und Lackwarenfabrik Johannes Großfuß
C. G. Haenel Waffen und Fahrradfabrik
C. G. Haenel Waffen und Fahrradfabrik
Rheinmetall-Borsig AG Soemmerda,
Mauserwerke AG,
Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG,
Waffenwerke Brünn
Gas operated, Single barrel 5-rounds revolver
Gas operated, Single barrel 5-rounds revolver
Nazi Germany had captured many models of foreign equipment. In the list below, only most prominent captured models are listed. For full listing of captured vehicles see List of foreign vehicles used by Nazi Germany in World War II
Motorcycles were often paired with a sidecar as a Wehrmachtsgespann [de].
^ "World War 2 Weapons". Military Dictionary. Archived from the original on 2008-12-06. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
^ John Walter, Guns of the Third Reich, Greenhill Books, 2004, p. 163
^ John Walter, Guns of the Third Reich, Greenhill Books, 2004, p. 163
^ John Walter, Guns of the Third Reich, Greenhill Books, 2004, p. 163
^ Panzerabwehrkanonen
Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted.
Web Gif Lesbian
Solo 1080 Vk
Ksusik Love Private Video
Depi Massage Cream
Brazzers House 3 Unseen Moments
List of World War II firearms of Germany - Wikipedia
List of German military equipment of World War II - Wikipedia
List of World War II firearms of Germany | Military Wiki ...
List of World War II weapons of Germany | Military Wiki ...
German Weapons during WW2 (Rifles, Guns, Mines, Vehicles)
15 Most Fearsome German Wonder Weapons of World War II
German Secret Weapons - 2. World War 2
German Weapons Of World War Ii
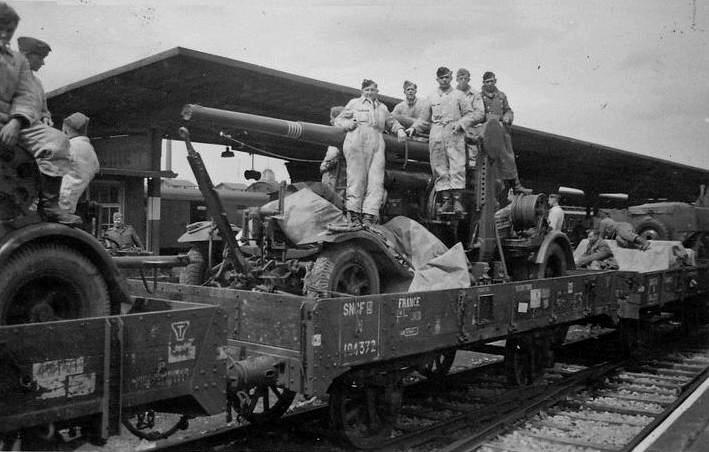
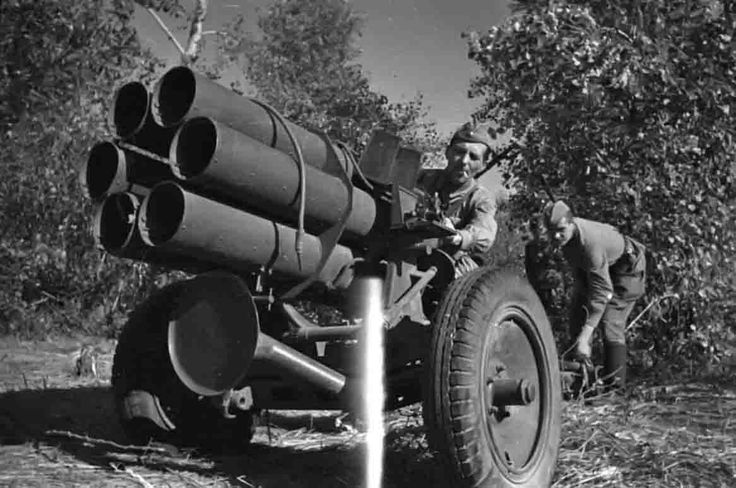
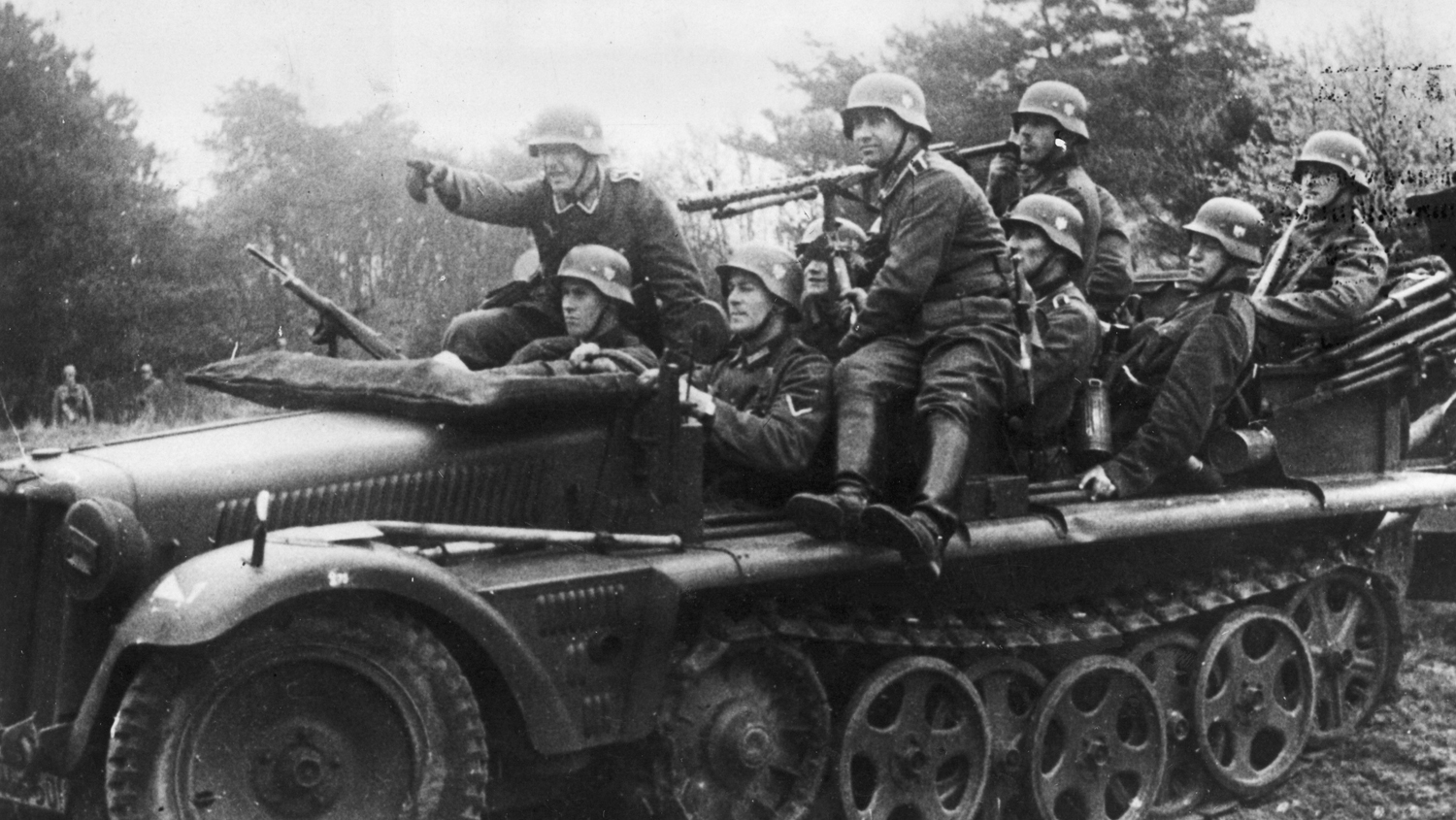
















/v-day-in-germany-3134873-5b7636b2c9e77c0057a127ec.jpg)
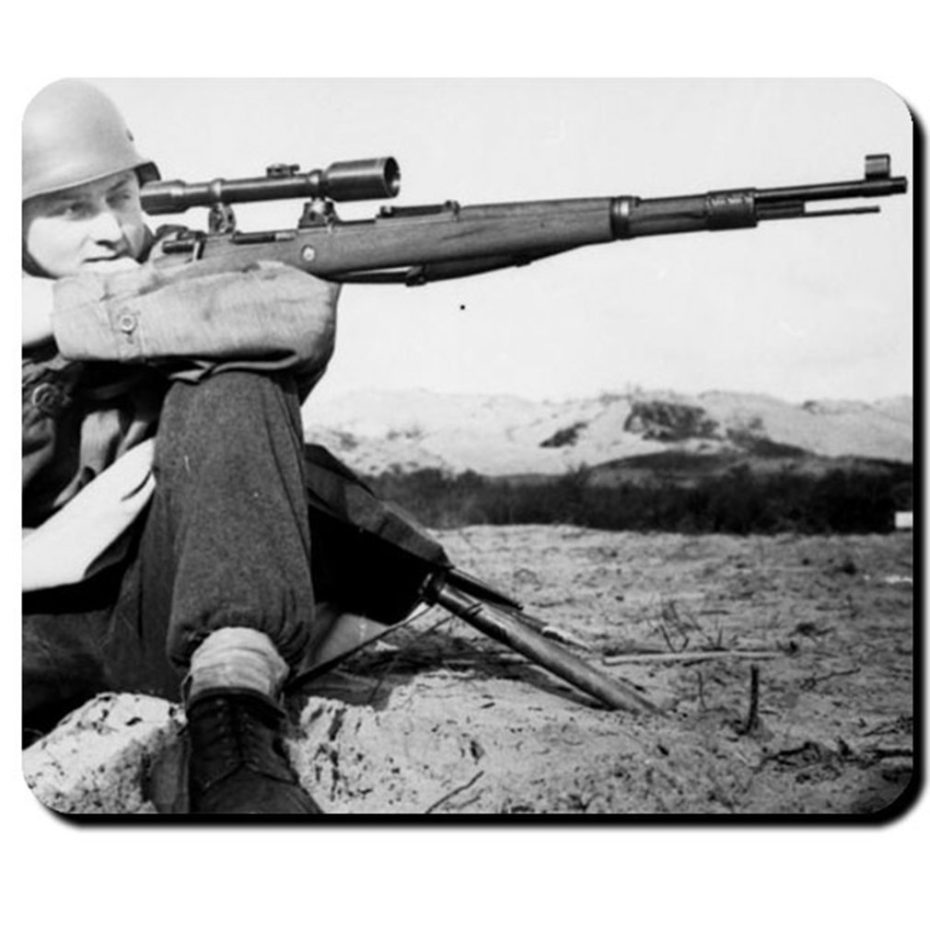


/m4-sherman-large-56a61c073df78cf7728b62eb.jpg)