German 43

🛑 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gewehr_43
Place of origin: Nazi Germany
Type: Semi-automatic rifle
Used by: See Users
In service: 1943–1945
In 1941, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union as part of Operation Barbarossa. Just prior to the opening of hostilities the Soviet Red Army had started re-arming its infantry, complementing its older bolt-action rifles with the new semi-automatic SVT-38s and SVT-40s. This was a shock to the Germans, who ramped up their own semi-automatic rifle development efforts significantly.
In 1941, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union as part of Operation Barbarossa. Just prior to the opening of hostilities the Soviet Red Army had started re-arming its infantry, complementing its older bolt-action rifles with the new semi-automatic SVT-38s and SVT-40s. This was a shock to the Germans, who ramped up their own semi-automatic rifle development efforts significantly.
The SVT series used a simpler gas-operated mechanism, which was soon emulated by Walther in its successor to the G41(W), producing the Gewehr 43 (or G43). The simpler, sturdier design and mechanism of the G43 made it lighter, easier to produce, more reliable and also much tougher than the Gewehr 41; German mountain troops would use them as ladder rungs during climbing. The addition of a 10-round stamped-steel detachable box magazine was an improvement over the integral box magazine of the G41(W). The Gewehr 43 was intended, like the G41, to be loaded using 5-round stripper clips without removing the magazine. Soldiers armed with the weapon typically carried one standard stripper clip pouch and a Gewehr 43 pouch with two spare magazines. The G43 utilises the same flapper-locked mechanism as its predecessor. The Gewehr 43 was put into production in October 1943, and followed in 1944 by the Karabiner 43 (K43), which was identical to the G43 in every way except for the letter stamped on the side. The name change from Gewehr to Karabiner (carbine) was due to the fact the barrel was actually two centimetres shorter than the standard Karabiner 98k and therefore the term Gewehr (meaning: long rifle) was somewhat unfitting. The Wehrmacht intended to equip each grenadier (infantry) company in the army with 19 G43s, including 10 with scopes, for issue as the company commander saw fit. This issue was never completely achieved. The iron sight line had a hooded pointed-post-type front sight, and a tangent-type rear sight with a V-shaped rear notch. These standard sight lines consisted of somewhat coarse aiming elements, making it suitable for rough field handling, aiming at distant area fire targets and low-light usage, but less suitable for precise aiming at distant or small point targets. It is graduated for 7.92×57mm Mauser s.S. Patrone cartridges loaded with 12.8 g (197 gr) s.S. (schweres Spitzgeschoß – "heavy pointed bullet") ball bullets from 100 to 1,200 m (109 to 1,312 yd) in 100 m (109 yd) increments.
Gewehr 43s were made by Berlin-Lübecker Maschinenfabrik in Lübeck (weapons coded "duv", and later "qve"), Walther (weapons coded "AC") and the Wilhelm Gustloff-Werke (weapons coded "bcd"). Walther used its satellite production facilities at Neuengamme concentration camp in addition to its main production facilities at Zella-Mehlis to make the rifles (It does not appear that complete weapons were assembled in the camps, similar to how Radom P35 pistols were assembled in occupied Radom, Poland without their barrels, which were built and installed by Steyr in Austria), Wilhelm Gustloff-Werke used some slave workers to augment its depleted staff from Buchenwald concentration camp. The total production by the end of the war is estimated to have been 402,713 of both models, including at least 53,435 sniper rifles: these G43/K43s were used as designated marksman/sniper weapons, fitted with the Zielfernrohr 43 (ZF 4) telescopic sight with 4× magnification. The weapon was originally designed for use with the Schiessbecher rifle grenade launcher (standard on the Karabiner 98k as well) and the Schalldämpfer suppressor, however these accessories were deemed unsuccessful in tests and were dropped even before the rifle made it to serial production.
The Gewehr 43 stayed in service with the Czechoslovak People's Army for several years after the war. Likewise the East German Border Troops and Volkspolizei were issued reworked G43 rifles, which are recognizable by a sunburst proof mark near the serial number and the serial number engraved by electropencil on removable components.
https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=CO0h1SGWvDQ
Перевести · 14.05.2016 · Shooting and discussing the WWII German Gewehr 43…
German Gewehr 43 Rifle WW2 Weapons Demo
Manuel at the VideoCamp in Berlin | Easy German 43
GERMAN LESSON 43: What is your relationship status? 💏 💏 💏
Public Transport in Berlin | Super Easy German (43)
German Lesson (43) - How to Say "You're Welcome" - A1
https://www.ww2-weapons.com/rifle-43
Перевести · 01.04.2021 · The rifle 43 was designed from the beginning for easy and fast production. Although the rifle 43 was not taken over as an official …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_submarine_U-43_(1939)
Length: 76.50 m (251 ft) o/a, 58.75 m …
Commissioned: 26 August 1939
Laid down: 15 August 1938
Launched: 23 May 1939
German submarine U-43 was a Type IXA U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The keel for U-43 was laid down in August 1938 at Bremen; she was launched in May 1939 and commissioned in August.
Between November 1939 and July 1943, the U-boat conducted 14 combat patrols, sinking 21 merchant ships for a total of 1…
German submarine U-43 was a Type IXA U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The keel for U-43 was laid down in August 1938 at Bremen; she was launched in May 1939 and commissioned in August.
Between November 1939 and July 1943, the U-boat conducted 14 combat patrols, sinking 21 merchant ships for a total of 117,036 gross register tons (GRT), damaging one ship of 10,350 GRT and another of 9,131 GRT - enough for it to be declared a total loss.
U-43 was sunk on 30 July 1943 southwest of the Azores by a torpedo dropped by a United States Navy aircraft; all 55 hands were lost.
https://www.ebay.com/b/german-g43/bn_7024879451
апр. 07, 2021 · german g43 product…
АВТОТЕХЦЕНТР "germanika" © 2017 ВСЕ ПРАВА ЗАЩИЩЕНЫ.ИНФОРМАЦИЯ НА САЙТЕ НЕ ЯВЛЯЕТСЯ ПУБЛИЧНОЙ ...
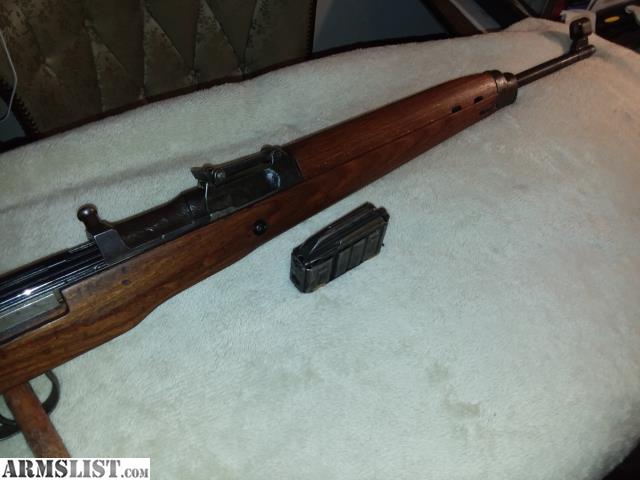
The Gewehr 43 or Karabiner 43 (abbreviated G43, K43, Gew 43, Kar 43) is a 7.92×57mm Mauser caliber semi-automatic rifle developed by Germany during World War II.
The Gewehr 43 or Karabiner 43 (abbreviated G43, K43, Gew 43, Kar 43) is a 7.92×57mm Mauser caliber semi-automatic rifle developed by Germany during World War II. The design was based on that of the earlier G41(W), but incorporating an improved short-stroke piston gas system similar to that of the Soviet Tokarev SVT-40,...
When did the Mauser Werke MG 42 come out?
When did the Mauser Werke MG 42 come out?
A limited run of about 1,500 of its immediate predecessor, the MG 39/41, was completed in 1941 and tested in combat trials. The weapon was officially accepted, and the main manufacturing of the production design began in 1942, as the MG 42, contracts going to Großfuß, Mauser-Werke, Gustloff-Werke and others.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/SM_U-43_(Germany)
Перевести · Строк: 48 · SM U-43 was one of 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy in World War I.She engaged in commerce warfare in the First Battle of the Atlantic, performing 11 patrols from 1915–1918.. U-43 was surrendered to the Allies at Harwich on 20 November 1918 in accordance with the requirements of the Armistice with Germany…
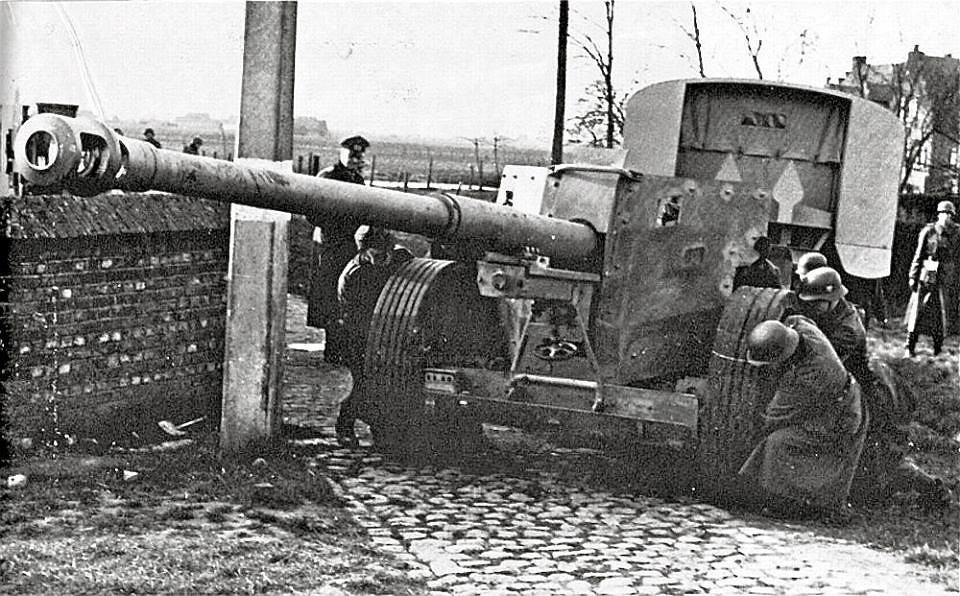
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/3.7_cm_FlaK_43
Перевести · The 3.7 cm Flak 43 was a light anti-aircraft gun used by Nazi Germany during World War II. It was derived from the 3.7-centimeter Flak 18/36/37 series of AA guns. It was provided with single- and twin-gun mounts, the latter being designated as the 3.7 cm Flak 43 …
РекламаБольшой выбор фильмов в хорошем качестве на ivi. Смотрите бесплатно!
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
German self-loading rifle Gewehr 43 and predecessor G-41 of the Second World War.
History, development, service, specifications and pictures.
Self-loading rifle 43 (Md 43, G-43), Md 41 M, Md 41 W
Type: semi-automatic infantry rifle and sniper rifle.
Already around the turn of the 19th to the 20th century numerous designs of automatic rifles were produced in Germany and one or two models were actually built. But it took until 1937, when the German army finally started to think about replacing the cylinder lock rifle Mauser 98 (Kar 98k) with a self-loading rifle.
The introduction of the M1 Garand self-loading rifle in the US Army in 1936 probably played a role in this, and the German ‘quality control’ department was always intent on increasing the efficiency of the Wehrmacht.
However, the first attempts were not successful and so it took until 1940 for the competing companies Mauser and Walther to bid for a production order with their models according to Wehrmacht specifications.
The results were the self-loading rifles Md 41 M (Mauser) and Md 41 W (Walter), or Gewehr 41 (G-41 M or G-41 W). ‘Md’ stands for ‘model’ and ‘Gewehr’ is the German term for rifle.
Both weapons were quite similar due to the exact specifications and used an unusual system to fire the 7.92 mm standard cartridge. It was the ‘Bang’ system, named after its Danish inventor. The powder gases were collected at the barrel muzzle and actuated with the help of a recoil amplifier and a gas piston at the barrel of the breech.
Although the weapon worked well in theory, as one could expect from Mauser, Walther’s model was determined to be better suited after army tests.
The Walther version was easier to produce, cheaper and much better suited for the hard service at the front and so the G-41 (W) was preferred.
A series of 3,400 units was sent to the Eastern Front at the end of 1941 for troop testing.
Although the Gewehr 41 (W) worked, it did not become very popular. The design of the muzzle led to constant pollution and therefore a continuous and careful care of the rifle was necessary.
In addition, the rifle was badly balanced with a too strong weight at the muzzle, which made it difficult to handle. And if that wasn’t enough, it was extremely heavy for an infantry rifle.
To complete the negative list, both models from Walther and Mauser had a built-in magazine for 10 cartridges of the 7.92 mm standard ammunition, which could only be loaded very slowly and laboriously.
Nevertheless, in 1943 several tens of thousands of rifles were built in Walther’s Berlin-Luebecker Maschinenfabrik. The rifle remained in use mainly on the Eastern front until the end of the war, but was not popular with the soldiers and was often exchanged for a better rifle.
After the start of Operation Barbarossa, German soldiers met the Russian semi-automatic Tokarev rifle. It was far from perfect, but still clearly superior to the Gewehr 41. In addition, the troop trials with the rifles Md 41 (M) and (W) showed early the weak points, which had to be improved.
The locking system of the Gewehr 41 was satisfactory, but the weight was too much and the muzzle area was considered a ‘built-in automatic blocking system’.
So in 1942 Walther delivered another rifle for troop testing, which was later called Gewehr 43. With this rifle the gas was already taken out in the first third of the barrel and directed upwards into a gas channel. Around this channel was a plate-like bulrush, which moved a rod, which activated a bolt carrier above the chamber; an almost identical system as with the Russian Tokarev rifle.
The locking system was the same as the swing flaps used on the G41 (W), which were controlled by the movement of the firing pin assembly, which in turn was triggered by the bolt.
The whole weapon was much lighter and better balanced than its predecessor. In addition, the permanently installed cartridge magazine was replaced by a plug gable box magazine, which improved fire speed and reloading times. The rifle 43 was designed from the beginning for easy and fast production.
Although the rifle 43 was not taken over as an official standard weapon in the Wehrmacht, but due to the simple and fast production it was easy to build the rifle from 1943 to the end of the war in 1945 in mass production at the company Walther and various other manufacturers according to an instruction of Hitler.
Thus, a total of about 450,000 pieces of the rifle 1943 were delivered to the German army.
From 1944 the production was further simplified by doing without the high quality solid wood, which made the weapon look worse on the outside. The latest versions had various tool markings and used plywood laminates or phonological plastic compounds.
So in 1944 another, even more simplified design appeared, which was introduced as Karabiner 43. Although called as a carbine, this weapon was only about 50 mm (c.2in) shorter.
Nevertheless, the quality of the mechanical components was always of a good standard and the rifle had an excellent reputation for accuracy and reliability. It remained in production until the end of the war and was later adopted by the Czech army as its standard sniper rifle, which is a compliment to the considerable firearms’ expertise of the Czechs.
The rifle 43 and its predecessor G 41 used the German 7.92 mm standard cartridge and were not affected by the introduction of the short cartridge for the assault rifle StG 44.
21.5in (54.60cm), 4 grooves, right hand twist
22in (54.90cm), 4 grooves, right hand twist
Carl Walther Waffenfabrik, Zella-Mehlis (Thuringia)
Carl Walther Waffenfabrik, Berlin-Lübecker Maschinenfabrik AG, Lübeck Gustloffwerke at Suhl
3,400 for troop trials; several tens of thousands mainly 1943
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
My name is Norman 'Kretaner' and since my childhood I am interested in history and strategy games. Later, I have learned programming and the development of computer games, and finally with the Internet, also web design. I'm in the fortunate position to combine all my interests with my work and to live on a place of my choice, on Crete. All information, figures, specifications and statistics used here had been compiled from a variety of sources and the large, over decades collected, library of the author about military history, WW2 and weapons.
Copyright © 2006-2021 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED - THE OPERATORS OF THIS SITE DISSOCIATE THEMSELVES FROM CONTENTS OF OTHER WEBSITES, WHICH ARE LINKED ON THESE PAGES. NOTE: VISITING THIS SITE WITH ENABLED AD BLOCKERS IS PROHIBITED !
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Ok
Dick S Son
Femdom Hd Free
Dildo Doggystyle
Skinny Russian Teen Fuck
Pubic Hair Bikini
Gewehr 43 - Wikipedia
Rifle 43 – WW2 Weapons
German submarine U-43 (1939) - Wikipedia
german g43 products for sale | eBay
Автотехцентр «GERMANIKA»
SM U-43 (Germany) - Wikipedia
3.7 cm Flak 43 - Wikipedia
German 43