From Theory to Practice: Vacuum Electrical Connections Clarified
In the realm of scientific inquiry along with industrial uses, maintaining a controlled environment is crucial for best outcomes. This is the moment that vacuum feedthroughs come into play, serving as crucial components that facilitate the smooth transmission of electrical signals as well as energy between the outside and the internal area of a vacuum system. These instruments are central in a range of areas, including semiconductor production, high-energy physics, and material studies, where regulated environments are essential to conduct experiments and produce high-quality materials.
Grasping the concept of vacuum feedthroughs is fundamental for anyone interested in engage with vacuum systems as well as to understand the intricacies of high-tech environments. These tiny but crucial elements must be designed to withstand the demands of vacuum settings meanwhile providing dependable electrical links. By bridging the gap between two realms, vacuum electrical feedthroughs enable scientists and engineers to investigate uncharted territories, making them vital resources in today's technology along with investigation.
Grasping Vacuous Electrified Connectors
Vacuum electrical feedthroughs are vital elements in a range of vacuous configurations, enabling the conveyance of electrical impulses and energy yet maintaining the purity in the vacuum environment. Such instruments exist constructed to prevent the introduction for pollutants emanating the air within the vacuum enclosure, which remains critical to protecting delicate tests or processes. Feedthroughs may be utilized for a range of applications, such as research-based studies, microchip production, as well as vacuous packaging.
Typically, the build in a vacuous connector typically involves sealing electrical conductors within an isolating material which is capable of withstand the high vacuum environment. Common substances employed to serve this function include ceramics as well as glass, which provide superior electrical insulation as well as elevated resistance against oxidation. This design should ensure the feedthrough is able to handle the functional requirements, such as temperature variations as well as radiation influence, while upholding a tight seal against leakage.
Aside from their basic role in providing electrical connections, vacuum electrified feedthroughs may also be tailored to satisfy specific application needs. This may encompass variations of the quantity of electrified links, various types of wires, and integrated features such as temperature sensors and sensors. With the advancement of technology progresses, the design and substances applied in vacuous feedthroughs persist to evolve, improving their efficacy and dependability in demanding conditions.
Applications of Vacuum Interface Devices
Vacuum interface devices play a essential role in various industrial applications where the quality of a vacuum state must be kept while allowing for signal connections. One of the main fields utilizing these devices is in the microchip industry, where vacuum chambers are often employed during the fabrication of microchips. These feedthroughs facilitate the essential electrical signals and power to devices such as measurement devices and monitoring devices without compromising the vacuum environment that are necessary for top-notch manufacturing processes.
In research environments, particularly within particle accelerators and nuclear fusion reactors, vacuum connectors enable the connection of sensors and devices to the internal systems. These instruments are important for monitoring parameters such as heat and plasma conditions. By providing a pathway for power connection that protects the vacuum conditions, these feedthroughs allow scientists to conduct meticulous experiments and gather essential data that guides further investigation and progress.
Additionally, vacuum feedthroughs are notable in the field of vacuum deposition technologies. They are used to supply power to vapor deposition systems that create thin films on various substrates. This application is vital in the production of thin films for optics and the development of new materials. The ability to retain a vacuum while providing electrical inputs ensures that these methods can be performed with great efficiency and quality, making vacuum interfaces an essential component in cutting-edge technology applications.
Development Factors and Issues
When creating vacuum electrical feedthroughs, a primary concerns is ensuring that the interface between the vacuum space and the external atmosphere is preserved without compromising the integrity of the system. Materials used must have favorable electrical properties while also being capable of enduring the vacuum environment. Typical materials like ceramics and certain metals are often preferred for their insulating properties and ability to corrosion, but these must be carefully selected to fit the application’s voltage and thermal needs.
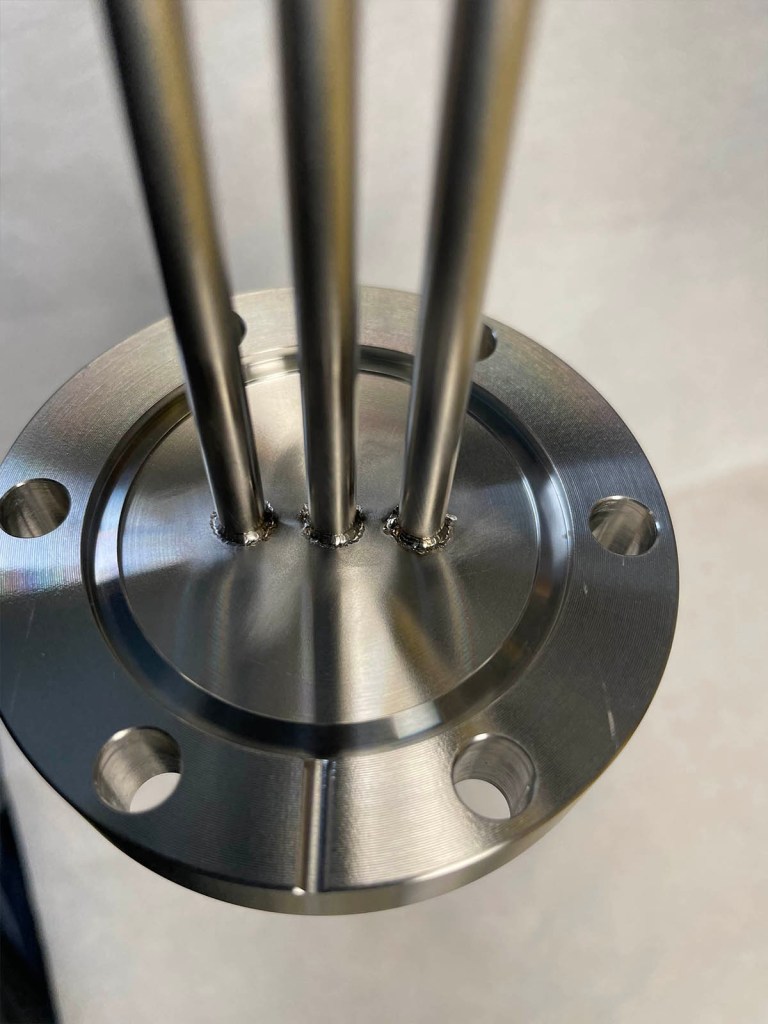
A further significant challenge in the design of vacuum feedthroughs is controlling the thermal expansion and contraction of materials. Various materials expand at varied rates when exposed to temperature changes, which can lead to tension at the junction points. This tension can cause electrical failures or even leaks. As a result, designers must carefully evaluate the thermal properties of the materials involved and think about using materials that have compatible thermal expansion coefficients to minimize these issues.
In conclusion, integrating vacuum feedthroughs into intricate systems can result in complications in terms of space limitations and mechanical design. The feedthrough must not only provide reliable electrical interfaces but also fit within the existing architecture of the vacuum chamber or equipment. This may involve compact designs and innovative mounting solutions to ensure that the feedthrough functions effectively without interfering with additional system components. Careful attention must be paid to alignment and sealing methods to promote long-term reliability in the operational environment.