Franco-Prussian War
Next part 1
Made with Beautifier
Original link from en.wikipedia.org
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 January 1871, the conflict was caused primarily by France's determination to reassert its dominant position in continental Europe, which appeared in question following the decisive Prussian victory over Austria in 1866. According to some historians, Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck deliberately provoked the French into declaring war on Prussia in order to induce four independent southern German states—Baden, Württemberg, Bavaria and Hesse-Darmstadt—to join the North German Confederation; other historians contend that Bismarck exploited the circumstances as they unfolded. All agree that Bismarck recognized the potential for new German alliances, given the situation as a whole.
France mobilised its army on 15 July 1870, leading the North German Confederation to respond with its own mobilisation later that day. On 16 July 1870, the French parliament voted to declare war on Prussia; France invaded German territory on 2 August. The German coalition mobilised its troops much more effectively than the French and invaded northeastern France on 4 August. German forces were superior in numbers, training, and leadership and made more effective use of modern technology, particularly railways and artillery.
A series of swift Prussian and German victories in eastern France, culminating in the Siege of Metz and the Battle of Sedan, resulted in the capture of the French Emperor Napoleon III and the decisive defeat of the army of the Second Empire; a Government of National Defense was formed in Paris on 4 September and continued the war for another five months. German forces fought and defeated new French armies in northern France, then besieged Paris for over four months before it fell on 28 January 1871, effectively ending the war.
In the waning days of the war, with German victory all but assured, the German states proclaimed their union as the German Empire under the Prussian king Wilhelm I and Chancellor Bismarck; with the notable exception of Austria, the vast majority of Germans were united under a nation-state for the first time. Following an armistice with France, the Treaty of Frankfurt was signed on 10 May 1871, giving Germany billions of francs in war indemnity, as well as most of Alsace and parts of Lorraine, which became the Imperial Territory of Alsace-Lorraine (Reichsland Elsaß-Lothringen).
The war had a lasting impact on Europe. By hastening the process of German unification, it significantly altered the balance of power on the continent; with the new German nation state supplanting France as the dominant European land power. Bismarck maintained great authority in international affairs for two decades, developing a reputation for adept and pragmatic diplomacy that raised Germany's global stature and influence. In France, it brought a final end to imperial rule and began the first lasting republican government. Resentment over France's defeat triggered a revolutionary uprising called the Paris Commune, which managed to seize and hold power for two months before its bloody suppression; the event would influence the politics and policies of the Third Republic.
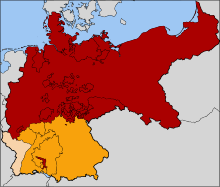
Map of the North German Confederation (red), four Southern German States (orange) and Alsace-Lorraine (beige)
The causes of the Franco-Prussian War are strongly rooted in the events surrounding the gradual march toward the unification of the German states under Otto von Bismarck. In the midst of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, the Empress Eugénie, Foreign Minister Drouyn de Lhuys and War Minister Jacques Louis Randon, worried that a Prussian victory might jeopardize France's status as the dominant power in Europe, gained after the Franco-Austrian War of 1859, unsuccessfully urged Napoleon to implement an armed mediation which would consist in a mobilization and the massing of troops at France's eastern borders while the bulk of the Prussian armies were still engaged in Bohemia, as a warning that no territorial changes could be effected in Germany without consulting France. As a result of Prussia's annexation of several German states which had sided with Austria during the war and the formation of the North German Confederation under Prussia's aegis, French public opinion stiffened and now demanded more firmness as well as territorial compensations. As a result, Napoleon demanded from Prussia a return to the French borders of 1814, with the annexation of Luxembourg, most of Saarland, and the Bavarian Palatinate. Bismarck flatly refused what he disdainfully termed France's politique des pourboires ("tipping policy"). He then communicated Napoleon's written territorial demands to Bavaria and the other southern German states of Württemberg, Baden and Hesse-Darmstadt, which hastened the conclusion of defensive military alliances with these states. France had been strongly opposed to any further alliance of German states, which would have significantly strengthened Prussia militarily.
The only result of French policy was the consent of Prussia to nominal independence for Saxony, Bavaria, Wurttemberg, Baden, and Hessia-Darmstadt, this was a small victory, and one without flavor for a French public that wanted territory and a French army that wanted revenge. The situation did not suit either France, which unexpectedly found itself next to the militarily powerful Prussian led North German Confederation, or Prussia, whose foremost objective was to complete the process of uniting the German states under its control. Thus, war between the two powers since 1866 was only a matter of time.
In Prussia, some officials considered a war against France both inevitable and necessary to arouse German nationalism in those states that would allow the unification of a great German empire. This aim was epitomized by Prussian Chancellor Otto von Bismarck's later statement: "I did not doubt that a Franco-German war must take place before the construction of a United Germany could be realised." Bismarck also knew that France should be the aggressor in the conflict to bring the four southern German states to side with Prussia, hence giving Germans numerical superiority. He was convinced that France would not find any allies in her war against Germany for the simple reason that "France, the victor, would be a danger to everybody – Prussia to nobody," and he added, "That is our strong point." Many Germans also viewed the French as the traditional destabilizer of Europe, and sought to weaken France to prevent further breaches of the peace.
The immediate cause of the war resided in the candidacy of Leopold of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, a Prussian prince, to the throne of Spain. France feared encirclement by an alliance between Prussia and Spain. The Hohenzollern prince's candidacy was withdrawn under French diplomatic pressure, but Otto von Bismarck goaded the French into declaring war by releasing an altered summary of the Ems Dispatch, a telegram sent by William I rejecting French demands that Prussia never again support a Hohenzollern candidacy. Bismarck's summary, as mistranslated by the French press Havas, made it sound as if the king had treated the French envoy in a demeaning fashion, which inflamed public opinion in France.
French historians François Roth and Pierre Milza argue that Napoleon III was pressured by a bellicose press and public opinion and thus sought war in response to France's diplomatic failures to obtain any territorial gains following the Austro-Prussian War. Napoleon III believed he would win a conflict with Prussia. Many in his court, such as Empress Eugénie, also wanted a victorious war to resolve growing domestic political problems, restore France as the undisputed leading power in Europe, and ensure the long-term survival of the House of Bonaparte. A national plebiscite held on 8 May 1870, which returned results overwhelmingly in favor of the Emperor's domestic agenda, gave the impression that the regime was politically popular and in a position to confront Prussia. Within days of the plebiscite, France's pacifist Foreign Minister Napoléon, comte Daru was replaced by Agenor, duc de Gramont, a fierce opponent of Prussia who, as French Ambassador to Austria in 1866, had advocated an Austro-French military alliance against Prussia. Napoleon III's worsening health problems made him less and less capable of reining in Empress Eugénie, Gramont and the other members of the war party, known collectively as the "mameluks". For Bismarck, the nomination of Gramont was seen as "a highly bellicose symptom".
The Ems telegram of 13 July 1870 had exactly the effect on French public opinion that Bismarck had intended. "This text produced the effect of a red flag on the Gallic bull", Bismarck later wrote. Gramont, the French foreign minister, declared that he felt "he had just received a slap". The leader of the monarchists in Parliament, Adolphe Thiers, spoke for moderation, arguing that France had won the diplomatic battle and there was no reason for war, but he was drowned out by cries that he was a traitor and a Prussian. Napoleon's new prime minister, Emile Ollivier, declared that France had done all that it could humanly and honorably do to prevent the war, and that he accepted the responsibility "with a light heart". A crowd of 15,000–20,000 people, carrying flags and patriotic banners, marched through the streets of Paris, demanding war. French mobilization was ordered early on 15 July. Upon receiving news of the French mobilization, the North German Confederation mobilized on the night of 15–16 July, while Bavaria and Baden did likewise on 16 July and Württemberg on 17 July. On 19 July 1870, the French sent a declaration of war to the Prussian government. The southern German states immediately sided with Prussia.
Napoleonic France had no documented alliance with other powers and entered the war virtually without allies. The calculation was for a victorious offensive, which, as the French Foreign Minister Gramont stated, was "the only way for France to lure the wary Austrians, Italians and Danes into the French alliance". The involvement of Russia on the side of France was not considered by her at all, since Russia made the lifting of restrictions on its naval construction on the Black Sea imposed on Russia by the Treaty of Paris (1856) following the Crimean War a precondition for the union. But Imperial France was not ready to do this. "Bonaparte did not dare to encroach on the Paris Treaty: the worse things turned out in the present, the more precious the heritage of the past became".
Opposing forces[edit]French[edit]
French soldiers drill at IIe Chambrière camp near Metz, 1870
The French Army consisted in peacetime of approximately 426,000 soldiers, some of them regulars, others conscripts who until March 1869 were selected by ballot and served for the comparatively long period of seven years. Some of them were veterans of previous French campaigns in the Crimean War, Algeria, the Franco-Austrian War in Italy, and in the Mexican campaign. However, following the "Seven Weeks War" between Prussia and Austria four years earlier, it had been calculated that, with commitments in Algeria and elsewhere, the French Army could field only 288,000 men to face the Prussian Army, when potentially 1,000,000 would be required. Under Marshal Adolphe Niel, urgent reforms were made. Universal conscription and a shorter period of service gave increased numbers of reservists, who would swell the army to a planned strength of 800,000 on mobilisation. Those who for any reason were not conscripted were to be enrolled in the Garde Mobile, a militia with a nominal strength of 400,000. However, the Franco-Prussian War broke out before these reforms could be completely implemented. The mobilisation of reservists was chaotic and resulted in large numbers of stragglers, while the Garde Mobile were generally untrained and often mutinous.
French infantry were equipped with the breech-loading Chassepot rifle, one of the most modern mass-produced firearms in the world at the time, with 1,037,555 available in French inventories. With a rubber ring seal and a smaller bullet, the Chassepot had a maximum effective range of some 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) with a short reloading time. French tactics emphasised the defensive use of the Chassepot rifle in trench-warfare style fighting—the so-called feu de bataillon. The artillery was equipped with rifled, muzzle-loaded La Hitte guns. The army also possessed a precursor to the machine-gun: the mitrailleuse, which could unleash significant, concentrated firepower but nevertheless lacked range and was comparatively immobile, and thus prone to being easily overrun. The mitrailleuse was mounted on an artillery gun carriage and grouped in batteries in a similar fashion to cannon.
The army was nominally led by Napoleon III, with Marshals François Achille Bazaine and Patrice de MacMahon in command of the field armies. However, there was no previously arranged plan of campaign in place. The only campaign plan prepared between 1866 and 1870 was a defensive one.
Prussians/Germans[edit]
Prussian field artillery column at Torcy in September 1870
The German army comprised that of the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia, and the South German states drawn in under the secret clause of the preliminary peace of Nikolsburg, 26 July 1866, and formalised in the Treaty of Prague, 23 August 1866.
Recruitment and organisation of the various armies were almost identical, and based on the concept of conscripting annual classes of men who then served in the regular regiments for a fixed term before being moved to the reserves. This process gave a theoretical peace time strength of 382,000 and a wartime strength of about 1,189,000.
German tactics emphasised encirclement battles like Cannae and using artillery offensively whenever possible. Rather than advancing in a column or line formation, Prussian infantry moved in small groups that were harder to target by artillery or French defensive fire. The sheer number of soldiers available made encirclement en masse and destruction of French formations relatively easy.
The army was equipped with the Dreyse needle gun renowned for its use at the Battle of Königgrätz, which was by this time showing the age of its 25-year-old design. The rifle had a range of only 600 m (2,000 ft) and lacked the rubber breech seal that permitted aimed shots. The deficiencies of the needle gun were more than compensated for by the famous Krupp 6-pounder (6 kg despite the gun being called a 6-pounder, the rifling technology enabled guns to fire twice the weight of projectiles in the same calibre) steel breech-loading cannons being issued to Prussian artillery batteries. Firing a contact-detonated shell, the Krupp gun had a longer range and a higher rate of fire than the French bronze muzzle loading cannon, which relied on faulty time fuses.
The Prussian army was controlled by the General Staff, under Field Marshal Helmuth von Moltke. The Prussian army was unique in Europe for having the only such organisation in existence, whose purpose in peacetime was to prepare the overall war strategy, and in wartime to direct operational movement and organise logistics and communications. The officers of the General Staff were hand-picked from the Prussian Kriegsakademie (War Academy). Moltke embraced new technology, particularly the railroad and telegraph, to coordinate and accelerate mobilisation of large forces.
French Army incursion[edit]Preparations for the offensive[edit]
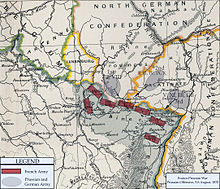
Map of the German and French armies near the common border on 31 July 1870
On 28 July 1870 Napoleon III left Paris for Metz and assumed command of the newly titled Army of the Rhine, some 202,448 strong and expected to grow as the French mobilization progressed.Marshal MacMahon took command of I Corps (4 infantry divisions) near Wissembourg, Marshal François Canrobert brought VI Corps (4 infantry divisions) to Châlons-sur-Marne in northern France as a reserve and to guard against a Prussian advance through Belgium.
A pre-war plan laid down by the late Marshal Niel called for a strong French offensive from Thionville towards Trier and into the Prussian Rhineland. This plan was discarded in favour of a defensive plan by Generals Charles Frossard and Bartélemy Lebrun, which called for the Army of the Rhine to remain in a defensive posture near the German border and repel any Prussian offensive. As Austria along with Bavaria, Württemberg and Baden were expected to join in a revenge war against Prussia, I Corps would invade the Bavarian Palatinate and proceed to "free" the four South German states in concert with Austro-Hungarian forces. VI Corps would reinforce either army as needed.
Unfortunately for Frossard's plan, the Prussian army mobilised far more rapidly than expected. The Austro-Hungarians, still reeling after their defeat by Prussia in the Austro-Prussian War, were treading carefully before stating that they would only side with France if the south Germans viewed the French positively. This did not materialize as the four South German states had come to Prussia's aid and were mobilizing their armies against France.
Occupation of Saarbrücken[edit]
Course of the first phase of the war up to the Battle of Sedan on 1 September 1870
Napoleon III was under substantial domestic pressure to launch an offensive before the full might of Moltke's forces was mobilized and deployed. Reconnaissance by Frossard's forces had identified only the Prussian 16th Infantry Division guarding the border town of Saarbrücken, right before the entire Army of the Rhine. Accordingly, on 31 July the Army marched forward toward the Saar River to seize Saarbrücken.
General Frossard's II Corps and Marshal Bazaine's III Corps crossed the German border on 2 August, and began to force the Prussian 40th Regiment of the 16th Infantry Division from the town of Saarbrücken with a series of direct attacks. The Chassepot rifle proved its worth against the Dreyse rifle, with French riflemen regularly outdistancing their Prussian counterparts in the skirmishing around Saarbrücken. However the Prussians resisted strongly, and the French suffered 86 casualties to the Prussian 83 casualties. Saarbrücken also proved to be a major obstacle in terms of logistics. Only one railway there led to the German hinterland but could be easily defended by a single force, and the only river systems in the region ran along the border instead of inland. While the French hailed the invasion as the first step towards the Rhineland and later Berlin, General Edmond Le Bœuf and Napoleon III were receiving alarming reports from foreign news sources of Prussian and Bavarian armies massing to the southeast in addition to the forces to the north and northeast.
Moltke had indeed massed three armies in the area—the Prussian First Army with 50,000 men, commanded by General Karl von Steinmetz opposite Saarlouis, the Prussian Second Army with 134,000 men commanded by Prince Friedrich Karl opposite the line Forbach-Spicheren, and the Prussian Third Army with 120,000 men commanded by Crown Prince Friedrich Wilhelm, poised to cross the border at Wissembourg.
Prussian Army advance[edit]Battle of Wissembourg[edit]
Bavarian infantry at the Battle of Wissembourg, 1870
Upon learning from captured Prussian soldiers and a local area police chief that the Prussian Crown Prince's Third Army was just 30 miles (48 km) north from Saarbrücken near the Rhine river town Wissembourg, General Le Bœuf and Napoleon III decided to retreat to defensive positions. General Frossard, without instructions, hastily withdrew his elements of the Army of the Rhine in Saarbrücken back across the river to Spicheren and Forbach.
Marshal MacMahon, now closest to Wissembourg, spread his four divisions 20 miles (32 km) to react to any Prussian-Bavarian invasion. This organization was due to a lack of supplies, forcing each division to seek out food and forage from the countryside and from the representatives of the army supply arm that was supposed to furnish them with provisions. What made a bad situation much worse was the conduct of General Auguste-Alexandre Ducrot, commander of the 1st Division. He told General Abel Douay, commander of the 2nd Division, on 1 August that "The information I have received makes me suppose that the enemy has no considerable forces very near his advance posts, and has no desire to take the offensive". Two days later, he told MacMahon that he had not found "a single enemy post ... it looks to me as if the menace of the Bavarians is simply bluff". Even though Ducrot shrugged off the possibility of an attack by the Germans, MacMahon tried to warn his other three division commanders, without success.
The first action of the Franco-Prussian War took place on 4 August 1870. This battle saw the unsupported division of General Douay of I Corps, with some attached cavalry, which was posted to watch the border, attacked in overwhelming but uncoordinated fashion by the German 3rd Army. During the day, elements of a Bavarian and two Prussian corps became engaged and were aided by Prussian artillery, which blasted holes in the city defenses. Douay held a very strong position initially, thanks to the accurate long-range rapid fire of the Chassepot rifles, but his force was too thinly stretched to hold it. Douay was killed in the late morning when a caisson of the divisional mitrailleuse battery exploded near him; the encirclement of the town by the Prussians then threatened the French avenue of retreat.
The fighting within the town had become extremely intense, becoming a door to door battle of survival. Despite an unceasing attack from Prussian infantry, the soldiers of the 2nd Division kept to their positions. The people of the town of Wissembourg finally surrendered to the Germans. The French troops who did not surrender retreated westward, leaving behind 1,000 dead and wounded and another 1,000 prisoners and all of their remaining ammunition. The final attack by the Prussian troops also cost 1,000 casualties. The German cavalry then failed to pursue the French and lost touch with them. The attackers had an initial superiority of numbers, a broad deployment which made envelopment highly likely but the effectiveness of French Chassepot rifle-fire inflicted costly repulses on infantry attacks, until the French infantry had been extensively bombarded by the Prussian artillery.
Battle of Spicheren[edit]
Map of the Prussian and German offensives, 5–6 August 1870
The Battle of Spicheren on 5 August was the second of three critical French defeats. Moltke had originally planned to keep Bazaine's army on the Saar River until he could attack it with the 2nd Army in front and the 1st Army on its left flank, while the 3rd Army closed towards the rear. The aging General von Steinmetz made an overzealous, unplanned move, leading the 1st Army south from his position on the Moselle. He moved straight toward the town of Spicheren, cutting off Prince Frederick Charles from his forward cavalry units in the process.
On the French side, planning after the disaster at Wissembourg had become essential. General Le Bœuf, flushed with anger, was intent upon going on the offensive over the Saar and countering their loss. However, planning for the next encounter was more based upon the reality of unfolding events rather than emotion or pride, as Intendant General Wolff told him and his staff that supply beyond the Saar would be impossible. Therefore, the armies of France would take up a defensive position that would protect against every possible attack point, but also left the armies unable to support each other.
While the French army under General MacMahon engaged the German 3rd Army at the Battle of Wörth, the German 1st Army under Steinmetz finished their advance west from Saarbrücken. A patrol from the German 2nd Army under Prince Friedrich Karl of Prussia spotted decoy fires close and Frossard's army farther off on a distant plateau south of the town of Spicheren, and took this as a sign of Frossard's retreat. Ignoring Moltke's plan again, both German armies attacked Frossard's French 2nd Corps, fortified between Spicheren and Forbach.
The French were unaware of German numerical superiority at the beginning of the battle as the German 2nd Army did not attack all at once. Treating the oncoming attacks as merely skirmishes, Frossard did not request additional support from other units. By the time he realized what kind of a force he was opposing, it was too late. Seriously flawed communications between Frossard and those in reserve under Bazaine slowed down so much that by the time the reserves received orders to move out to Spicheren, German soldiers from the 1st and 2nd armies had charged up the heights. Because the reserves had not arrived, Frossard erroneously believed that he was in grave danger of being outflanked, as German soldiers under General von Glume were spotted in Forbach. Instead of continuing to defend the heights, by the close of battle after dusk he retreated to the south. The German casualties were relatively high due to the advance and the effectiveness of the Chassepot rifle. They were quite startled in the morning when they had found out that their efforts were not in vain—Frossard had abandoned his position on the heights.
Battle of Wörth[edit]
The Battle of Wörth began when the two armies clashed again on 6 August near Wörth in the town of Frœschwiller, about 10 miles (16 km) from Wissembourg. The Crown Prince of Prussia's 3rd army had, on the quick reaction of his Chief of Staff General von Blumenthal, drawn reinforcements which brought its strength up to 140,000 troops. The French had been slowly reinforced and their force numbered only 35,000. Although badly outnumbered, the French defended their position just outside Frœschwiller. By afternoon, the Germans had suffered 10,500 killed or wounded and the French had lost a similar number of casualties and another 9,200 men taken prisoner, a loss of about 50%. The Germans captured Fröschwiller which sat on a hilltop in the centre of the French line. Having lost any hope for victory and facing a massacre, the French army disengaged and retreated in a westerly direction towards Bitche and Saverne, hoping to join French forces on the other side of the Vosges mountains. The German 3rd army did not pursue the French but remained in Alsace and moved slowly south, attacking and destroying the French garrisons in the vicinity.
Battle of Mars-La-Tour[edit]
Heinrich XVII, Prince Reuss, on the side of the 5th Squadron I Guards Dragoon Regiment at Mars-la-Tour, 16 August 1870. Emil Hünten, 1902
About 160,000 French soldiers were besieged in the fortress of Metz following the defeats on the frontier. A retirement from Metz to link up with French forces at Châlons was ordered on 15 August and spotted by a Prussian cavalry patrol under Major Oskar von Blumenthal. Next day a grossly outnumbered Prussian force of 30,000 men of III Corps (of the 2nd Army) under General Constantin von Alvensleben, found the French Army near Vionville, east of Mars-la-Tour.
Despite odds of four to one, the III Corps launched a risky attack. The French were routed and the III Corps captured Vionville, blocking any further escape attempts to the west. Once blocked from retreat, the French in the fortress of Metz had no choice but to engage in a fight that would see the last major cavalry engagement in Western Europe. The battle soon erupted, and III Corps was shattered by incessant cavalry charges, losing over half its soldiers. The German Official History recorded 15,780 casualties and French casualties of 13,761 men.
On 16 August, the French had a chance to sweep away the key Prussian defense, and to escape. Two Prussian corps had attacked the French advance guard, thinking that it was the rearguard of the retreat of the French Army of the Meuse. Despite this misjudgment the two Prussian corps held the entire French army for the whole day. Outnumbered 5 to 1, the extraordinary élan of the Prussians prevailed over gross indecision by the French. The French had lost the opportunity to win a decisive victory.
Battle of Gravelotte[edit]
The "Rifle Battalion 9 from Lauenburg" at Gravelotte
The Battle of Gravelotte, or Gravelotte–St. Privat (18 August), was the largest battle during the Franco-Prussian War. It was fought about 6 miles (9.7 km) west of Metz, where on the previous day, having intercepted the French army's retreat to the west at the Battle of Mars-La-Tour, the Prussians were now closing in to complete the destruction of the French forces. The combined German forces, under Field Marshal Count Helmuth von Moltke, were the Prussian First and Second Armies of the North German Confederation numbering about 210 infantry battalions, 133 cavalry squadrons, and 732 heavy cannons totaling 188,332 officers and men. The French Army of the Rhine, commanded by Marshal François-Achille Bazaine, numbering about 183 infantry battalions, 104 cavalry squadrons, backed by 520 heavy cannons, totaling 112,800 officers and men, dug in along high ground with their southern left flank at the town of Rozérieulles, and their northern right flank at St. Privat.
On 18 August, the battle began when at 08:00 Moltke ordered the First and Second Armies to advance against the French positions. The French were dug in with trenches and rifle pits with their artillery and their mitrailleuses in concealed positions. Backed by artillery fire, Steinmetz's VII and VIII Corps launched attacks across the Mance ravine, all of which were defeated by French rifle and mitrailleuse firepower, forcing the two German corps' to withdraw to Rezonville. The Prussian 1st Guards Infantry Division assaulted French-held St. Privat and was pinned down by French fire from rifle pits and trenches. The Second Army under Prince Frederick Charles used its artillery to pulverize the French position at St. Privat. His XII Corps took the town of Roncourt and helped the Guard conquer St. Privat, while Eduard von Fransecky's II Corps advanced across the Mance ravine. The fighting died down at 22:00.
The next morning the French Army of the Rhine retreated to Metz where they were besieged and forced to surrender two months later. A grand total of 20,163 German troops were killed, wounded or missing in action during the August 18 battle. The French losses were 7,855 killed and wounded along with 4,420 prisoners of war (half of them were wounded) for a total of 12,275.
Siege of Metz[edit]
With the defeat of Marshal Bazaine's Army of the Rhine at Gravelotte, the French retired to Metz, where they were besieged by over 150,000 Prussian troops of the First and Second Armies. Further military operations on the part of the army under Bazaine's command have drawn numerous criticisms from historians against its commander. It is stated with malicious irony that his occupation at that time was writing orders on hygiene and discipline, as well as playing dominoes. Bazaine's surprising inactivity was a great relief to Moltke, who now had time to improve his lines around Metz and intensify the hunt for MacMahon. At this time, Napoleon III and MacMahon formed the new French Army of Châlons to march on to Metz to rescue Bazaine. Napoleon III personally led the army with Marshal MacMahon in attendance. The Army of Châlons marched northeast towards the Belgian border to avoid the Prussians before striking south to link up with Bazaine. The Prussians took advantage of this maneuver to catch the French in a pincer grip. Moltke left the Prussian First and Second Armies besieging Metz, except three corps detached to form the Army of the Meuse under the Crown Prince of Saxony. With this army and the Prussian Third Army, Moltke marched northward and caught up with the French at Beaumont on 30 August. After a sharp fight in which they lost 5,000 men and 40 cannons, the French withdrew toward Sedan. Having reformed in the town, the Army of Châlons was immediately isolated by the converging Prussian armies. Napoleon III ordered the army to break out of the encirclement immediately. With MacMahon wounded on the previous day, General Auguste Ducrot took command of the French troops in the field.
Battle of Sedan[edit]
On 1 September 1870, the battle opened with the Army of Châlons, with 202 infantry battalions, 80 cavalry squadrons and 564 guns, attacking the surrounding Prussian Third and Meuse Armies totaling 222 infantry battalions, 186 cavalry squadrons and 774 guns. General De Wimpffen, the commander of the French V Corps in reserve, hoped to launch a combined infantry and cavalry attack against the Prussian XI Corps. But by 11:00, Prussian artillery took a toll on the French while more Prussian troops arrived on the battlefield. The struggle in the conditions of encirclement turned out to be absolutely impossible for the French — their front was shot through with artillery fire from three sides through and through. The French cavalry, commanded by General Margueritte, launched three desperate attacks on the nearby village of Floing where the Prussian XI Corps was concentrated. Margueritte was mortally wounded leading the very first charge, dying 4 days later, and the two additional charges led to nothing but heavy losses. By the end of the day, with no hope of breaking out, Napoleon III called off the attacks. The French lost over 17,000 men, killed or wounded, with 21,000 captured. The Prussians reported their losses at 2,320 killed, 5,980 wounded and 700 captured or missing. By the next day, on 2 September, Napoleon III surrendered and was taken prisoner with 104,000 of his soldiers. It was an overwhelming victory for the Prussians, for they not only captured an entire French army, but the leader of France as well. The defeat of the French at Sedan had decided the war in Prussia's favour. One French army was now immobilised and besieged in the city of Metz, and no other forces stood on French ground to prevent a German invasion. Nevertheless, the war would continue. Subsequently, the Germans could not resist the temptation and drove the drooping columns of thousands of French prisoners in full view of the besieged garrison of Metz (which, of course, did not help to raise the morale of the French).
Surrender of Metz[edit]
Bazaine, a well-known Bonapartist, at this time allowed himself to be carried away by illusory plans for a political role in France. Unconventional military plans were put forth, by which the Germans would allow the army under Bazaine's command to withdraw from the fortress of Metz to retreat to the south of France, where it would remain until the German armies captured Paris, eliminated the political usurpers and made room for the legitimate imperial authorities with the support of Bazaine's army. Even ignoring moral issues and potential public outcry, this plan seems completely unrealistic. Bismarck and Moltke answered Bazaine's offer of “cooperation” against the “republican menace” with an indifferent shrug. The German press, undoubtedly at the instigation of Bismarck, widely covered this topic, and reported the details of Bazaine's negotiations. The French press could only remain completely silent on this issue. With whom Bazaine negotiated - still raises questions among historians. "For a decade, the French were considered him (M. Edmond Regnier) a sinister figure, almost certainly an agent of Bismarck. They would have been more justified in thinking him a buffoon". Undoubtedly, the politically motivated actions of Commander Bazaine led to the passivity of the encircled army at Metz and contributed to the defeat of not only this army, but the country as a whole. Bazaine's army surrendered on October 26. 173,000 people surrendered, with the Prussians capturing the huge amount of military equipment located in Metz. After the war, Marshal Bazaine was convicted by a French military court.
Government of National Defence[edit]
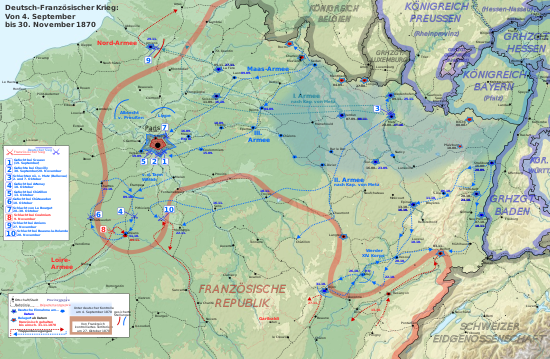
Course of the second phase of the war (part 1–1 September to 30 November)