Female Organs

🛑 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
MedicalNewsToday uses cookies to improve your experience and to show you personalized ads. Privacy Policy.
Medically reviewed by Carolyn Kay, M.D. — Written by Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA on November 5, 2019
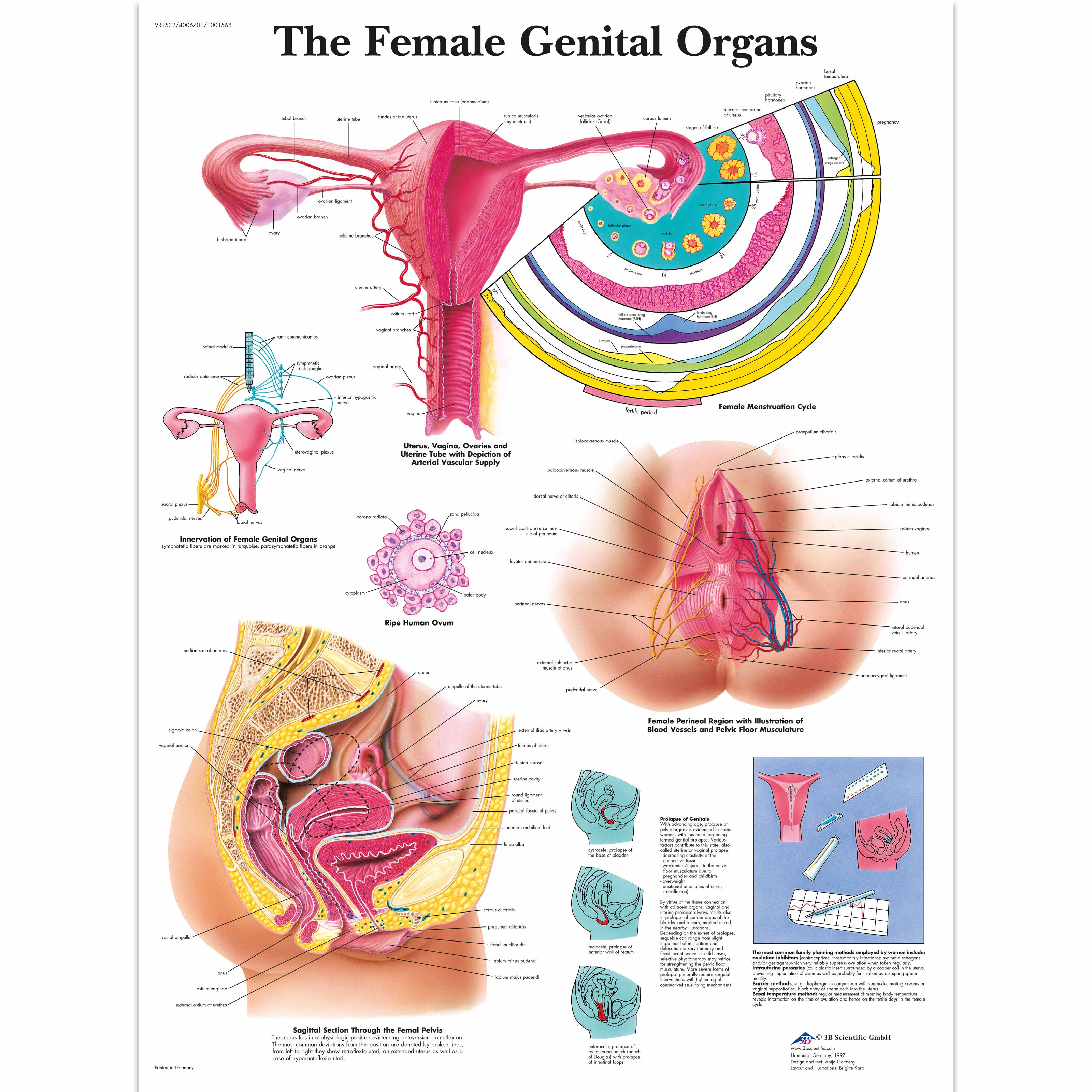
Female anatomy includes the external genitals, or the vulva, and the internal reproductive organs, which include the ovaries and the uterus.
One major difference between males and females is their reproductive organs. Anatomy specific to females generally relates to sexual function, reproduction, and hormone control.
Males and females have physically different sexual anatomy, but all sex organs come from the same bundle of cells during fetal development. A baby’s biological sex is determined at the moment the father’s sperm meets the mother’s egg.
This article will look in detail at the structure and function of the female internal and external organs.
Below is a 3D model of female anatomy, which is fully interactive.
Explore the model using your mouse pad or touchscreen to understand more about female anatomy.
The external female anatomy includes the pubis and the vulva. The following sections discuss these in more detail.
The mons pubis, or public mound, is the fleshy area on the pelvic bone where females typically grow pubic hair.
Share on Pinterest
Female reproductive organs are very different to those of males.
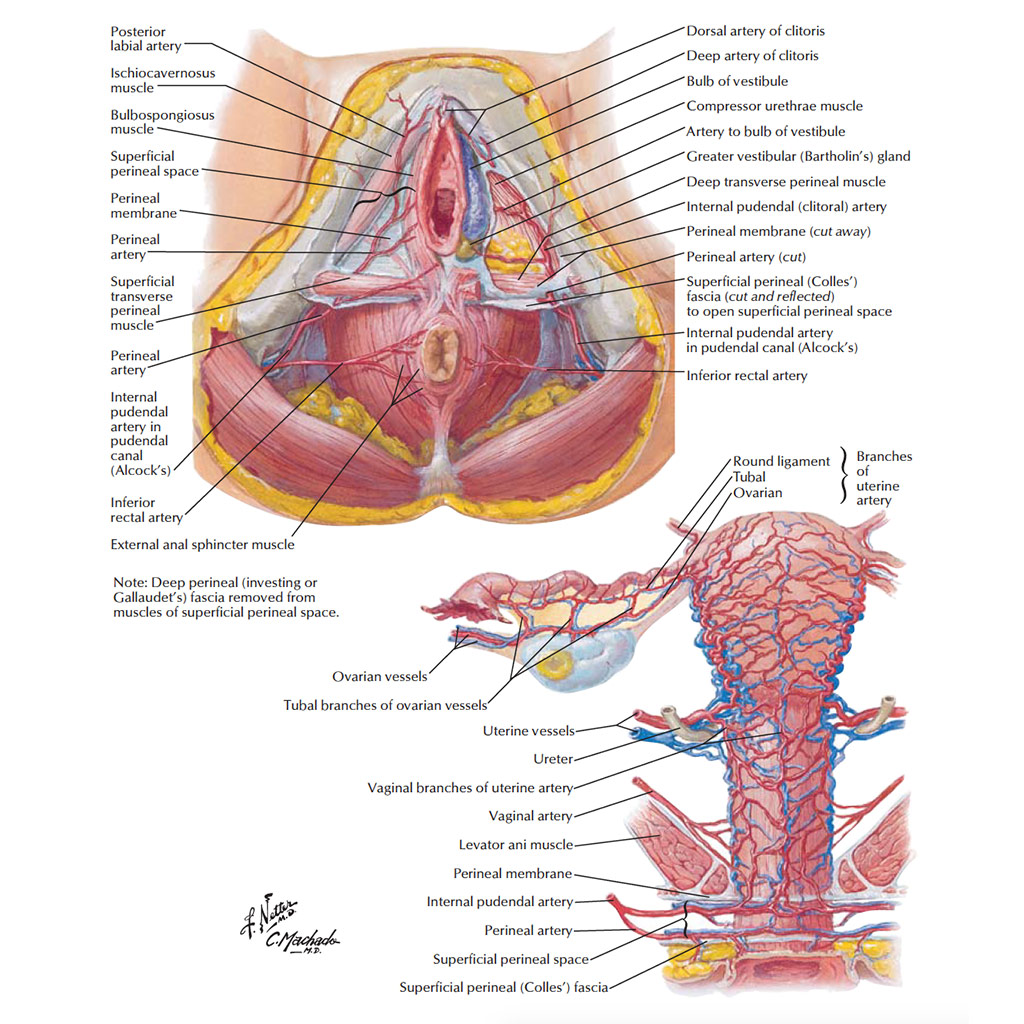
The vulva refers to the external parts of a female’s genitals. It consists of several parts, including the labia majora, the labia minora, and the glans clitoris.
The list below provides more detail on these parts:
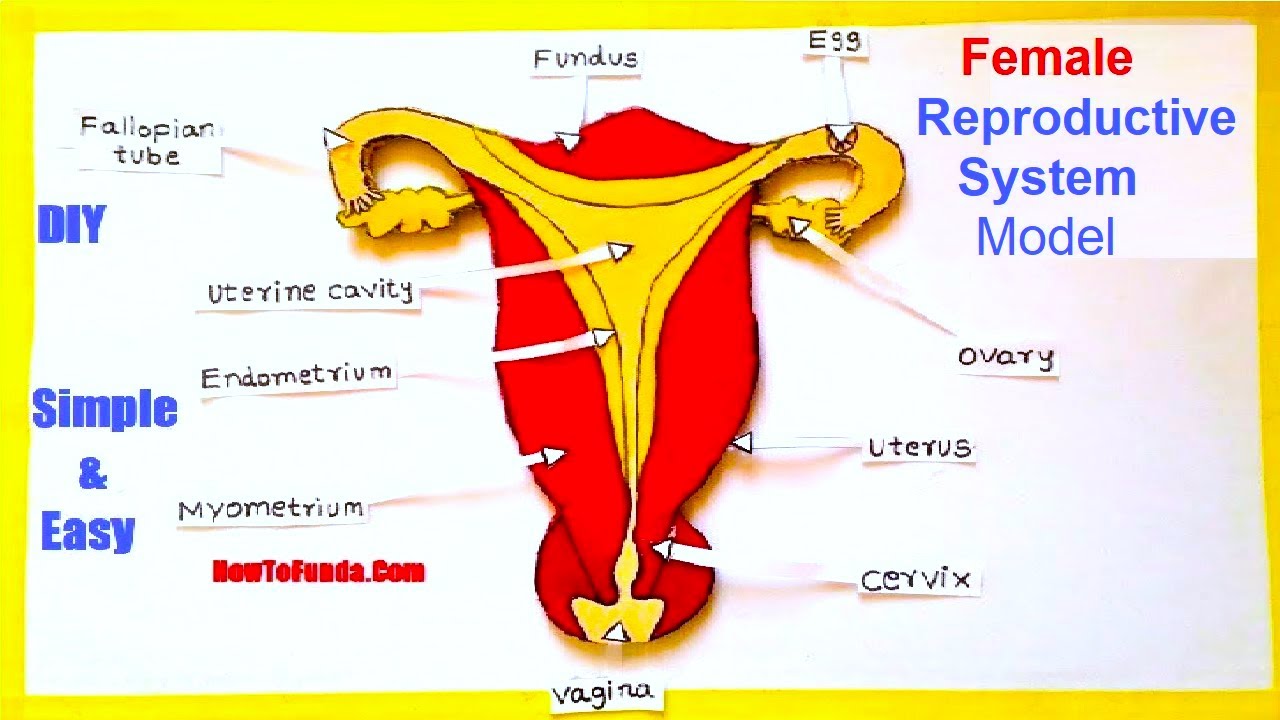
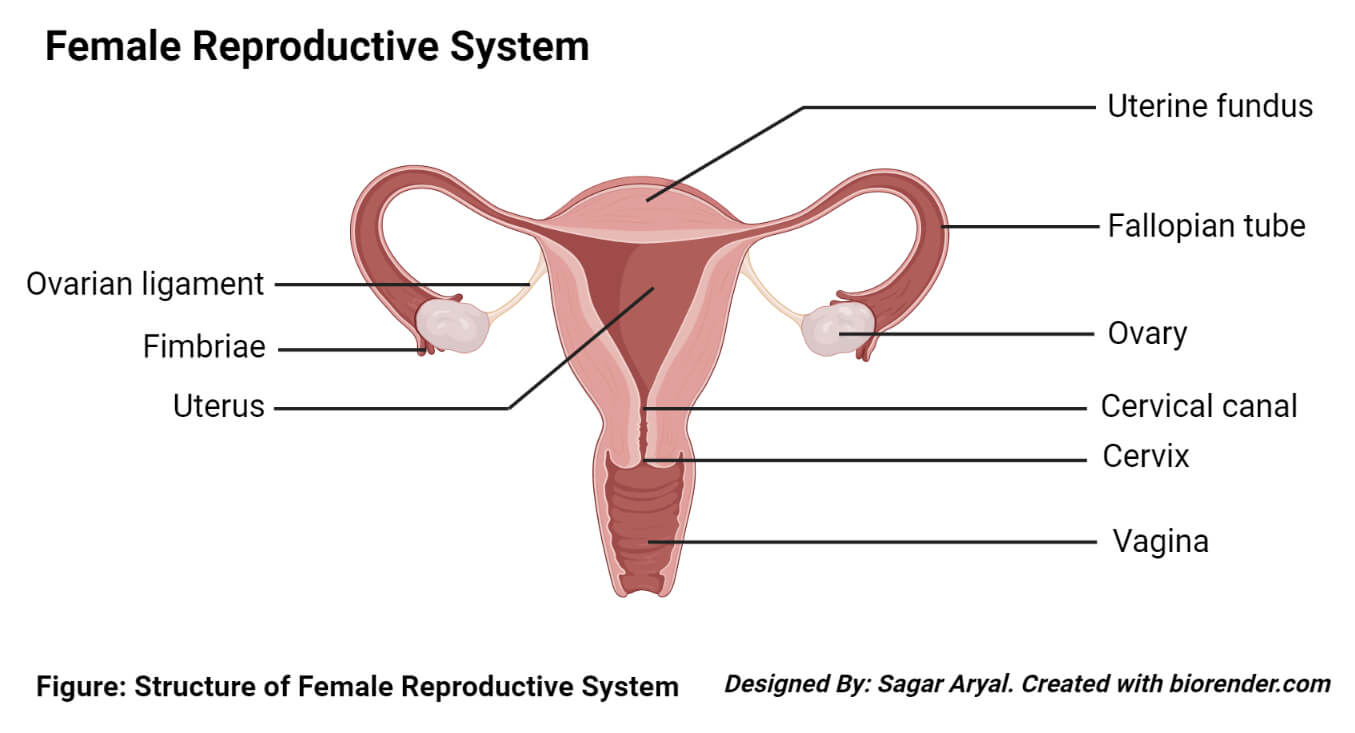
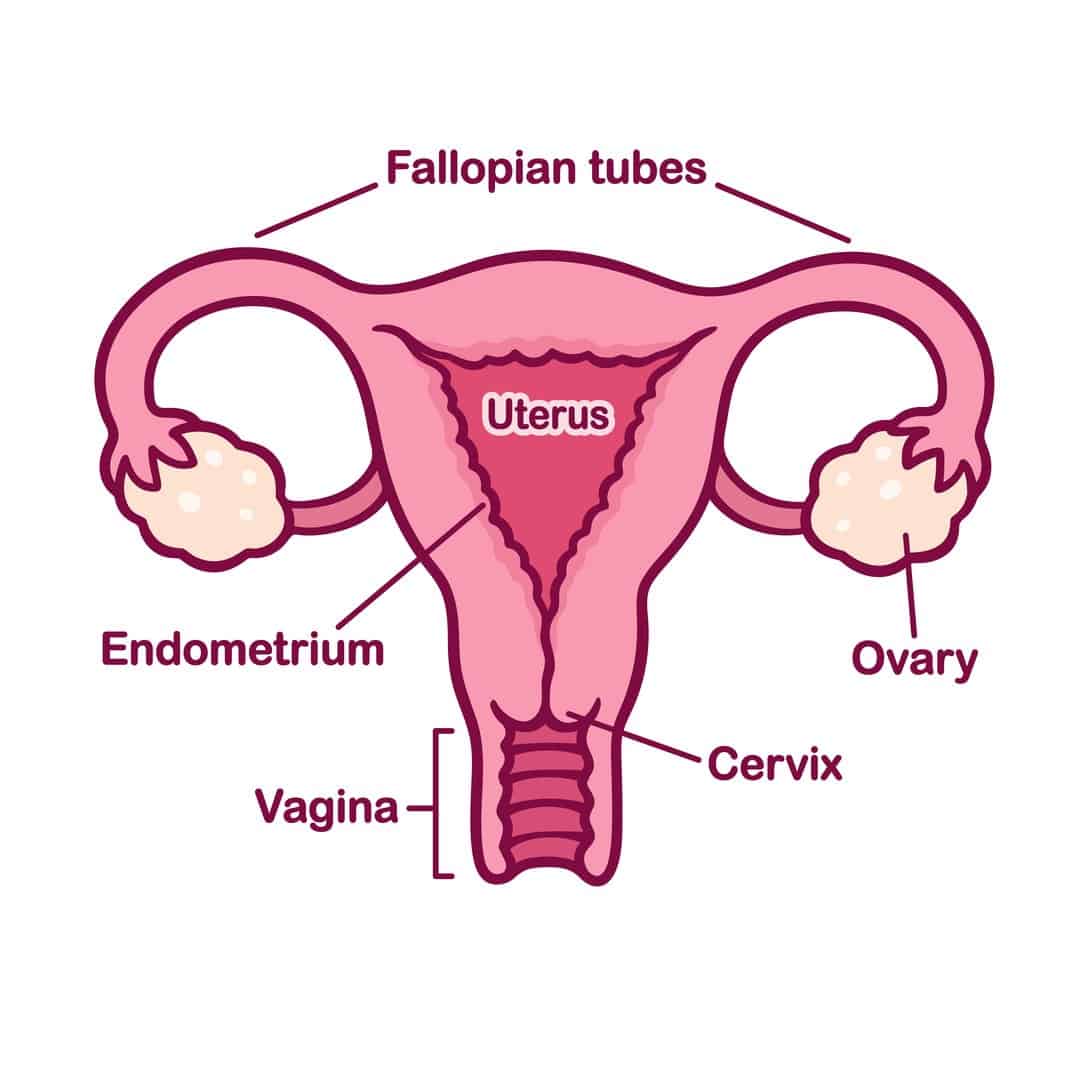
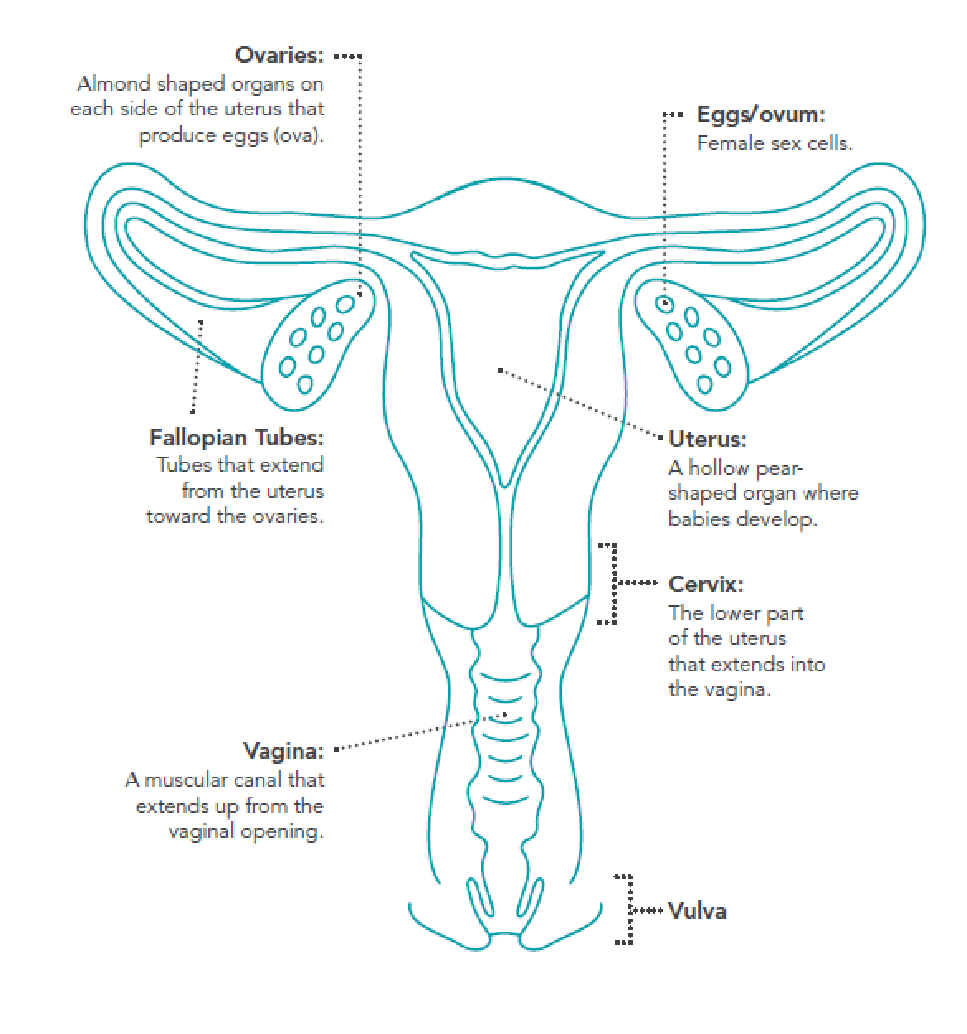
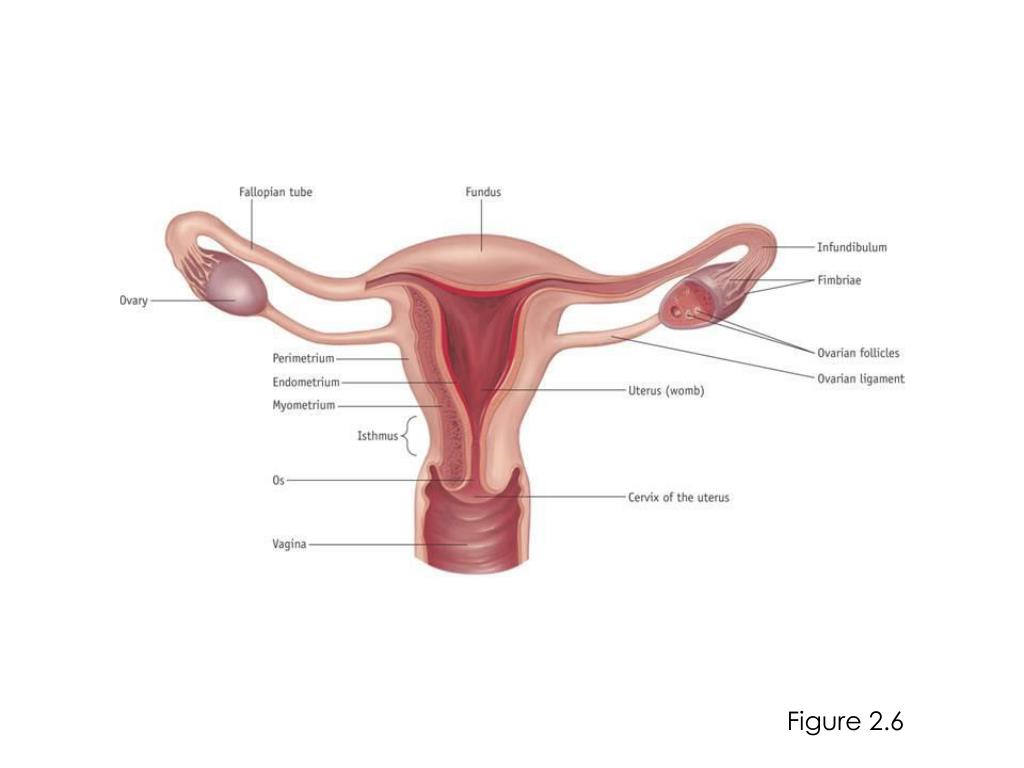
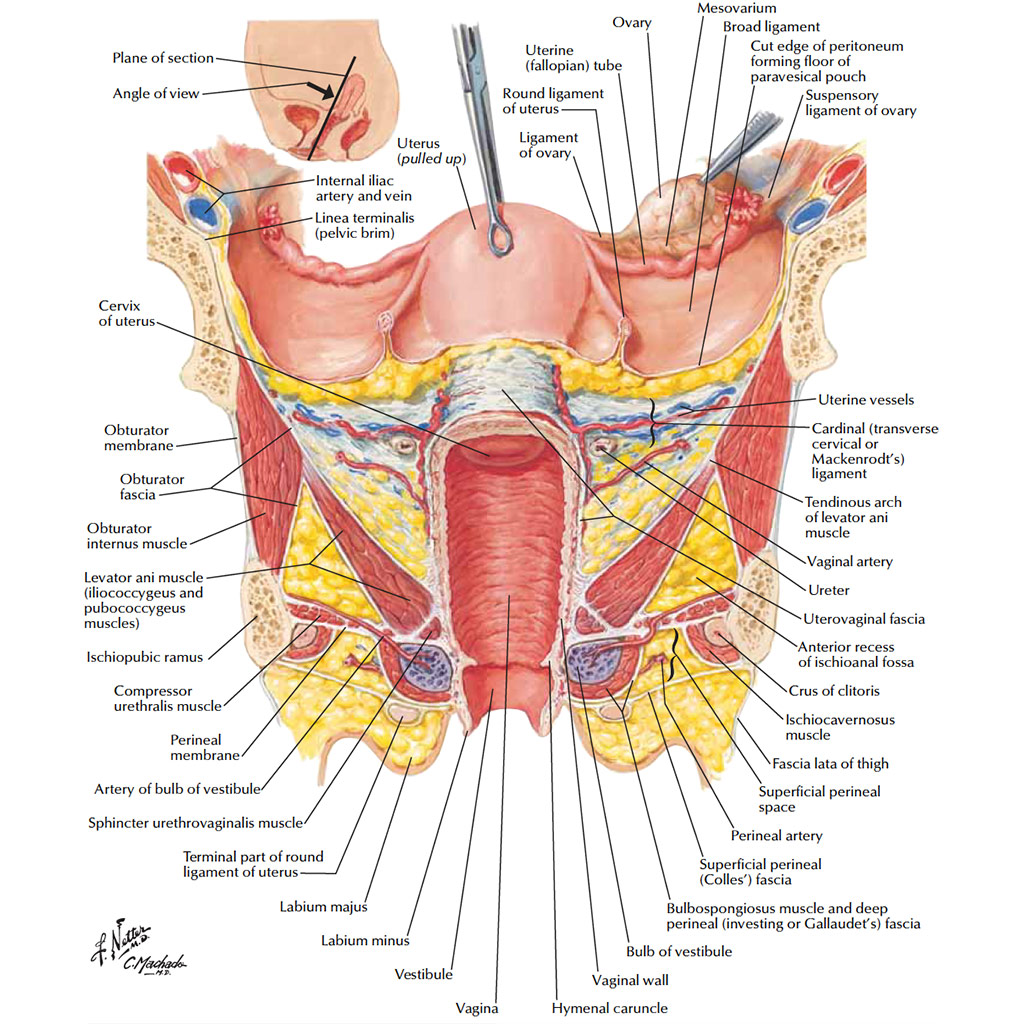
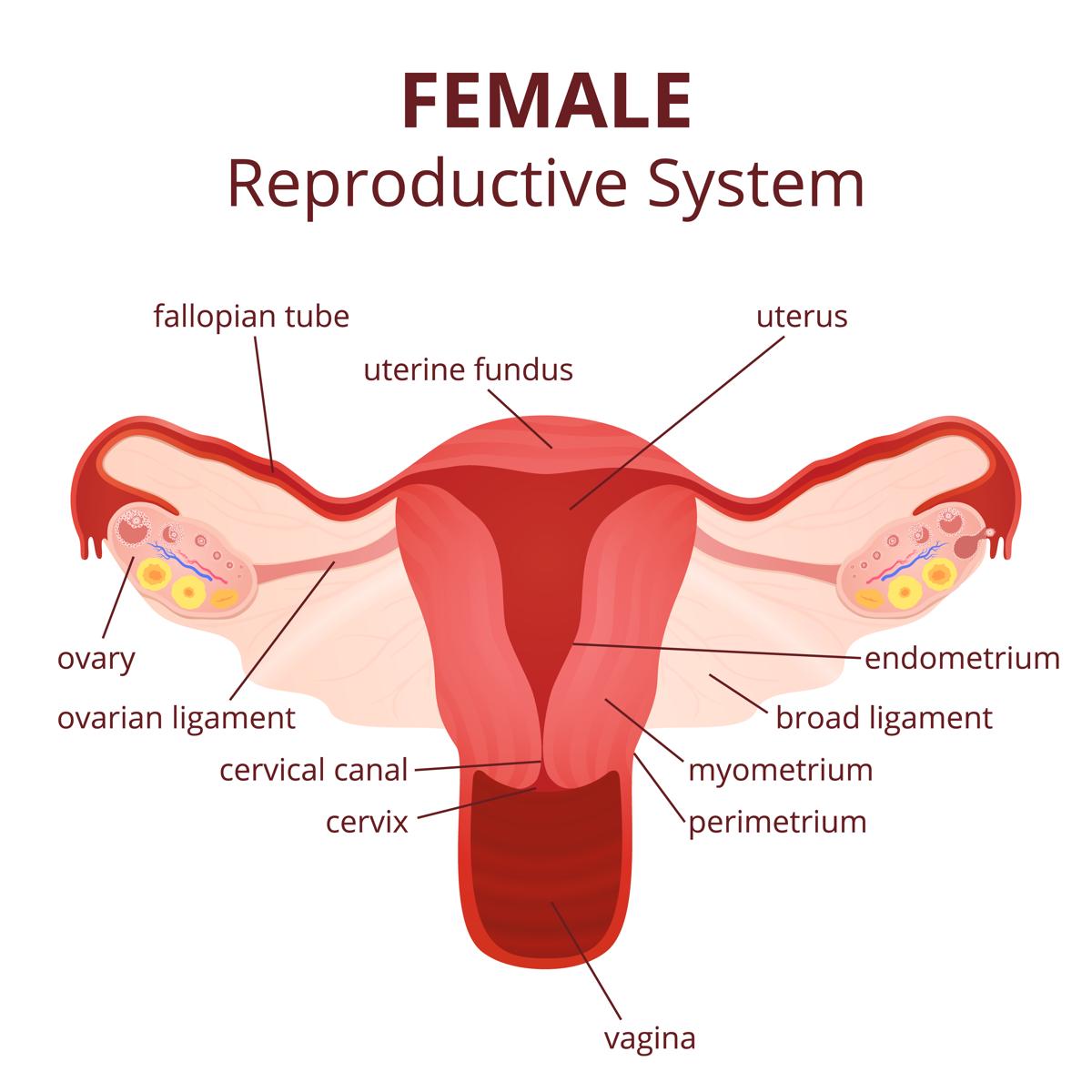
The internal female anatomy begins at the vagina, which is the canal that leads from the vulva to the uterus.
The cervix separates the vagina from the uterus, and the fallopian tubes connect the ovaries with the uterus.
The following sections discuss these organs in more detail.
As mentioned above, the vagina is the canal that connects the vulva with the uterus. The opening to the vagina is part of the vulva.
The vagina can vary in size, but the average length is about 2.5 to 3 inches. That said, it expands in length during arousal.
It also contains special structures called Bartholin’s glands. These are two “pea-sizedTrusted Source” glands that sit on either side of the vaginal opening. These glands are responsible for secreting lubrication to keep the vaginal tissues from becoming too dry.
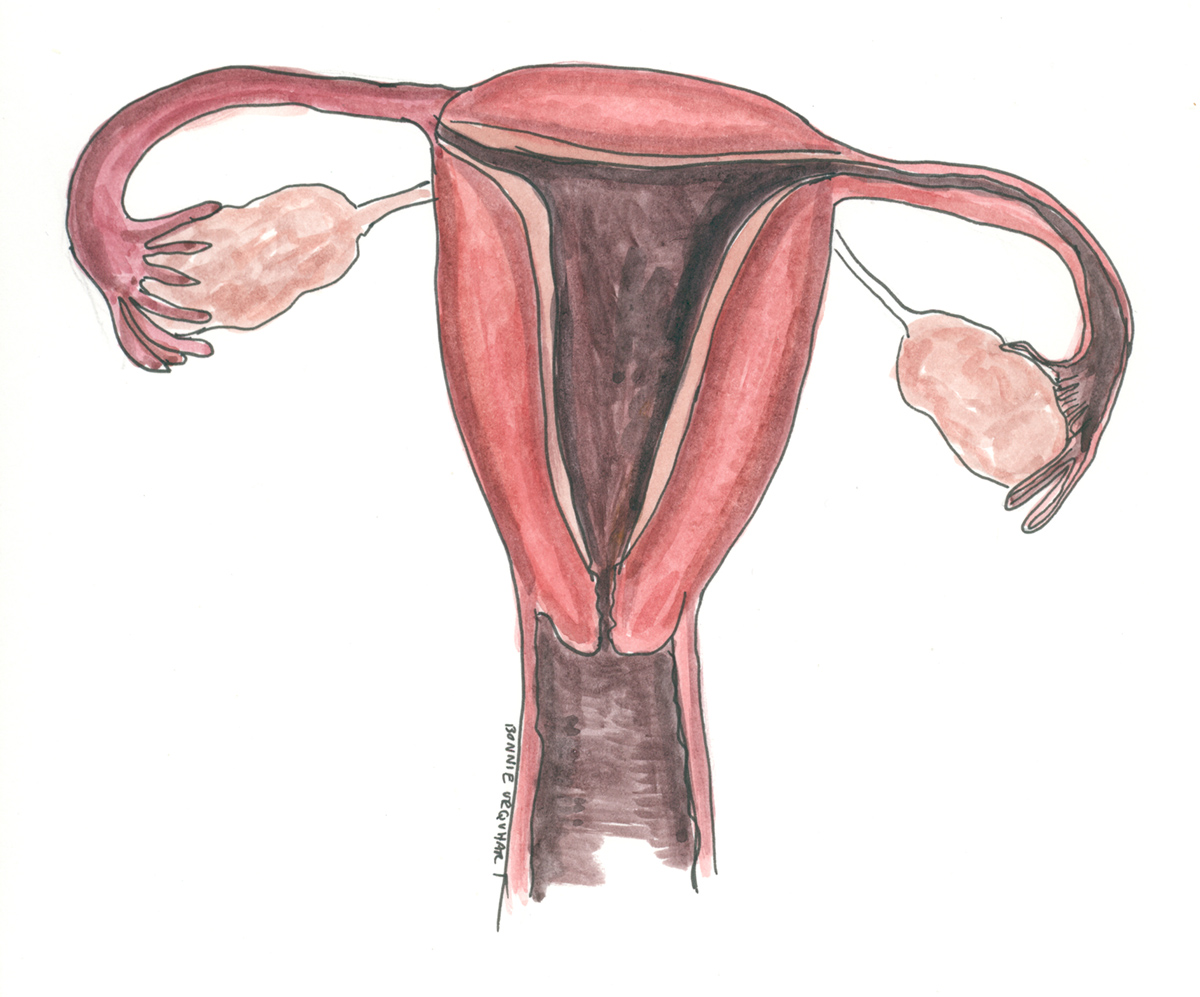
The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus. It is a cylinder-shaped area of tissue that separates the vagina from the rest of the uterus.
During birth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to move through the vagina.
Share on Pinterest
The uterus holds the fetus during pregnancy.
The uterus is located in the middle of the pelvic cavity. This muscular sac will house the fetus during pregnancy.
During a female’s monthly menstrual cycle, the lining of the uterus thickens with blood in preparation for the release of an egg from one of the ovaries. This is to prepare a nourishing environment for a fetus if pregnancy occurs.
If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining sheds. This is called the menstrual period. It occurs every around 28 days, though cycle length varies between females.
The upper portion of the uterus is connected to the ovaries by the fallopian tubes.
The ovaries are egg-shaped organs attached to fallopian tubes on the left and right sides of the body. Each ovary is roughly the size of an almond. Most females are born with two ovaries that produce eggs.
In addition to producing eggs, the ovaries also produce hormones. Namely, they release estrogen and progesterone.
The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus. When the ovaries release an egg, the egg travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus for potential fertilization.
If a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube, doctors call this an ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency because the fallopian tube can rupture.
The hymen is a membrane of tissue that covers the external vaginal opening. Not all females have a hymen, however.
The hymen can rupture as a result of pelvic injury, sports activity, pelvic examination, sexual intercourse, or childbirth. The absence of a hymen does not mean that a female has been sexually active.
Knowledge is power. Get our free daily newsletter.
Dig deeper into the health topics you care about most. Subscribe to our facts-first newsletter today.
Share on Pinterest
The breasts supply milk to the infant after childbirth.
Many people consider breasts “accessory organs” to the female reproductive system, as they are responsible for supplying milk to an infant after childbirth.
The major external components of the breasts include the:
Internally, the breasts are primarily composed of fat. The amount of fat can determine breast size. However, breast size has no bearing on the amount of milk someone is able to produce.
The internal anatomy of the breasts include the:
The female body contains many organs that work together to achieve a variety of functions.
The shape and size of many of these organs naturally vary from person to person. However, if a female is concerned that any part of their anatomy might not be “normal,” they can talk to their doctor.
Last medically reviewed on November 5, 2019
Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Medically reviewed by Carolyn Kay, M.D. — Written by Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA on November 5, 2019
Medically reviewed by Carolyn Kay, MD
Keep up with the ever-changing world of medical science with new and emerging developments in health.
© 2004-2021 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK, a Red Ventures Company. All rights reserved. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional
© 2004-2021 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK, a Red Ventures Company. All rights reserved. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional
Female anatomy includes the external genitals, or the vulva, and the internal reproductive organs, which include the ovaries and the uterus. One major difference between males and females is their reproductive organs. Anatomy specific to females generally relates to sexual function, reproduction, and hormone control.
www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326898
What are the external female genital organs?
What are the external female genital organs?
Together they comprise the female reproductive system, supporting sexual and reproductive activities. The external genital organs, or vulva, are held by the female perineum. These are the mons pubis, labia majora and minora, clitoris, vestibule, vestibular bulb and glands.
What is the female reproductive organ called?
What is the female reproductive organ called?
Reproductive Organs Although a woman’s external genitals are commonly referred to as the “vagina,” the vagina is actually one of several organs that comprise this section of a woman’s body. Collectively, these parts are called the vulva. Rich with nerves, the vulva can provide sexual pleasure when properly stimulated.
www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/fe…
Are there any stock photos of female organs?
Are there any stock photos of female organs?
624 female organs picture stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free.
www.shutterstock.com/search/female+orga…
Is it normal for females to have organs?
Is it normal for females to have organs?
The female body contains many organs that work together to achieve a variety of functions. The shape and size of many of these organs naturally vary from person to person. However, if a female is concerned that any part of their anatomy might not be “normal,” they can talk to their doctor. Last medically reviewed on November 5, 2019
www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326898
https://www.shutterstock.com/search/female+organs+picture
Перевести · 634 female organs picture stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See female organs picture stock video clips. of 7. uterus and cervix human body art the uterus female uterus woman reproductive organs women reproductive organs female organ anatomy woman reproduction anatomy of the uterus the female …
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326898
Перевести · 05.11.2019 · Female anatomy includes the external genitals, or the vulva, and the internal reproductive organs, which include the ovaries and the uterus. One major difference between males and females is their...
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/female-reproductive-organs
Перевести · 21.12.2020 · The female sex organs consist of both internal and external genitalia. Together they comprise the female reproductive system, supporting sexual and reproductive activities.The external genital organs, or vulva, are held by the female …
https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/female-reproductive-organs
Перевести · 19.01.2018 · The clitoris is a crucial element for sexual arousal in most women. This small sexual organ at the top of the vagina at the junction of the labia minora appears outside the folds of skin like a...
Же́нская репродуктивная систе́ма человека — одна из систем органов организма женщины, образующая наряду с мужской репродуктивную систему человека, ответственную за продолжение рода, и состоящая из женских внутренних и наружных половых органов.
Reproductive System: Female Genital Organs
YouTube › BlueLink: University of Michigan Anatomy
Anatomy of Female Reproductive System
A General Overview on the Female Reproductive System
Ultrasound Training of the Female Reproductive Organs
Anatomy of female reproductive system
anatomysystem.com/?tag=female-organs
Перевести · Diagrams: female organs Picture Of Female Reproductive System Diagram 1024×1204
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/.../what-are-parts-female-sexual-anatomy
Перевести · 2 дн. назад · Sexual anatomy that’s typically called female includes the vulva and internal reproductive organs like the uterus and ovaries What are the external parts? The vulva …
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Japanese Anal Dildo
Ebony Lesbians Sex
Cute Press
Desperate Vk
Sex Milf Big Tits Teens
Female Organs Picture Images, Stock Photos & Vectors ...
Female reproductive organs: Anatomy and functions | Kenhub
female organs | Anatomy System - Human Body Anatomy ...
Female Sexual Anatomy | Vulva, Vagina and Breasts
Female Organs













%3afill(FFFFFF%2ctrue)%3aformat(jpeg)/images/container/female-reproductive-organs/Female_reproductive_organs_1.png)