Female Genital

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
The trusted provider of medical information since 1899
Ranitidine (Withdrawn from US Market)
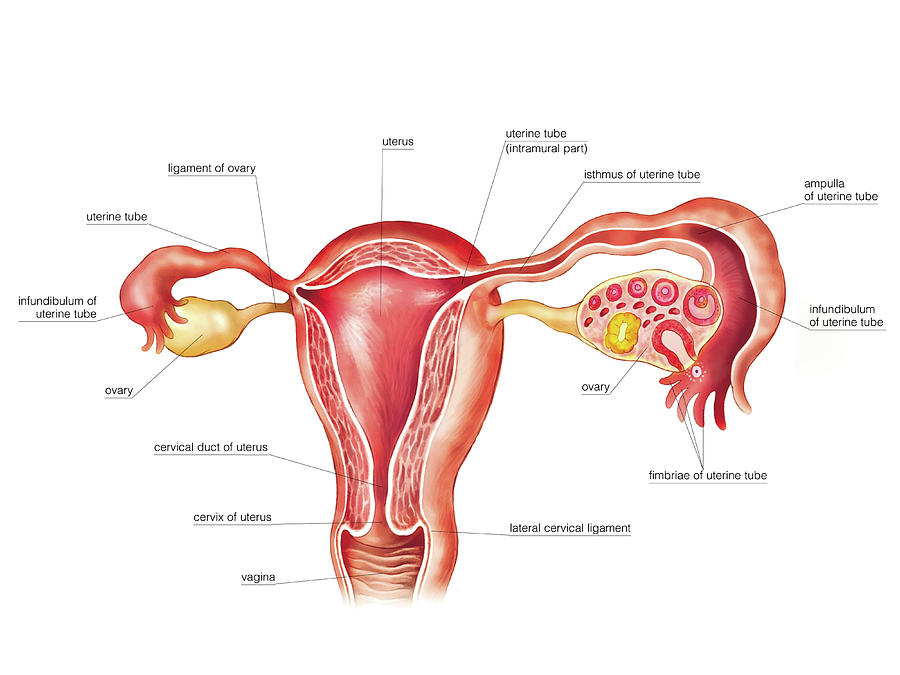
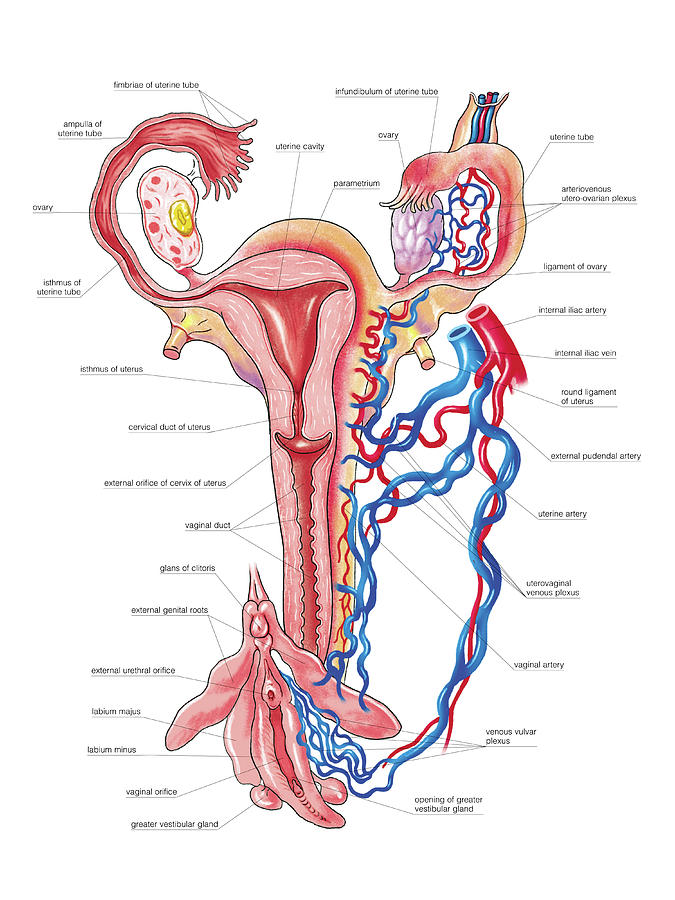
Biology of the Female Reproductive System
Overview of the Female Reproductive System
Effects of Aging on the Female Reproductive System
Cervical cancer develops in the lower part of the uterus, known as the cervix. In the US, cervical cancer is the third most common gynecological cancer among women and is common among young women. Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for cervical cancer?
, MD, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio;
, MD, Medical University of South Carolina
Last full review/revision Apr 2019| Content last modified Apr 2019
Click here for the Professional Version
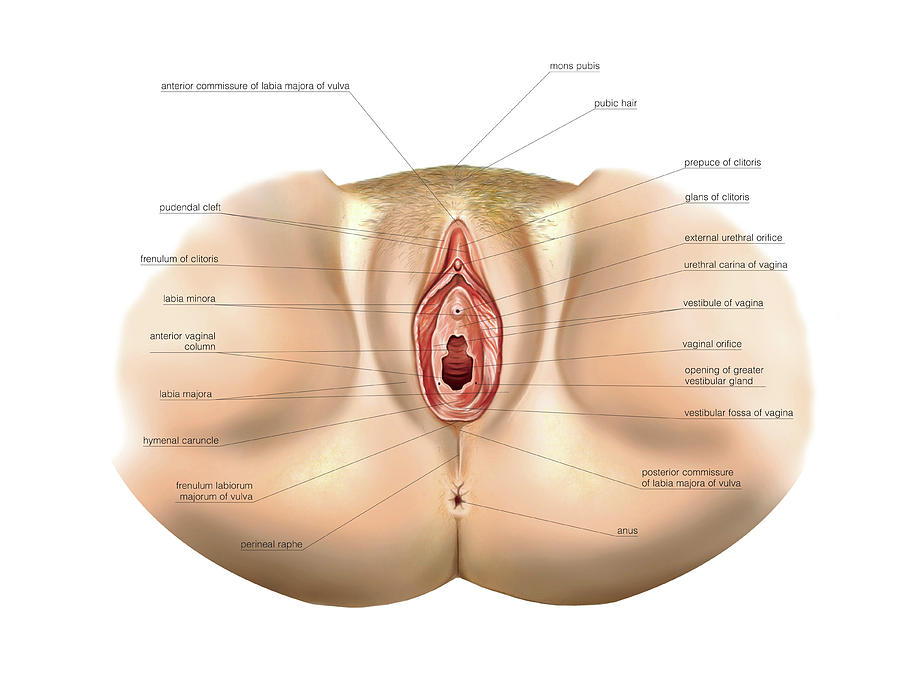
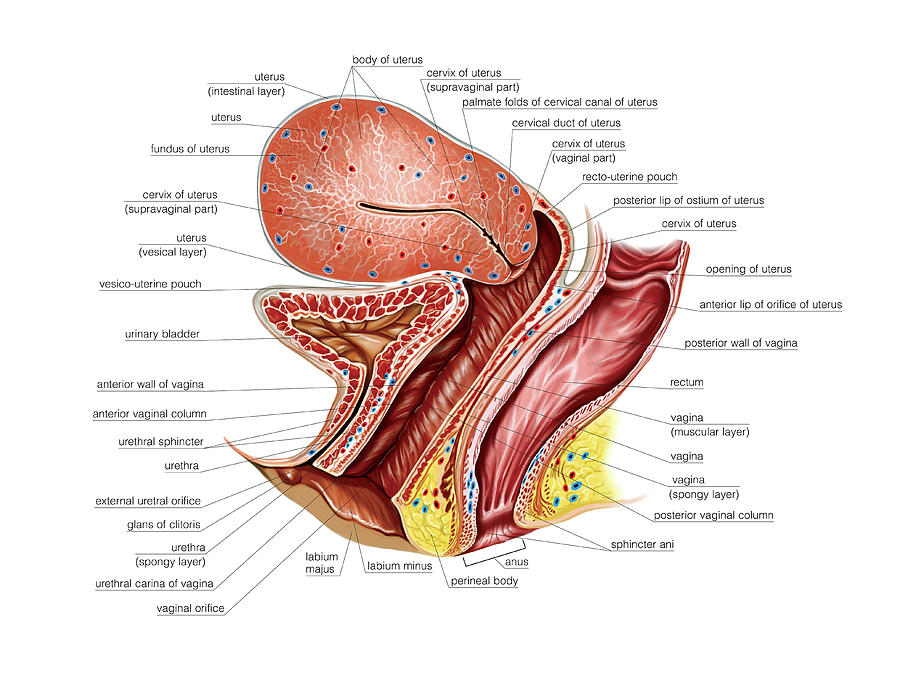
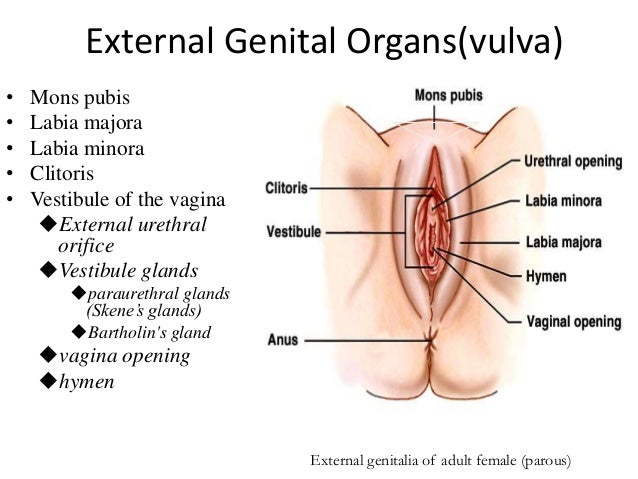
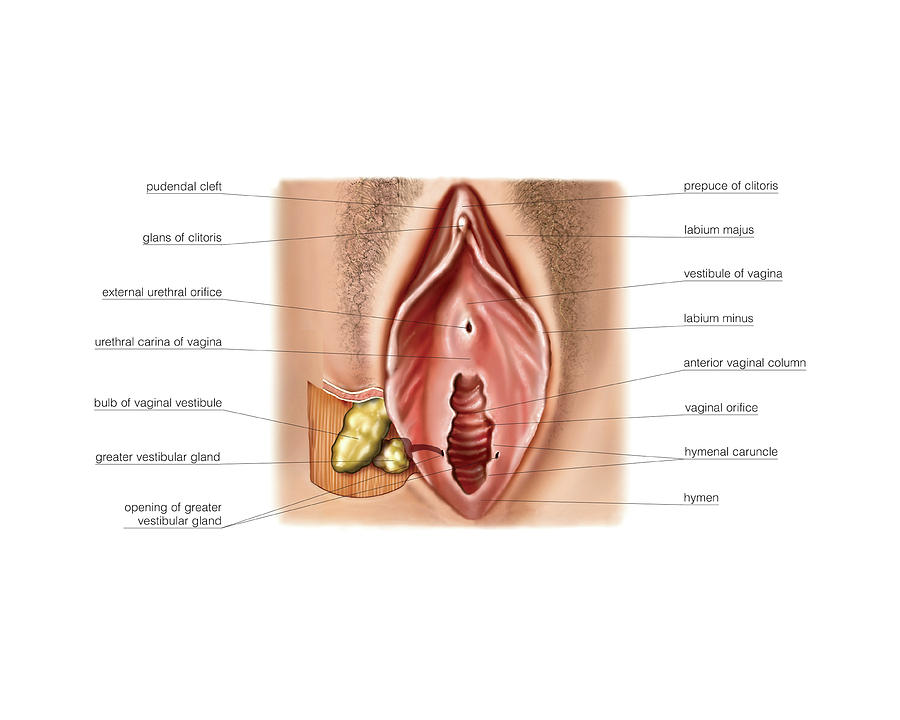
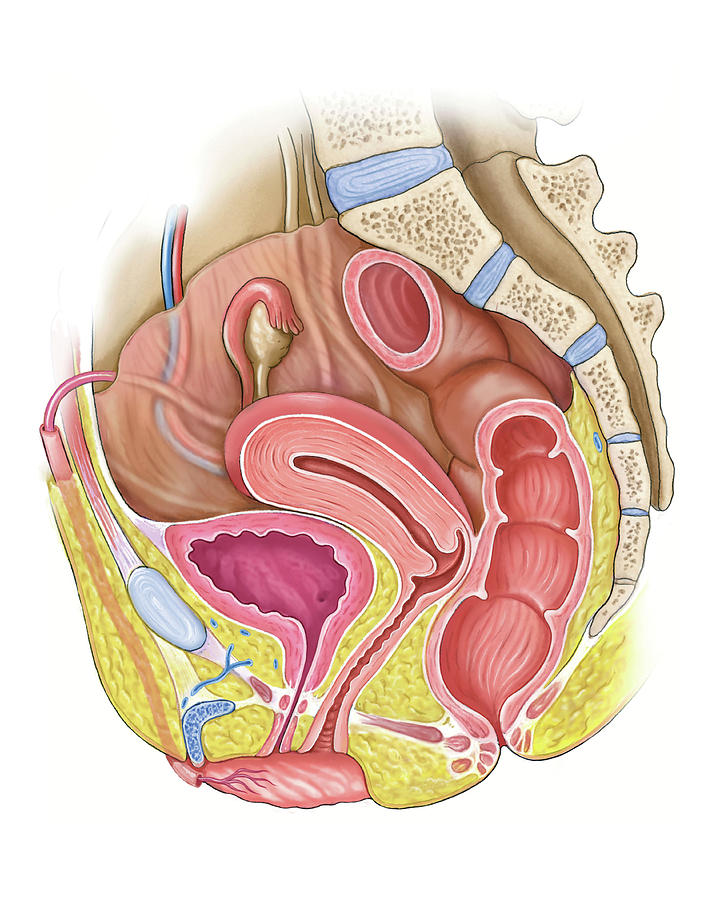
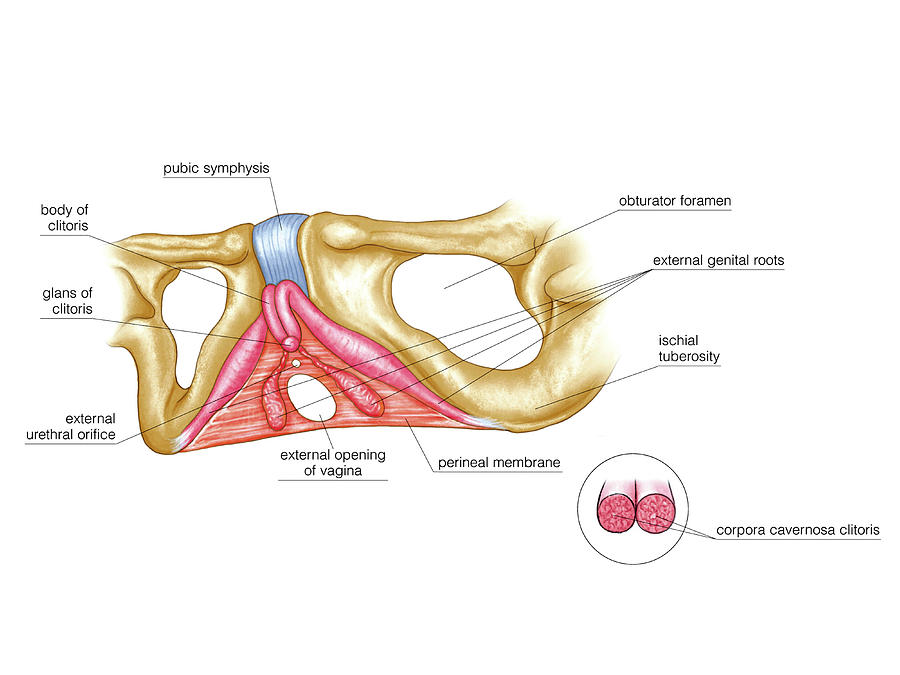
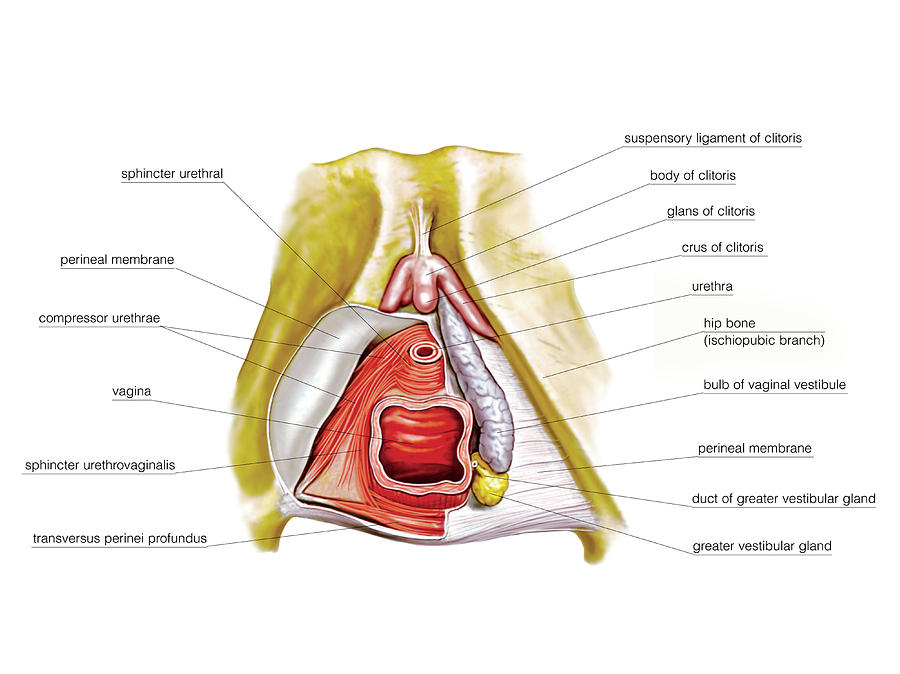
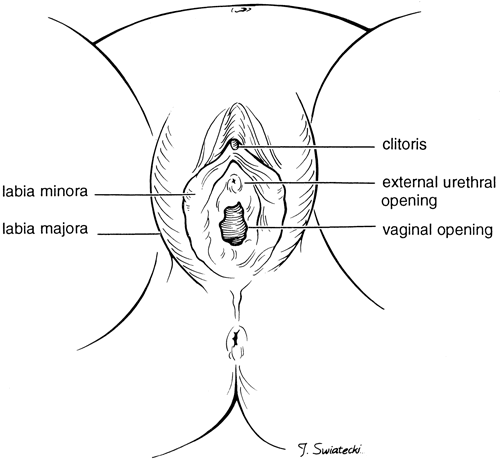
The external genital organs include the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, Bartholin glands, and clitoris. The area containing these organs is called the vulva.
The external genital organs have three main functions:
Protecting the internal genital organs from infectious organisms
The mons pubis is a rounded mound of fatty tissue that covers the pubic bone. During puberty, it becomes covered with hair. The mons pubis contains oil-secreting (sebaceous) glands that release substances that are involved in sexual attraction (pheromones).
The labia majora (literally, large lips) are relatively large, fleshy folds of tissue that enclose and protect the other external genital organs. They are comparable to the scrotum in males. The labia majora contain sweat and sebaceous glands, which produce lubricating secretions. During puberty, hair appears on the labia majora.
The labia minora (literally, small lips) can be very small or up to 2 inches wide. The labia minora lie just inside the labia majora and surround the openings to the vagina and urethra. A rich supply of blood vessels gives the labia minora a pink color. During sexual stimulation, these blood vessels become engorged with blood, causing the labia minora to swell and become more sensitive to stimulation.
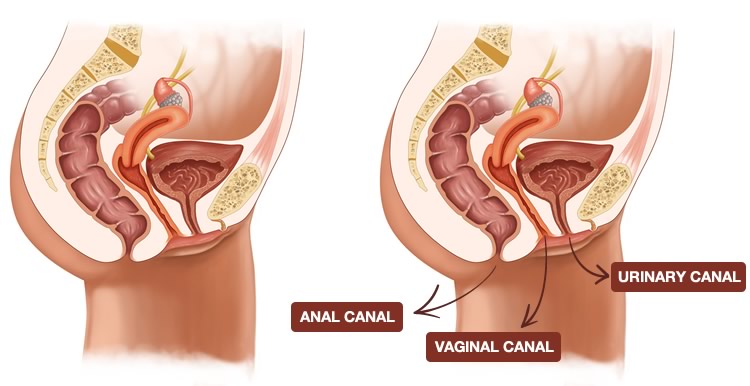
The area between the opening of the vagina and the anus, below the labia majora, is called the perineum. It varies in length from almost 1 to more than 2 inches (2 to 5 centimeters).
The labia majora and the perineum are covered with skin similar to that on the rest of the body. In contrast, the labia minora are lined with a mucous membrane, whose surface is kept moist by fluid secreted by specialized cells.
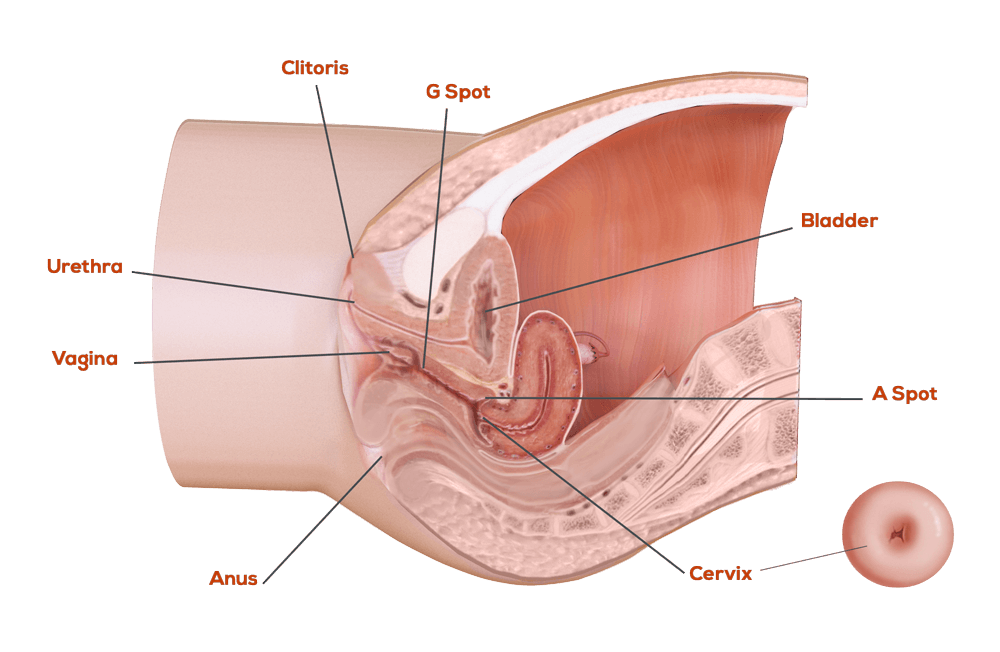
The opening to the vagina is called the introitus. The vaginal opening is the entryway for the penis during sexual intercourse and the exit for blood during menstruation and for the baby during birth.
When stimulated, Bartholin glands (located beside the vaginal opening) secrete a thick fluid that supplies lubrication for intercourse.
The opening to the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder to the outside, is located above and in front of the vaginal opening.
The clitoris, located between the labia minora at their upper end, is a small protrusion that corresponds to the penis in the male. The clitoris, like the penis, is very sensitive to sexual stimulation and can become erect. Stimulating the clitoris can result in an orgasm.
Click here for the Professional Version
© 2020 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA)
Overview of the Female Reproductive System
Biology of the Female Reproductive System
Overview of the Female Reproductive System
Effects of Aging on the Female Reproductive System
Cervical cancer develops in the lower part of the uterus, known as the cervix. In the US, cervical cancer is the third most common gynecological cancer among women and is common among young women. Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for cervical cancer?
, MD, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio;
, MD, Medical University of South Carolina
Last full review/revision Apr 2019| Content last modified Apr 2019
Click here for the Professional Version
The external genital organs include the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, Bartholin glands, and clitoris. The area containing these organs is called the vulva.
The external genital organs have three main functions:
Protecting the internal genital organs from infectious organisms
The mons pubis is a rounded mound of fatty tissue that covers the pubic bone. During puberty, it becomes covered with hair. The mons pubis contains oil-secreting (sebaceous) glands that release substances that are involved in sexual attraction (pheromones).
The labia majora (literally, large lips) are relatively large, fleshy folds of tissue that enclose and protect the other external genital organs. They are comparable to the scrotum in males. The labia majora contain sweat and sebaceous glands, which produce lubricating secretions. During puberty, hair appears on the labia majora.
The labia minora (literally, small lips) can be very small or up to 2 inches wide. The labia minora lie just inside the labia majora and surround the openings to the vagina and urethra. A rich supply of blood vessels gives the labia minora a pink color. During sexual stimulation, these blood vessels become engorged with blood, causing the labia minora to swell and become more sensitive to stimulation.
The area between the opening of the vagina and the anus, below the labia majora, is called the perineum. It varies in length from almost 1 to more than 2 inches (2 to 5 centimeters).
The labia majora and the perineum are covered with skin similar to that on the rest of the body. In contrast, the labia minora are lined with a mucous membrane, whose surface is kept moist by fluid secreted by specialized cells.
The opening to the vagina is called the introitus. The vaginal opening is the entryway for the penis during sexual intercourse and the exit for blood during menstruation and for the baby during birth.
When stimulated, Bartholin glands (located beside the vaginal opening) secrete a thick fluid that supplies lubrication for intercourse.
The opening to the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder to the outside, is located above and in front of the vaginal opening.
The clitoris, located between the labia minora at their upper end, is a small protrusion that corresponds to the penis in the male. The clitoris, like the penis, is very sensitive to sexual stimulation and can become erect. Stimulating the clitoris can result in an orgasm.
Click here for the Professional Version
© 2020 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA)
Overview of the Female Reproductive System
Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world. The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community. The legacy of this great resource continues as the Merck Manual in the US and Canada and the MSD Manual outside of North America. Learn more about our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
© 2021 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA
This Site Uses Cookies and Your Privacy Choice Is Important to Us
We suggest you choose Customize My Settings to make your individualized choices. Accept All Cookies means that you are choosing to accept third-party Cookies and that you understand this choice. See our Privacy Policy
Customize My Settings Accept All Cookies
https://www.lecturio.com/magazine/female-genitalia
Перевести · 02.09.2015 · The external female genital (vulva, pudendum) reaches from the outside to the hymen. Some authors also consider the female urethra as an external female sexual organ. Urinary and genital apparatus are summarized by the term genitourinary system (or, urogenital system). Image: Nerves innervating the urinary system.
https://www.merckmanuals.com/.../female-external-genital-organs
Перевести · External Female Genital Organs The area between the opening of the vagina and the anus, below the labia majora, is called the perineum. It varies in length from almost 1 to more than 2 inches (2 to 5 …
Же́нское обреза́ние, также калечащие операции на женских половых органах или нанесение увечий женским гениталиям — частичное или полное …
Текст из Википедии, лицензия CC-BY-SA
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Female_genital_mutilation
Areas: Africa, Southeast Asia, Middle East, and within …
Definition: "Partial or total removal of the external …
Numbers: Over 200 million women and girls in 27 …
Возраст: Days after birth to puberty
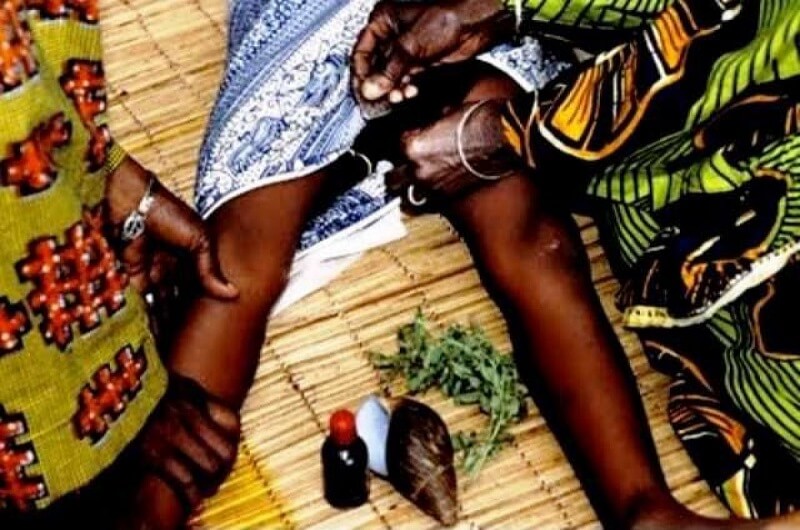
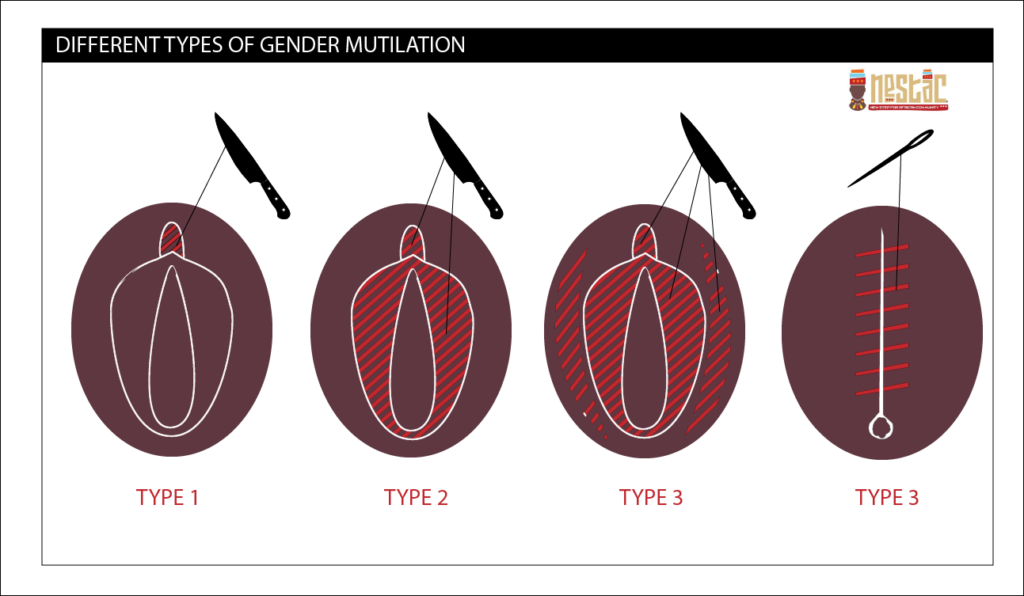
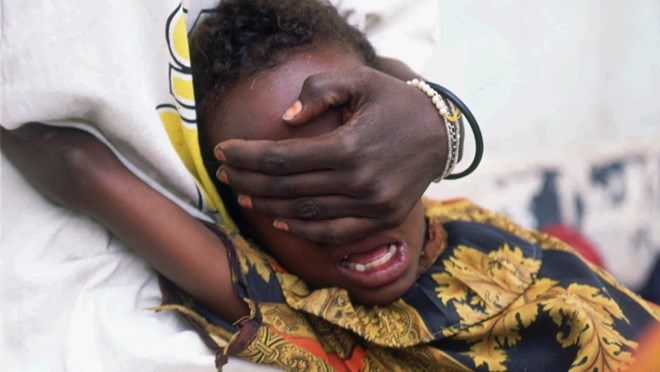
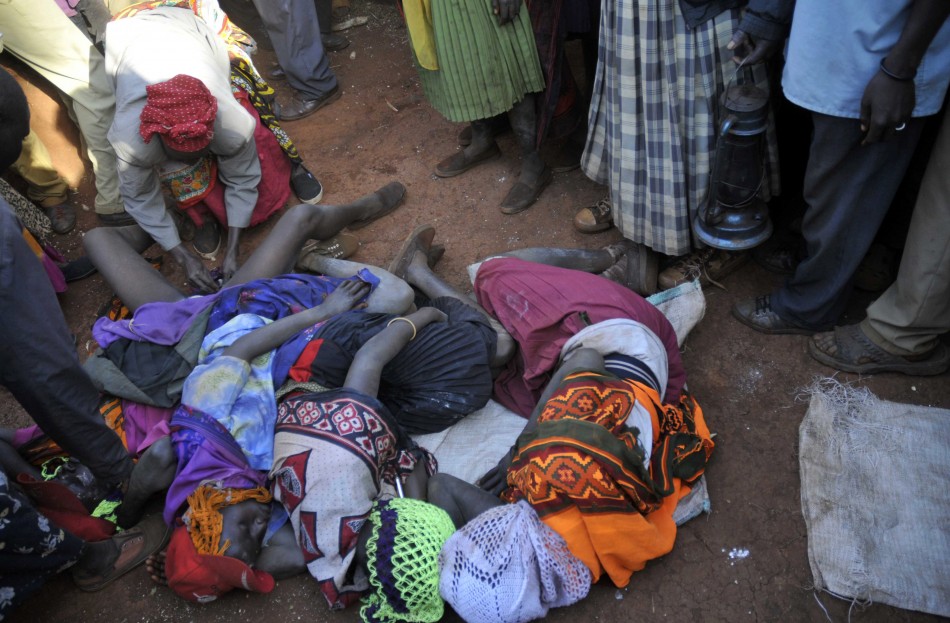
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found in Africa, Asia and the Middle East, and within communities from countries in which FGM is common. UNICEF estimated in 2016 that 200 million women living today in 30 countries—27 African countries, Indonesia, Iraqi Kurdistan and Yemen—have undergone the procedures.
Typically …
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found in Africa, Asia and the Middle East, and within communities from countries in which FGM is common. UNICEF estimated in 2016 that 200 million women living today in 30 countries—27 African countries, Indonesia, Iraqi Kurdistan and Yemen—have undergone the procedures.
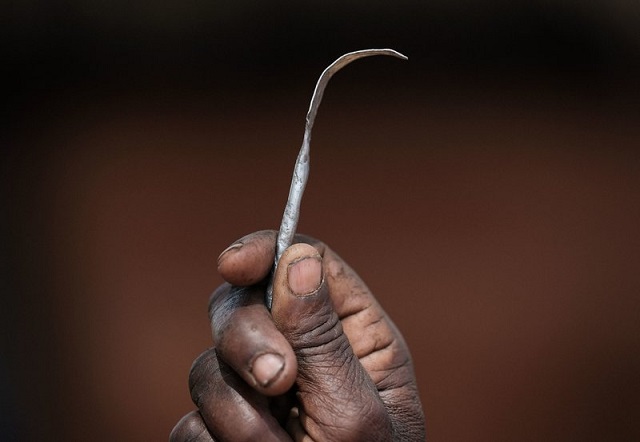
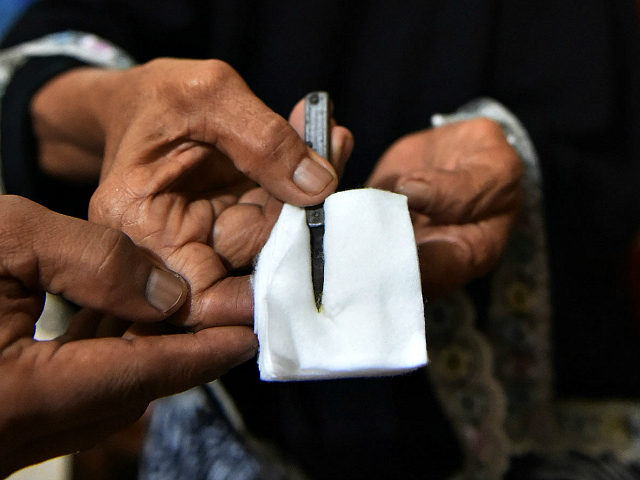
Typically carried out by a traditional circumciser using a blade, FGM is conducted from days after birth to puberty and beyond. In half of the countries for which national figures are available, most girls are cut before the age of five. Procedures differ according to the country or ethnic group. They include removal of the clitoral hood and clitoral glans; removal of the inner labia; and removal of the inner and outer labia and closure of the vulva. In this last procedure, known as infibulation, a small hole is left for the passage of urine and menstrual fluid; the vagina is opened for intercourse and opened further for childbirth.
The practice is rooted in gender inequality, attempts to control women's sexuality, and ideas about purity, modesty and beauty. It is usually initiated and carried out by women, who see it as a source of honour, and who fear that failing to have their daughters and granddaughters cut will expose the girls to social exclusion. Adverse health effects depend on the type of procedure; they can include recurrent infections, difficulty urinating and passing menstrual flow, chronic pain, the development of cysts, an inability to get pregnant, complications during childbirth, and fatal bleeding. There are no known health benefits.
There have been international efforts since the 1970s to persuade practitioners to abandon FGM, and it has been outlawed or restricted in most of the countries in which it occurs, although the laws are often poorly enforced. Since 2010, the United Nations has called upon healthcare providers to stop performing all forms of the procedure, including reinfibulation after childbirth and symbolic "nicking" of the clitoral hood. The opposition to the practice is not without its critics, particularly among anthropologists, who have raised difficult questions about cultural relativism and the universality of human rights.
https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Labeled_photographs_of_human_female...
Перевести · 19.02.2021 · Media in category "Labeled photographs of human female genitalia" The following 104 files are in this category, ... External Genital Organs (Female).jpg 746 × 901; 85 KB. Female anatomy.jpg. Female genitalia inner.JPG. Female genitalia marked.JPG. Female …
Kenya Fighting to End Female Genital Mutilation by 2023
What is Female Genital Mutilation (FGM)?
Fight Against FGM (Female Genital Mutilation)
UN Highlights Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation
Sudan moves to ban female genital mutilation
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/external-female-genitalia
Перевести · 21.07.2015 · The external female genitalia are a part of the female reproductive system, and include the: mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, hymen, vestibular bulb and vestibular glands…
https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Hairless_female_genitalia
Перевести · 27.05.2020 · Genitalia of a 29-year-old woman after childhood female genital cutting - 20071014.jpg 438 × 646; 71 KB Hanabira.jpg 525 × 414; 213 KB Human vulva.jpg 470 × 679; 151 KB
https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Female_genitalia
Перевести · 01.07.2018 · Female human genitalia (26 C, 2 F) A A Cholinergic-Regulated Circuit Coordinates the Maintenance and Bi-Stable States of a Sensory-Motor Behavior during Caenorhabditis elegans Male …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Female_genital_disease
A female genital disease is a condition of disease that affects the female reproductive system, a term that describes both anatomical and physiological aspects of a biological system, affected to the detriment of health of an individual. With regards to the female genital tract, the human female genital tract is two aspects of anatomy, internal and external, together representing a part of the whole anatomical part of the whole anatomy of the female, existing for the purpose of the fulfillment of the female organism's sexual functioning (procreation
A female genital disease is a condition of disease that affects the female reproductive system, a term that describes both anatomical and physiological aspects of a biological system, affected to the detriment of health of an individual. With regards to the female genital tract, the human female genital tract is two aspects of anatomy, internal and external, together representing a part of the whole anatomical part of the whole anatomy of the female, existing for the purpose of the fulfillment of the female organism's sexual functioning (procreation). Internal structures include the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, and vagina, and external structures include the clitoris, labia majora and labia minora.
The International Classification of Diseases groups genital and urinary diseases together, irrespective of gender difference, as genitourinary, due the proximity of function of the two respective bodily systems.
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Open Couple
Porno Creampie Online
Who Is Cute
Erotic Hd 1080
Nipples Erotic
Female External Genital Organs - Women's Health Issues ...
Female genital mutilation - Wikipedia
Category:Labeled photographs of human female genitalia ...
External female genitalia: Anatomy and blood supply | Kenhub
Category:Hairless female genitalia - Wikimedia Commons
Category:Female genitalia - Wikimedia Commons
Female genital disease - Wikipedia
Female Genital



















%3abackground_color(FFFFFF)%3aformat(jpeg)/images/library/6130/Normal_Vagina.png)