Fdau University

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
Scientia et studium, quaestīo et cogitation
государственное высшее учебное заведение
Китай, Шанхай, р-н Янпу, Улица Ханьдань, д. 220
Университе́т Фуда́нь (кит. трад. 復旦大學, упр. 复旦大学, пиньинь Fùdàn Dàxué) — одно из самых престижных и старейших высших учебных заведений в Китае. Расположен в Шанхае. Неизменно входит в топ-100 лучших университетов мира[1]. Является членом лиги C9 и Universitas 21[2]. Состоит из 4 кампусов. Основан в 1905 году в конце правления династии Цин.
В университете ведется изучение и исследование физико-математических, гуманитарных, социальных и медицинских наук.
Университет был основан в 1905 году и носил тогда название Фуданьской публичной школы. В качестве названия нового учебного заведения было выбрано два иероглифа — «фу» (復) и «дань» (旦), в сочетании переводимые как «небо светит день за днем». Первым руководителем школы стал выдающийся китайский философ и педагог начала XX века Ма Сянбо (马相伯). Девиз университета (博学而笃志,切问而近思) дословно переводится как «Учиться усердно и быть верным устремлениям, спрашивать настойчиво и отвечать с рвением» (слова из гл. 16.6 «Цзы Чжан…» конфуцианского памятника «Лунь юй»: [Цзы Ся сказал:] Углублять знания, закалять волю, пытливо расспрашивать, всесторонне обдумывать [- все это основа человеколюбия]. Пер. Л. С. Переломова).
В 1911 году во время Синьхайской революции на территории университета базировалась революционная армия Гуанфу. В 1917 году заведение получило статус частного университета и стало называться Частный университет Фудань (私立復旦大學), где также имелись средняя и подготовительная школы. В 1927 году в университете были основаны факультеты журналистики, права и педагогики, тем самым количество факультетов достигло 17.
В 1937 году университет переезжает в Чунцин. Переезд был связан с перемещением Гоминьдана во внутренние районы страны, где Чунцин стал временной столицей гоминьдановского правительства. В декабре 1941 решением Национального правительства во главе с Гоминьданом, Частный университет Фудань, базировавшийся до сего времени в Чунцине, был преобразован в государственный и получил название Национального университета Фудань (國立復旦大學) с У Наньсюанем (吴南轩) во главе. Пять лет спустя университет переехал обратно в Шанхай.
После образования Китайской Народной Республики в названии университета был убрана приставка «Национальный» и университет получил своё нынешнее наименование. Университет Фудань стал одним из первых университетов в стране, где была внедрена советская модель высшего образования. Структура университета претерпела полную реорганизацию. В состав университета было введено несколько факультетов порядка 10 других учебных заведений востока Китая. Высшее учебное заведение было существенно расширено, его общая площадь увеличилась в 7 раз[3].
В 1970-х годах университет постепенно отказывался от советской модели образования и внедрял современные (в том числе и западные) методы образования.
В апреле 2000 года произошло слияние университета с Шанхайским медицинским университетом.
Университет Фудань состоит из 17 институтов и 69 факультетов. Ведётся обучение по 73 бакалаврским специальностям, 156 магистерским и 201 докторантской специальностям. Также в состав университета входят 7 исследовательских центров социальных наук, 9 исследовательских центров фундаментальных наук. Университет реализует около 40 государственных программ Министерства образования КНР. В настоящее время структуры университета в общей сложности охватывают 77 исследовательских институтов, 112 междисциплинарных институтов и 5 научных лабораторий.
Ежегодно в университет поступает более 45 000 студентов и аспирантов, включая студентов, обучающихся по программам дистанционного обучения. Кроме того, в университете обучается порядка 1800 иностранных студентов.
Университет имеет высококвалифицированный преподавательский состав, состоящий из более 2400 преподавателей, включая 1350 профессоров и 30 академиков Академии наук Китая и Китайской инженерной академии.
Кроме того, в состав университета входят 10 госпиталей, таких как Чжуншаньский и Хуашаньский госпитали, которые предоставляют медицинские услуги населению и на базе которых ведётся обучение студентов медицинских специальностей университета.
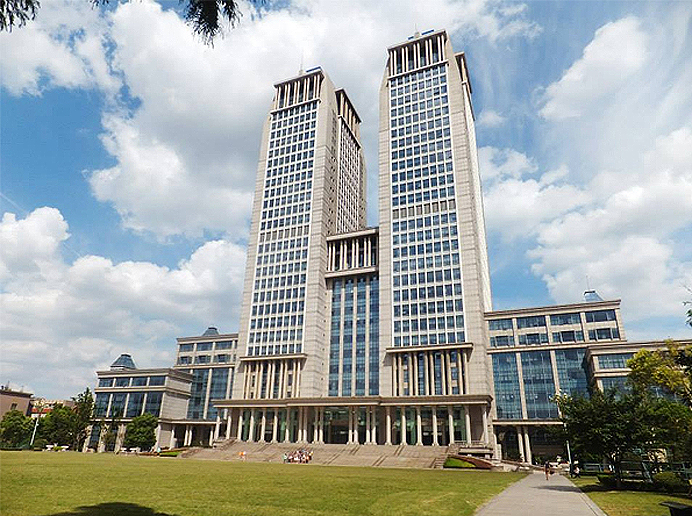
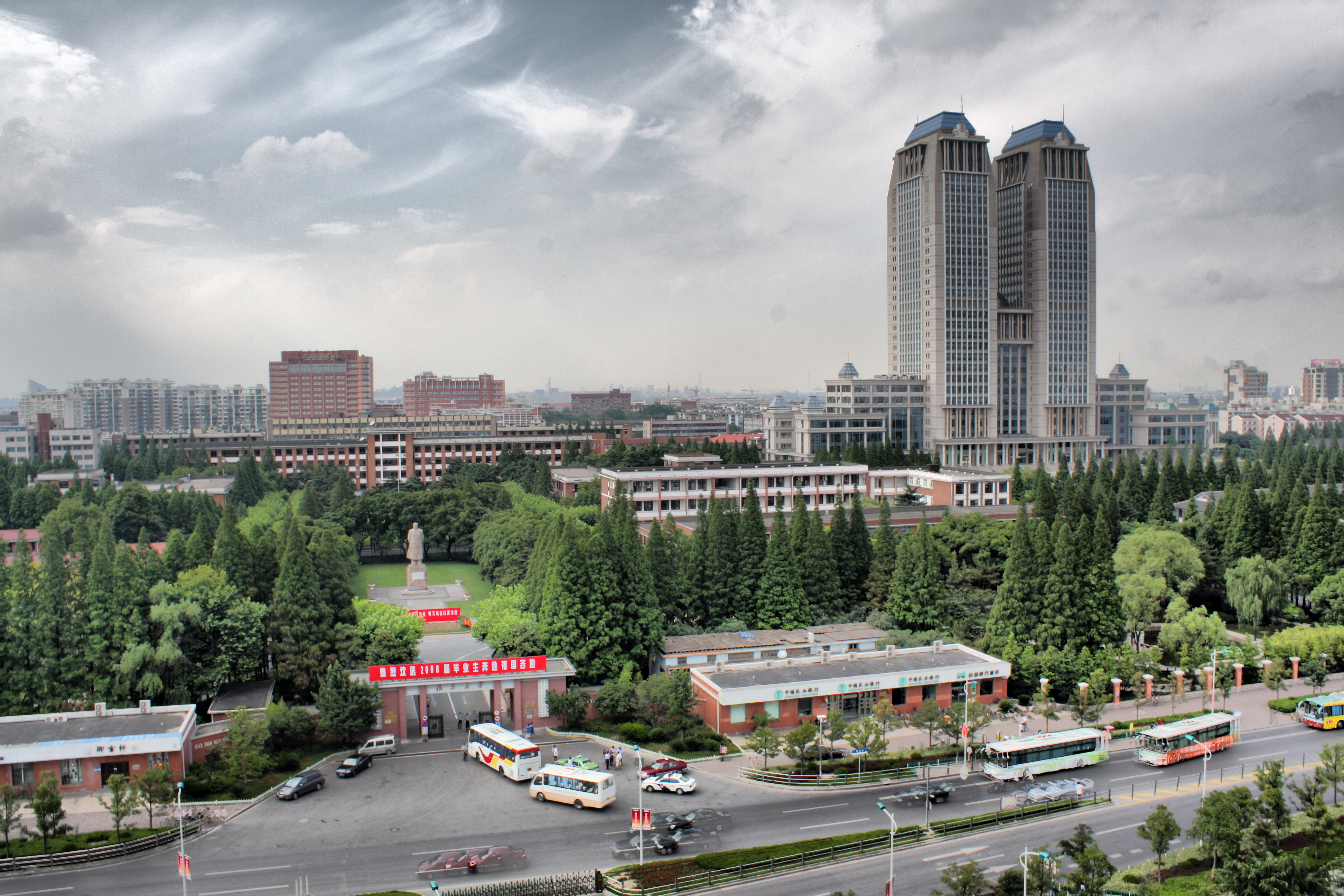
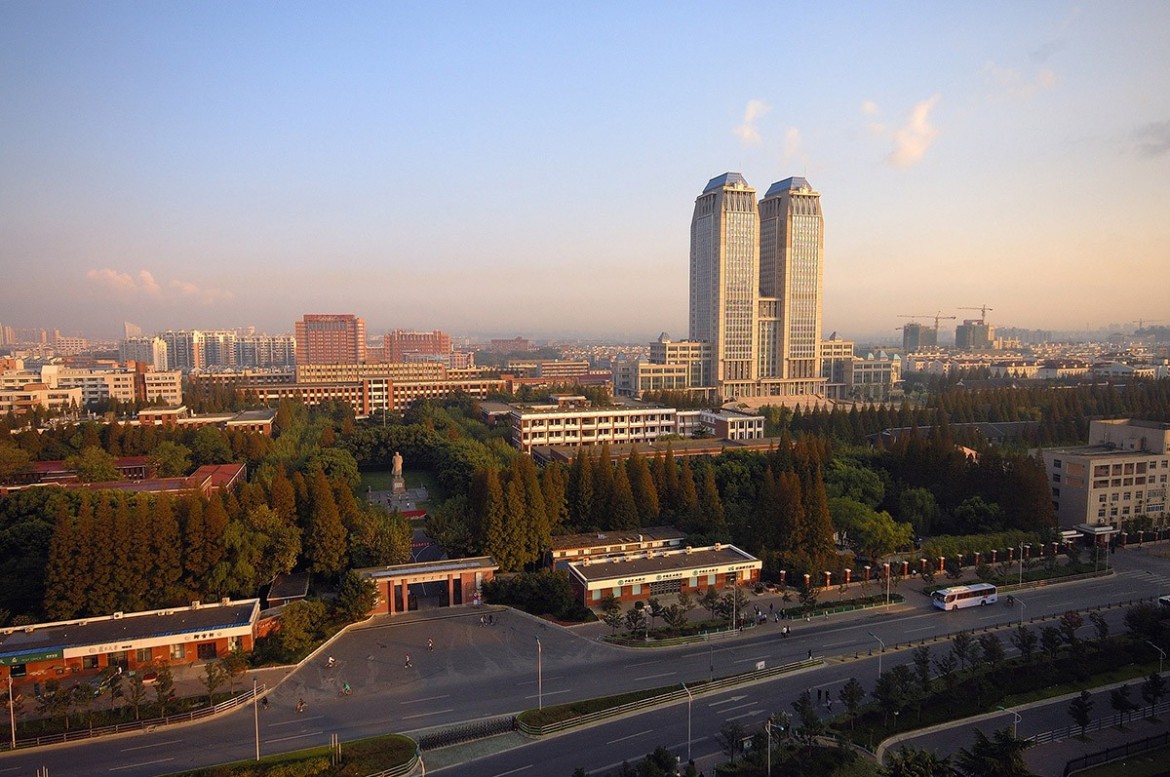
Университет Фудань состоит из 4 кампусов — Ханьдань (邯鄲), Фэнлинь (楓林), Чжанцзян (張江) и Цзянвань (江灣). Все четыре кампуса расположены в центре Шанхая.
В настоящее время ассоциации выпускников Университета Фудань объединяют многих людей в Китае, США, Японии, Австралии, Канаде, Тайване. Среди выпускников университета много известных в Китае и за рубежом политиков, учёных и бизнесменов.
↑ QS World University Rankings. Дата обращения: 30 июня 2016.
↑ Universitas 21 (англ.) // Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. — 2016-06-11.
↑ Фуданьский университет // Вестник высшей школы. — Высшая школа, 1959. — Т. 17. — С. 910.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Fudan Public School (1905)
Fudan College
Private Fudan University (1917–1941)
National Fudan University (1941–1949)
博学而笃志,切问而近思[1] Scientia et studium, quaestīo et cogitatio (Latin)
Rich in knowledge and tenacious of purposes, inquiring with earnestness and reflecting with self-practice[2]
14,800 (including doctoral students)
604 acres
Urban:
Handan campus
Fenglin campus
Jiangwan campus Suburban:
Zhangjiang campus
Fudan University (simplified Chinese: 复旦大学; traditional Chinese: 復旦大學; pinyin: Fùdàn Dàxué) is a major public research university in Shanghai, China. It is widely considered one of the most prestigious and selective universities in China.[4] Founded in 1905, shortly before the end of China's imperial Qing dynasty, Fudan was the first university established independently by the Chinese people.[5][6] Fudan is a member of the elite C9 League and a Chinese Ministry of Education Class A Double First Class University.[7]
Fudan is renowned for its liberal atmosphere and rigorous academics. It is an important academic center for Chinese humanities, natural sciences, and medical studies. Fudan enjoys the reputation of The No.1 Academy of Jiangnan ("江南第一学府").[8] For the past hundred years, Fudan has made significant contributions to the development of the country, the rejuvenation of the nation, the well-being of the society, and the advance of the national education, science, medicine, and technology.[9] Fudan has cultivated a number of outstanding talents and many prominent figures for modern China. Notable Fudan alumni include Chen Yinke, Chen Wangdao, Chu Coching, Yan Fu, Yu Youren and "China's Kissinger" Wang Huning.
Fudan is a collegiate university with five colleges – Zhide (志德), Tengfei (腾飞), Keqing (克卿), Renzhong (任重), and Xide (希德). It is now composed of four campuses in Shanghai – Handan (邯郸), Fenglin (枫林), Zhangjiang (张江), and Jiangwan (江湾) – which share the same central administration. Fudan has 17 hospitals affiliated.
In the 2020 QS Asian University Rankings, Fudan University is ranked 4th in China and 7th in Asia.[10] In recent years, it consistently ranks in the world's top 100 universities according to some of the most-widely read university rankings in the world such as the Academic Ranking of World Universities, the QS World University Rankings, and the Times Higher Education World University Rankings.[11][12][13]
Fudan University, formerly romanized as Fuh Tan, was founded as Fudan Public School in 1905, by Ma Xiangbo, SJ, who had resigned from Aurora University. The two Chinese characters Fu (复, means "again") and Dan (旦, means "morning", "light" ), meaning both "(heavenly light shines) day after day" and "Aurora Revived", were chosen by Ma on the recommendation of Yu Youren, from the Confucian Classic Shangshu Dazhuan (Chinese: 尚书大传): "Itinerant as the twilight, sun glows and moon luminesces" (Chinese: 日月光华,旦复旦兮). The university motto "Scientia et studium, quaestīo et cogitatio" comes from Analects Book 19.6 (Chinese: 博学而笃志,切问而近思), which means "rich in knowledge and tenacious of purposes, inquiring with earnestness and reflecting with self-practice".
In 1911, during the Xinhai Revolution, the college was occupied as headquarters of the Guangfu Army and closed down for almost one year.[citation needed]
In 1917, Fudan Public School became a private university named the Private Fudan University, and also had a middle school and university-preparatory school. In 1929, Fudan reorganized its departments, expanding to include departments of journalism, municipals[clarification needed], law, and education.[citation needed]
After the Japanese invasion of China in 1937, Fudan moved with the Kuomintang government to the inland city of Chongqing, the wartime Chinese capital. On 25 December 1941, the First Meeting of Fifth Conference of the Highest Executive Authority of the National Government of the Republic of China voted to change Fudan University (Chongqing) to a public university with Wu Nanxuan as its president. Fudan University then became National Fudan University. After the end of World War II, it moved back to Shanghai.[citation needed]
After the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949, Fudan lost its "National" appellation and became Fudan University to reflect the fact that all universities under the new socialist state would be public. Fudan was the first university to be reorganized by the new government in 1952 and modeled on Soviet education. The original departments were changed, with arts and sciences departments from at least ten other universities in eastern China being added.[citation needed] Parts of Aurora University merged into Fudan in 1952.
In the late 1970s, after the Cultural Revolution, the university was converted to a modern, comprehensive[clarification needed] university.[citation needed]
Fudan University and Shanghai Medical University merged on 27 April 2000.[citation needed]
In December 2019, Fudan University changed its charter, removing the phrase "academic independence and freedom of thought" (學術獨立和思想自由) and including a "pledge to follow the Communist party's leadership" (學校堅持中國共產黨的領導), leading to protests among the students.[14][15] It also said that Fudan University had to “equip its teachers and employees” with “Xi Jinping Thought”, leading to concerns about the diminishing academic freedom of Fudan.[16][17]
Fudan University comprises 17 full-time schools, 69 departments, 73 bachelor's degree programs, 22 disciplines and 134 sub-disciplines authorized to confer PhD degrees, 201 master's degree programs, 6 professional degree programs, 7 key social science research centers of Ministry of Education P.R.C, 9 national basic science research and training institutes and 25 post-doctoral research stations. It has 40 national key disciplines granted by the Ministry of Education, nationally third. At present, it has 77 research institutes, 112 cross-disciplinary research institutes, and 5 national key laboratories. See a list of schools and departments at Fudan.
Fudan University enrolls over 45,000, including full-time students and students in continuing education and online education. Additionally, there are nearly 1,760 international students, ranking second nationally.
Fudan University has a high-level research faculty of over 2,600 full-time teachers and researchers, including 1,350 professors and associate professors, 47 academicians of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Engineering, nearly 660 doctoral supervisors, 26 special professors and 2 lecture professors of "Cheungkong Scholars Program", 3 distinguished professors and 10 special professors of Fudan University, 6 principal scientists of Project 973 and 25 "Young Experts with Prominent Contributions to the Country".
Fudan University has 17 affiliated hospitals, such as Zhongshan Hospital and Huashan Hospital, integrating medical service, medicine education, and research.
Fudan University has an "International Student's Dormitory", a building reserved as living quarters for any students from countries other than China studying either degree or non-degree programs. Notable alumni include Jennifer Chu and Audrey Lamsam of Arcadia, California, who started a nonprofit organization called "Food4Me" in 2012. This organization first stemmed from their studies as non-degree Chinese students at the university.
Fudan is a member of Universitas 21, an international consortium of research-driven universities.
The Guanghua Twin Towers (Chinese: 光华楼) at the center of the Handan campus reach 140.5 meters, reportedly the highest buildings ever constructed in a university campus in Asia, and 2nd around the world.
The High School Affiliated to Fudan University, located on the Handan campus, is one of the most prestigious high schools all over China mainland.
Fudan University Library was formally established in 1922, previously known as the Reading Room of Wu Wu (1918). Today it comprises the Liberal Arts Library, the Science Library and the Medical Library, with a total floor of 29,000 square meters.
By the end of 2004, the Library's collection composed of more than 4.4588 million copies and articles, including books, journals, bound volumes of newspapers, and audio-visual recordings. Of all these 400,000 are thread-bound books of Chinese classics (including 7,000 rare copies), 100,000 are books published during the reign of the Republic of China, and 1.392 million are foreign books. Additionally, there are 32,000 Chinese and foreign journals and periodicals. Every year 100,000 new books will be added to enlarge the collection. The library subscribes to around 7,000 printed journals.
The library has access to 24,000 full-text e-journals and over 150 CD and online databases. It has eight open stacks, two general reading rooms and 19 reading rooms with specialized functions, totaling 2,400 seats. The library is open for 112 hours weekly and serves more than 7,000 visiting readers daily.
The Fudan University Library is divided into the China Academic Humanities and Social Sciences Library (CAHSL), the National Foreign Textbook Center for East China (sponsored by the Ministry of Education), the Documentation and Information Center for Liberal Arts, and the Central Stacks for Foreign Books of Liberal Arts. Additionally, the library has the Shanghai Electronic Documents Searching Center for Graduates, the CD Searching Center shared by the universities in Northeast Shanghai, and the General Search Station for Updated Science and Technology Information Authorized by the Ministry of Education, the Search Station for Updated Science and Technology Information Authorized by the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee. The library edits and publishes two journals: China Index and Information Services of the Higher Education Institutions in Shanghai.
The library's integrated computer management system has been upgraded several times. In addition to general services, the Library provides services of international online information retrieval, various types of e-resources searching, interlibrary loans, document delivery service, online consultation, updated information search, user training, tape duplication, multimedia viewing, document duplication, and binding, etc. The courses of literature and information retrieval are designed for Library users of different levels.
The QS World University Rankings 2021 ranked Fudan at 34th in its global rankings while it was 7th in the independent regional QS Asian University Rankings (2021)[27] and 3rd in QS BRICS University Rankings (2019),[28] respectively. Further, ARWU (2020) put it at a position among 100th globally.[29] It is among the top 100 universities in the world and top five in mainland China in all of the above league tables.
According to the 2021 QS World University by Subject, the university was ranked among the top 50 in the world in "Social Sciences & Management", "Natural Science" and "Engineering & Technology" subjects, while it falls within the global top 100 in "Arts and Humanities" and "Life Science and Medicines" related fields.[30]
Regarding research output in natural science and life science, the Nature Index 2020 ranks the university 7th in China, 8th in the Asia-Pacific and 27th in the world among the global academic universities.[31]
Fudan University's undergraduate program is extremely selective. Fudan is one of the five universities (together with Tsinghua University, Peking University, Zhejiang University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University) in China whose undergraduate programs are the hardest for students to get in: less than 0.2% of National College Entrance Examination ("Gaokao") takers can make it (As a comparison, the five most selective Ivy League schools in 2012 let in three times the percentage (0.6%) of SAT-takers.).[32] Fudan has been placed consistently among the three most selective universities (with Tsinghua University and Peking University) in China for the last twenty years.[33][34][35][36]
Fudan has reconstructed its course system to suit education goals. A course scheme of general education, specialized education and basic education in arts and sciences has been implemented. Encompassing a complete and comprehensive range of disciplines, the courses of general education enable students to receive education in diverse fields. All of the 70-plus undergraduate majors of Fudan have been put into seven general categories so that students can benefit on a broader scale from the systematic discipline training. According to the Education Scheme for Arts and Sciences, course modules are determined by discipline systems and course suits, and credits by course modules. In this sense, Fudan provides students with more options for their college studies. In contrast with the traditional syllabus, the new module has appropriately decreased the gross credits and class hours. Along with minor programs and extracurricular academic activities, it contributes greatly to the intellectual development of undergraduate students, exposing them to a wider range of knowledge.
The Graduate School of Fudan University was established on 6 November 1984 and the Graduate School of Shanghai Medical University on 25 January 1985. Both were among the first 22 graduate schools after China's universities officially resumed enrolling graduate students. With the merger of Shanghai Medical University and Fudan University in April 2000, the two graduate schools were joined to be a new Graduate School of Fudan University. Therefore, a comprehensive graduate education structure is formed with disciplines in humanities, law, sciences, engineering, medicine, and management.
Starting from the 1950s, Fudan has enrolled international students – one of the first few institutions in China to do so. Since then, Fudan has accepted and trained over 10,000 foreign students from 100 countries and regions worldwide. At the end of 2006, there were 2,812 international students studying at Fudan University, ranked number 2 in the nation. Half of them were actively pursuing degrees, the rest were general visiting scholars. In addition, Fudan enrolls over 1700 short-term students each year.
The international student programs consist of degree programs and non-degree programs.[37] The university has also established a Bachelor of Arts program called the "Chinese language for international students" and there have been seven groups of graduates. Besides all levels of Chinese language teaching, the university has opened courses such as Chinese literature, Chinese history, Chinese economy, Chinese philosophy, and Chinese law for interested international students. These courses will introduce students to basic knowledge of Chinese social economy, history, and culture, according to their different requirements. In addition, several graduate programs are offered in English. For instance Master of Business Administration, Master of Public Health, as well as other programs offered in conjunction with partner universities a
复旦大学 Fudan University
Фуданьский университет — Википедия
Fudan University - Wikipedia
Fudan University - Главная | Facebook
Университет Фудань | Стоимость | Поступление
Denise Crosby Topless
Pam Greir Nude
Please Stop Fucking My Ass
Fdau University