Examining Nerve Disorder: Factors, Signs, and Treatments
Neuropathy is a concept that denotes a variety of conditions that influence the peripheral nervous system, which is responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body. This condition can cause multiple symptoms, including discomfort, loss of sensation, tingling, and weakness, commonly affecting a person's daily activities and quality of life. Grasping neuropathy is essential for not only patients and healthcare providers, as it provides understanding into the underlying mechanisms that could be interfering with the normal functioning of nerves.
The causes of neuropathy are varied and can arise from a variety of factors, including glycemic issues, injury, viral infections, and exposure to poisons. Each of these causes leads to various neuropathic conditions and symptoms, making the diagnosis process crucial for proper management. In this article, we will examine the intricacies of neuropathy, studying its causes, symptoms, and the treatments available to help those affected recover control over their health and well-being.
Reasons of Peripheral Nerve Damage
Neuropathy refers to injury or disruption of the peripheral nerves, which can occur due to a wide range of underlying causes. One of the most prevalent factors is diabetes. Diabetic neuropathy arises from prolonged high blood sugar levels, which can lead to damage to the nerves over time. This kind of nerve damage often affects the legs and toes, resulting in sensations like tingling, discomfort, or numbness.
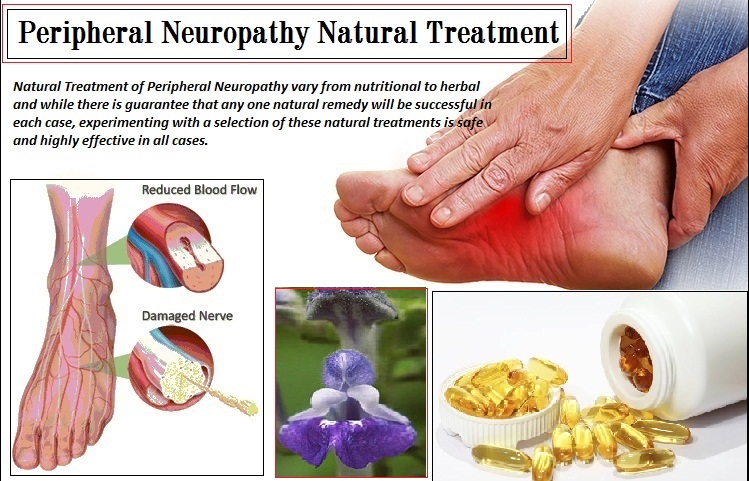
Another significant cause of nerve damage is exposure to toxins, including lead, mercury, and arsenic and specific medications. Cancer treatment, for example, can lead to nerve injury as a result of treatment. Additionally, chronic alcohol consumption can cause nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamins thiamine, pyridoxine, and cobalamin, which contribute to damage to the peripheral nerves. These substances hinder the normal activity and repair processes of peripheral nerves.
Illnesses and autoimmune diseases also play a key role in the development of neuropathy. Infections like Lyme borreliosis, herpes zoster, and HIV can directly impact nerve health. Likewise, autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or RA, may lead the body's immune system to mistakenly attack the nerves, resulting in neuropathic symptoms. Comprehending these causes is crucial for successful diagnosis and management of nerve damage.
Symptoms of Neuropathy
Nerve damage presents a variety of signs that can vary considerably based on the type and extent of nerve damage. Frequent signs include tingling or numbness, often referred to as "prickling sensations," particularly in the upper extremities and lower extremities. Patients may also experience a burning sensation or heightened sensitivity to touch, making even simple activities uncomfortable.
As neuropathy progresses, it can lead to a lack of coordination and balance issues, increasing the risk of falls. Muscle weakness may also develop, affecting one's ability to carry out daily activities. In some cases, this weakness can result in difficulty walking or gripping items, further making more difficult daily life.
In addition to physical symptoms, nerve damage can have an emotional and psychological impact. Patients may experience stress or mood disorders due to chronic pain and restrictions on movement. This link of physical and mental health highlights the necessity of addressing neuropathy holistically for better quality of life.
Treatment Options for Neuropathy
As we dealing with neuropathy, the treatment strategy mainly depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For diabetic neuropathy, controlling blood sugar levels is vital. Healthcare professionals often recommend lifestyle changes such as nutritional adjustments, regular exercise, and weight management. In some cases, medications like anti-seizure drugs or antidepressants may be prescribed to help alleviate pain associated with nerve damage.
For individuals with neuropathy due to nutritional shortfalls, supplementation can be significant. B vitamins, particularly B12, are important for nerve health. In such cases, dietary adjustments or supplements can substantially benefit symptoms. Additionally, physical therapy may be indicated to help improve strength, coordination, and function, empowering those affected to maintain mobility and reduce discomfort.
In more severe instances, complex treatments might be necessary. These could include surgical procedures to relieve pressure on compressed nerves or other interventional approaches to manage pain. Alternate therapies, including acupuncture and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), can also offer relief. Ultimately, a personalized treatment plan tailored by healthcare providers is important for addressing neuropathy properly.