Dominated Strategy

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
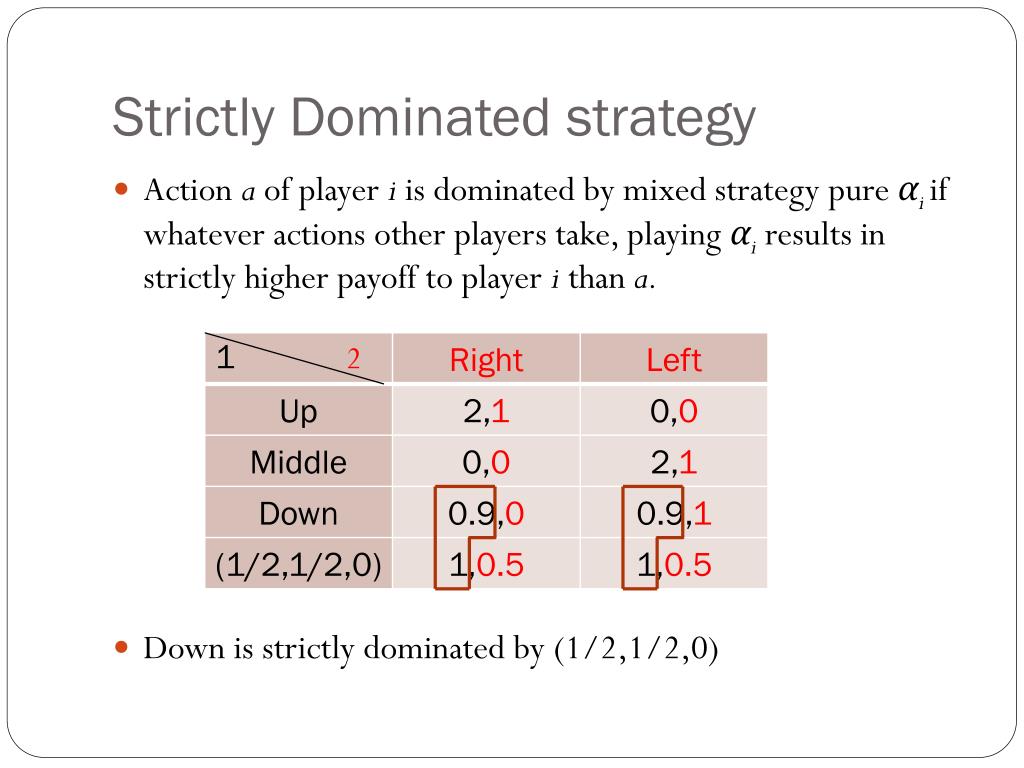
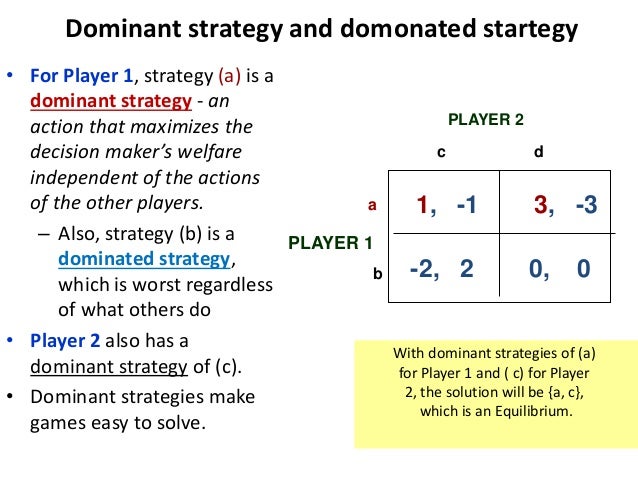
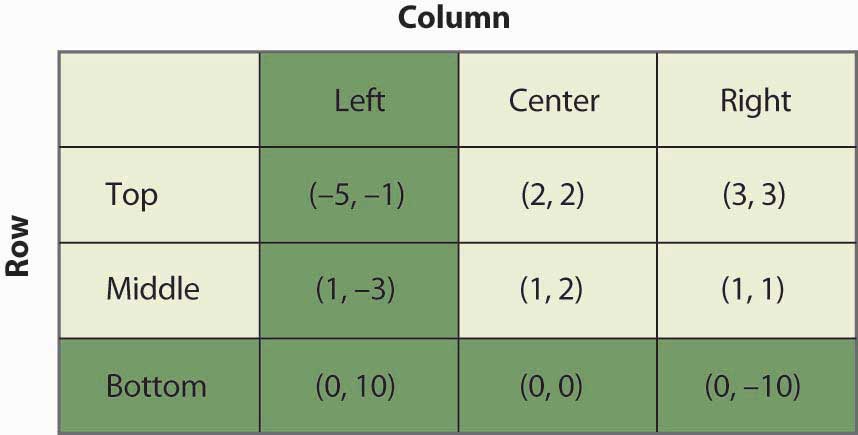
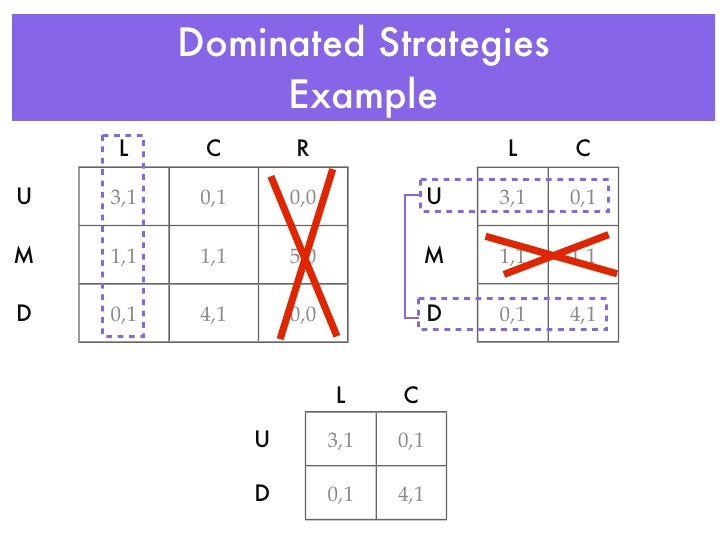
Dominated Strategy. A strategy is dominated if, regardless of what any other players do, the strategy earns a player a smaller payoff than some other strategy. Hence, a strategy is dominated if it is always better to play some other strategy, regardless of what opponents may do. If a player has a dominant strategy than all others are dominated, ...
Accordingly, a strategy is a dominant strategy if choosing it leads a player to better outcomes than the other strategies that they can choose. Conversely, a strategy is a dominated strategy if choosing it leads a player to worse outcomes than the other strategies that they can choose.
effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance/
What are some examples of dominant strategies?
What are some examples of dominant strategies?
In scenarios where there is only one player, there can still be dominant and dominated strategies. For example, consider a situation where you are walking along a street, and you know that you need to cross the road. As you reach the first of two possible (and identical) crosswalks that you can use, the light turns red.
effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance/
How to take strategic dominance into account?
How to take strategic dominance into account?
In order to take strategic dominance into account, you should first assess the situation that you’re in, and take into account all the possible moves that you and your opponents can make, as well as the outcomes of those moves, and the favorability of each outcome.
effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance/
Which is the dominant strategy for both firms?
Which is the dominant strategy for both firms?
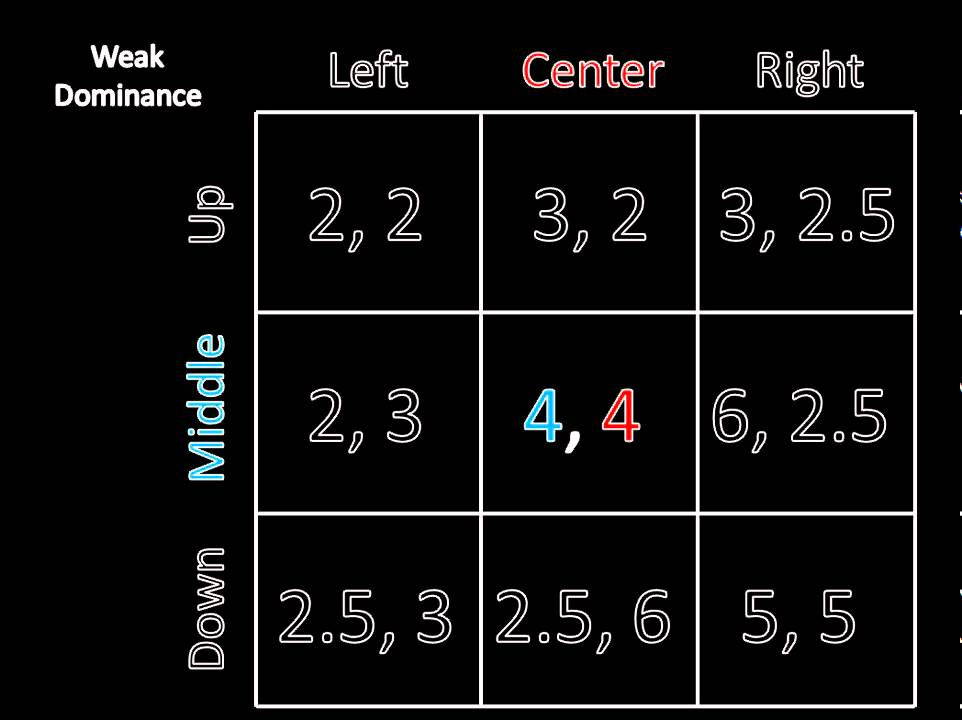
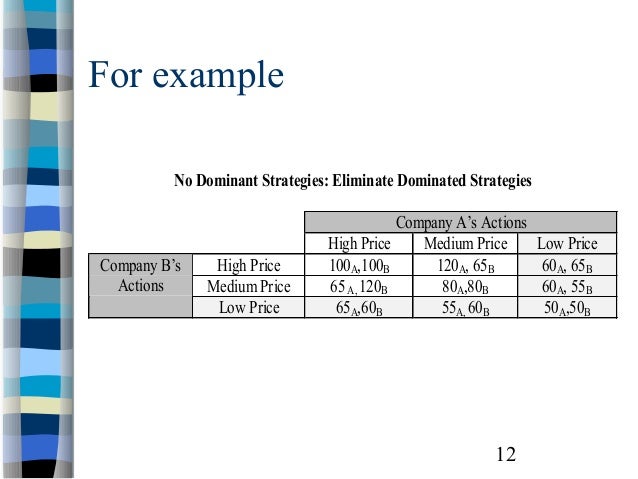
The following matrix shows the payoffs: In the example on dominant strategy, we identified that hiring a lawyer is a dominant strategy for both firms. Hence, we can conclude that not hiring a lawyer is the dominated strategy for both firms. Now, let’s see what happens in a game in which there are more than two strategies available to each player.
xplaind.com/948574/dominated-strategy
https://www.gametheory.net/dictionary/DominatedStrategy.html
Перевести · Dominated Strategy. A strategy is dominated if, regardless of what any other players do, the strategy earns a player a smaller payoff than some other strategy. …
https://effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance
Перевести · Strategic Dominance: A Guide to Dominant and Dominated Strategies Dominant strategies. A dominant strategy is a strategy that leads to a better outcome for a player than the other... Dominated strategies. A dominated strategy is a strategy that leads to a worse outcome for a player than …
Домини́рование в теории игр — ситуация, при которой одна из стратегий некоторого игрока дает больший выигрыш, нежели …
Текст из Википедии, лицензия CC-BY-SA
https://xplaind.com/948574/dominated-strategy
Перевести · A dominated strategy is a strategy which doesn’t result in the optimal outcome in any case. A strategy is dominated if there always exist a course of action which results in higher payoff no matter …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strategic_dominance
When a player tries to choose the "best" strategy among a multitude of options, that player may compare two strategies A and B to see which one is better. The result of the comparison is one of:
• B is equivalent to A: choosing B always gives the same outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
• B strictly dominates A: choosing B always gives a better outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
When a player tries to choose the "best" strategy among a multitude of options, that player may compare two strategies A and B to see which one is better. The result of the comparison is one of:
• B is equivalent to A: choosing B always gives the same outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
• B strictly dominates A: choosing B always gives a better outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
• B weakly dominates A: choosing B always gives at least as good an outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do, and there is at least one set of opponents' action for which B gives a better outcome than A. (Notice that if B strictly dominates A, then B weakly dominates A. Therefore, we can say "B dominates A" as synonymous of "B weakly dominates A".)
• B and A are intransitive: B and A are not equivalent, and B neither dominates, nor is dominated by, A. Choosing A is better in some cases, while choosing B is better in other cases, depending on exactly how the opponent chooses to play. For example, B is "throw rock" while A is "throw scissors" in Rock, Paper, Scissors.
• B is weakly dominated by A: There is at least one set of opponents' actions for which B gives a worse outcome than A, while all other sets of opponents' actions give A the same payoff as B. (Strategy A weakly dominates B).
• B is strictly dominated by A: choosing B always gives a worse outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other player(s) do. (Strategy A strictly dominates B).
This notion can be generalized beyond the comparison of two strategies.
• Strategy B is strictly dominant if strategy B strictly dominates every other possible strategy.
• Strategy B is weakly dominant if strategy B weakly or strictly dominates all other strategies, but some (or all) strategies are only weakly dominated by B.
• Strategy B is strictly dominated if some other strategy exists that strictly dominates B.
• Strategy B is weakly dominated if some other strategy exists that weakly dominates B.
Strategy: A complete contingent plan for a player in the game. A complete contingent plan is a full specification of a player's behavior, describing each action a player would take at every possible decision point. Because information sets represent points in a game where a player must make a decision, a player's strategy describes what that player will do at each information set.
Rationality: The assumption that each player acts in a way that is designed to bring about what he or she most prefers given probabilities of various outcomes; von Neumann and Morgenstern showed that if these preferences satisfy certain conditions, this is mathematically equivalent to maximizing a payoff. A straightforward example of maximizing payoff is that of monetary gain, but for the purpose of a game theory analysis, this payoff can take any desired outcome. E.g., cash reward, minimization of exertion or discomfort, promoting justice, or amassing overall “utility” - the assumption of rationality states that players will always act in the way that best satisfies their ordering from best to worst of various possible outcomes.
Common Knowledge: The assumption that each player has knowledge of the game, knows the rules and payoffs associated with each course of action, and realizes that every other player has this same level of understanding. This is the premise that allows a player to make a value judgment on the actions of another player, backed by the assumption of rationality, into consideration when selecting an action.
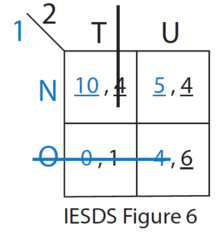
Iterated elimination of strictly dominated strategies (IESDS)
Game Theory - Dominant and Dominated Strategies
Game Theory 101 (#3): Iterated Elimination of Strictly Dominated Strategies
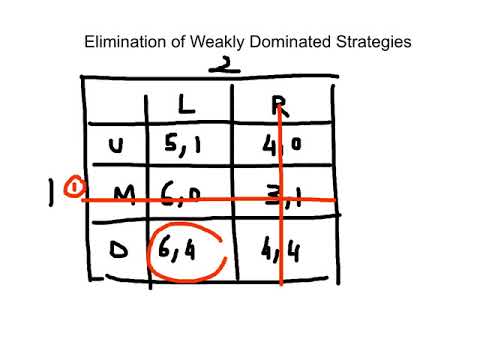
Lab 5.5 Elimination of weakly dominated strategies
GTO-3-02: Strictly Dominated Strategies and Iterative Removal
Iterative Deletion of Dominated Strategies
www.econ.uiuc.edu/~hrtdmrt2/Teaching/GT_2015_19/L3.pdf
Dominant and Dominated Strategies Definition A strategy s i ∈S i is a strictly dominant strategy for player i if for all ~s i 6= s i and all s −i ∈S −i, u i(s i,s −i) > u i(~s i,s −i). A strictly dominant strategy for i …
https://people.math.umass.edu/~lr7q/ps_files/teaching/math456/lecture2.pdf
De nition 1. (Dominated strategy) For a player a strategy s is dominated by strategy s 0if the payo for playing strategy s is strictly greater than the payo for playing s, no matter what the strategies of the …
www.econ.uiuc.edu/~hrtdmrt2/Teaching/GT_2016_19/L2.pdf
I A strategy is a complete contingent plan for playing the game, which specifies a feasible decision for each of a player’s information sets in the game. I Recall that his decision must be the same for each decision node in an information set. I A strategy …
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Dominated Strategy. A strategy is dominated if, regardless of what any other players do, the strategy earns a player a smaller payoff than some other strategy. Hence, a strategy is dominated if it is always better to play some other strategy, regardless of what opponents may do. If a player has a dominant strategy than all others are dominated, ...
Accordingly, a strategy is a dominant strategy if choosing it leads a player to better outcomes than the other strategies that they can choose. Conversely, a strategy is a dominated strategy if choosing it leads a player to worse outcomes than the other strategies that they can choose.
effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance/
What are some examples of dominant strategies?
What are some examples of dominant strategies?
In scenarios where there is only one player, there can still be dominant and dominated strategies. For example, consider a situation where you are walking along a street, and you know that you need to cross the road. As you reach the first of two possible (and identical) crosswalks that you can use, the light turns red.
effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance/
How to take strategic dominance into account?
How to take strategic dominance into account?
In order to take strategic dominance into account, you should first assess the situation that you’re in, and take into account all the possible moves that you and your opponents can make, as well as the outcomes of those moves, and the favorability of each outcome.
effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance/
Which is the dominant strategy for both firms?
Which is the dominant strategy for both firms?
The following matrix shows the payoffs: In the example on dominant strategy, we identified that hiring a lawyer is a dominant strategy for both firms. Hence, we can conclude that not hiring a lawyer is the dominated strategy for both firms. Now, let’s see what happens in a game in which there are more than two strategies available to each player.
xplaind.com/948574/dominated-strategy
https://www.gametheory.net/dictionary/DominatedStrategy.html
Перевести · Dominated Strategy. A strategy is dominated if, regardless of what any other players do, the strategy earns a player a smaller payoff than some other strategy. Hence, a strategy is …
https://effectiviology.com/strategic-dominance
Перевести · Strategic Dominance: A Guide to Dominant and Dominated Strategies Dominant strategies. A dominant strategy is a strategy that leads to a better outcome for a player than the other... Dominated strategies. A dominated strategy is a strategy that leads to a worse outcome for a player than …
Домини́рование в теории игр — ситуация, при которой одна из стратегий некоторого игрока дает больший выигрыш, нежели другая, при любых …
Текст из Википедии, лицензия CC-BY-SA
https://xplaind.com/948574/dominated-strategy
Перевести · A dominated strategy is a strategy which doesn’t result in the optimal outcome in any case. A strategy is dominated if there always exist a course of action which results in higher payoff no matter …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strategic_dominance
When a player tries to choose the "best" strategy among a multitude of options, that player may compare two strategies A and B to see which one is better. The result of the comparison is one of:
• B is equivalent to A: choosing B always gives the same outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
• B strictly dominates A: choosing B always gives a better outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
When a player tries to choose the "best" strategy among a multitude of options, that player may compare two strategies A and B to see which one is better. The result of the comparison is one of:
• B is equivalent to A: choosing B always gives the same outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
• B strictly dominates A: choosing B always gives a better outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other players do.
• B weakly dominates A: choosing B always gives at least as good an outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do, and there is at least one set of opponents' action for which B gives a better outcome than A. (Notice that if B strictly dominates A, then B weakly dominates A. Therefore, we can say "B dominates A" as synonymous of "B weakly dominates A".)
• B and A are intransitive: B and A are not equivalent, and B neither dominates, nor is dominated by, A. Choosing A is better in some cases, while choosing B is better in other cases, depending on exactly how the opponent chooses to play. For example, B is "throw rock" while A is "throw scissors" in Rock, Paper, Scissors.
• B is weakly dominated by A: There is at least one set of opponents' actions for which B gives a worse outcome than A, while all other sets of opponents' actions give A the same payoff as B. (Strategy A weakly dominates B).
• B is strictly dominated by A: choosing B always gives a worse outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other player(s) do. (Strategy A strictly dominates B).
This notion can be generalized beyond the comparison of two strategies.
• Strategy B is strictly dominant if strategy B strictly dominates every other possible strategy.
• Strategy B is weakly dominant if strategy B weakly or strictly dominates all other strategies, but some (or all) strategies are only weakly dominated by B.
• Strategy B is strictly dominated if some other strategy exists that strictly dominates B.
• Strategy B is weakly dominated if some other strategy exists that weakly dominates B.
Strategy: A complete contingent plan for a player in the game. A complete contingent plan is a full specification of a player's behavior, describing each action a player would take at every possible decision point. Because information sets represent points in a game where a player must make a decision, a player's strategy describes what that player will do at each information set.
Rationality: The assumption that each player acts in a way that is designed to bring about what he or she most prefers given probabilities of various outcomes; von Neumann and Morgenstern showed that if these preferences satisfy certain conditions, this is mathematically equivalent to maximizing a payoff. A straightforward example of maximizing payoff is that of monetary gain, but for the purpose of a game theory analysis, this payoff can take any desired outcome. E.g., cash reward, minimization of exertion or discomfort, promoting justice, or amassing overall “utility” - the assumption of rationality states that players will always act in the way that best satisfies their ordering from best to worst of various possible outcomes.
Common Knowledge: The assumption that each player has knowledge of the game, knows the rules and payoffs associated with each course of action, and realizes that every other player has this same level of understanding. This is the premise that allows a player to make a value judgment on the actions of another player, backed by the assumption of rationality, into consideration when selecting an action.
Iterated elimination of strictly dominated strategies (IESDS)
Game Theory - Dominant and Dominated Strategies
Game Theory 101 (#3): Iterated Elimination of Strictly Dominated Strategies
Lab 5.5 Elimination of weakly dominated strategies
GTO-3-02: Strictly Dominated Strategies and Iterative Removal
Iterative Deletion of Dominated Strategies
www.econ.uiuc.edu/~hrtdmrt2/Teaching/GT_2015_19/L3.pdf
Dominant and Dominated Strategies Definition A strategy s i ∈S i is a strictly dominant strategy for player i if for all ~s i 6= s i and all s −i ∈S −i, u i(s i,s −i) > u i(~s i,s −i). A strictly dominant strategy for i …
https://people.math.umass.edu/~lr7q/ps_files/teaching/math456/lecture2.pdf
De nition 1. (Dominated strategy) For a player a strategy s is dominated by strategy s 0if the payo for playing strategy s is strictly greater than the payo for playing s, no matter what the strategies of the …
www.econ.uiuc.edu/~hrtdmrt2/Teaching/GT_2016_19/L2.pdf
I A strategy is a complete contingent plan for playing the game, which specifies a feasible decision for each of a player’s information sets in the game. I Recall that his decision must be the same for each decision node in an information set. I A strategy …
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Lesbian College Students
Erotic College Coeds
Bbw Granny Hairy Asshole In Toilet
Nude Asian Hairy Pussy
Porno Pikap Public Agent
Dominated Strategy - Game Theory .net
Strategic Dominance: A Guide to Dominant and Dominated ...
Dominated Strategy | Definition | Example
Strategic dominance - Wikipedia
Dominant and Dominated Strategies
Lecture 2: Dominated strategies and their elimination
Dominant and Dominated Strategies
Dominated Strategy