Diesel Generators for Rapid Load Acceptance Meeting Power Demands Efficiently
Introduction
Diesel generators are essential power sources that play a crucial role in providing reliable electricity in various applications. One of the key advantages of diesel generators is their ability to rapidly accept loads, making them ideal for situations where quick response and stable power supply are required. This article explores the significance of diesel generators in rapid load acceptance scenarios, their working principles, key components, and best practices for optimal performance.
Importance of Rapid Load Acceptance
Rapid load acceptance refers to the ability of a generator to quickly adjust its power output in response to sudden changes in electrical load demand. In many applications, such as hospitals, data centers, telecommunications facilities, and industrial plants, maintaining a stable power supply is critical for ensuring uninterrupted operations. Diesel generators are preferred in such scenarios due to their capability to respond swiftly to load variations and provide reliable power within seconds.
In emergency situations, such as power outages or grid failures, diesel generators can start and reach full load capacity quickly, ensuring that essential systems and equipment remain operational. The ability of diesel generators to handle rapid load changes makes them indispensable in applications where power reliability is paramount.
Working Principles of Diesel Generators
Diesel generators operate on the principle of converting chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into mechanical energy through the process of combustion. The mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy using an alternator or generator. The key components of a diesel generator system include the engine, alternator, fuel system, cooling system, control panel, and exhaust system.
When a load is applied to a diesel generator, the engine control unit (ECU) senses the change in demand and adjusts the fuel injection rate to increase the power output. The combustion process in the engine produces high-pressure gases that drive the pistons, generating mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy by the alternator, which produces the required voltage and frequency to match the load demand.
To achieve rapid load acceptance, diesel generators are designed with robust engine systems that can respond quickly to load changes without compromising performance or efficiency. Advanced control systems and electronic governors ensure precise control over fuel delivery and engine speed, enabling the generator to reach full load capacity within seconds.
Key Components of Diesel Generators for Rapid Load Acceptance
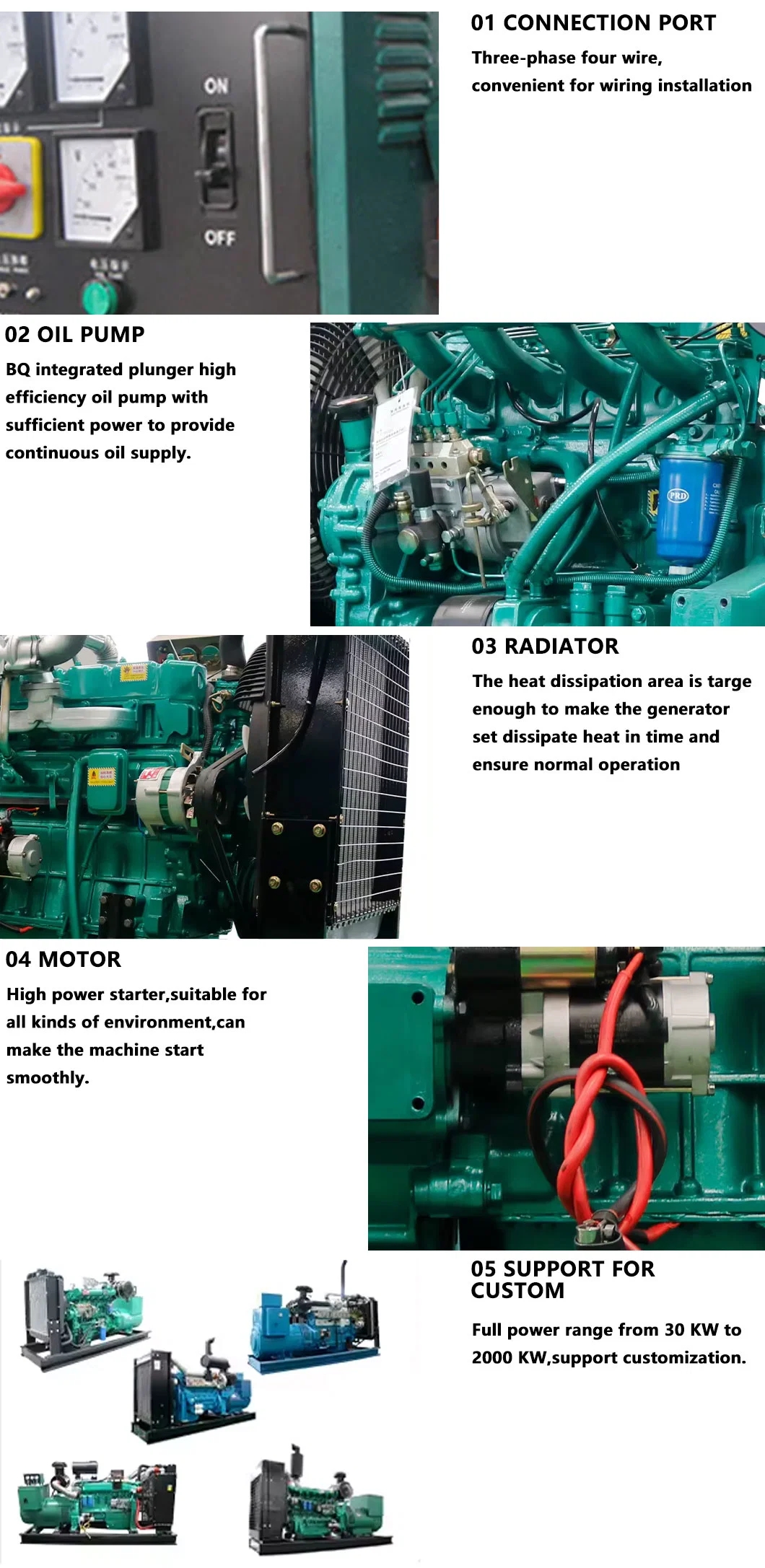
1. Engine: The engine is the heart of a diesel generator system and plays a crucial role in determining its performance and response time. High-quality engines with advanced fuel injection systems and turbocharging capabilities are essential for rapid load acceptance. Modern diesel engines are designed to deliver high power output with minimal emissions and fuel consumption.
2. Alternator: The alternator is responsible for converting the mechanical energy generated by the engine into electrical energy. The alternator's design and efficiency directly impact the generator's ability to handle rapid load changes and maintain voltage stability under varying conditions. High-quality alternators with robust insulation and low harmonic distortion are preferred for applications requiring rapid load acceptance.
3. Control Panel: The control panel of a diesel generator houses the monitoring and control systems that regulate the generator's operation. Advanced control panels feature intuitive interfaces, real-time data monitoring, and remote communication capabilities to ensure seamless operation and quick response to load variations. The control panel allows operators to adjust settings, monitor performance parameters, and troubleshoot issues efficiently.
4. Fuel System: The fuel system of a diesel generator includes the fuel tank, fuel lines, filters, and injectors responsible for delivering diesel fuel to the engine. An efficient and reliable fuel system is essential for ensuring continuous operation and rapid response to load changes. Proper fuel filtration, storage, and monitoring systems help maintain fuel quality and prevent engine issues during peak load conditions.
5. Cooling System: The cooling system of a diesel generator is designed to dissipate the heat generated during the combustion process and maintain optimal operating temperatures. Efficient cooling systems, such as radiators, heat exchangers, and coolant circulation pumps, are essential for preventing overheating and ensuring reliable performance during rapid load acceptance. 75kw diesel generator of the cooling system is critical for prolonging the generator's lifespan and preventing breakdowns.
Best Practices for Optimal Performance
To ensure optimal performance and rapid load acceptance capability, diesel generator operators and maintenance personnel should adhere to best practices that enhance reliability and efficiency. Some key best practices include:
1. Regular Maintenance: Scheduled maintenance tasks, such as oil and filter changes, fuel system inspections, cooling system checks, and electrical testing, are essential for keeping the diesel generator in top condition. Routine maintenance helps identify potential issues early, prevent breakdowns, and ensure reliable operation during load variations.
2. Load Testing: Periodic load testing is recommended to assess the generator's performance under varying load conditions and verify its rapid load acceptance capability. Load testing helps identify any issues related to voltage stability, frequency regulation, and response time, allowing operators to make necessary adjustments for optimal performance.
3. Fuel Quality Management: Proper fuel quality management is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of a diesel generator. Regular fuel testing, filtration, and storage practices can help prevent fuel contamination, microbial growth, and degradation that may affect the generator's performance during rapid load changes.
4. Remote Monitoring: Implementing remote monitoring systems and telematics solutions enables real-time monitoring of the generator's performance, status, and alerts. Remote monitoring allows operators to track key parameters, receive notifications of potential issues, and take proactive measures to ensure continuous operation and rapid response to load variations.
5. Training and Education: Providing training programs for operators and maintenance personnel on diesel generator operation, maintenance procedures, and emergency response protocols is essential for enhancing performance and safety. Well-trained personnel are better equipped to handle rapid load changes, troubleshoot issues, and optimize the generator's efficiency.
Conclusion
Diesel generators play a vital role in meeting power demands efficiently, especially in scenarios requiring rapid load acceptance and uninterrupted power supply. Their robust design, advanced technology, and reliable performance make them indispensable in critical applications where power reliability is paramount. By understanding the working principles, key components, and best practices for optimal performance, operators can maximize the capabilities of diesel generators and ensure seamless operation during load variations. With continuous advancements in engine technology and control systems, diesel generators are poised to remain a reliable and efficient power source for various industries and applications.