Comprehending the Basics of Company Corporations
Organization companies are complicated entities governed by a set of policies and structures that specify their operations and purposes. At its core, a corporation is a lawful entity that is distinctive and different from its owners, who are called investors. This splitting up is essential as it supplies the shareholders with minimal responsibility, implying their individual assets are secured from the company's obligations and financial debts. Firms can sustaining beyond the life-span of their founders, can have home, participate in agreements, file a claim against and be sued. This makes them an extremely favored structure for lots of organizations, varying from tiny startups to huge multinational conglomerates.
Among the defining characteristics of firms is their ability to elevate funding through the issuance of shares. Shareholders purchase the corporation by acquiring shares, which represent a part of ownership in the company. This ownership supplies prospective financial returns in 2 main kinds: rewards and capital gains. Rewards are earnings distributed to shareholders, while resources gains emerge from the sale of shares at a cost greater than their acquisition cost. Additionally, companies are handled by a board of directors elected by the shareholders. This board makes significant decisions and manages the basic administration of the business, making certain that the rate of interests of the investors are prioritized. However, the day-to-day operations are generally handled by police officers and supervisors who might or might not be investors themselves.
Recognizing the Structure and Feature of Business CorporationsCompany firms are complex entities that play a crucial function in the global economic climate, structured to balance the rate of interests of different stakeholders including investors, clients, and employees. At its core, a company is a lawful entity unique from its owners, efficient in working out much of the legal rights and incurring the responsibilities of an all-natural individual. This separation offers an important benefit: limited obligation for its shareholders, suggesting that most of the times, the personal possessions of the financiers are protected from the company's financial institutions. Corporations are regulated by a board of supervisors, elected by investors, that makes key plan decisions and looks after the overall instructions of the company. The everyday procedures, nonetheless, are managed by managers and officers that take care of the tactical elements of running business. Another fundamental facet of firms is their ability to raise capital either through the sale of supply or by providing bonds, which offers them with substantial growth possibilities not readily available to non-corporate entities. Moreover, firms undergo particular governing environments depending upon their geographic and functional jurisdictions, which can affect whatever from tax commitments to functional transparency. Comprehending these aspects is important for any individual took part in or with corporate ventures, as they mount the potential and limitations within which firms operate.
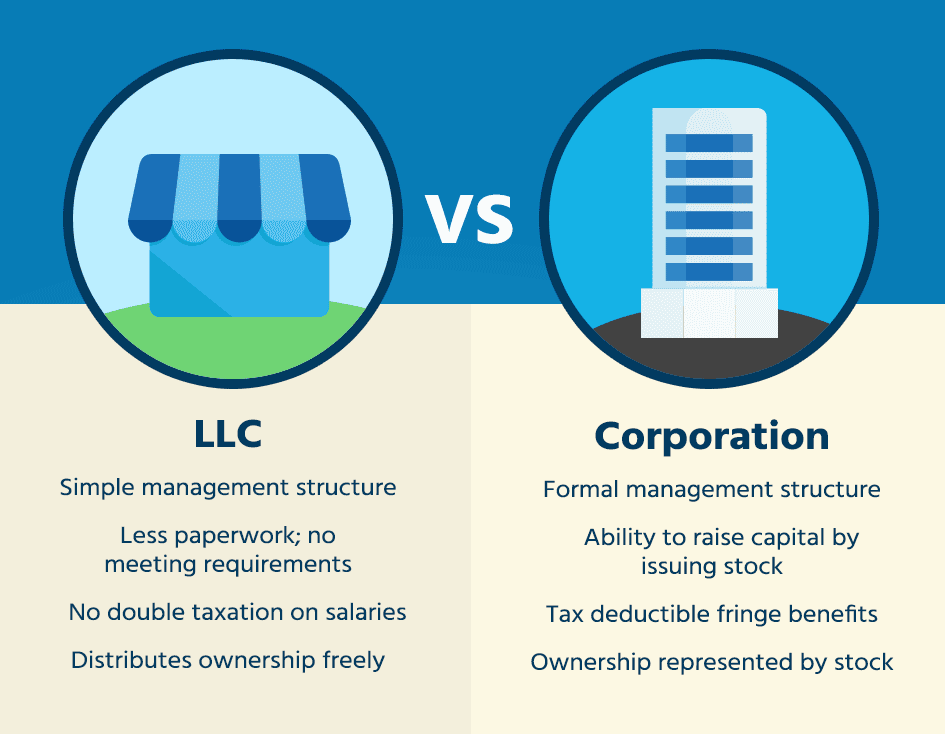
Comprehending the Legal Framework of Company CompaniesCompany corporations are intricate entities governed by numerous lawful frameworks depending upon their geographical location, market, and functional needs. When developing https://nx.dayibin.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=260435 , founders should initially choose the sort of firm they wish to develop, such as a C firm, S company, or a Minimal Responsibility Firm (LLC), each with its own lawful effects and tax obligation frameworks. As an example, C companies are exhausted individually from their proprietors, possibly bring about increase tax of business earnings if revenue is distributed as returns. On the other hand, S firms and LLCs use pass-through taxation, indicating revenues and losses pass straight to proprietors' individual income tax return, staying clear of the dual tax problem. These entities must stick to particular eligibility requirements, such as limitations on the number of shareholders and types of allowable shareholders, which can restrict their applicability depending on the company's development approach.
One more crucial element of business companies is their conformity with both state and federal laws, which commonly entails regular filings, maintaining correct records, and making sure transparency in economic reporting. These requirements are made to safeguard shareholders' rate of interests and supply clear functional guidelines for managing business. Corporations need to adhere to legislations that govern worker relations, ecological security, consumer security, and much more, all of which can substantially affect their operational techniques and public understanding.
The legal structure of a company forms its capability to raise resources. As an example, openly traded corporations can bring in financial investments via the sale of supply, which can supply significant resources yet requires adherence to stringent regulatory criteria such as those enforced by the Stocks and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. These criteria consist of routine disclosure of financial standing, potential dangers, and other operational details with filings such as the 10-K and 10-Q reports. At the same time, exclusive corporations might look for capital with exclusive positionings, which are much less managed however limit the pool of potential financiers.
Generally, the selection of company structure has far-reaching ramifications for governance, taxation, governing compliance, and financing choices. Each type of corporation uses distinct advantages and limitations, deciding a vital calculated step that can impact the organization's long-term stability and success. Comprehending these legal nuances is vital for anybody associated with forming, taking care of, or spending in a company corporation.
Structural Characteristics and Management Practices in Service FirmsThe architecture of modern-day service corporations is created to sustain a huge range of activities while stabilizing the intricacies of international operation, innovation, and regulatory conformity. At the core of a company's framework are its administration structures, which define the duties and duties of crucial officers and the board of supervisors. These people are tasked with steering the business towards productivity while making sure moral conformity and liability. The board of supervisors, usually consisted of a mix of independent members and elderly execs, plays a crucial function in setting calculated goals and managing executive monitoring to make sure that company purposes are fulfilled and business policies are adhered to. Administration practices within these companies are tailored in the direction of maximizing effectiveness and promoting an efficient business society. Strategies such as lean administration, agile methodologies, and continuous improvement processes are frequently utilized to enhance performance and adjust to transforming market conditions. Furthermore, firms must browse complicated lawful landscapes, adapting to brand-new laws and standards that may differ significantly across various jurisdictions. This demands a durable legal group and an aggressive technique to corporate governance, ensuring that the company not only meets its legal responsibilities however likewise expects potential governing adjustments that could impact its operations. The interaction in between structure, monitoring techniques, and regulative compliance develops a delicate balance that needs consistent interest and refinement to make sure lasting success and sustainability.
In the complex globe of company firms, strategic factors to consider play a crucial function in determining both the short-term functional success and the long-term sustainability of an enterprise. These factors to consider include a wide range of aspects consisting of market positioning, affordable evaluation, advancement in item and service offerings, and adjustment to progressing innovations and consumer preferences. For instance, market positioning calls for a comprehensive understanding of the affordable landscape. A firm should recognize not simply its primary rivals but additionally assess possible threats from brand-new market entrants and replacement items. This comprehensive evaluation help in tailoring approaches that take advantage of the firm's strengths while mitigating its weak points. Innovation is important in keeping relevance and competitiveness in swiftly transforming markets. Today's corporations are expected to consistently evolve their line of product and solutions to meet brand-new customer demands and to stay in advance of technical developments. A technology company might spend heavily in research and advancement to pioneer brand-new technologies or enhance existing ones, guaranteeing they continue to be at the center of the market. Additionally, strategic alignment and integration throughout numerous departments such as advertising, money, and procedures are vital. This control makes sure that the firm's strategic objectives are executed cohesively across all levels of the company, maximizing effectiveness and performance. Last but not least, in today's global economic situation, understanding and implementing approaches that think about international market fads and financial problems is indispensable. This worldwide viewpoint not only opens new markets but additionally branches out risk, which is important for the stability and development of any kind of business company. Jointly, these tactical factors to consider form the backbone of a firm's efforts to not just endure yet flourish in the competitive world of organization.