Cognitive Interest Of Younger Students

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
The webpage at https://eng.refertimacuan.com4308810-formation-of-cognitive-interest-in-primary-school-children/ might be temporarily down or it may have moved permanently to a new web address.
The webpage at https://eng.refertimacuan.com4308810-formation-of-cognitive-interest-in-primary-school-children/ might be temporarily down or it may have moved permanently to a new web address.
This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.
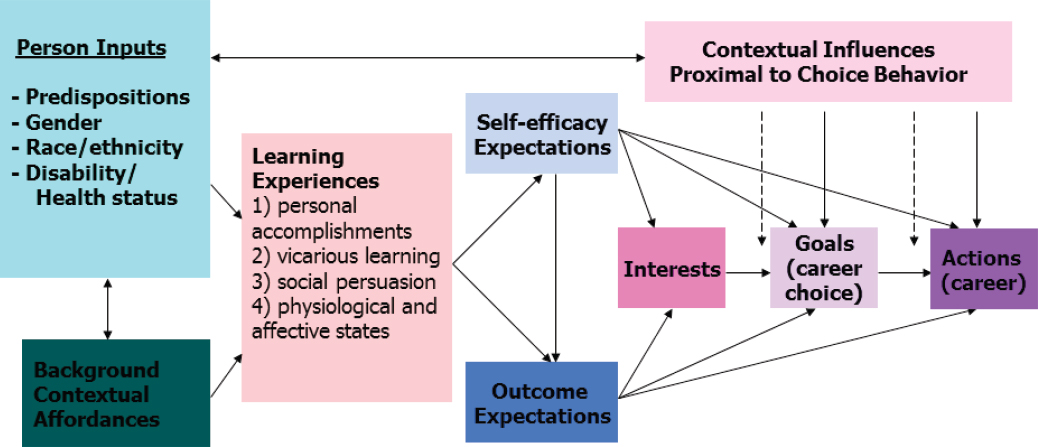
Students’ engagement becomes essential factors in learning process because students have to participate in learningprocess. Not only the students but also the teachers have to make a good atmosphere during classroom activities. They have to createlesson, assignment and also project that interested to the students. Students’ cognitive engagement involves the students to thinkduring academic task, they have to have motivated to improve their ability in learning and also they have to participate and active inthe classroom. This paper is literary study.
Available via license: CC BY-NC 4.0
Content may be subject to copyright.
Scientific Journal of Linguistics, Literature and Language
Student’s Cognitive Engagement in Learning Process
Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, STKIP PGRI Sumatera Barat. 2500. Indonesia
Abstract—Students’ engagement becomes essential factors in learning process because students have to participate in learning
process. Not only the students but also the teachers have to make a good atmosphere during classroom activities. They have to create
lesson, assignment and also project that interested to the students. Students’ cognitive engagement involves the students to think
during academic task, they have to have motivated to improve their ability in learning and also they have to participate and active in
the classroom. This paper is literary study.
Keywords—Cognitive engagement; Learning process.
Student Engagement is an important thing in
learning process especiallly in learning English
because it can improve the students’ ability about
the material. Nowadays, teacher only as instructor
in the class when students interactive on learning
process. It is hopefully that students are engaged
and participate in the classroom. It is supported by
Christenson et al (2012:162) that the student
engagement is further important because it affords
teacher the moment to moment feedback they need
during the lessons to assess how well their efforts to
motivate students are working to give feedback
during learning prosess. It means that, the teachers
are not only to be instructor but also they have to
give feedback by motivating the students during
teaching and learning process in order that they
know of improving the ability of their students.
Student engagement as student willingness to
participate in routine school activities, such as
attending classes, submitting required work, and
following teachers instructions in class. It includes
participating in the classroom activities in learning
English. Futhermore, to increase students’
engagement, the teachers may create lessons,
assignments, or projects that motivate to student
interests or that stimulate their curiosity. For
example, teachers can give students choice about
the topics they are asked to write about or they may
let students choose the way they will investigate
about a topic or demonstrate what they have
learned. Student engagement has been defined as
participation in educationally effective, both inside
and outside the classroom. It means that the
students not only participate in classroom but also
they have to be active outside of the classroom.
In learning English, students should be following
the subject matter to get the high score of education
in the classroom. With cognitive engagement,
students can be motivated, interest and interactive
to follow studying in the classroom. Moreover, in
students’ engagement, teacher gives opportunity to
students to participate during they are learning.
Students engagement is one of things that
has been included in teaching learning process. The
students have to participate in learning process and
they also have to have creativity in making the task
because of that they have to improve their ability in
learning material. According to Riley and Louis
(2000:56) student engagement is quite similar to the
‘social cohesion’ variable as a dependent measure
for her test of the effects of community like school
qualities on students. It means that, students
engagement is the thing to see the qualities of
students’ in the classroom. In other hand, student
engagement in the classroom considers how
students do in learning, and how engaged students
in participation, communicative and interactive
between teacher and students in the classroom.
Student engagement also refers to student’s
willingness, need, desire and active to participate
in, and be successful in the learning process.
According to Abbott (2016) there are some
forms of students’ engagement, it can be seen
1. Intellectual engagement:To increase
student engagement in a course or subject,
teachers may create lessons, assignments, or
projects that appeal to student interests or
that stimulate their curiosity. For example,
teachers may give students more choice
over the topics they are asked to write about
(so students can choose a topic that
specifically interests them) or they may let
investigate a topic or demonstrate what they
2. Emotional engagement: Educators may use
a wide variety of strategies to promote
positive emotions in students that will
facilitate the learning process, minimize
negative behaviors, or keep students from
3. Behavioral engagement:Teachers may
establish classroom routines, use consistent
cues, or assign students roles that foster
behaviors more conducive to learning. For
example, elementary school teachers may
use cues or gestures that help young
students refocus on a lesson if they get
4. Physical engagement:Teachers may use
physical activities or routines to stimulate
“kinesthetic learning” refers to the use of
physical motions and activities during the
5. Social engagement:Teachers may use a
variety of strategies to stimulate engagement
through social interactions. For example,
students may be paired or grouped to work
collaboratively on projects, or teachers may
create academic contests that students.
6. Cultural engagement:Schools may take
active steps to make students from diverse
cultural backgrounds—particularly recently
arrived immigrant or refugee students and
their families—feel welcomed, accepted,
In addition, Blumenfeld and Paris (2004, 62-
63), drawing on Bloom (1956), usefully identify
three dimensions to student engagement, as
Students who are behaviourally engaged
would typically comply with behavioural
norms, such as attendance and involvement,
and would demonstrate the absence of
Students who engage emotionally would
experience affective reactions such as
interest, enjoyment, or a sense of belonging
Cognitively engaged students would be
invested in their learning, would seek to go
beyond the requirements, and would relish
Cognitive engagement is the extent to which
students’ are able to take on the learning task. This
includes the amount of effort students are willing to
invest in working on the task. Clarke (2002:133)
states that cognitive engagement involves the
thinking that students do while engaged in
academic learning task. It means that, cognitive
engagement is engaged students in learning task
which related students thinking and knowledge in
Furthermore, Sharan and Than (2008:41)
describes that cognitive engagement is related to
motivational goals and self regulated learning. It
means that, how the students classroom do in
learning which purpose to motivation for their self
and how to arrange their strategy in learning to get
a good mark in English learning. In addition, in
teaching and learning process, the teachers have
motivate the student in order that they can
participate or active in the classroom.
Christenson et al. (2012:161) states that
cognitive in students engagement is related to
strategic learning strategies, and active self
regulation. This type can be seen with investment in
learning, flexible problem solving, independent
work styles and so on. In this case, the students and
the teachers have to have their own strategy in
learning to make good atmosphere in that learning.
The researcher had better discuss about the
forms of cognitive engagement. Clarke (2002:133)
states that four forms of cognitive engagement:
Where students cognitive processing is driven by
higher-order or metacognitive component.
Where students use task-specific planning and
self monitoring, for task where information
rather than acquisition is required.
Which students garner help from external
In which student respond passively with little
mental investment, often to instruction which has
short circuited their self-regulatory cognitive
This theory explains the forms of cognitive
engagement, if students active in the learning, so
that cognitive engagement is maximally and
interaction between teacher and student be positive
Furthermore, Robb (2004:15) describes that
students who are cognitively engaged in the
learning process think deeply about the newly
presented information and use self regulated
learning strategies that increase their understanding
of the material. The self-regulated student is able to
differentiate between facts and skills they do or do
not know and possess. He/she is able to assess the
academic task and set goals for studying. In
addition, the self-regulated learner monitors and
regulates his/her cognitions and behaviours, and
implements adjustments to the learning approach
when needed to ensure academic success.
In addition, Evertson and Weinstein
(2011:224) explain that self-regulated learning is
the highest forms of cognitive engagement.
Engagement in self regulated learning is somewhat
taxing. When task make cognitive demands, student
may engage in self regulated learning. They may
also shift the mental burden by calling upon
available external resources such as willing and
knowledgeable peer. Self regulated learning will be
shown to consist of specific cognitive activities,
such as deliberate planning and monitoring, which
learners carry out as they encounter academic tasks.
Learning is a process of someone in
developing their knowledge, behaviour; experience
in life. According to Bianco et al (2009:206) state
that English learning is unlike the teaching and
learning of other foreign language in ways beyond
issues of scale or size. It means that learning
English is not the same with other language because
students learn English as foreign language . The
students will learn English as a foreign language to
use as way to communication in the world.
Furthermore, English learning is not only learning
about the language, but also it is way to
communication. Littlejohn and Hicks (2003:07)
suggest that English learning is tremendous energy
and imagination, in which the students feel that a
whole new world is opening up for them as they
learn to express themselves in another language. It
can be said that English learning is learning English
as foreign language to make the students able to
communicate to other in expressing their ideas.
In addition, Toohey (2000:14) states that
learning is a process that takes place in a
participation framework, not in an individual is the
community, or at least those participating in the
learning context. It means English learning process
is a process of learning English as foreign language
in the school. Learning English language, the
students can use to communicate with the other.
Then it also can increase their knowledge. In
conclusion, English learning process is the process
of teaching and learning of the students to develop
their ability in English language. In learning
process the teacher will teach them about the
materials to increase their knowledge. Then, the
teacher will give them some exercises that occur
with materials to know their understanding and to
get value of them. So that the teacher know what
will do to the future to teach them well.
Cognitive engagement is really important to
influencing a learner’s active use of purposeful in
classroom learning and by using this engagement
the students can be motivated, interested and
interactive to follow studying in the classroom.
Thus, students engagement is really significant in
learning process because they want to get feedback
from instruction who give from their teacher, and
known students effors to learn and also to motivate
students work in classroom activity.
engagement gives opportunity to students active
maximally in learning and can applicant their
learning in real life situation. In learning process
especially in learning English, the students should
be following the subject matter to get the high score
of education in the classroom. With students’s
engagement, students can be motivated, interest and
interactive to follow studying in the classroom.
Moreover, in students’ engagement teacher gives
opportunity to the students to participate while they
are learning. So that, the teachers have to create the
lesson, assignment, project in learning that can
make the students interested in learning process.
[1] Bloom, B.S. (ed .) (1956). Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: the
Classification of Educational Goals. New York: D McKay & Co,
[2] Christenson, S. L, Amy L. R and Chaty, W. (2012). Handbook of
Research on Students Engagement. USA:Springer Science.
[3] Clarke, D. (2002). Perspective on practice and meaning in mathematics
and science classroom. New York: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
[4] Evertson, C. M and Weinstein, C. S. (2006). Handbook of Classroom
Management: Research, Practice and Comtemporary Issues. New
[5] Riley, K. A and Louis, K. (2000). Leadership for change and school
reform international perspectives. Canada and USA: Routledge
[6] Robb, M. K. (2004). Factors that Influences Cognitive Engagement
andAcademic Success of Pre-Licensure Baccalaureate Millennial
Nursing Students. Indiana University of Pennsylvania.
[7] Sharan, S and Geok, I. T. (2008). Organizing schools for productive
[8] Toohey, K. (2000). Learning English at School: identify, Social
Relations and Classroom Practice. Aberystwyth, UK: Cambrian
[9] http://edglossary.org/student-engagement/
ResearchGate has not been able to resolve any citations for this publication.
A team of researchers centred at the University of Melbourne, each with particular areas of expertise, contributed their analyses of a shared collection of videotape, interview, and documentary data. The result is a variegated picture of science and mathematics classrooms that challenges a research tradition that converges on the truth. In this book, we surround you with different images of the classroom. It is hoped that some will address issues of interest, some will confirm beliefs you have long held, some will challenge these same beliefs, and some may surprise you. The resulting account should appeal to educational researchers, research students, and practitioners with an interest in optimising the effectiveness of classrooms as environments for learning.
This book offers an alternative approach to secondary school organization. In line with the definition formulated by John Dewey's philosophy of education, the new approach aims to promote productive learning. The book shows the way to extricate schools from their past in order to respond more successfully to the requirements of the information age in which we are living today. The chapters treat the primary components of teachers' work in schools in light of systems' theory as opposed to the organization of instruction prevalent in today's schools that is designed in light of bureaucratic theory. The book demonstrates how the current principles of organization impede the change and improvement of instruction and by necessity create boredom and the routinization of teachers' and students' activity in schools.
Handbook of Research on Students Engagement
Christenson, S. L, Amy L. R and Chaty, W. (2012). Handbook of Research on Students Engagement. USA: Springer Science.
Handbook of Classroom Management: Research, Practice and Comtemporary Issues
Evertson, C. M and Weinstein, C. S. (2006). Handbook of Classroom Management: Research, Practice and Comtemporary Issues. New Jersey: Routledge.
Leadership for change and school reform international perspectives
Riley, K. A and Louis, K. (2000). Leadership for change and school reform international perspectives. Canada and USA: Routledge Falmer.
Factors that Influences Cognitive Engagement andAcademic Success of Pre-Licensure Baccalaureate Millennial Nursing Students
Robb, M. K. (2004). Factors that Influences Cognitive Engagement andAcademic Success of Pre-Licensure Baccalaureate Millennial Nursing Students. Indiana University of Pennsylvania.
August 2007 · Evaluation & Research in Education
The current study combines multiple lines of research on student/teacher relationships, to identify characteristics of liked teachers and examine the impact of liking or disliking the teacher on student learning and motivation. The study compared motivation data related to liked and disliked teachers from 125 students. Participants completed two versions of a motivation survey assessing their ... [Show full abstract] goals, perceived ability, effort and persistence. The findings suggest that when students like a teacher they experience motivational and achievement benefits.
December 2014 · New Directions for Institutional Research
This chapter describes the impact that participation in the Carnegie Classification for Community Engagement had on the institutions of higher learning that applied for the classification. This is described in terms of changes in direct community engagement, monitoring and reporting on community engagement, and levels of student and professor involvement in service learning and engagement ... [Show full abstract] projects.
August 2015 · Communication Teacher
This assessment examined the presence of anti-citizenship behavior (ACB) in the college classroom by (1) identifying the types of ACB college students use in their classes, (2) identifying the reasons why students use ACB, and (3) exploring the link between ACB and student learning outcomes. The results indicated that (1) participants report four types of ACB (i.e., participatory, technological, ... [Show full abstract] physical, and etiquette) used in their classes; (2) participants attribute the use of ACB to either their classmates or their instructors; and (3) perceived classmates’ use of ACB is negativ
Incest Porn Son Mother Mom
Mom Incest Less
Instant Incest
Incest Son Anal
Japanese Incest Jav
Effective tools and techniques of formation of cognitive ...
Formation of cognitive interest in primary school children ...
(PDF) Student’s Cognitive Engagement in Learning Process
Monitoring the Students’ Cognitive Interest in Math Class
Intellectual and Cognitive Development in Children and ...
Cognitive Interest - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Cognitive Interest Of Younger Students











/172601177-56a7934c5f9b58b7d0ebd68d.jpg)









/2795729-psychology-paper-topics-5b06ee8c119fa8003aba74b5.png)





/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)