Chinet litepaper
Chinet team
Abstract
“Potentially, blockchain can free talented people from intermediaries: it will reduce the dependence of authors on producers, startups on venture capitalists. Money transfers have already become cheaper, easier and faster, and in the future, the most fair elections can be held on the blockchain, where every vote will be taken into account.”
– Vitaly Buterin (founder of Ethereum)
“Bitcoin is the beginning of something great: a currency without a state, something necessary and extremely important ... but it will take a long time to establish universal trust in it.”
– Nassim Taleb (American economist, publicist and Ph.D.)
“We can talk about three eras of currency: a currency based on a commodity / product, a currency based on a political basis, and now it is a currency with a mathematical foundation.”
– Paul Graham (Creator of Yahoo Store)
“Bitcoin will do to banks what email did to the postal industry.”
- Bill Gates (Microsoft co-founder)
“Virtual currencies may have long-term potential, especially if innovation leads to a faster, more reliable and efficient payment system.”
– Chris Dixon (co-founder of Hunch)
“Within a decade, cryptocurrencies will change the Internet, the financial system and money in a way that ensures the protection of the rights and position of the individual. Cryptocurrencies will contribute to your privacy, comparable in importance to the creation of a printing press, a personal computer and the Internet.”
– Tyler Winklevoss (co-founder of Gemini cryptocurrency exchange)
"Asymptotically ideal money is a modified version of ideal money that starts with some imperfections but gradually moves towards the ideal over time."
from John F. Nash Jr.'s lecture, "Ideal Money and Asymptotically Ideal Money"
Introduction
Due to the ambiguous attitude of some countries and state regulators towards digital currencies in general, our team decided to keep the confidentiality of the team members. We believe that a crypto project or digital currency should not be tied to any state and fall into anyone's jurisdiction. The only body that has influence on a crypto project should be the community gathered around this project. We still believe and try to preserve the freedom and independence of the Internet.
At this stage of the adoption of cryptocurrencies by the world community, P2P relationships and markets for information goods and services and intellectual property are most suitable for their use. The volume of these markets is more than 5 trillion dollars. A significant part of these volumes can be served by digital currencies. Our primary goal is to popularize cryptocurrency and dApps among ordinary users and further promote blockchain technologies to serve business processes.
In this document, we will consider only the general directions for the development of the Chinet project, without deepening into the technical component. The Litepaper will be interesting for users to understand the general concept of the project. It will be important for us to receive feedback and comments from the community in order to approve or adjust some of the tasks. More technical details will be provided in a Whitepaper currently under development.
The launch of Chinet was announced in advance, the blockchain started without a premine, thereby leveling the chances of the community and developers to mine the coin. With this action, we secured the status of a decentralized project.
An overview of the technologies used by Chinet
The CryptoNote protocol
The CryptoNote protocol is a privacy-focused protocol for creating cryptocurrencies. It was first introduced in 2014 by an anonymous group of developers and has since been used to create several private and confidential cryptocurrencies.
The CryptoNote protocol uses several cryptographic techniques to enhance the privacy and security of cryptocurrency transactions. One of the key features of the protocol is ring signatures, which allow users to sign transactions without revealing their identity. This makes it difficult for outside observers to determine who sent a transaction or how much was sent.
Another key feature of the CryptoNote protocol is stealth addresses, which allow users to generate a unique address for each transaction. This makes it difficult for outside observers to link multiple transactions to the same user.
The first cryptocurrency to use the CryptoNote protocol was Bytecoin, which was launched in 2012. However, Bytecoin faced several controversies, including allegations of a pre-mine and lack of transparency, which led to its delisting from several cryptocurrency exchanges.
In 2014, a group of developers forked the Bytecoin codebase to create a new cryptocurrency called Monero. Monero was designed to be more transparent and community-driven than Bytecoin, with a focus on privacy and security.
Since its launch, Monero has become one of the most popular privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, with a market capitalization of over $3 billion as of January 2023. Its popularity is due in part to its strong privacy features, which make it difficult for outside observers to determine the identity of users or the amount of cryptocurrency being sent.
The CryptoNote protocol has played a significant role in the development of private and confidential cryptocurrencies. While it has faced some controversy and criticism, its strong privacy features have made it an attractive option for those seeking a more private and secure alternative to traditional cryptocurrencies. As the cryptocurrency industry continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how the CryptoNote protocol and other privacy-focused technologies shape the future of digital currencies.
Decentralized applications, or dApps
Decentralized applications, or dApps, are a promising new technology that offer several possibilities for users and businesses. DApps are built on decentralized networks, typically using blockchain technology, and are designed to be secure, transparent, and free from the control of any single entity or authority.
One of the most significant possibilities for dApps is in the realm of financial services. Decentralized finance, or DeFi, has emerged as a significant use case for dApps. DeFi platforms offer users access to decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading services, which can operate without intermediaries, lowering transaction costs and increasing transparency.
Another significant possibility for dApps is in the area of supply chain management. DApps can be used to track goods and products in real-time, from manufacturing to delivery. By utilizing a decentralized network, supply chain DApps can offer increased transparency and traceability, reducing the potential for fraud and errors.
Decentralized social media platforms have also emerged as a possibility for users who value privacy and control over their data. These dApps can operate without a centralized authority, allowing users to interact and share content without the threat of censorship or data breaches.
DApps can also be used for gaming, offering users the ability to participate in decentralized games and competitions, with provably fair results and no centralized authority controlling the game's outcome.
The prospects for dApp development are promising, with new use cases and applications being developed constantly. Interoperability is a significant challenge that dApps will need to overcome, as the number of blockchain networks and dApps grows. DApps that can operate seamlessly across multiple networks will offer users more flexibility and convenience.
As dApps move beyond the early adopter phase, developers will need to focus on improving the user experience to attract a broader user base. DApps that are easy to use and offer intuitive interfaces will be more successful in attracting new users.
Scalability remains a significant challenge for dApps, with many current applications struggling to handle large volumes of transactions. DApp developers will need to focus on developing scalable solutions to ensure their applications can handle the demands of a larger user base.
In conclusion, dApps offer several possibilities for users and businesses, and their development prospects are promising. As the dApp ecosystem continues to evolve, we can expect to see new use cases and applications emerge, offering increased transparency, privacy, and security to users. DApps have the potential to disrupt traditional centralized systems, and their growth will depend on their ability to provide value to users and compete with traditional centralized systems.
AI language models
AI language models have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with computers and process natural language. These models are already being used for a variety of applications, including chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated content creation.
One of the most exciting possibilities for AI language models is their ability to generate human-like responses to natural language prompts. This has the potential to enable more natural and intuitive interactions with computers, making it easier for people to perform tasks and get information.
Another possibility for AI language models is their ability to learn and adapt over time. As these models are trained on more data and exposed to more natural language, they can improve their accuracy and effectiveness. This has the potential to make AI language models even more useful for a wider range of applications.
AI language models also have the potential to revolutionize industries such as journalism, marketing, and content creation. These models can be used to generate news articles, product descriptions, and social media posts, freeing up human writers to focus on more creative and strategic tasks.
In addition, AI language models can be used to improve accessibility for people with disabilities. For example, text-to-speech and speech-to-text applications can enable people with hearing or speech impairments to interact more easily with computers and mobile devices.
The problem of the lack of mass implementation of blockchain technologies
The mass adoption of blockchain technologies, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized applications (dApps) has faced several obstacles, despite their potential to disrupt various industries. One significant challenge is the complexity and usability of these technologies, which can be intimidating and confusing for average users. User interfaces of wallets, exchanges, and dApps need to be more user-friendly, and the management of private keys and understanding of underlying concepts must be simplified.
Scalability and performance issues have also plagued prominent blockchain networks like Ethereum, leading to slow transaction times and high fees. These limitations make cryptocurrencies and dApps less appealing for everyday use, particularly for microtransactions or time-sensitive operations. Furthermore, the evolving legal and regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies creates uncertainty, potentially deterring businesses and users from adopting them due to concerns about compliance, taxation, and legal issues.
Security and privacy concerns have also hindered widespread implementation. High-profile hacks, scams, and other security breaches in the crypto space have fueled skepticism and mistrust. Additionally, the pseudonymous nature of many cryptocurrencies raises privacy concerns, as transactions can potentially be traced and analyzed to reveal users' identities.
Another challenge is the fragmentation of the blockchain ecosystem, with numerous platforms, protocols, and cryptocurrencies often being incompatible with each other. This lack of interoperability makes it difficult for users and businesses to navigate the landscape and limits the potential for seamless integration of blockchain technologies into existing systems.
The lack of awareness and education about the benefits and potential use cases of blockchain technologies, cryptocurrencies, and dApps has also contributed to slow adoption. Misconceptions, fear, and resistance can result from limited understanding. Moreover, the volatile nature of cryptocurrency prices can deter users and businesses from using them for transactions, as fluctuations in value can lead to losses or gains. The association of cryptocurrencies with illicit activities, market manipulation, and speculative bubbles has further contributed to a negative perception.
Lastly, implementing blockchain technologies can require significant investments in infrastructure, resources, and expertise. For example, the energy consumption associated with Proof of Work consensus mechanisms in some cryptocurrencies raises sustainability concerns and can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
To address these challenges and accelerate mass implementation, efforts should be directed towards simplifying user interfaces, improving scalability and performance, fostering a clear and supportive regulatory environment, enhancing security and privacy, promoting interoperability, raising awareness, and addressing infrastructure and resource concerns. By tackling these issues, the full potential of blockchain technology can be realized, leading to widespread adoption and significant disruption across various industries.
How Chinet solves some problems of blockchain technologies
Easy to use private wallet
Cryptocurrency private wallets are an essential tool for those who want to securely store and transact their digital assets. However, for many people, the complexity and technical nature of these wallets are intimidating, making it difficult for them to participate in the crypto space. This is why the new Chinet wallet is being developed.
The Chinet wallet will be designed to be highly accessible and easy to use, bringing the power of CryptoNote transactions to everyone. With this single cross-platform wallet, users will be able to securely send and receive untraceable financial transactions with ease, just like using a banking app.
One of the key features of the wallet will be its emphasis on security and anonymity. The wallet will use advanced encryption methods to keep user data and assets safe from prying eyes, while also providing complete anonymity for users who value privacy.
The Chinet wallet will also boast a user-friendly interface that is intuitive and easy to navigate. Even those who are new to the world of cryptocurrencies will quickly get up to speed and start making transactions in no time.
The Chinet will be a game-changer in the world of cryptocurrency private wallets, offering a user-friendly and accessible platform for secure, anonymous, and easy transactions. With its advanced security features and intuitive design, the Chinet wallet will be a great option for anyone looking to get involved in the world of cryptocurrencies.
Chinet and e-commerce
The Chinet is focused on making it easy for merchants to integrate the cryptocurrency into their existing e-commerce platforms and payment services.
To achieve this goal, the Chinet team is developing plugins and other elements specifically for e-commerce engines. These plugins will allow merchants to deploy and use Chinet on major e-commerce platforms with ease. We also create guides and documentation to help merchants get started with Chinet. This documentation will make it easy for merchants to understand how to integrate Chinet into their existing e-commerce platforms, reducing the time and effort needed for deployment. In addition, our team will be committed to providing ongoing support so that merchants can successfully use Chinet in their e-commerce business.
Moreover, Chinet is set to be integrated into popular cryptocurrency payment services, making it even easier for merchants to accept payments. This integration will allow customers to pay with Chinet across a wide range of e-commerce platforms, increasing Chinet's reach as a popular payment method.
With these developments, Chinet is set to become a major player in the e-commerce space. By providing merchants with easy-to-use tools and comprehensive documentation for integrating cryptocurrency into their platforms, Chinet will enable customers to use this secure and anonymous digital currency for their online purchases.
Chinet subnet on the Avalanche blockchain
Avalanche is an open, programmable smart contracts platform for decentralized applications. Most people know Avalanche as an EVM-compatible blockchain that has gained significant traction. However, there is much more to Avalanche, including many more blockchains!
Many Avalanche users are only familiar with the C-Chain, which forked the Ethereum Geth client to add support for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), but there are actually 3 chains in Avalanche’s Primary Network. But in addition, one of Avalanche’s core innovations is the ability to create highly scalable and customizable blockchains called Subnets.
With limited blockspace and demand rising, fees have risen on the C-Chain. And while there are improvements that can be made, scaling to meet demand requires more blockspace or more efficient use of existing blockspace (i.e. off-chain computation via Layer 2s). Subnets are Avalanche’s solution to this problem.
Instead of forcing all transactions to take place on a single, shared state, Subnets allow developers to launch their own blockchains– creating more blockspace and computation to meet demand.
A Subnet is a sovereign network which defines its own rules regarding its membership and token economics. It is composed of a dynamic subset of Avalanche validators working together to achieve consensus on the state of one or more blockchains. Each blockchain is validated by exactly one Subnet, and a Subnet can have many blockchains. A validator may be a member of many Subnets.
Subnets are independent, they specify their own execution logic, determine their own fee regime, maintain their own state, facilitate their own networking, and provide their own security. They don’t share execution thread, storage1 or networking with other Subnets including the Primary Network, effectively allowing the network to scale up easily while enabling lower latency, higher transactions per second (TPS), and lower transaction costs provided by the Avalanche Consensus.
A Subnet manages its own membership, it can create its own token economics and rules, and may require that its constituent validators have certain properties.
The Avalanche ecosystem has grown popular over the past year for a number of reasons and quite a few of Avalanche’s strong points are directly applicable to prospective Subnets. Each of the following functionalities can be leveraged by Subnets launching their own blockchain:
Fast finality: Avalanche’s consensus mechanism is unique in that it reaches finality on a transaction within a single block, which typically takes 2 seconds on the C-Chain. Similarly, Subnets can achieve this fast finality on their blockchains by using Avalanche’s consensus mechanism.
Unbounded number of validators: Allowing more validators on a network means more decentralization. Avalanche’s consensus mechanism is able to maintain fast block times while increasing to an unbounded number of validators. This is in contrast to many other PoS consensus mechanisms that slow down as the number of nodes in the network increases.
Future Subnet Interoperability: Most Subnets will likely want to connect to existing blockchains in order to onboard users. While native interoperability within the ecosystem isn’t available yet, the Ava Labs team is in the process of building out Cross-Subnet Transfers, bridging Avalanche’s Primary Network (P, X, and C Chains) and Subnets alike. In the meantime, each Subnet can choose a 3rd party option to support bridging to and from their ecosystem.
Chinet builds its subnet on the Avalanche blockchain, with its own set of rules focused on fast, low-fee transactions.
The Chinet subnet will be friendly to developers of smart contracts and decentralized applications in the field of financial services and governance. Below are some of them.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Asset Issuance, Automated Market Makers (AMMs), Borrowing & Lending, Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), Derivatives, Insurance, Peer-to-Peer Payments, Prediction Markets, Stablecoins.
Institutions, Enterprises, and Governments: Asset Issuance & Trading, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC), Debt Financing, Digital Identity, Document Tracking, Fund Management, Insurance, Intellectual Property, Lending, Real Estate, Supply Chain, Trade Finance.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Art, Certifications and Licenses, Collectibles, Credentials, In-game Items, Music.
Chinet AI language model
The Chinet team is developing and training an AI language model that will become an indispensable assistant when writing smart contract code in Golang. Even users with no programming experience will be able to create decentralized applications using Chinet AI.
The growing popularity of decentralized applications (dApps) and the rise of blockchain technology have placed smart contracts at the forefront of modern software development. Smart contracts are self-executing, autonomous pieces of code that run on blockchain networks, enabling trustless transactions and agreements between parties. As more developers and ordinary users venture into creating smart contracts, AI language models can play a vital role in simplifying the development process and enhancing the overall experience. We will explore how AI language models can assist both programmers and non-programmers in coding smart contracts for decentralized applications.
AI language models, such as OpenAI's GPT series, have been fine-tuned to understand programming languages, including those used for smart contracts like Solidity or Vyper. By providing a high-level description of the desired functionality or a few lines of code, AI language models can generate relevant code snippets or entire smart contracts. This capability can help developers and non-programmers alike to create smart contracts more efficiently, without having to master every aspect of the programming language.
Smart contracts often involve financial transactions, and even minor errors can lead to significant financial losses or vulnerabilities. AI language models can analyze smart contract code to identify potential issues, such as syntax errors, logical inconsistencies, or security vulnerabilities. By offering suggestions for improvements and best practices, AI language models can help users create more secure and reliable smart contracts, minimizing the risk of exploitation.
Testing and debugging are essential steps in the smart contract development process, as they help ensure the code's correctness and reliability. AI language models can assist users in generating test cases and identifying potential bugs or vulnerabilities in the smart contract code. By automating these time-consuming tasks, AI language models can streamline the development process and help users focus on higher-level design and implementation challenges.
For both experienced developers and non-programmers, learning the intricacies of smart contract programming languages and blockchain platforms can be a daunting task. AI language models can provide code examples, explanations, and recommendations to help users learn the necessary skills more quickly. By reducing the learning curve, AI language models can make smart contract development more accessible and encourage the adoption of decentralized applications.
AI language models can be integrated into development environments and collaboration platforms, streamlining the smart contract development process for both developers and non-programmers. By offering real-time code suggestions, error detection, and best practices, AI language models can facilitate more effective collaboration among team members, leading to higher-quality smart contracts and more efficient development workflows.
Proper documentation is essential for maintaining and understanding code, but it is often overlooked or considered a tedious task by developers. AI language models can help generate code comments and documentation automatically based on the code's context and structure, ensuring that the code is well-documented and easier to understand for both the original developer and other team members.
AI language models have the potential to revolutionize smart contract development for decentralized applications by simplifying the coding process, enhancing security, automating testing and debugging, facilitating learning, and promoting collaboration. As AI language models continue to advance, they are likely to become indispensable tools in the world of smart contract development, making it more accessible and efficient for both programmers and ordinary users. Embracing AI-powered assistance in smart contract development will not only save time and effort but also lead to more secure, reliable, and successful decentralized applications.
Economics of the coin and some technical data
Mainnet specification

*Coin supply
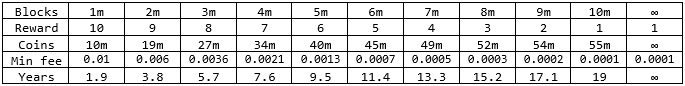
The reward for miners will decrease evenly every 1 million blocks until it equals 1 coin. The coin supply will be 55 million in the first 19 years and 0.525 million each year thereafter. The minimum fee will be reduced by 40% every 1 million blocks to a value of 0.0001. This solution will avoid high transaction costs when the value of the coin will rise relative to fiat currencies. The value of the minimum fee will be very low, but still enough to protect the network from DDoS attacks.
A more detailed specification and description of the Chinet mainnet will be provided in the next version of the Whitepaper.
Subnet specification

Token economics
The token supply will be 55 million. All tokens will be stored on a secure smart contract. The exchange of the token will take place through a specialized exchanger at the rate of 1 CHN = 1 CHNT. The token can only be exchanged for CHN and no other digital asset. Users will need the token to work with smart contracts and decentralized applications in the Chinet subnet. The specialized exchanger will provide a POS function for CHN coins, so that users do not miss out on profits while using the CHNT token.
A more detailed specification and description of the Chinet subnet will be provided in the next version of the Whitepaper.
Conclusion
Let's summarize the key points of the project:
1. Chinet is a cryptocurrency with the possibility of private transactions.
2. The private wallet will have a user-friendly, intuitive interface.
3. A set of plugins, payment services, and guides for e-commerce merchants will drive the mainstream use of Chinet.
4. The launch of the Chinet subnet will allow the community to run smart contracts and decentralized applications, with high transaction rates and fees approaching zero.
5. The AI language model will make the development of smart contracts and decentralized applications accessible to everyone.
The first goal of the project is to cover the markets of information products and services, as well as P2P relationships. Next is the integration of Chinet into business process maintenance.
Disclaimer
Cryptocurrency investments are inherently high risk. Before using any cryptocurrency, it is important to consider the nature, complexity, and risk. Do not invest more than you can afford to lose. It is important not to use coins without considering the possible loss, since the type of change in these currencies is highly volatile and the Chinet team is unable to regulate market-defined prices. We strongly suggest seeking advice from your own financial, investment, tax, or legal adviser. The Chinet Development Team will always act in good faith and is not liable for the use of Chinet by other community members, persons, or institutions.