Central Valley Escorts

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the region of California. For other uses, see Central Valley (disambiguation) .
Flat valley that dominates central California
Topography, major regions, and cities of the Central Valley
This section needs additional citations for verification . Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources . Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. ( January 2017 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message )
^ Official records for Sacramento were kept exclusively at the airport since 10 November 1941. [15]
^ Official records for Fresno kept September 1881 to 15 August 1887 at downtown, 16 August 1887 to June 1939 at Fresno City Offices, July 1939 to 20 August 1949 at Chandler Field, and at Fresno Yosemite Int'l since 21 August 1949. For more information, see Threadex
^ Jump up to: a b "California Central Valley" . American Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on October 29, 2016.
^ "Central Valley" . Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey .
^ "California's Central Valley: Producing America's Fruits and Vegetables" . House Committee on Natural Resources. Archived from the original on June 23, 2015 . Retrieved May 15, 2017 .
^ "Federal Agencies Release Data Showing California Central Valley Idle Farmland Doubling During Drought" . landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov . Archived from the original on April 10, 2016.
^ Jump up to: a b c d Bittman, Mark (October 10, 2012). "Everyone Eats There" . The New York Times . Archived from the original on October 13, 2012 . Retrieved October 10, 2012 . Central Valley, which is really two valleys: the San Joaquin to the south and Sacramento to the north. All told,[sic] the Central Valley is about 450 miles long, from Bakersfield up to Redding, and is 60 miles at its widest, between the Sierra Nevada to the east and the Coast Ranges to the west.
^ Jump up to: a b c d "A Statistical Tour of California's Great Central Valley" . California Research Bureau . California State Library. Archived from the original on May 3, 2009 . Retrieved July 27, 2009 .
^ Jennings, Joanne Elgart (November 1, 2010). "California's Central Valley Finds Itself on the Political Map" . PBS Newshour. Archived from the original on January 25, 2018 . Retrieved January 23, 2018 . About 6.5 million people live here, making it the state's fastest growing region, according to the 2010 U.S. Census. Between 1990 and 2009, the population here grew 44 percent (compared with 24 percent growth statewide).
^ "Hmong" . Science and Environment Podcast . University of California Merced . Archived from the original on July 21, 2011 . Retrieved September 20, 2010 .
^ "Physiographic divisions of the conterminous U. S." U.S. Geological Survey. Archived from the original on December 5, 2007 . Retrieved December 6, 2007 .
^ Benke, Arthur C.; Cushing, Colbert E. (2005). Rivers of North America . Academic Press. p. 554 . ISBN 0-12-088253-1 .
^ "California Central Valley grasslands" . Terrestrial Ecoregions . World Wildlife Fund . Retrieved November 13, 2011 .
^ Philip Garone, The Fall and Rise of the Wetlands of California's Great Central Valley (University of California Press; 2011)
^ Minkoff-Zern, Laura-Anne (2014). "Hunger Amidst Plenty: Farmworker Food Insecurity and Coping Strategies in California". Local Environment . 19 (2): 204–219. doi : 10.1080/13549839.2012.729568 . S2CID 154653581 – via ESBCO Host.
^ "Climate of California" . Western Regional Climate Center . .www.wrcc.dri.edu. Archived from the original on July 21, 2009 . Retrieved July 26, 2009 .
^ ThreadEx
^ Jump up to: a b "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved August 17, 2020 .
^ "Station Name: CA SACRAMENTO EXECUTIVE AP" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved July 19, 2020 .
^ "WMO Climate Normals for SACRAMENTO/EXECUTIVE ARPT CA 1961–1990" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved July 19, 2020 .
^ https://www.sacbee.com/news/databases/article5555742.html
^ "SACRAMENTO 5 ESE, CALIFORNIA" . Western Regional Climate Center.
^ "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved December 3, 2012 .
^ "Station Name: CA FRESNO YOSEMITE INTL AP" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved April 22, 2014 .
^ "WMO Climate Normals for FRESNO/AIR TERMINAL CA 1961–1990" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved March 11, 2014 .
^ "Average Weather for Fresno, CA – Temperature and Precipitation" . The Weather Channel . Retrieved September 20, 2011 .
^ "Sacramento River Basin National Water Quality Assessment Program: Study Unit Description" . United States Geological Survey . ca.water.usgs.gov. Archived from the original on August 13, 2009 . Retrieved July 26, 2009 .
^ "Restoring the San Joaquin River: Following an 18-year legal battle, a great California river once given up for dead is on the verge of a comeback" . Natural Resources Defense Council . www.nrdc.org. September 17, 2007. Archived from the original on July 9, 2009 . Retrieved July 26, 2009 .
^ Gorelick, Ellen. "Tulare Lake" . Tulare Historical Museum . www.tularehistoricalmueseum.org. Archived from the original on February 19, 2010 . Retrieved July 26, 2009 .
^ "Delta Subsidence in California: The sinking heart of the State" (PDF) . United States Geological Survey . ca.water.usgs.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 10, 2011 . Retrieved July 26, 2009 .
^ "Sacramento-San Joaquin River System, California" . American Rivers . America's Most Endangered Rivers Report: 2009 Edition. Archived from the original on January 17, 2010 . Retrieved July 26, 2009 .
^ The Columbia is the largest, with an average discharge of 265,000 cu ft/s (7,500 m 3 /s). The Sacramento comes next with a flow of 30,215 cu ft/s (855.6 m 3 /s), and even though the Colorado is much longer, its discharge is only about 10,000 cu ft/s (280 m 3 /s) to 22,000 cu ft/s (620 m 3 /s) (that is before diversions started; the river is currently dry at the mouth). Other significant rivers include the Klamath 17,010 cu ft/s (482 m 3 /s), Skagit 16,598 cu ft/s (470.0 m 3 /s), Snohomish 13,900 cu ft/s (390 m 3 /s), and San Joaquin 10,397 cu ft/s (294.4 m 3 /s).
^ "California's Central Valley" . National Public Radio. November 11, 2002. Archived from the original on October 16, 2010 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ Jump up to: a b Stene, Eric A. "The Central Valley Project: Introduction" . U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. Archived from the original on May 27, 2010 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ "Ecosystem Restoration: Systemwide Central Valley Chinook Salmon" (PDF) . CALFED Bay-Delta Program. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 27, 2010 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ "California State Water Project Overview" . California State Water Project . California Department of Water Resources. April 15, 2009. Archived from the original on May 27, 2010 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ "California State Water Project Today" . California State Water Project . California Department of Water Resources. July 18, 2008. Archived from the original on September 1, 2010 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ Anderson, David (July 4, 1999). "A temporary diversion" . Times-Standard . Archived from the original on January 3, 2010 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ "The Hetch Hetchy Aqueduct" . Aquafornia. August 19, 2008. Archived from the original on January 10, 2013 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ "Mokelumne Aqueduct" . Aquafornia. August 19, 2008. Archived from the original on January 10, 2013 . Retrieved May 27, 2010 .
^ "Sacramento Flood Protection" . Archived from the original on August 9, 2011.
^ Hart, Daniel (October 4, 2019). "Goliath Recap: Nothing Here, Is What It Seems. He's Back!" . RSC! . Ready Steady Cut.
^ BERGON, FRANK (August 30, 2019). "San Joaquin Valley's rich diversity shows America what it is becoming" . Fresno Bee . Archived from the original on September 14, 2019 . Retrieved October 2, 2019 .
^ "Archived copy" (PDF) . Archived (PDF) from the original on June 19, 2016 . Retrieved March 29, 2016 . CS1 maint: archived copy as title ( link )
^ “California Agricultural Production Statistics”
^ Reilly, Thomas E. (2008). Ground-Water Availability in the United States: U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1323 . Denver, CO: U.S. Geological Survey. p. 84. ISBN 978-1-4113-2183-0 .
^ Pollan, Michael (December 16, 2007). "Our Decrepit Food Factories" . The New York Times magazine . Archived from the original on November 18, 2011 . Retrieved November 13, 2011 .
^ Purdum, Todd S. (September 6, 2000). "California's Central Valley. Where the Mountains Are Almonds" . The New York Times . Retrieved December 16, 2008 . The state's 6,000 growers produce more than 600 million pounds a year, more than 70 percent of the world's supply and virtually 100 percent of domestic production.
^ "Production/Crops for almonds with shell" (database) . Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Statistics Division, FAOSTAT. 2013. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016 . Retrieved December 22, 2015 .
^ Parker, Timothy S. (October 27, 2011). "United States Fact Sheet: US agriculture income population food education employment unemployment federal funds farms top commodities exports counties financial indicators poverty food security farm income Rural Nonmetro Urban Metropolitan America USDA organic Census of Agriculture" . Ers.usda.gov. Archived from the original on June 26, 2012 . Retrieved November 13, 2011 .
^ Flores, Christina (March 1, 2011). "They Rule the Valley: The Story of How Large Central Valley Landholders Became the Primary Beneficiaries of the Central Valley Project" . UC Berkeley. Cite journal requires |journal= ( help )
Rivers of California's Central Valley watershed (north-to-south)
The Central Valley is a flat valley that dominates the interior of California . It is 40 to 60 miles (60 to 100 km) wide and stretches approximately 450 miles (720 km) from north-northwest to south-southeast, inland from and parallel to the Pacific Ocean coast. It covers approximately 18,000 square miles (47,000 km 2 ), [1] about 11% of California's total land area (or about the size of the Dominican Republic ). The valley is bounded by the Coast Ranges to the west and the Sierra Nevada to the east.
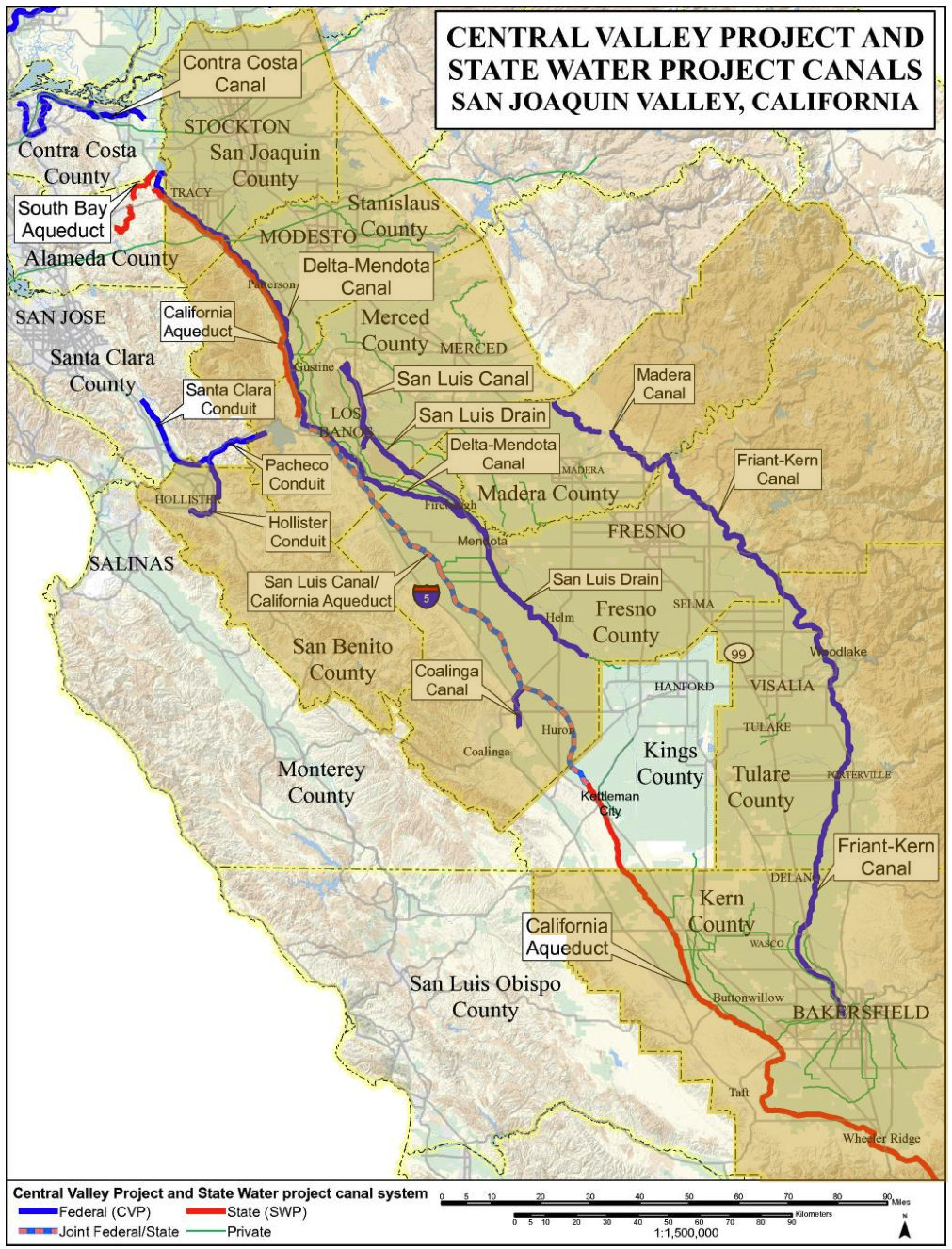
It is California's most productive agricultural region and one of the most productive in the world, providing more than half of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts grown in the United States. [3] More than 7 million acres (28,000 km 2 ) of the valley are irrigated via an extensive system of reservoirs and canals. [4] The valley also has many major cities, including the state capital Sacramento ; as well as Redding , Chico , Stockton , Modesto , Fresno , Visalia , and Bakersfield .
The Central Valley watershed comprises 60,000 square miles (160,000 km 2 ), or over a third of California. It consists of three main drainage systems: the Sacramento Valley in the north, which receives well over 20 inches (510 mm) of rain annually; the drier San Joaquin Valley in the south; and the Tulare Basin and its semi-arid desert climate at the southernmost end. The Sacramento and San Joaquin river systems drain their respective valleys and meet to form the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta , a large expanse of interconnected canals , stream beds , sloughs , marshes , and peat islands. [5] The delta empties into the San Francisco Bay , and then ultimately flows into the Pacific. [5] The waters of the Tulare Basin essentially never flow to the ocean (with the exception of Kings River waters diverted northward for irrigation), though they are connected by man-made canals to the San Joaquin. They could drain there again naturally if they were ever to rise high enough.
Older names include "the Great Valley," a name still often seen in scientific references (e.g. Great Valley Sequence ), and "Golden Empire," a booster name that is still referred to by some organizations (e.g. Golden Empire Transit , Golden Empire Council , etc.).
The Central Valley is roughly parallel to the Pacific coastline, outlined by the southern end of the Cascade Range in the north, Sierra Nevada in the east, and Tehachapi Mountains in the south, and the California Coast Ranges and San Francisco Bay in the west. The broad valley floor is carpeted by alluvial plains forming vast agricultural regions, and dotted with numerous population centers.
Subregions and their counties commonly associated with the valley include: [6]
There are four main population centers in the Central Valley, each roughly equidistant from the next, from south to north: Bakersfield , Fresno , Sacramento , and Redding . While there are many communities large and small between these cities (see below), these four cities act as hubs for regional commerce and transportation.
About 7.2 million people live in the Central Valley today, and it is the fastest growing region in California. [7]
There are 12 Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSA) and 1 Micropolitan Statistical Area (μSA) in the Central Valley. Below, they are listed by MSA and μSA population. The largest city is Fresno followed by the state capital Sacramento . The following metropolitan and micropolitan statistical areas listed from largest to smallest:
After English and Spanish, Hmong is the third most commonly spoken language in the Central Valley. [8]
The flatness of the valley floor contrasts with the rugged hills or gentle mountains that are typical of most of California's terrain. The valley is thought to have originated below sea level as an offshore area depressed by subduction of the Farallon Plate into a trench further offshore. The San Joaquin Fault is a notable seismic feature of the Central Valley.
The valley was enclosed by the uplift of the Coast Ranges , with its original outlet into Monterey Bay . Faulting moved the Coast Ranges, and a new outlet developed near what is now San Francisco Bay . Over the millennia, the valley was filled by the sediments of these same ranges, as well as the rising Sierra Nevada to the east; that filling eventually created an extraordinary flatness just barely above sea level; before California's massive flood control and aqueduct system was built, the annual snow melt turned much of the valley into an inland sea.
The one notable exception to the flat valley floor is Sutter Buttes , the remnants of an extinct volcano just to the northwest of Yuba City , which is 44 miles (71 km) north of Sacramento .
Another significant geologic feature of the Central Valley lies hidden beneath the delta. The Stockton Arch is an upwarping of the crust beneath the valley sediments that extends southwest to northeast across the valley.
The Central Valley lies within the California Trough physiographic section, which is part of the larger Pacific Border province, which in turn is part of the Pacific Mountain System . [9] [10]
The Central Valley was formerly a diverse expanse of grassland, containing areas of prairie , desert grassland (at the southern end), oak savanna , riparian forest , marsh , several types of seasonal vernal pools , and large lakes such as now-dry Tulare Lake (which was the largest freshwater lake in the United States west of the Mississippi), Buena Vista Lake and Kern Lake . However, much of the Central Valley environment has been removed or altered by human activity including the introduction of exotic plants , especially grasses. The valley's grasslands, wetlands, and riparian forests constitute the California Central Valley grasslands , a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion . The foothill oak woodlands and chaparral that fringe the valley have been categorized as the California interior chaparral and woodlands ecoregion. [11]
The dominant grass of the valley was Nassella pulchra mixed with other species, but today only 1% of the grassland in the valley is original and intact. Grassland flowers include California poppy ( Eschscholzia californica ), lupins , and purple owl's clover ( Castilleja exserta ), which can still be seen, especially in Antelope Valley in the Tehachapi Mountains . Riverside trees include willows, western sycamore ( Platanus racemosa ), box elder ( Acer negundo ), Fremont cottonwood ( Populus fremontii ), and the endemic valley oak ( Quercus lobata ).
The Central Valley was once home to large populations of pronghorn antelope ( Antilocapra americana ), elk including the endemic tule elk subspecies ( Cervus elaphus nannodes ), mule deer ( Odocoileus hemionus ), California ground squirrels , gophers , mice, hare, rabbits and kangaroo rats , along with their predators including the San Joaquin kit fox , which is now an endangered subspecies surviving on the hillsides of the San Joaquin Valley. The wetlands of the Valley were an important habitat for wintering waterbirds and migrating birds of other kinds. Reptiles and amphibians of the valley include the endemic San Joaquin coachwhip snake ( Masticophis flagellum ruddocki ), blunt-nosed leopard lizard ( Gambelia sila ), Gilbert's skink ( Eumeces gilberti ) and the western aquatic garter snake ( Thamnophis couchii ). There are also a number of endemic invertebrates. The Central Valley is also home to a wide variety of endemic fish species, including the Sacramento Pikeminnow , Sacramento Perch , Sacramento Blackfish , and Sacramento Splittail , among others.
The Great Valley Grasslands State Park preserves an example of the native grass habitat in the valley, while oak savanna habitats remain near Visalia . There are areas of wetland and riverside woodland in the north especially on the Sacramento River system including the Nature Conservancy 's Cosumnes River Preserve just south of Sacramento, Gray Lodge Wildlife Area , Butte Sink Wildlife Management Area , and other patches in the delta area. Remaining vernal pools include Pixley National Wildlife Refuge between Tulare, California , and Bakersfield and Jepson Prairie Preserve in the delta. There are large blocks of desert scrubland in the southern San Joaquin Valley and in the Carrizo Plain , which is just outside the valley but has a similar landscape.
The wetlands have been the target of rescue operations to restore areas nearly destroyed by agriculture. [12]
All these patches of natural habitat are disconnected and this is particularly damaging for wildlife that is used to migrating along the rivers of the valley. Agriculture, the creation of grazing land, and the draining of lakes and rivers have radically altered the habitats of the Valley. Most of the grassland has been overtaken by new species, most of the vernal pools have been destroyed with only those on the higher slopes remaining, the marshland has been drained, and the riverbank woodlands have nearly all been affected. [ citation needed ]
The valley gives its name to Valley fever , which is primarily a disease of the lungs that is common in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. It is ca
Cntral Valley Escorts | Форум
Central Valley (California) - Wikipedia
Центральная долина – Валье Сентраль - описание продукта на Gastronom.ru
Каталог вин региона Центральная Долина Чили Central Valley Chile
Japan Doggystyle
Jessica Jaymes Iafd
Charlie Cooper Porn Star
Central Valley Escorts