Binary Tree Paths
Sergei Golitsynhttps://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: ["1"]
Solution
Trees. We all love trees. What do we know about trees? BFS, DFS, in-order, pre-order, post-order =) a lot of exciting approaches.
This problem can be solved by pre-order approach. What is it mean? In the pre-order approach, we process the node and then the left and right subtree.
In our example, we process 1, then 2, check left --> null, process right subtree 5.
Then return upper and process 3.
A hope it is clear for you guys. If you have some questions, please ask me here --> https://t.me/crack_code_interview
So, we should add a String or string builder to save result strings. That is interesting that depending on the type of our strings, we will have different results.
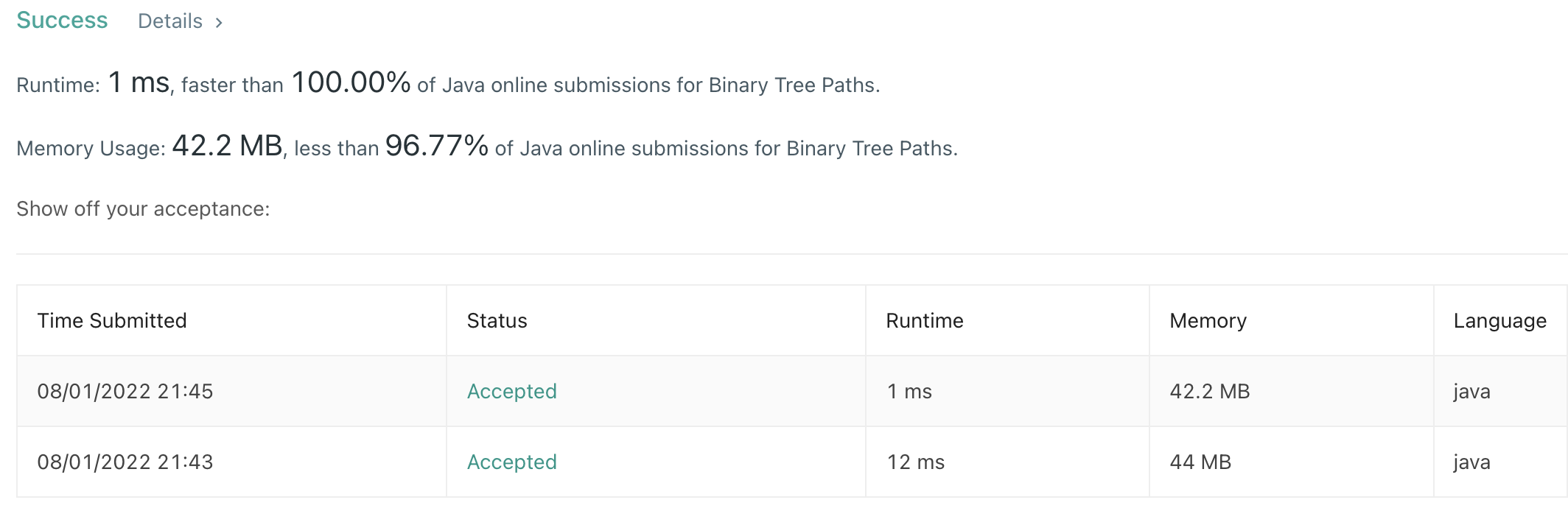
1ms with StringBuilder and 12ms with String. Huge, huge difference.
List<String> rez = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
preOrder(new StringBuilder(), root);
return rez;
}
private void preOrder(StringBuilder sb, TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
sb.append("->");
sb.append(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
rez.add(sb.toString().substring(2));
} else {
preOrder(new StringBuilder(sb), root.left);
preOrder(new StringBuilder(sb), root.right);
}
}
// Remove comments for tests
// private void preOrder(String sb, TreeNode root){
// if (root == null){
// return;
// }
// sb += "->" + root.val;
// if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
// rez.add(sb.substring(2));
// } else {
// preOrder(sb, root.left);
// preOrder(sb, root.right);
// }
// }