Beginning with Theoretical Concepts to Practical Use: Comprehending Vacuum-based Electrical Feedthroughs
Vacuum feed-throughs serve a key function in numerous research and commercial applications by facilitating the transmission of electrical currents or power into a vacuum chamber while not compromising the purity of the vacuum conditions. These specific components permit researchers and technicians to perform tests or operate processes inside a vacuum and ensuring that the surrounding conditions remains unaffected. With technology continues to advance, the significance of vacuum feedthroughs has only grown, requiring a more thorough understanding of their construction, operation, and impacts.
In settings such as particle accelerators, semiconductor fabs, and vacuum gauges, maintaining a good vacuum state is crucial for peak functioning. Vacuum electrical feedthroughs serve as the bridge between the external and internal frameworks, allowing for the safe and efficient conveyance of electronic currents. This article will examine the complexities of these components, investigating their design, operating principles, and the critical function they serve in contemporary technology. Grasping these devices is vital for those engaged in domains that rely heavily on vacuum systems.
Basics of Evacuated Electrónica Feedthroughs
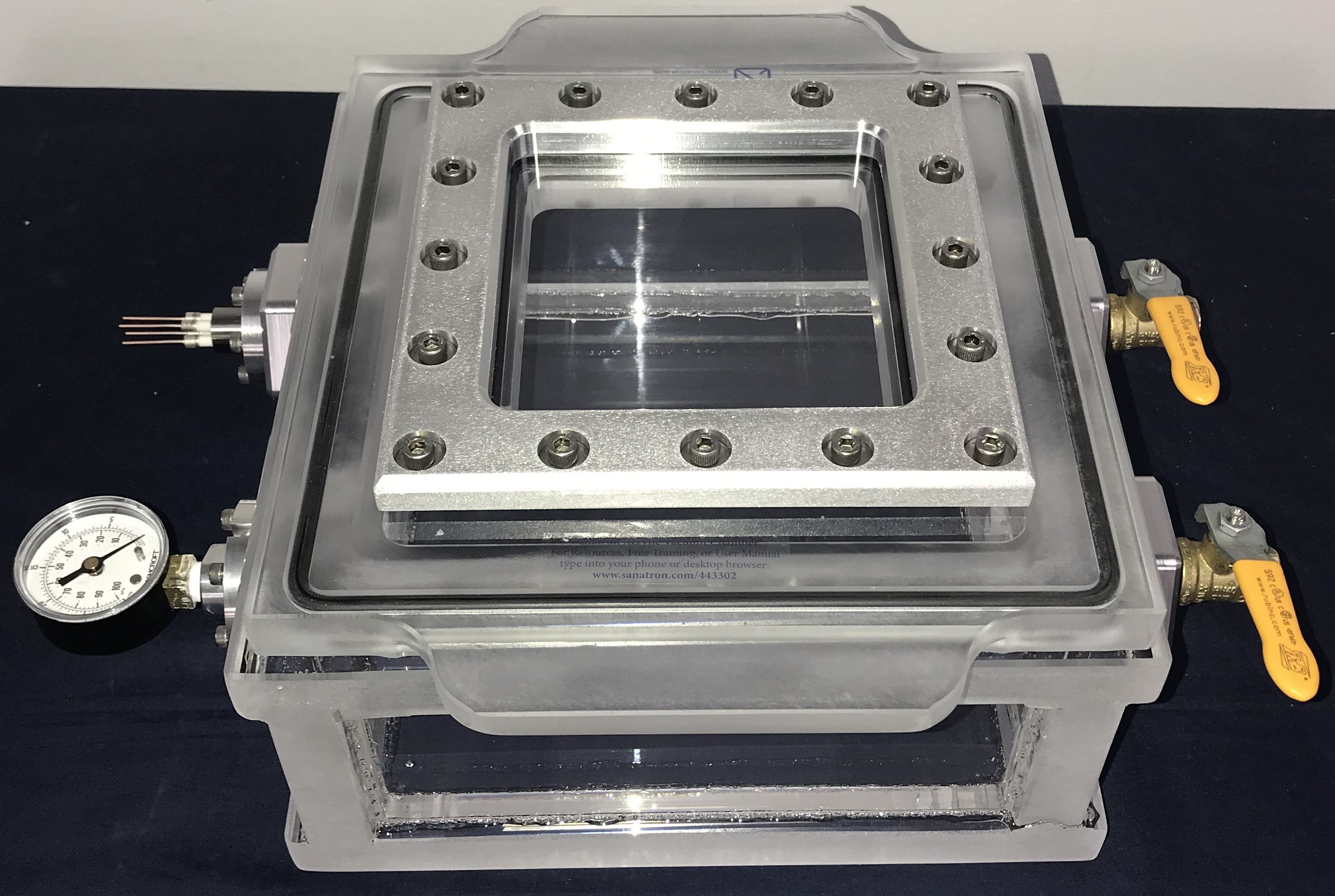
Pumped electrical connections are crucial components used in various scientific and industrial applications that involve the transmission of electrical currents through a sealed barrier. They serve as the link between the surrounding environment and the sealed chamber, allowing for the required electrical connections while preserving the integrity of the vacuum. This capability is essential in fields such as chip manufacturing, material science, and particle physics, where even the smallest interference can affect the experimental outcomes.
At their core, vacuum feedthroughs consist of electrical elements, usually conductive wires or pins, that are enclosed within a feedthrough structure which is made of materials such as ceramics or glass. The design guarantees the conductive pathways are insulated from the ambient environment, avoiding contamination and maintaining the desired vacuum pressure. Various configurations and materials can be employed to accommodate various requirements, such as high voltage applications or extreme temperatures.
The efficacy of vacuum electrical feedthroughs is affected by several elements, including the choice of materials, seal integrity, and the particular application conditions. Ensuring a robust seal is essential, as it stops gas loss that could undermine the vacuum. Additionally, careful consideration of thermal and electrical properties is necessary to ensure consistency and longevity in the intended application, making the choice of appropriate feedthrough types a key aspect of system design.
Uses in Various Sectors
Vacuum feedthroughs play a significant role in the semiconductor industry, where they are essential for maintaining the vacuum environment in fabrication equipment. These feedthroughs enable electrical signals to pass into vacuum chambers without hurting the integrity of the vacuum. This capability is critical for processes such as thin film deposition and ion implantation, where a regulated environment is vital for achieving superior semiconductor materials.
In the field of vacuum technology, these feedthroughs are broadly utilized in research facilities and laboratories. They facilitate experiments that require a vacuum environment, such as material science studies and surface analysis. By enabling researchers to connect instruments and sensors directly to samples in a vacuum state, these feedthroughs enhance the precision and dependability of experimental results.
Moreover, vacuum electrical feedthroughs find applications in the aerospace industry, particularly in satellite and spacecraft design. These components are used in different systems, including power distribution and communication modules, ensuring that electrical connections can be made while maintaining the necessary vacuum conditions. Their trustworthiness is essential for the success of missions, as failure of any system can lead to serious operational issues.
Challenges and Upcoming Innovations
One of the key challenges faced in the creation of vacuum electrical feedthroughs is guaranteeing their long-term durability under extreme environmental conditions. These elements must endure high temperatures, corrosive substances, and vacuum levels without degrading or losing performance. Researchers are diligently exploring advanced materials and novel designs to improve resilience, seeking solutions that can considerably extend the lifespan of feedthroughs in rigorous applications.
Another significant issue is the precise manufacturing of vacuum feedthroughs with consistent quality and performance. Variability in fabrication can lead to defects that weaken the integrity of the vacuum seal or the electrical connections. To tackle this, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing and microfabrication, are being investigated. These methods have the capability to create more reliable and compact feedthroughs while improving production scalability and decreasing costs.
Looking to the future, the integration of smart technologies into vacuum feedthroughs offers thrilling opportunities. As industries increasingly adopt automation and remote monitoring, embedding sensors within feedthroughs can provide valuable real-time data on their performance and environment. This innovation could foster predictive maintenance and facilitate proactive adjustments, ultimately boosting operational efficiency and reliability in systems reliant on vacuum electrical feedthroughs.