Beginning with Numbness through Suffering: The Nerve-related Journey
Neuropathy is a condition that impacts the nervous system, resulting in a range of issues that can differ greatly from person to individual. For many, the experience starts as a loss of feeling or prickling sensation, often in the hands and feet, which can slowly escalate to pain or soreness. Comprehending what neuropathy truly is requires delving into the complex web of the nervous system and realizing how its malfunction can deeply affect daily life.
As the nerves struggle to send signals properly, individuals may face not only sensory issues but also challenges in mobility and coordination. The shift from loss of feeling to discomfort can be alarming and confusing, prompting numerous individuals to seek answers about the root causes and potential treatments for their condition. Through this exploration, we aim to illuminate the complexities of nerve damage, providing insight into its symptoms, identification, and the path that numerous individuals endure in pursuit of relief.
Grasping Nerve Disorders
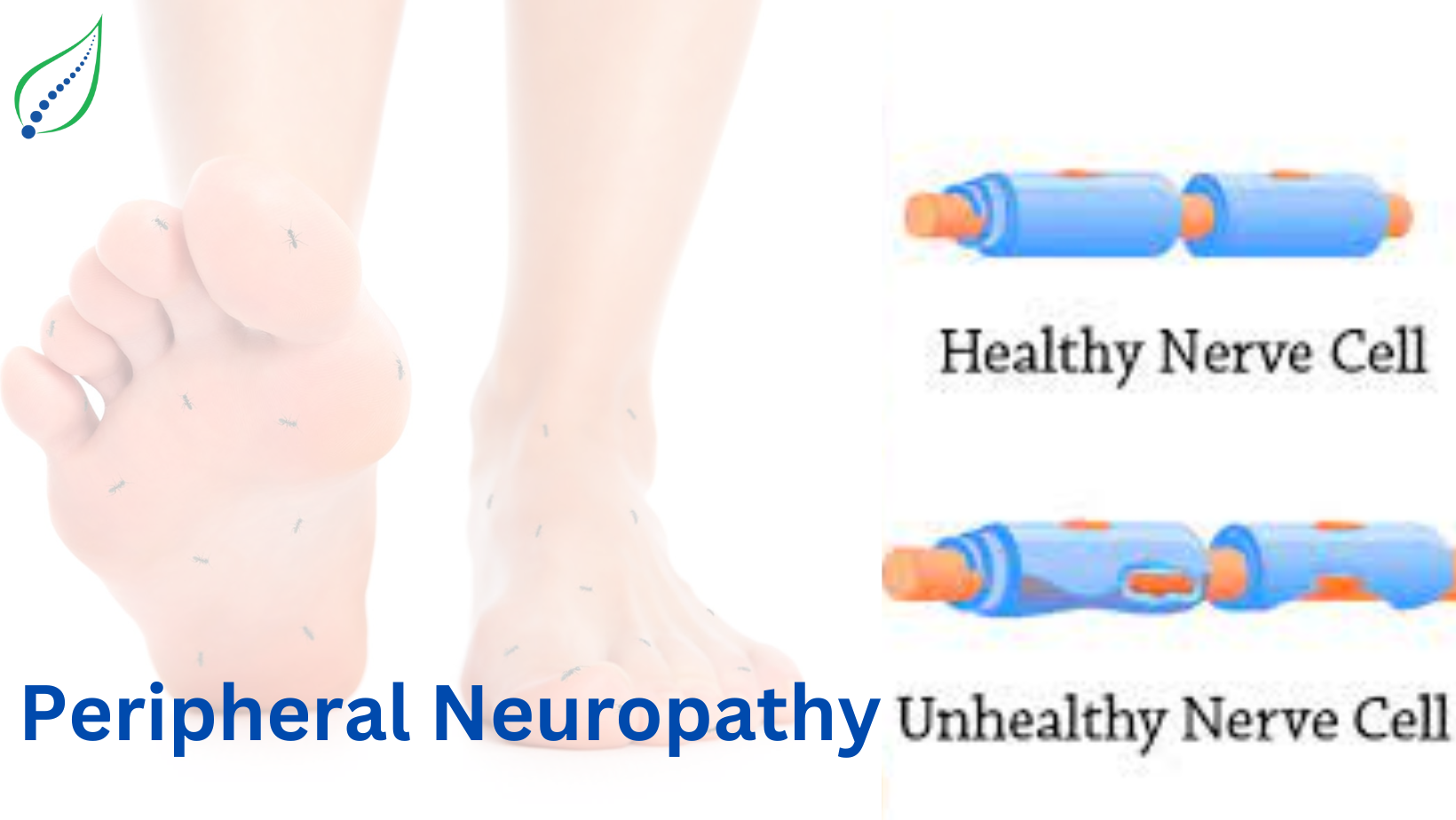
Nerve disorder refers to multiple ailments that develop as nerve fibers are injured or not functioning properly. This condition can influence various types nerves, including sensory, efferent and automatic nerves. The symptoms felt by individuals can be quite diverse, from tingling and decreased sensitivity to a searing ache and muscle weakness in the impacted regions. The intensity of these symptoms often depends on the kind of neuropathy and the level of nerve damage.
There are multiple causes of neuropathy, including diabetes, pathogens, genetic conditions, and exposure to toxins. Peripheral neuropathy, one of the frequent forms, primarily targets the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, which associate the CNS to the arms and legs and internal systems. Diabetes is a primary reason of neuropathy, as high blood sugar levels can harm nerves over time. Other factors can include nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, and particular pharmaceuticals.
The identification of neuropathy typically involves a mixture of health assessments, patient history, and evaluation methods, such as nerve function tests and serological examinations. new promise neuropathy differs depending on the root cause and may include therapeutic agents to manage symptoms, physical therapy, and modifications in daily habits. Comprehending the specifics of neuropathy is crucial for successful treatment and for improving the living standards for those suffering.
Signs and Diagnosis
Nerve damage presents a variety of symptoms that can vary considerably from individual to individual. Typical experiences include tingling, loss of sensation, and a stinging sensation, often beginning in the fingers or toes. Certain people may also experience intense, jabbing pains or increased sensitivity to touch, which can make it difficult to daily activities. Weakness in the muscles can happen, impacting mobility and coordination, making it difficult to perform simple tasks like fastening buttons or walking.
Identifying neuropathy involves a thorough evaluation of patient history and clinical assessments. Healthcare professionals often perform tests to assess sensory and muscle functions, which can include reflex assessments, tests for vibration sensitivity, and temperature sensitivity tests. In some instances, more advanced tests like nerve conduction studies or electromyography may be required to ascertain the degree of nerve injury and find the underlying cause of the symptoms.
Identifying the specific kind of neuropathy is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. Different types of neuropathy are linked with various conditions, such as sugar diabetes, infections, or autoimmune diseases. Once a determination is established, healthcare providers can suggest appropriate interventions, which may include medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle modifications aimed at relieving symptoms and improving the quality of life for those impacted.
Treatment Options
Treatment for neuropathy aims to relieve symptoms and address the underlying issues. Pain relief is a primary focus, often utilizing medications such as anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and topical analgesics to control discomfort. OTC pain relievers, including NSAIDs, may provide short-term relief for certain individuals. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol can significantly enhance symptoms and overall nerve health.
Physical therapy can be beneficial for those experiencing weakness or loss of coordination due to neuropathy. A physiotherapist can develop customized exercise regimens that help strengthen weakened muscles and boost mobility. Job therapy may also assist individuals in adapting daily activities to reduce discomfort and enhance living standards. Implementing adaptive strategies and assistive devices can empower people with neuropathy to manage their daily challenges more efficiently.
For those with neuropathy caused by specific conditions like diabetes, addressing the root cause is vital. This may involve working closely with medical professionals to manage blood sugar levels or addressing other underlying conditions. In some cases, complementary treatments like acupuncture, massage, or cognitive behavioral therapy have proven effective in alleviating neuropathic pain. It is crucial for individuals to consult with their healthcare team to create a comprehensive care strategy tailored to their individual needs.