Basic Terms of Hacking
Sudhanshu1. Phishing
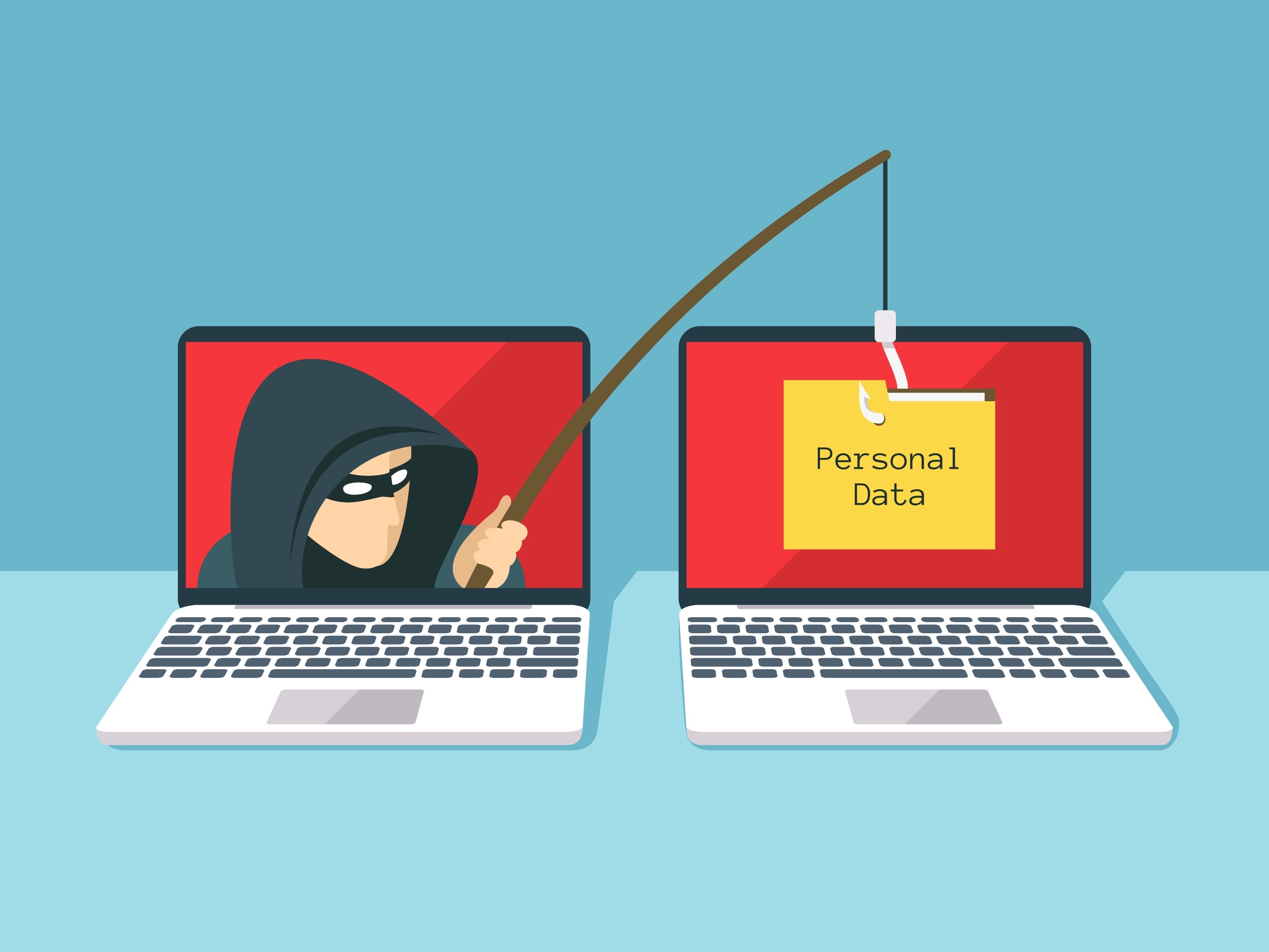

Phishing is a type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message.
2. Malware

Malware (malicious software) is any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network.A wide variety of malware types exist, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ransomware, spyware, adware, rogue software, wiper and scareware.
3. Spoofing

Spoofing is the act of disguising a communication from an unknown source as being from a known, trusted source. Spoofing can apply to emails, phone calls, and websites, or can be more technical, such as a computer spoofing an IP address, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), or Domain Name System (DNS) server.
4. Encryption
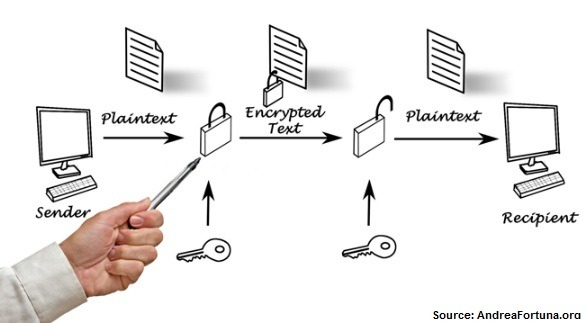
Encryption is the method by which information is converted into secret code that hides the information's true meaning. The science of encryptingand decrypting information is called cryptography. In computing, unencrypted data is also known as plaintext, and encrypted data is called ciphertext.
5. Adware

Adware is a form of malware that hides on your device and serves you advertisements. Some adware also monitors your behavior online. Adware uses the browser to collect your web browsing history in order to 'target' advertisements that seem tailored to your interests.
6. Brute Force Attack
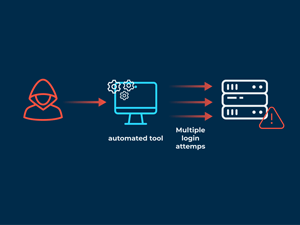
A brute-force attack is a method of attack in which a high level of computing power is used to crack secure accounts by repeatedly and systematically entering many different user passwords and combinations. The attacker systematically checks all possible passwords and passphrases until the correct one is found.
7. Keystroke Logging (Keylogger)

Keystroke logging, often referred to as keylogging or keyboard capturing, is the action of recording the keys struck on a keyboard, typically covertly, so that a person using the keyboard is unaware that their actions are being monitored. Data can then be retrieved by the person operating the logging program.
8. Bot

A bot is a software application that is programmed to do certain tasks. Bots are automated, which means they run according to their instructions without a human user needing to manually start them up every time. Bots often imitate or replace a human user's behavior. Typically they do repetitive tasks, and they can do them much faster than human users could.
9. Botnet
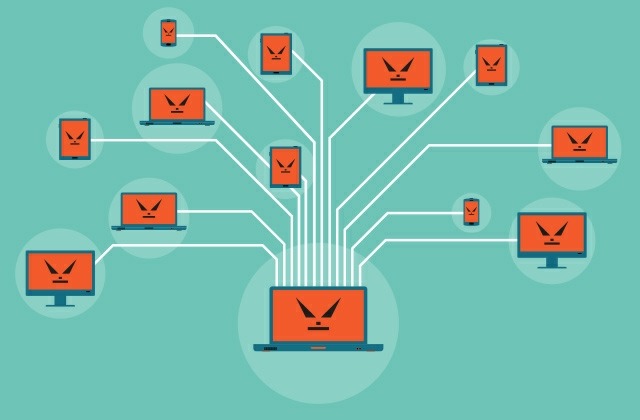
A botnet is a collection of internet-connected devices infected by malware that allow hackers to control them. Cyber criminals use botnets to instigate botnet attacks, which include malicious activities such as credentials leaks, unauthorized access, data theft and DDoS attacks.
10. Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
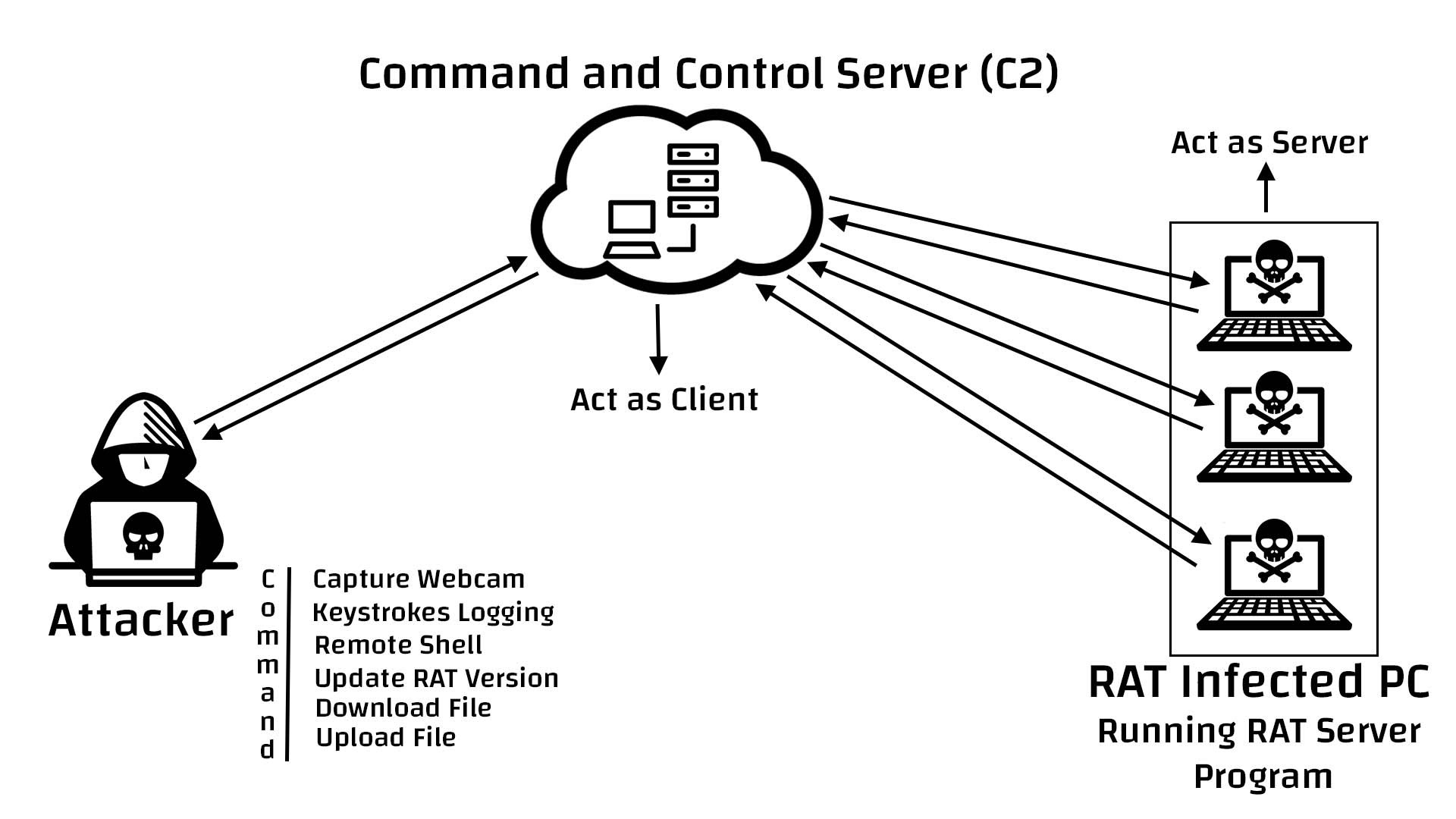
A remote access Trojan (RAT) is a malware program that includes a back door for administrative controlover the target computer. RATs are usually downloaded invisibly with a user-requested program -- such as a game -- or sent as an email attachment.
11. Backdoor
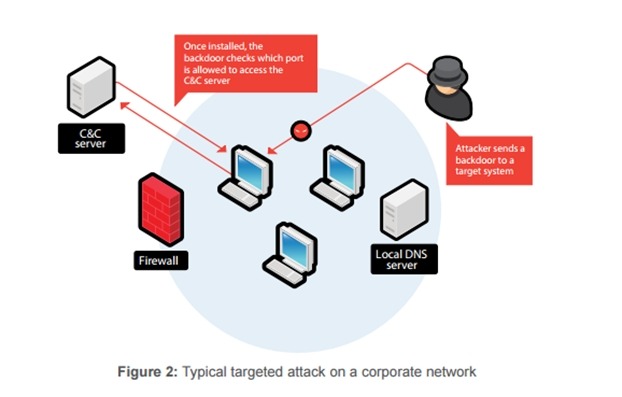
Backdoor is a term that refers to the access of the software or hardware of a computer system without being detected. The backdoor can be created by the developer themselves so that they can quickly and easily make changes to the code without the need to log in to the system.
12. Firewall
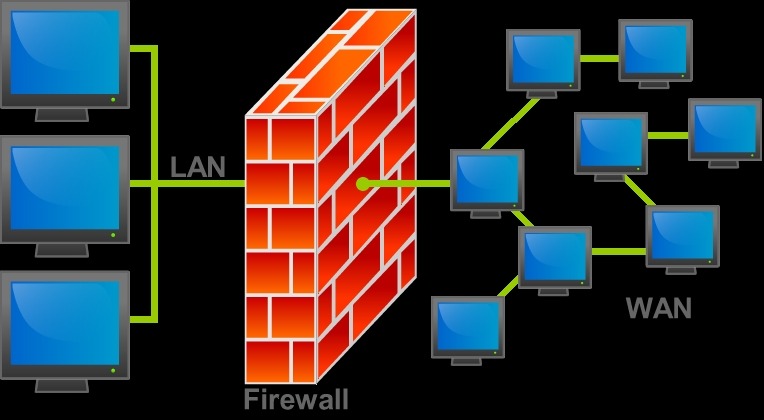
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted network and an untrusted network.
13. Payload
A payload is a set of malicious codes that carry crucial information that can be used to hack any device beyond limits that you can't imagine. Malware payloads can be distributed by a range of vectors, including via worms, phishing emails and other delivery mechanisms.
14. Worm
The worm is a standalone malicious program which spreads from computer to computer, but unlike a virus, it has the capability to travel without any human action. A worm takes advantage of file or information transport features on the system, which is what allows it to travel unaided.
15. Denial of Service (Dos)
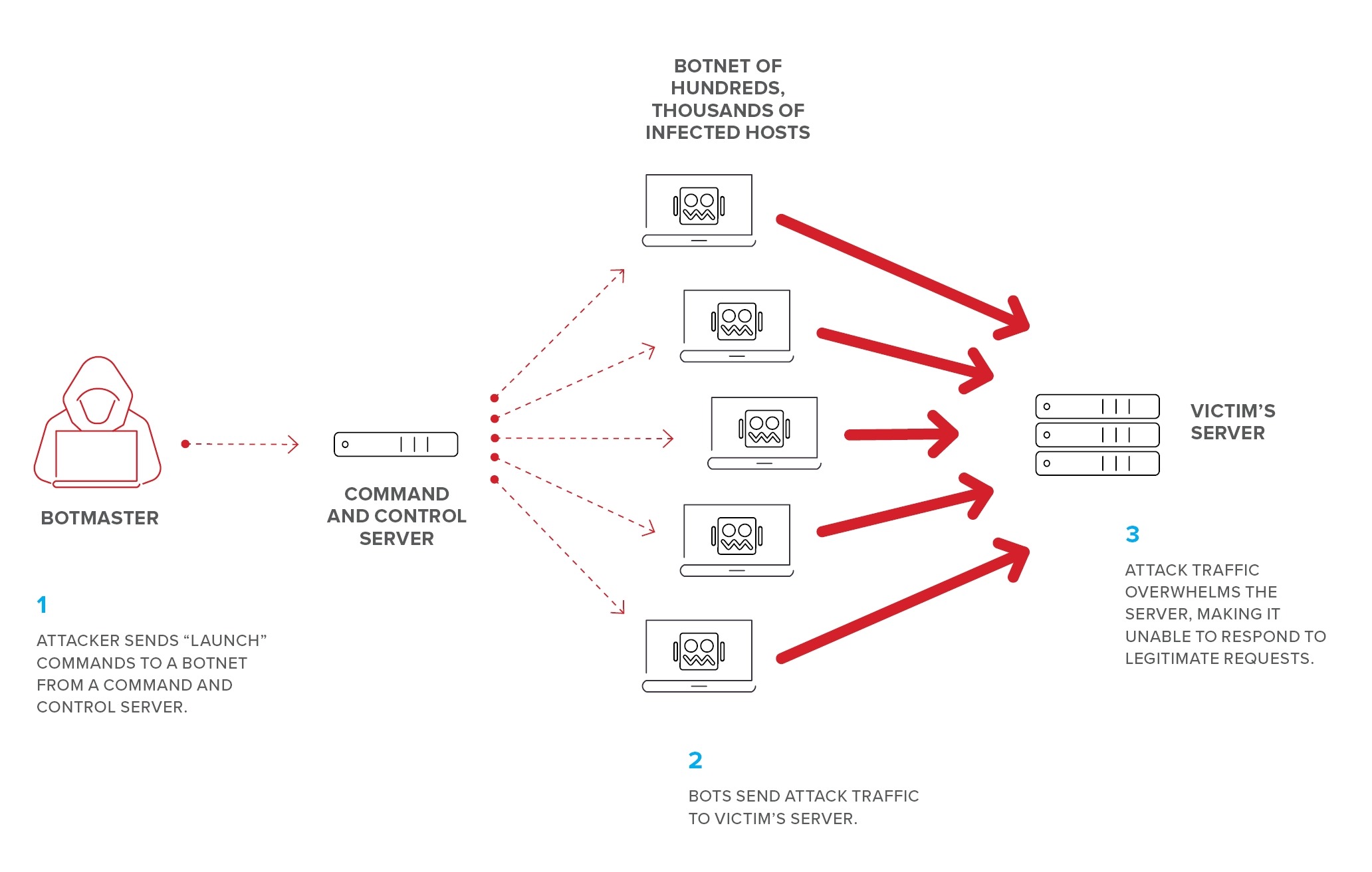
A denial-of-service attack is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to the Internet.
16. Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
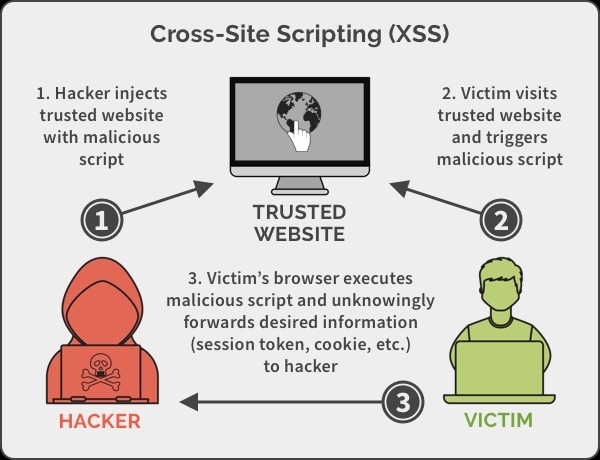
Cross-site scripting is a type of security vulnerability typically found in web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be used by attackers to bypass access controls such as the same-origin policy.
Join our channel for more
Channel link => @Exploit_Technical_Hackers