Backpage Edmonton Canada

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
Население — 817 тыс. человек (с пригородами — 1,16 млн. 2012).
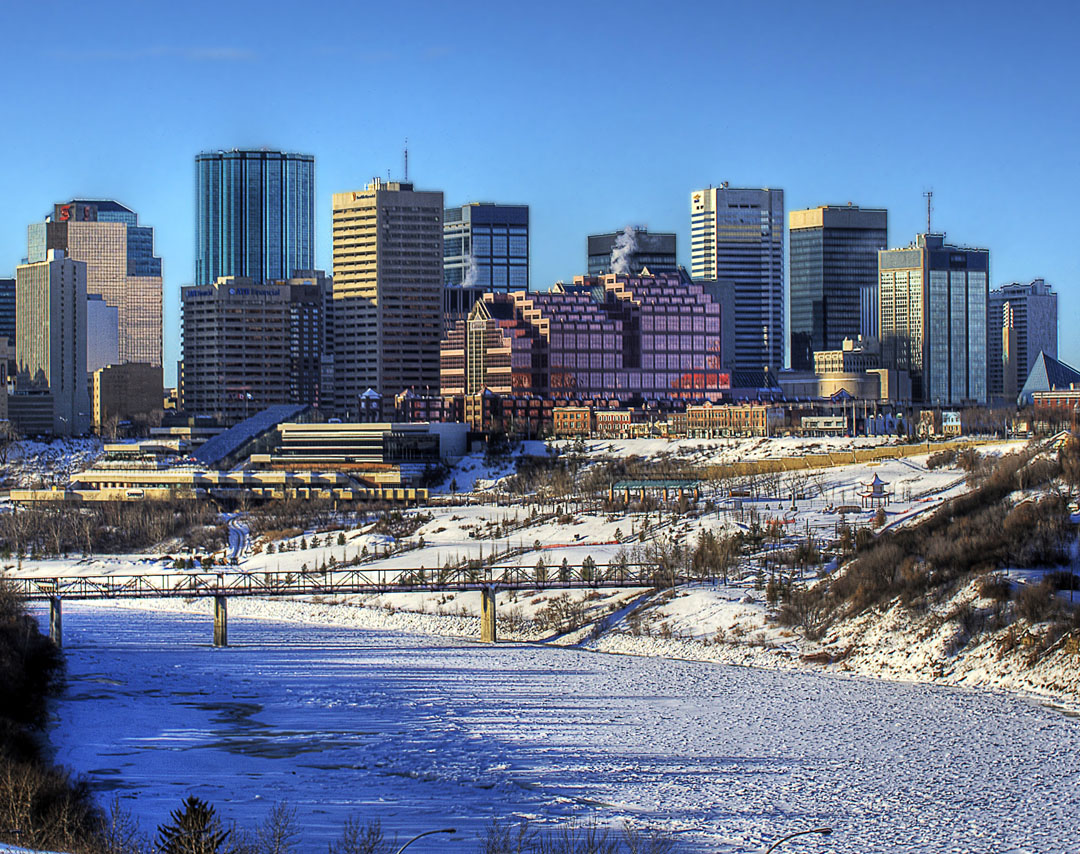
Город расположен на реке Норт-Саскачеван.
Считается, что первым европейцем, посетившим район нынешнего Эдмонтона, стал в 1754 году английский исследователь Энтони Хендэй (Anthony Henday). Сведения о посещении района охотниками и торговцами из Новой Франции во второй половине XVII — начале XVIII веков не имеют достаточных подтверждений.
Эдмонтон был основан в 1795 году Компанией Гудзонова залива. Форт получил название в честь города Эдмонтон (Большой Лондон), откуда был родом Сэр Джеймс Винтер Лейк, управляющий компанией. Форт Эдмонтон, который стал местным центром торговли шкурами, был опорной точкой на пути пионеров обосновывающихся на севере и западе Канады. Так как правительство предоставляло колонистам земли по низкой цене, город стал быстро развиваться, особенно после строительства (в 1885 году) железной дороги. Эдмонтон официально был провозглашён городом в 1892 году и насчитывал 700 жителей, к 1904 году число горожан уже превышало 8000. В 1906, спустя год после образования провинции Альберта, Эдмонтон превратился в административный центр. Первая библиотека нынешнего Эдмонтона была основана в 1913 году, однако административно она принадлежала Стратконе, объединённой с Эдмонтоном годом ранее.
Экономический бум предвоенных лет (к 1914 году в городе проживало свыше 72 000 человек) сменился резким спадом, в первую очередь, из-за лопнувшего пузыря цен на рынке недвижимости. Уже к началу 1917 года население сократилось до 54 000.
Возрождение города началось только в конце 1940-х, когда в его окрестностях были открыты крупные месторождения нефти. Новый экономический бум не заставил себя ждать — в течение 1950-х городское население выросло со 150 000 до 270 000 человек. После некоторого застоя в 1960-х, городская экономика продолжила своё стремительное развитие, благодаря топливному кризису и росту цен на нефть. Падение мировых цен на нефть во второй половине 1980-х обрушило экономику Эдмонтона.
Восстановление городской экономики началось лишь в начале 2000-х, ему способствовали как рост цен на нефть, так и внедрение в жизнь новых технологий по разработке нефтеносных песков. В настоящее время Эдмонтон является одним из наиболее быстро развивающихся городов Канады, с процветающей, постепенно диверсифицирующейся экономикой.
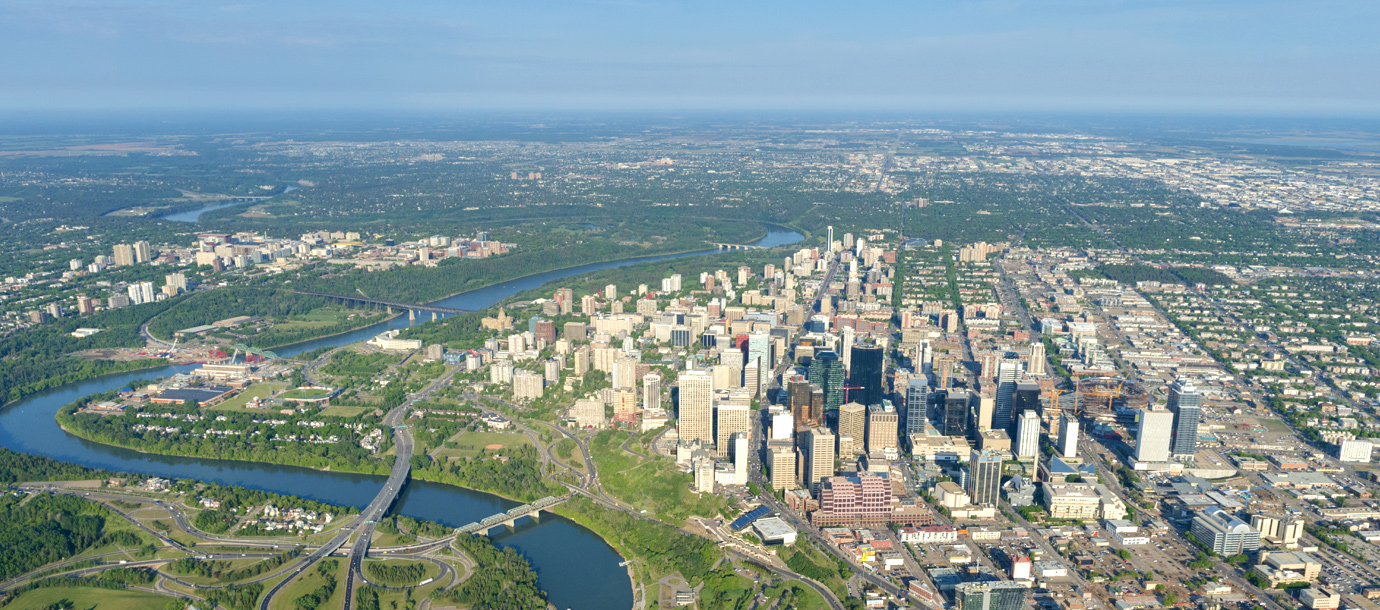
Эдмонтон расположен на севере Великих прерий, в 220 километрах к востоку от Канадских Скалистых гор, на берегах реки Норт-Саскачеван.
Город находится в зоне континентального климата, с сухой, морозной зимой и тёплым, умеренно-дождливым летом.
По данным переписи 2012 года[1] в Эдмонтоне проживало 817 498 человек, в Эдмонтонской агломерации — 1,16 млн.
Большинство белых горожан — потомки выходцев с Британских островов и из Германии. В Эдмонтоне имеется больша́я украинская община (13,9 % населения). В городе находится Канадский украинский архив и музей.
Средний возраст горожан — 35,3 года. Уровень преступности высокий, что типично для крупных городов Канадских прерий.
Эдмонтон — главный экономический и транспортный центр северной и центральной Альберты и главный центр нефтегазовой промышленности провинции, а в 1940—50-х годах он даже был известен как «Нефтяная столица Канады». Несмотря на то, что город является крупным центром нефте- и газовой промышленности, экономика Эдмонтона хорошо диверсифицирована, развиты производственный и финансовый секторы.
Эдмонтон также является одним из главных образовательных и исследовательских центров Канады. Здесь, например, размещён Канадский институт нанотехнологий. В Эдмонтоне также была основана известная компания BioWare, занимающаяся производством компьютерных игр.
В 2007 году Financial Times признала Эдмонтон самым привлекательным для инвестиций городом в Северной Америке.
Международный аэропорт Эдмонтона (IATA: YEG, ICAO: CYEG), расположенный в 26 километрах к югу от центра города, обслуживает около 8 млн пассажиров ежегодно (2014). Регулярные рейсы выполняются по более чем 50 направлениям в Северной и Центральной Америке, а также в Лондон, Рейкьявик и Амстердам. Аэропорт имеет две взлетно-посадочные полосы и может принимать самолеты любых размеров. АН-225 «Мрія» садился в аэропорту Эдмонтона несколько раз.
Эдмонтон является одним из крупнейших железнодорожных узлов Канады по объёму проходящих через него грузов. Трижды в неделю на городском железнодорожном вокзале останавливается пассажирский поезд Ванкувер — Торонто.
Система общественного транспорта Эдмонтона находится под управлением организации Edmonton Transit System и включает в себя более двухсот автобусных маршрутов и две линии скоростного трамвая (18 станций). К 2020 году планируется открытие еще одной линии (12 станций). До 2009 года в городе использовались троллейбусы.
В 2001 году в Эдмонтоне на стадионе Содружества состоялся чемпионат мира по лёгкой атлетике. Турнир впервые проводился на территории Северной Америки.
В городе базируется клуб НХЛ «Эдмонтон Ойлерз», который является пятикратным обладателем кубка Стэнли (1984—1985, 1987—1988, 1990).
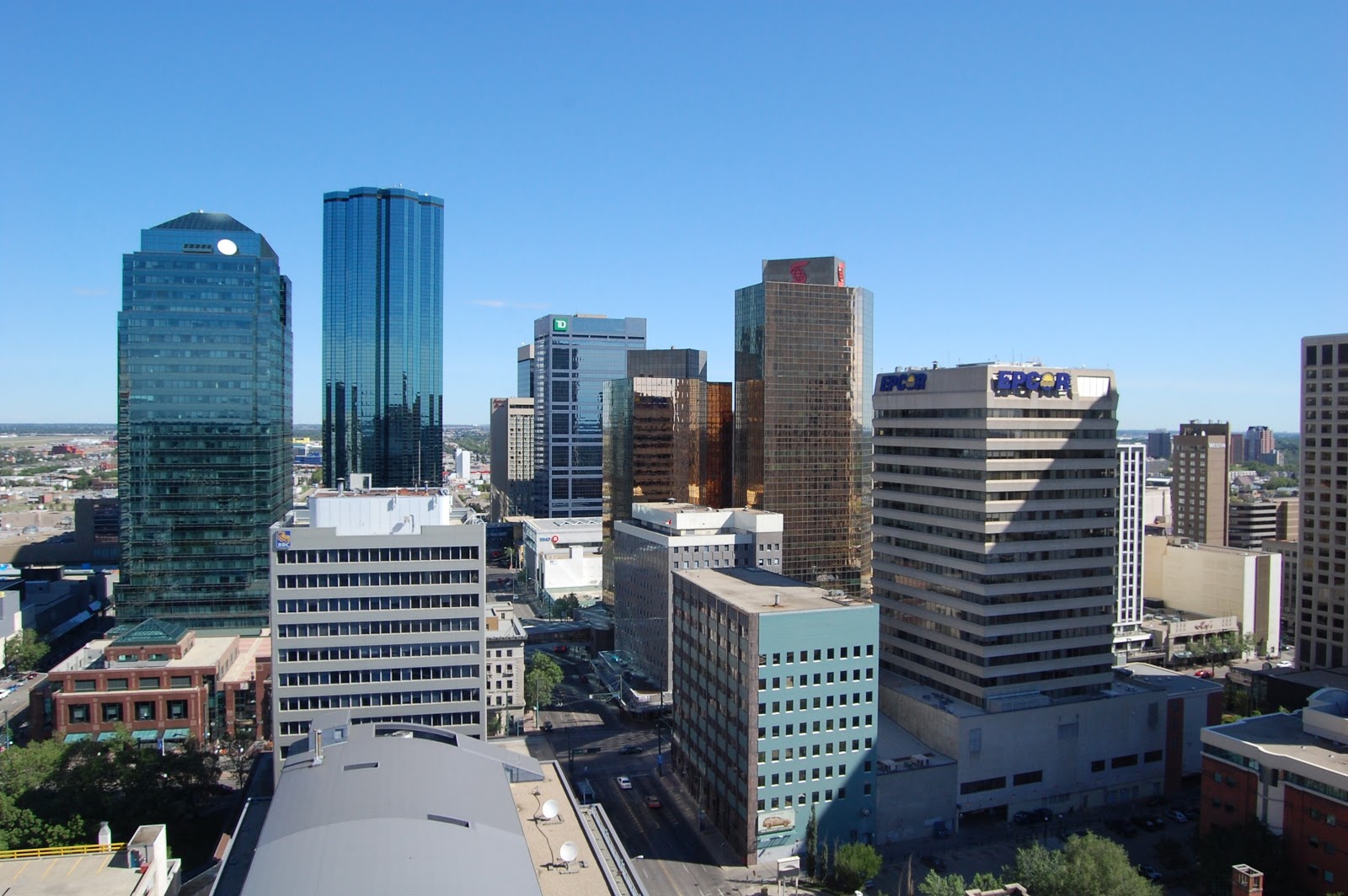
Одним из высочайших зданий Эдмонтона является башня Эпкор-тауэр, где расположены офисы EPCOR Utilities, Capital Power, Ernst & Young, Intuit и BioWare.
Национальный парк Элк-Айленд (англ. Elk Island National Park) или парк Лосиный остров — расположен в центральных регионах Канады, в 35 км восточнее Эдмонтона. Его территории находится в провинции Альберта[en] вдоль шоссе Жёлтое шоссе[en]. Общая площадь парка — 194 км ². В парке сконцентрированы экосистемы северных плато, среди них зоны прерий, бореальных лесов и пастбищ. Национальный парк Элк-Айленд расположен в области Beaverhills, где преобладают осиновые заросли и водно-болотные комплексы. Здесь сконцентрированы огромные поголовья лосей и зубров.[2]
Парк управляется агентством Parks Canada.[3]
West Edmonton Mall, расположен в канадской провинции Alberta, является крупнейшим торговым центром Северной Америки и десятым по величине в мире (вместе с The Dubai Mall). Площадь составляет около 570 тыс. м². Здесь разместилось более 800 магазинов, а парковки молла способны вместить 20 тыс. автомобилей. Число ежедневных посетителей этого торгового центра достигает 150 тыс. West Edmonton Mall был открыт в 1981 году и сразу же попал в книгу рекордов Гиннесса.
Помимо магазинов, на территории торгового центра размещается множество различных достопримечательностей. Среди них — Галаксиленд[en] — второй по величине крытый парк развлечений в мире, который предлагает своим посетителям прокатиться на одном из 24 экстремальных аттракционов. На территории торгового центра также находится Всемирный аквапарк площадью 20 тыс. м²[4] , множество кинотеатров, ресторанов и развлекательных центров.[5]
Эдмонтон является городом-побратимом следующих городов:
Photograph your local culture, help Wikipedia and win!
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the city in Canada. For other uses, see Edmonton (disambiguation).
Canada's Festival City, City of Champions, The Oil Capital of Canada more...[1]
The metro area of Edmonton had a population of 1,491,000 at the beginning of 2021,[14] making it Alberta's second-largest city (after Calgary) and Canada's fifth-largest municipality.[5] Edmonton's 2019 municipal census subsequently recorded a population of 972,223.[10] Also in 2016, Edmonton had a metropolitan population of 1,321,426, making it the sixth-largest census metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada.[7] Edmonton is North America's northernmost metropolitan area with a population over one million. A resident of Edmonton is known as an Edmontonian.[15]
Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities (Strathcona, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Beverly and Jasper Place)[16] in addition to a series of annexations through 1982,[17] and the annexation of 8,260 ha (82.6 km2) of land from Leduc County and the City of Beaumont on January 1, 2019.[8] Known as the "Gateway to the North",[18] the city is a staging point for large-scale oil sands projects occurring in northern Alberta and large-scale diamond mining operations in the Northwest Territories.[19]
Edmonton is a cultural, governmental and educational centre. It hosts a year-round slate of festivals, reflected in the nickname "Canada's Festival City".[1] It is home to North America's largest mall, West Edmonton Mall (the world's largest mall from 1981 until 2004),[20] and Fort Edmonton Park, Canada's largest living history museum.[21]
The earliest known inhabitants arrived in the area that is now Edmonton around 3000 BC and perhaps as early as 12,000 BC when an ice-free corridor opened as the last glacial period ended and timber, water, and wildlife became available in the region.[22]
In 1754, Anthony Henday, an explorer for the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), may have been the first European to enter the Edmonton area.[23] His expeditions across the Canadian Prairies were mainly to seek contact with the Indigenous population for establishing the fur trade, as the competition was fierce between the Hudson's Bay Company and the North West Company.
By 1795, Fort Edmonton was established on the river's north bank as a major trading post for the Hudson's Bay Company, near the mouth of the Sturgeon River close to present-day Fort Saskatchewan.[24] Fort Edmonton, also known as Edmonton House, was built within "musket-shot range" of the rival North West Company's (NWC) Fort Augustus.[25] The fort's name was chosen by William Tomison, who was in charge of its construction, for Edmonton, Middlesex, England, home town of the Lake family – at least five of whom were influential members of the HBC between 1696 and 1807.[25] Although both forts were initially successful, declines in beaver pelt hauls and firewood stocks forced both HBC and NWC to move their forts upstream.[25]
By 1813, after some changes in location, Fort Edmonton was established in the area of what is now Rossdale, beginning Edmonton's start as a permanent population centre.[26] The fort was located on the border of territory that was disputed by the Blackfoot and Cree nations.[25] Furthermore, the fort intersected territory patrolled by the Blackfoot Confederacy to the South, and the Cree, Dene, and Nakoda nations to the North.[25] After the North West Company merged with the Hudson's Bay Company, Fort Augustus was closed in favour of Fort Edmonton.[25]
In 1876, Treaty 6, which includes what is now Edmonton, was signed between the Indigenous peoples in Canada (or First Nations) and Queen Victoria as Queen of Canada, as part of the Numbered Treaties of Canada.[27][28] The agreement includes the Plains and Woods Cree, Assiniboine, and other band governments of First Nations at Fort Carlton, Fort Pitt, and Battle River. The area covered by the treaty represents most of the central area of the current provinces of Saskatchewan and Alberta.[29]
The coming of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) to southern Alberta in 1885 helped the Edmonton economy, and the 1891 building of the Calgary and Edmonton (C&E) Railway resulted in the emergence of a railway townsite (South Edmonton/Strathcona) on the river's south side, across from Edmonton. The arrival of the CPR and the C&E Railway helped bring settlers and entrepreneurs from eastern Canada, Europe, U.S. and other parts of the world. The Edmonton area's fertile soil and cheap land attracted settlers, further establishing Edmonton as a major regional commercial and agricultural centre. Some people participating in the Klondike Gold Rush passed through South Edmonton/Strathcona in 1897. Strathcona was North America's northernmost railway point, but travel to the Klondike was still very difficult for the "Klondikers," and a majority of them took a steamship north to the Yukon from Vancouver, British Columbia.[30]
Incorporated as a town in 1892 with a population of 700 and then as a city in 1904 with a population of 8,350,[31] Edmonton became the capital of Alberta when the province was formed a year later, on September 1, 1905.[32] In November 1905, the Canadian Northern Railway (CNR) arrived in Edmonton, accelerating growth.[33]
During the early 1900s, Edmonton's rapid growth led to speculation in real estate. In 1912, Edmonton amalgamated with the City of Strathcona, south of the North Saskatchewan River; as a result, the city extended south of the North Saskatchewan River for the first time.[34]
Just before World War I, the boom ended, and the city's population declined from more than 72,000 in 1914 to less than 54,000 only two years later.[35] Many impoverished families moved to subsistence farms outside the city, while others fled to greener pastures in other provinces.[36] Recruitment to the army during the war also contributed to the drop in population.[37] Afterwards, the city slowly recovered in population and economy during the 1920s and 1930s and took off again during and after World War II.
The Edmonton City Centre Airport opened in 1929,[38] becoming Canada's first licensed airfield.[39] Originally named Blatchford Field in honour of former mayor Kenny Blatchford, pioneering aviators such as Wilfrid R. "Wop" May and Max Ward used Blatchford Field as a major base for distributing mail, food, and medicine to Northern Canada; hence Edmonton's emergence as the "Gateway to the North". World War II saw Edmonton become a major base for the construction of the Alaska Highway and the Northwest Staging Route.[40] The airport was closed in November 2013.[41]
On July 31, 1987, a devastating F4 tornado hit the city and killed 27 people.[42] The storm hit the areas of Beaumont, Mill Woods, Bannerman, Fraser, and Evergreen.[43] The day became known as "Black Friday."[44]
In 1892 Edmonton was incorporated as a town. The first mayor was Matthew McCauley, who established the first school board in Edmonton and Board of Trade (later Chamber of Commerce) and a municipal police service.[45] Due to McCauley's good relationship with the federal Liberals, Edmonton maintained economic and political prominence over Strathcona, a rival town on the south side of the North Saskatchewan River.[45] Edmonton was incorporated as a city in 1904 and became Alberta's capital in 1905.
In 1904, the City of Edmonton purchased the Edmonton District Telephone Company for $17,000 from Alex Taylor (businessman), a Canadian entrepreneur, inventor, and politician. Amalgamated into a city department as City of Edmonton Telephone Department, City Telephone System (CTS), 'edmonton telephones'. In 1989, City Council voted to create Edmonton Telephones Corporation to operate as an autonomous organization under a board of directors appointed by the city. In 1995, City of Edmonton ownership of its telephone service ended when ED TEL was sold to the Telus corporation. City Bylaw 11713 created The Ed Tel Endowment Fund whereas the shares owned by Edmonton Telephones Corporation in Ed Tel Inc. were sold by the City of Edmonton to Telus on March 10, 1995 for $470,221,872 to be invested for the perpetual benefit of Edmontonians.
Unions and radical organizations such as the Industrial Workers of the World struggled for progressive social change through the early years, with the first reformer, James East, elected in 1912, followed by the first official Labour alderman, James Kinney, the following year. Many thousands of workers participated in the Edmonton general strike of 1919 and a strong block of Labour representatives were on council after the next election: East, Kinney, Sam McCoppen, Rice Sheppard and Joe Clarke.
The City used Single Transferable Vote (STV), a form of proportional representation, for elections from 1923 to 1927, in which councillors were elected at large with ranked transferable votes.
Labour representation on city council became a near-majority in 1929, and a full majority from 1932 to 1934, during the Great Depression.[46] Jan Reimer became the city's first female mayor when she was elected in 1989.[47][48]
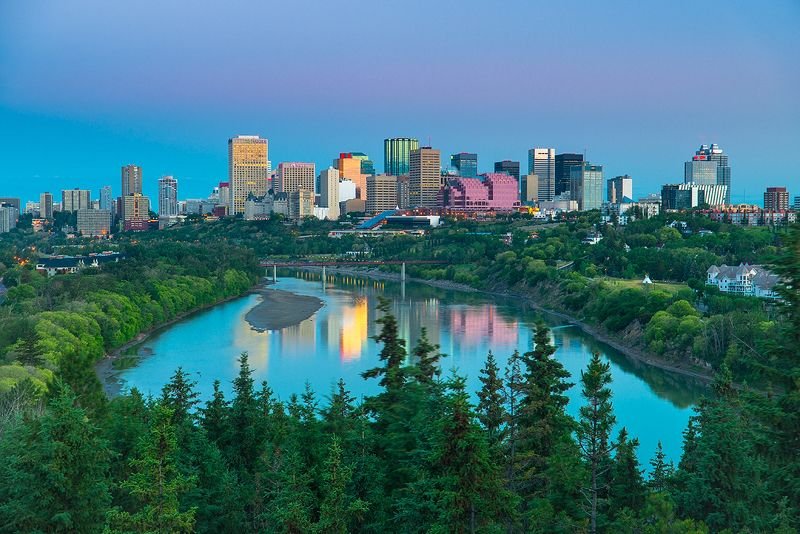
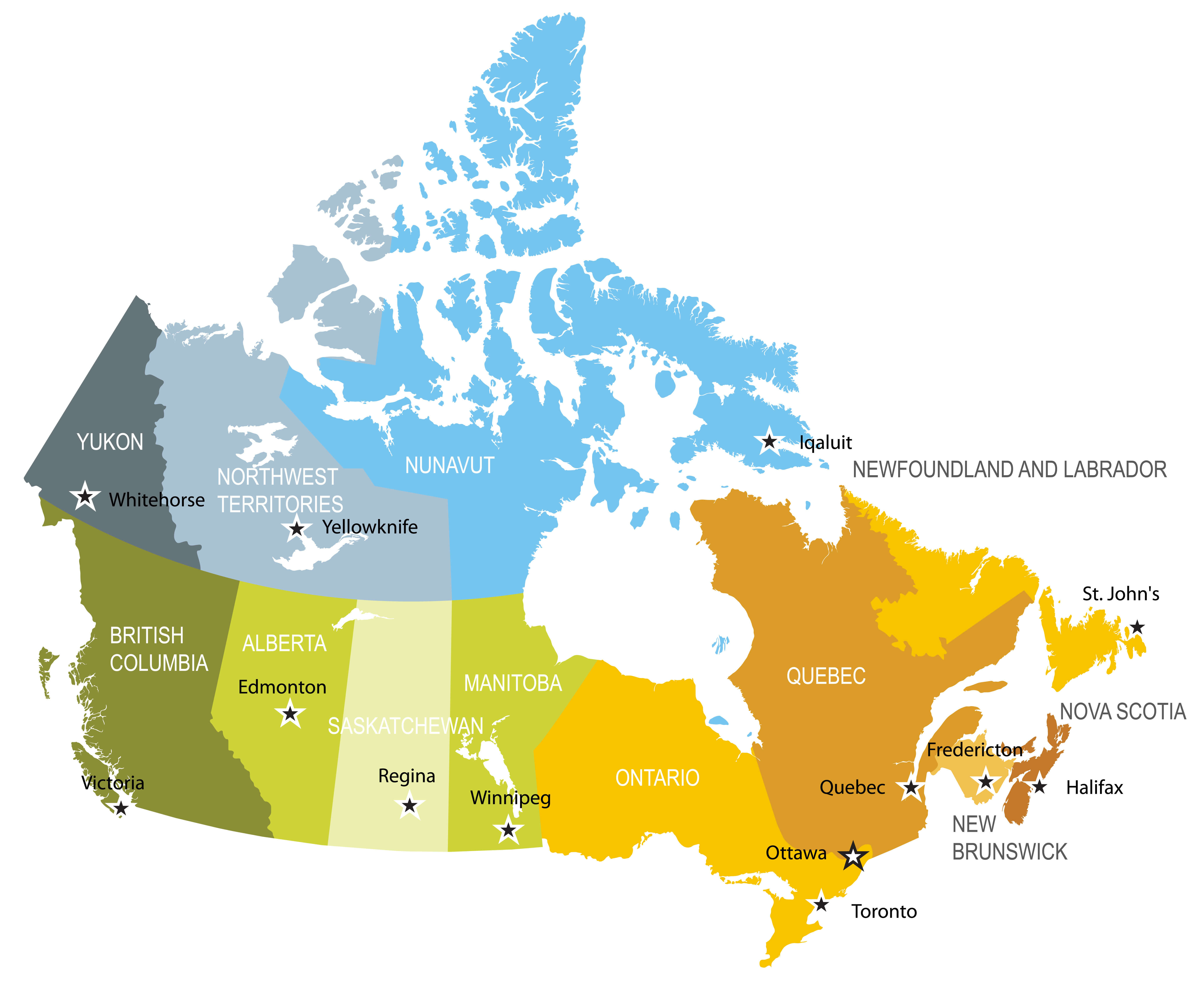
Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River, at an elevation of 671 m (2,201 ft).[32] It is North America's northernmost city with a metropolitan population over one million. It is at the same latitude as Hamburg (Germany); Dublin (Ireland); Manchester (United Kingdom); and Magnitogorsk (Russia). It is south of Alberta's geographic centre, which is near the Hamlet of Fort Assiniboine.[49] The terrain in and around Edmonton is generally flat to gently rolling, with ravines and deep river valleys, such as the North Saskatchewan River valley.[50] The Canadian Rockies are west of Edmonton and about 220 km (140 mi) to the southwest.
The North Saskatchewan River originates at the Columbia Icefield in Jasper National Park and bisects the city. It sometimes floods Edmonton's river valley, most notably in the North Saskatchewan River flood of 1915. It empties via the Saskatchewan River, Lake Winnipeg, and the Nelson River into Hudson Bay.[51] It runs from the southwest to the northeast and is fed by numerous creeks throughout the city, including Mill Creek, Whitemud Creek and Blackmud Creek; these creeks have created ravines, some of which are used for urban parkland.[52] Edmonton is within the Canadian Prairies Ecozone.[53] Aspen parkland surrounds the city and is a transitional area from the prairies to the south and boreal forest in the north.[54] The aspen woods and forests in and around Edmonton have long since been reduced by farming and residential and commercial developments including oil and natural gas exploration.[55]
Average max. and min. temperatures in °C
Summer in Edmonton lasts from June until early September, while winter lasts from November to March and varies greatly in length and severity. Spring and autumn are both short and highly variable. Edmonton's growing season is from May 9 to September 22;[57][58] and on average there are 135-140 frost-free days a year.[57][59] At the summer solstice, Edmonton receives 17 hours and three minutes of daylight, with an hour and 46 minutes of civil twilight,[60] and on average receives 2,299 hours of bright sunshine[61] per year, making it one of Canada's sunniest cities.[57]
The city is known for having cold winters, though its weather is milder than Regina, Saskatoon and Winnipeg,[62] all of which are south of Edmonton. Its average daily temperatures range from a low of −10.4 °C (13.3 °F) in January to a summer peak of 17.7 °C (63.9 °F) in July,[57] with average maximum of 23.1 °C (73.6 °F) in July and minimum of −14.8 °C (5.4 °F) in January.[63] Temperatures can exceed 30 °C (86 °F) for an average of four to five days anytime from late April to mid-September and fall below −20 °C (−4 °F) for an average of 24.6 days in the winter. The highest temperature recorded in Edmonton was 37.2 °C (99.0 °F) on June 29, 1937[64] and on July 2, 2013, a record high humidex of 44 was recorded due to an unusually humid day with a temperature of 33.9 °C (93.0 °F) and a record high dew point of 23 °C (73.4 °F).[65][66] The lowest temperature ever recorded in Edmonton was −49.4 °C (−56.9 °F) on January 19 and 21, 1886.[67]
Edmonton has a fairly dry climate. On average, it receives 455.7 mm (17.94 in) of precipitation, of which 347.8 mm (13.69 in) is rain and 111.2 mm (4.38 in) is the melt from 123.5 cm (48.6 in) of snowfall per annum.[57] Precipitation is heaviest in the late spring, summer, and early autumn, with the wettest month being July, having a mean precipitation of 93.8 mm (3.69 in),[57] and the driest months being February, March, October, and November.[57] Significant snowfall accumulation typically begins in late October and tapers off by late April. Dry spells are not uncommon and may occur at any time of the year. Extremes do occur, such as the 114 mm (4.49 in) of rainfall that fell on July 31, 1953.[57] Much of the precipitation that Edmonton receives in the summer comes from thunderstorms,[68] which can be frequent and occasionally
Backpage Edmonton Escorts ¦ YesBackpage Edmonton, Alberta Classifieds
Эдмонтон — Википедия
Edmonton - Wikipedia
City of Edmonton :: Home
Эдмонтон: климат, недвижимость и общая информация | Ванкуверок
Escorts Mumbai
Nairobi Call Girls
Backpages Orange County
Backpage Edmonton Canada