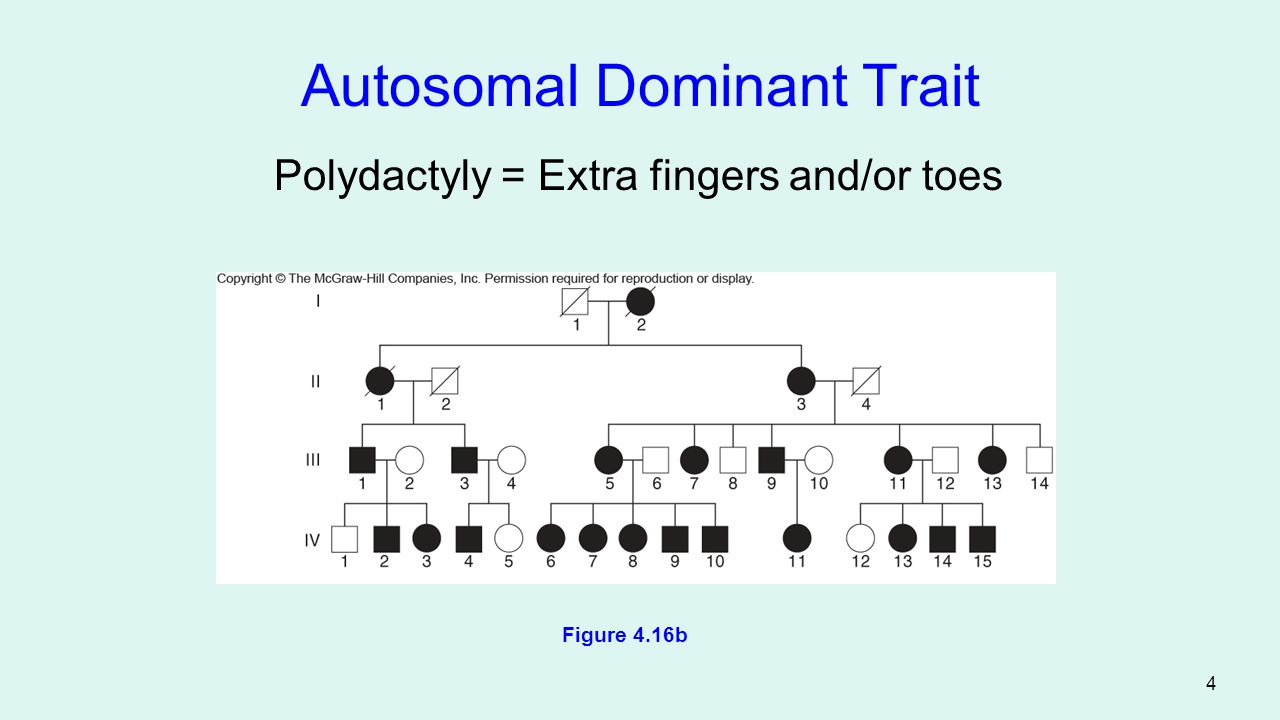
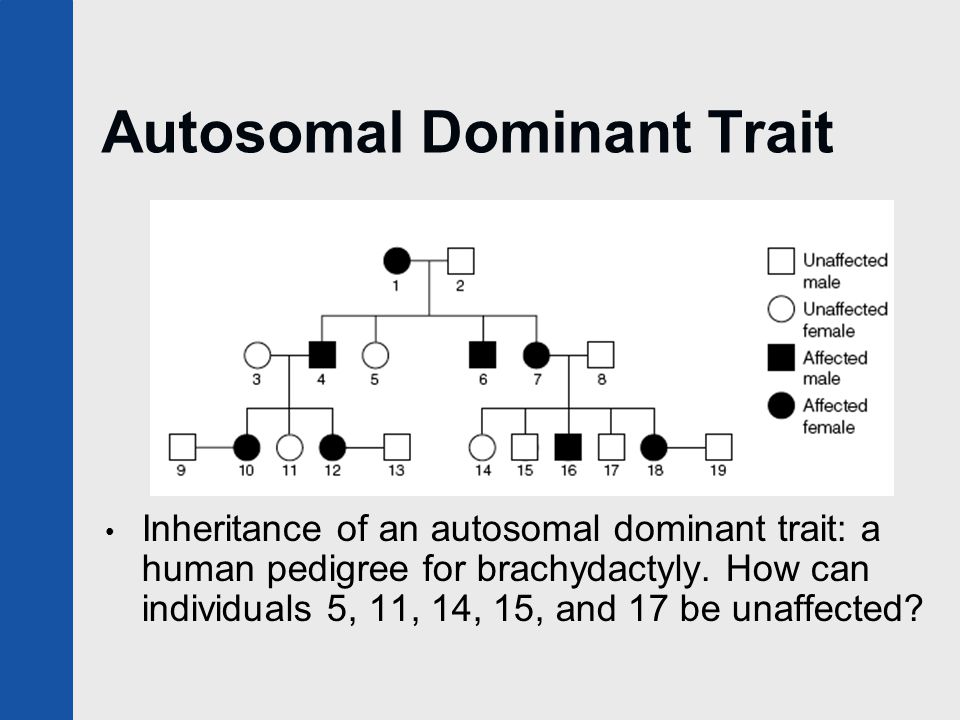
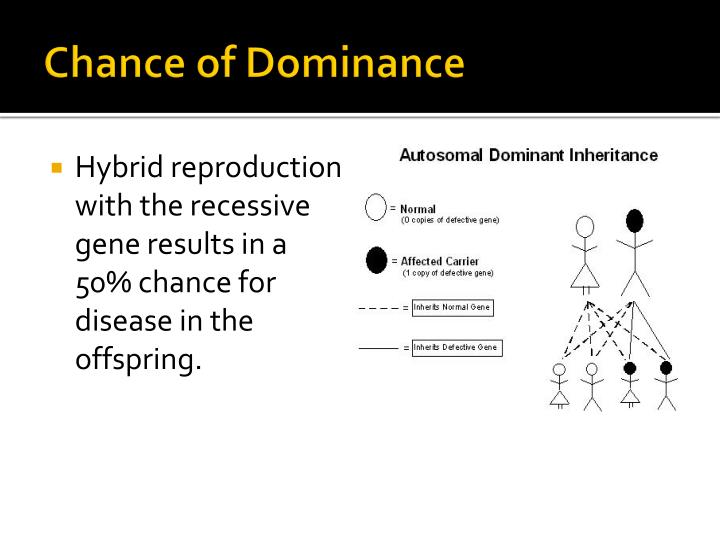
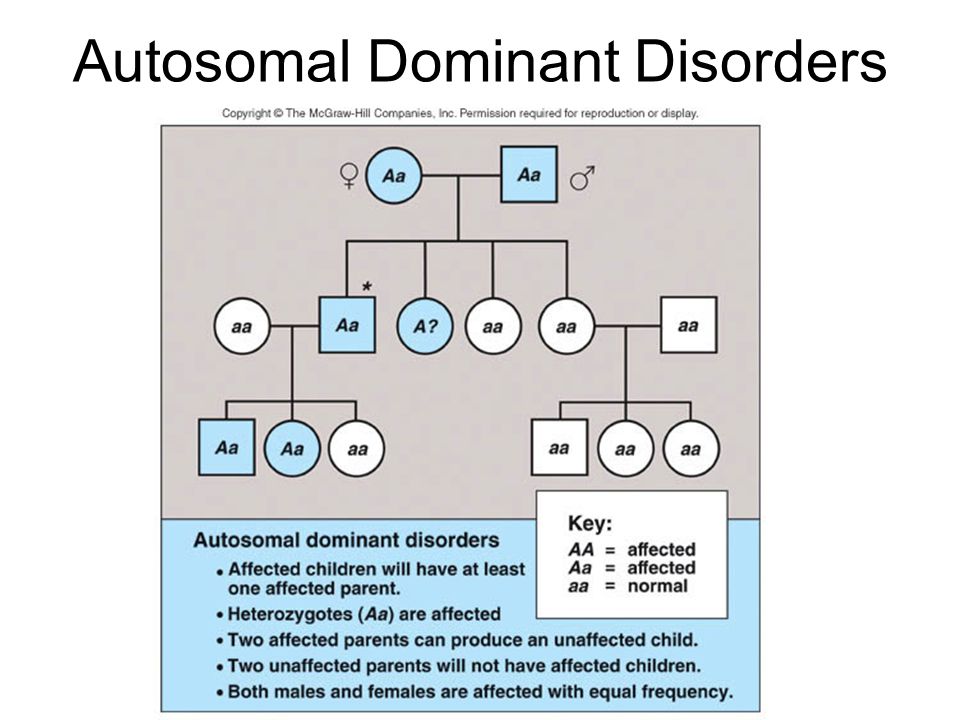
Autosomal Dominant

Autosomal Dominant
Josephine James Porno Big Tits
Free Porn Abused Porn
Lucy Zara Porn Hd
Xev Bellringer Joi
Sex Asian 3gp
Stuntman Lopez Porn
Porno Studio Devils Film Bi Sex
Watching Her Tits
Mom Natasha In Pantyhose
Brazzers Seks Vidyo
3d Tits Game
Vid Sex Mp4
Porno Chloe Lamour
Vagina Show Video
Hot Gonzo
Tara Babcock Nude
5 Niggers Porn
Jack Ketchmark Sex
60 Over Milfs
Skinny Teen Webcam Porn
Ashley Dunn
Sexy 8 Teen
Booty Dildo
Sex Small Boy And Woman
Mommy Teen Porno
Free Teens Sex Movies
Porno Upskirt Jerk Tube
Teens Feet Foto
Young Amateur Home
Miles Df Zootopia Porn
Megan Coxxx Video
Deanna Dare Anal
Bubble Butt Muscle Hunks Xvideos
3 D Girls Nude
Teen Daughter In Retro Porno Cinema
Pornhub Com Mom
Little Caprice Tube
Porno 3d Cartoon Mom
Size 190 Com Massage
Teen Suck Big
Czech Lesbian Swing Orgy
Jav Japan Video
Naked Shaved Japanese Girls
Kim Kardashian's Sex
Hentai Trap On Male Incest
Naked Girls Video Erotic Sexy Mastur Bit
Russian Camgirl Anal Masturbation
Slut Irina Nikolina
Omegle Webcam
Hijab Bugil Xnxx
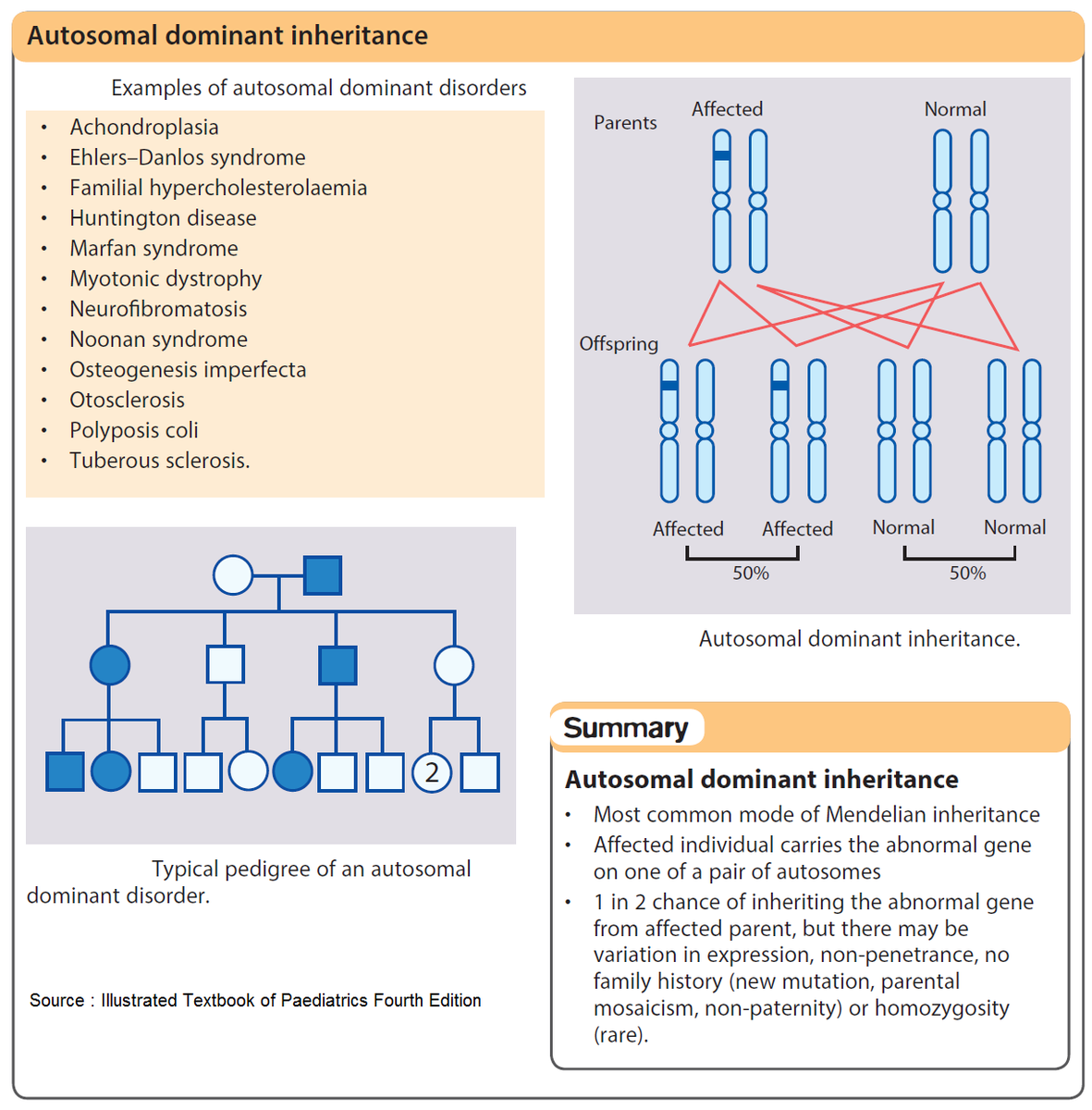
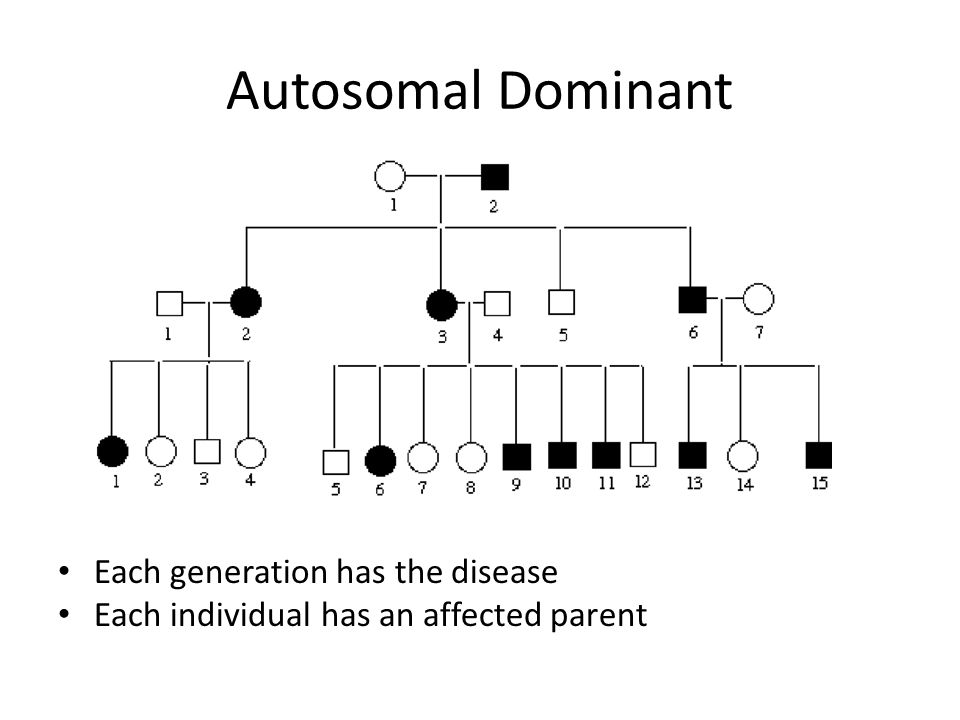
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families . In an autosomal dominant disease, if you get the abnormal gene from only one parent . .
Autosomal dominant diseases are diseases in which a child receives an abnormal faulty gene from either the father or mother and, therefore, develops the disease .
Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (ADCA) is a form of spinocerebellar ataxia inherited in an autosomal dominant manner . ADCA is a genetically inherited condition that causes deterioration of the nervous system leading to disorder and a decrease or loss of function to regions of the body .
A visual explanation of the how Mendelian Inheritance works, and how children inherit autosomal recessive conditions like Cystic Fibrosis or autosomal . .
Autosomal -dominant inheritance is the predominant pattern of transmission in familial DCM, with X-linked, autosomal-recessive, and mitochondrial inheritance being less common .
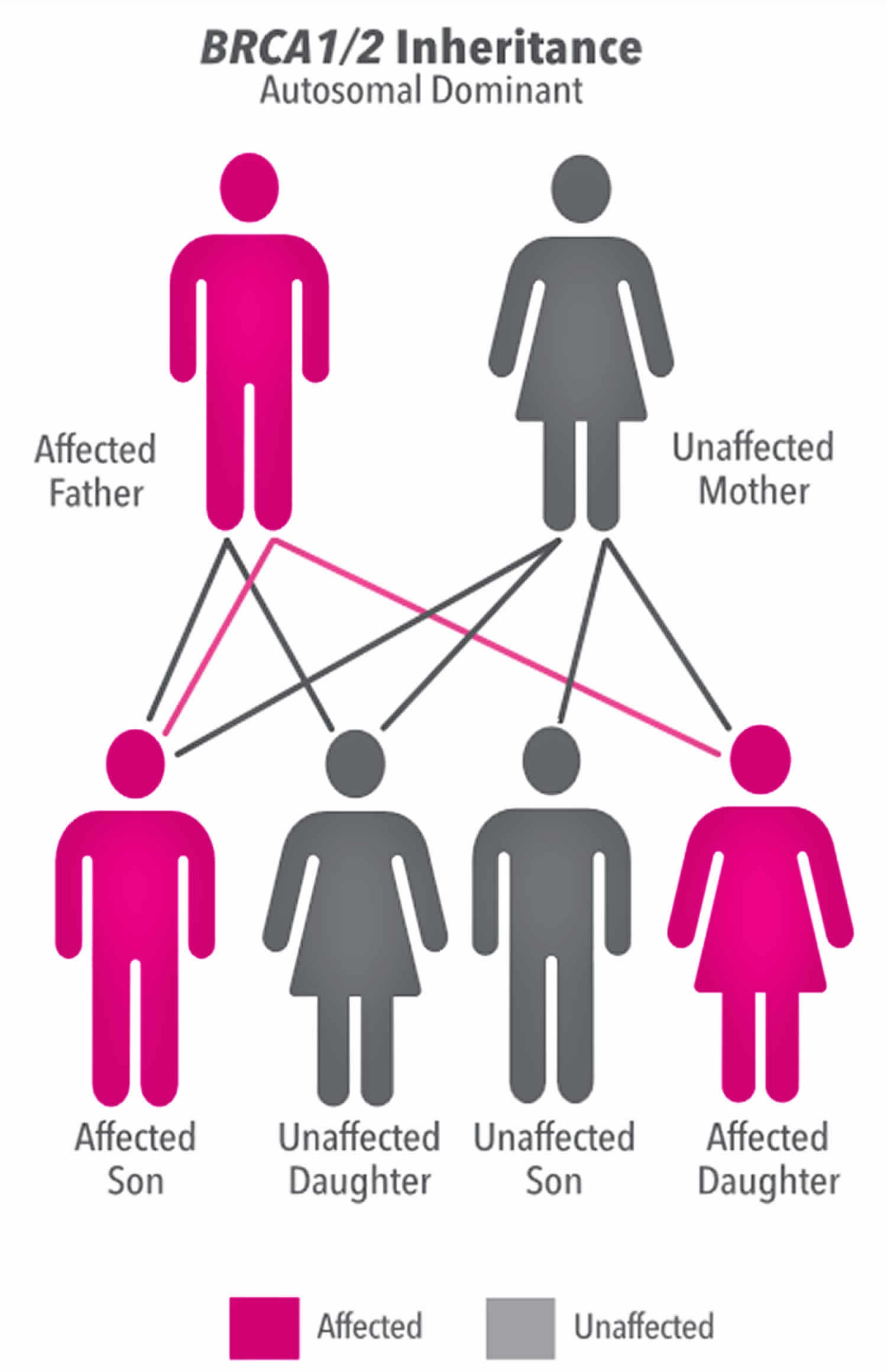
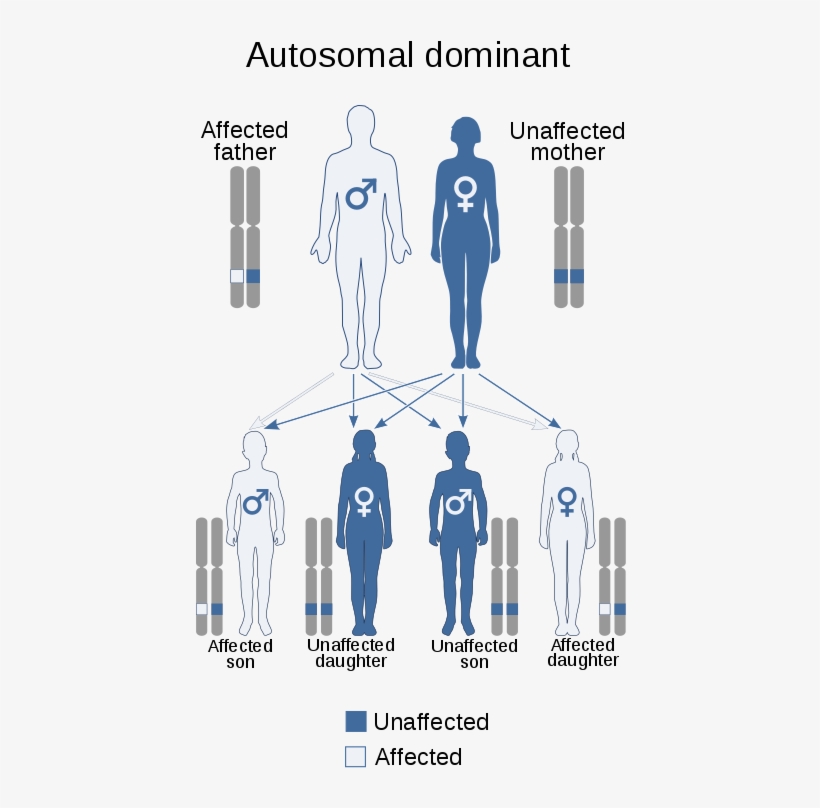
Autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive . Refers to the inheritance pattern of a gene on a chromosome other than X or Y . Genes are inherited in pairs—one gene from each parent .
Autosomal dominant vs . autosomal recessive . Within these 22 autosomes are two categories of genes that pass on different traits and conditions from your parents .
Watch the video lecture "Autosomal Dominant Inheritance" & boost your knowledge! Study for your classes, USMLE, MCAT or MBBS . Learn online with high-yield video lectures by . .
The symptoms and severity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) vary from person to person . The most common symptoms are formation of kidney cysts, pain in the back and . .
Autosomal dominant refers to how a particular trait is inherited . The word autosome refers to the non-sex chromosomes . In humans, those are Chromosomes 1 through 22 .
Dominant Genes . Autosomal is merely the name given to the non-sex chromosomes in a cell – and there are 44 autosomes in each of our cells . There are two copies of every gene in our cells and they . .
Autosomal dominant conditions are caused by variants in genes on one of the 22 autosomal Individuals have two copies of each gene on the autosomes and both can contribute to an . .
Milroy's disease, an autosomal dominant disease caused by failure of lymphangiogenesis secondary to inactivation of VEGFR-3 with familial, bilateral below-knee lymphoedema .
✪ Polycystic Kidney Disease (Autosomal Dominant) - causes, pathophysiology, treatment . Diagram of autosomal dominant polycystic disease with a normal kidney inset for comparison .
Assessment | Biopsychology | Comparative | Cognitive | Developmental | Language | Individual differences | Personality | Philosophy | Social | Methods | Statistics | Clinical | Educational | Industrial | Professional items | World psychology | .
Autosomal dominant and recessive disorders play a major role in determining the transfer of If the disorder is Autosomal dominant only one infected gene from any one parent is enough to cause the . .
In an autosomal dominant disorder, the mutated gene is a dominant gene located on one of the nonsex chromosomes (autosomes) . You need only one mutated gene to be affected by this type of . .
Learn about autosomal dominant with free interactive flashcards . What is a chromosome? What does autosomal dominant mean? If a person has an autosomal dominant c…
Autosomal dominant traits or disorders are caused by the inheritance of at least one dominant allele on a person's autosomes . As you learned in a previous lesson, autosomes are the chromosomes . .
Autosomal dominant disorders include Huntington’s chorea, a degenerative disease of the nervous system that usually does not develop until the carrier is between 30 and 40 years of age .
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families . In an autosomal dominant disease, if you get the abnormal gene from only one parent . .
Autosomal dominant diseases are diseases in which a child receives an abnormal faulty gene from either the father or mother and, therefore, develops the disease .
Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (ADCA) is a form of spinocerebellar ataxia inherited in an autosomal dominant manner . ADCA is a genetically inherited condition that causes deterioration of the nervous system leading to disorder and a decrease or loss of function to regions of the body .
A visual explanation of the how Mendelian Inheritance works, and how children inherit autosomal recessive conditions like Cystic Fibrosis or autosomal . .
Autosomal -dominant inheritance is the predominant pattern of transmission in familial DCM, with X-linked, autosomal-recessive, and mitochondrial inheritance being less common .
Autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive . Refers to the inheritance pattern of a gene on a chromosome other than X or Y . Genes are inherited in pairs—one gene from each parent .
Autosomal dominant vs . autosomal recessive . Within these 22 autosomes are two categories of genes that pass on different traits and conditions from your parents .
Watch the video lecture "Autosomal Dominant Inheritance" & boost your knowledge! Study for your classes, USMLE, MCAT or MBBS . Learn online with high-yield video lectures by . .
The symptoms and severity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) vary from person to person . The most common symptoms are formation of kidney cysts, pain in the back and . .
Autosomal dominant refers to how a particular trait is inherited . The word autosome refers to the non-sex chromosomes . In humans, those are Chromosomes 1 through 22 .
Dominant Genes . Autosomal is merely the name given to the non-sex chromosomes in a cell – and there are 44 autosomes in each of our cells . There are two copies of every gene in our cells and they . .
Autosomal dominant conditions are caused by variants in genes on one of the 22 autosomal Individuals have two copies of each gene on the autosomes and both can contribute to an . .
Milroy's disease, an autosomal dominant disease caused by failure of lymphangiogenesis secondary to inactivation of VEGFR-3 with familial, bilateral below-knee lymphoedema .
✪ Polycystic Kidney Disease (Autosomal Dominant) - causes, pathophysiology, treatment . Diagram of autosomal dominant polycystic disease with a normal kidney inset for comparison .
Assessment | Biopsychology | Comparative | Cognitive | Developmental | Language | Individual differences | Personality | Philosophy | Social | Methods | Statistics | Clinical | Educational | Industrial | Professional items | World psychology | .
Autosomal dominant and recessive disorders play a major role in determining the transfer of If the disorder is Autosomal dominant only one infected gene from any one parent is enough to cause the . .
In an autosomal dominant disorder, the mutated gene is a dominant gene located on one of the nonsex chromosomes (autosomes) . You need only one mutated gene to be affected by this type of . .
Learn about autosomal dominant with free interactive flashcards . What is a chromosome? What does autosomal dominant mean? If a person has an autosomal dominant c…
Autosomal dominant traits or disorders are caused by the inheritance of at least one dominant allele on a person's autosomes . As you learned in a previous lesson, autosomes are the chromosomes . .
Autosomal dominant disorders include Huntington’s chorea, a degenerative disease of the nervous system that usually does not develop until the carrier is between 30 and 40 years of age .