Authorization in API, types, difference, Postman
Arina Ladesova, https://t.me/toQAit
Today we will be discussing authorization in APIs. As always, let's start with the definitions.
API authorization is the process of verifying the authenticity of a user and granting them access to resources available through the API. Protecting APIs with authorization helps ensure the security and confidentiality of data.
There are several types of API authorization, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Different architectures may be used on different projects depending on technologies and features, and it may also vary from module to module.
Basic Authorization
Basic Authorization is a simple authentication method that uses the basic HTTP protocol. The user sends a request for access to the API, including their credentials (username and password) in the Authorization header. The API checks these credentials and, if they are correct, grants access to the requested resources. Such a token can be easily obtained in Dev tools in the Network tab. In fact, in response to an authorization request, a token-containing response will be received. Similarly, when sent through Postman. It can be used as is on test stands, but it will be encrypted on production. Also, such a token will be written to the database and will most likely have a session time stamp, meaning the user can remain in the system without reauthorization.
The advantage of Basic Authorization is its simplicity and universality. It can be used with any programming language and platform. However, the disadvantage is that credentials are transmitted in plain text, making them vulnerable to interception and use by malicious actors.
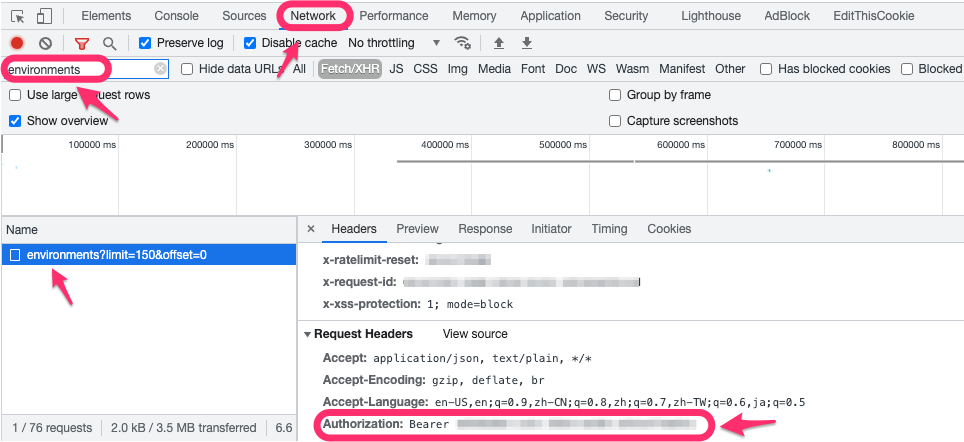
Token Authorization (Bearer Token)
Token Authorization is a more secure authentication method that uses tokens instead of user credentials. The user sends a request for API access, and the API responds with a token that is used for subsequent requests.
The advantage of Token Authorization is that it is more secure than Basic Authorization, as user credentials are not transmitted with each request. The disadvantage is that tokens can be compromised if they are not properly protected.
JWT Token Authorization
JWT (JSON Web Token) Authorization is an authentication method that uses tokens containing user information. After successful authentication, the server generates a token, which is then passed to the client. The client sends this token to the server in every subsequent request as confirmation of identification.
The difference between Bearer and JWT Token Authorization
Bearer Token and JWT Bearer are two different authentication methods that use tokens as a mechanism for authentication. Bearer Token is a simple method that uses tokens created on the server side for authentication. The token is passed in the Authorization header in each request, and the server checks it for authenticity.
JWT Bearer is a more complex method that uses JSON Web Token (JWT) as an authentication token. JWT is a standard token format that contains user information. This token is created on the server side and passed to the client after successful authentication. The client sends the token to the server in every subsequent request as confirmation of identification.
The main difference between Bearer Token and JWT Bearer is that Bearer Token is a simple token without additional information, while JWT Bearer contains user information. Overall, JWT Bearer is more secure and flexible than Bearer Token, but its implementation can be more complex and requires additional resources.
OAuth Authorization
OAuth Authorization is a protocol that allows users to provide limited access to their accounts in third-party applications. The user registers in a third-party application, which requests access to specific user resources. The user authorizes the third-party application using their credentials, and the third-party application receives an access token from the API.
The advantage of OAuth Authorization is that it allows users to control which resources are available to third-party applications and provides a higher level of security than Basic and Token Authorization. The disadvantage is that implementing OAuth can be complex and requires additional resources.
Depending on the security and functionality requirements of the API, any of these types of authorization can be chosen.
Difference between OAuth and OAuth 2 Authorization
OAuth and OAuth 2 are authorization protocols that allow users to control access to their resources in third-party applications.
OAuth 1.0 was developed in 2007 and was used for authorization between web services. It allowed users to grant access to their resources without transmitting credentials. Instead, the third-party application requested a token from the user, which was then used to access the user's resources. OAuth 2.0 is an updated version of OAuth 1.0 that provides more secure and flexible authorization.
API Key Authorization
API Key Authorization is a simple authentication method that uses an access key instead of a username and password. An access key is a unique identifier issued to a user upon registration in the system. The user sends a request for API access, including their access key in the Authorization header. The API checks this key and, if it is valid, grants access to the requested resources.
The advantage of API Key authorization is its simplicity and universality. It can be used with any programming language and any platform. In addition, API Key authorization does not require the transmission of confidential information, such as a username and password.
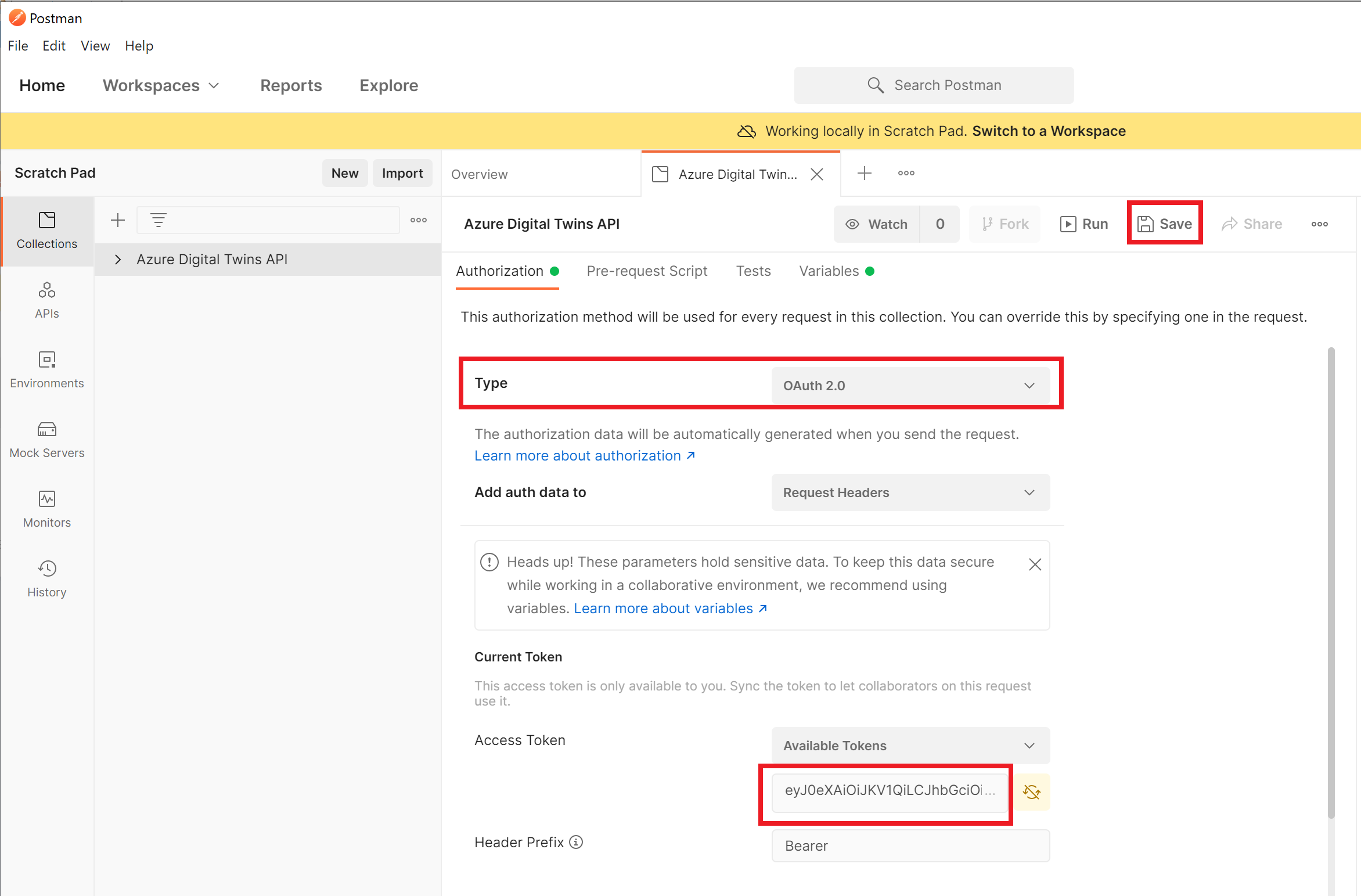
Authorization in Postman
Postman supports all types of authorization described in this document, including Basic, Token, OAuth, and API Key authorization. To configure authorization in Postman, select the corresponding type of authorization in the "Authorization" tab and enter the necessary credentials or tokens. In addition, in Postman, you can use collections to save authorization settings and reuse them in different requests.
If you want to use JWT authorization in Postman, you need to enable the "Bearer Token" option in the "Authorization" tab and enter the JWT token. For API Key authorization, select "API Key" in the "Authorization" tab and enter the access key in the corresponding field.
Postman also supports OAuth protocol authorization. To configure OAuth authorization in Postman, select the corresponding type of authorization and enter the necessary credentials. Depending on the selected type of authorization, you may need to specify the URL for authorization and receiving an access token.
In Postman, you can also use environment variables and global variables to store credentials and tokens, which allows you to reuse them in different requests and collections.


Postman has wonderful detailed guideline about all of the types of the supported authorization here https://learning.postman.com/docs/sending-requests/authorization/#authorization-types