Arabic Muslim

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MUSLIM
Bangladesh: 151,900,000
India: 207,000,000
Indonesia: 225,000,000
Pakistan: 213,095,000
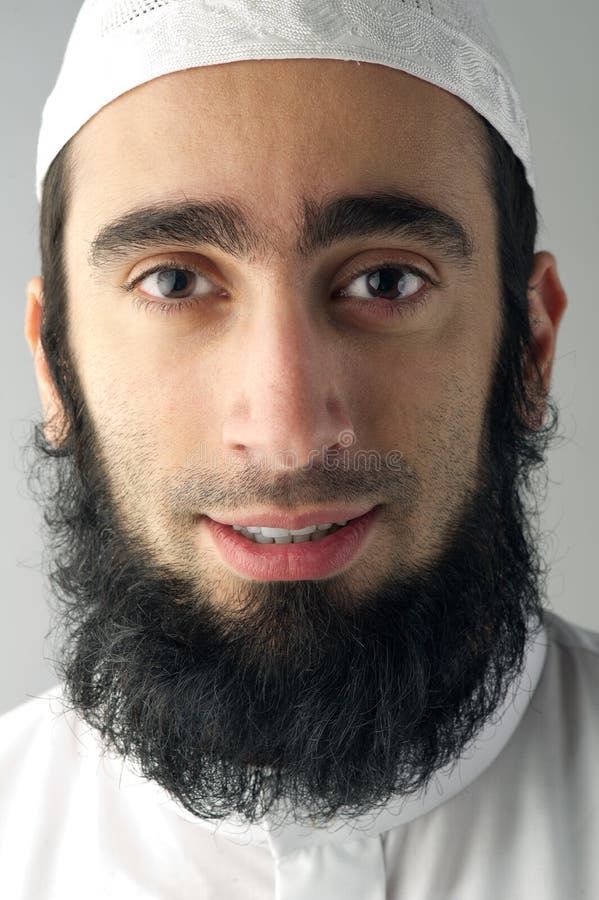
Muslims (Arabic: مسلم, romanized: Muslim) are people who follow or practice Islam, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion. The derivation of "Muslim" is from an Arabic word meaning "submitter (to God)". Muslims consider the Quran, their holy book, to be the verbatim word of God as revealed to the Islamic prophet and messenger Muhammad. The majority of Muslims also follow their own versions of compilations claimed to be the teachings an…
Muslims (Arabic: مسلم, romanized: Muslim) are people who follow or practice Islam, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion. The derivation of "Muslim" is from an Arabic word meaning "submitter (to God)". Muslims consider the Quran, their holy book, to be the verbatim word of God as revealed to the Islamic prophet and messenger Muhammad. The majority of Muslims also follow their own versions of compilations claimed to be the teachings and practices of Muhammad (sunnah) as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith).
The beliefs of Muslims include: that God (Arabic: الله Allah) is eternal, transcendent and absolutely one (tawhid); that God is incomparable, self-sustaining and neither begets nor was begotten; that Islam is the complete and universal version of a primordial faith that has been revealed before through many prophets including Abraham, Ishmael, Isaac, Moses, and Jesus; that these previous messages and revelations have been partially changed or corrupted over time (tahrif) and that the Quran is the final unaltered revelation from God.
As of 2015, 1.8 billion or about 24.1% of the world population are Muslims. By the percentage of the total population in a region considering themselves Muslim, 91% in the Middle East–North Africa (MENA), 81% in Central Asia, 65% in the Caucasus, 40% in Southeast Asia, 31% in South Asia, 30% in Sub-Saharan Africa, 25% in Asia–Oceania, around 6% in Europe, and 1% in the Americas.
Most Muslims are of one of two denominations; Sunni (75–90%) and Shia (12-17%). About 12% of Muslims live in Indonesia, the largest Muslim-majority country; 31% of Muslims live in South Asia, the largest population of Muslims in the world; 20% in the Middle East–North Africa, where it is the dominant religion; and 15% in Sub-Saharan Africa. Muslims are the overwhelming majority in Central Asia, the majority in the Caucasus and widespread in Southeast Asia. India is the country with the largest Muslim population outside Muslim-majority countries. Sizeable Muslim communities are also found in the Americas, China, and Europe. Islam is the fastest-growing major religion in the world.
https://www.learnreligions.com/arabic-language-in-islam-2004035
Перевести · 25.06.2019 · Arabic is considered by many to be an Islamic language, central to the religious practice of Muslims; most non-Arabic Muslims make an effort to learn it.
YouTube › The Wedding Filmmakers Ltd
Ramadan Music Arabic - Background Muslim Music No Copyright / Islamic Instrumental Music for videos
Arabic/muslim Girl name with Ayisha
Latest Arabic muslim baby girl names with meaning
5 Things I Love About Muslim Culture
https://teachmideast.org/articles/arab-middle-eastern-and-muslim-whats-the-difference
Перевести · Arab is an ethno-linguistic category, identifying people who speak the Arabic language as their mother tongue (or, in the case of immigrants, for example, whose parents or grandparents spoke Arabic as their native language). Arabic is a Semitic language, closely related to Hebrew and Aramaic. While Arabs speak the same language, there is enormous ...
https://www.thegospelcoalition.org/article/common-confusions-arabs-muslims
“Arab” vs. “Muslim”
Arabic Center
Our Response
“Arab” and “Muslim” are not synonymous terms. Muslims are followers of the religion of Islam. Arabs are an ethno-linguistic group of people, most of whom are Muslim in religion but many of whom are not. Their origins lie in the Arabian Peninsula, but they burst into the larger world in the 7th and 8th centuries with the dramatic conquests that followed the dea…
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arabs
Canada: 750,925
Germany: 1,155,390
Israel: 1,700,000
United Kingdom: 500,000
The Arabs are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world. In modern usage the term refers to those who originate from an Arab country, whose native language is Arabic; this contrasts with the narrower traditional definition which referred to the descendants of the Tribes of the Arabian Peninsula. The term can encompass all Arabic-speaking peoples living from the Atlantic Coast of Mauritania, to the Ahwaz region of Iran, including the Arab states in Western Asia, Northern Africa, the Horn of Africa, Western Indian Ocean islands(inclu…
The Arabs are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world. In modern usage the term refers to those who originate from an Arab country, whose native language is Arabic; this contrasts with the narrower traditional definition which referred to the descendants of the Tribes of the Arabian Peninsula. The term can encompass all Arabic-speaking peoples living from the Atlantic Coast of Mauritania, to the Ahwaz region of Iran, including the Arab states in Western Asia, Northern Africa, the Horn of Africa, Western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros), and Southern Europe (like Sicily, Malta, and formerly in Al-Andalus / Iberian Peninsula). They also live, in significant numbers, in the Americas, Western Europe, Indonesia, Israel, Turkey, India and Iran. The Arab diaspora is established around the world. Though Islam started in Arabia, Arabic is the language of Islamic scripture, and most Arabs are Muslims. However, only about 20% of Muslims are Arabs.
The first mention of Arabs appeared in the mid-9th century BCE, as a tribal people in Eastern and Southern Syria and the north of the Arabian Peninsula. The Arabs appear to have been under the vassalage of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–612 BCE), as well as the succeeding Neo-Babylonian (626–539 BCE), Achaemenid (539–332 BCE), Seleucid and Parthian empires. The Nabataeans, an Arab people, formed their Kingdom near Petra in the 3rd century BC. Arab tribes, most notably the Ghassanids and Lakhmids, begin to appear in the Southern Syrian Desert from the mid 3rd century CE onward, during the mid to later stages of the Roman and Sasanian empires.
Before the expansion of the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661 C.E.), "Arab" referred to any of the largely nomadic and settled Semitic people from the Arabian Peninsula, Syrian Desert and Lower Mesopotamia, with some even reaching what is now northern Iraq. Today, according to Pan Arabs "Arab" refers to a large number of people whose native regions form the Arab world due to the spread of Arabs and the Arabic language throughout the region during the early Muslim conquests of the 7th and 8th centuries and the subsequent Arabisation of indigenous populations. The Arabs forged the Rashidun (632–661), Umayyad (661–750), Abbasid (750–1517) and the Fatimid (901–1071) caliphates, whose borders reached Southern France in the west, China in the east, Anatolia in the north and the Sudan in the south. This was one of the largest land empires in history. In the early 20th century, the First World War signalled the end of the Ottoman Empire, which had ruled much of the Arab world since conquering the Mamluk Sultanate in 1517. The end culminated in the 1922 defeat and dissolution of the empire and the partition of its territories, forming the modern Arab states. Following the adoption of the Alexandria Protocol in 1944, the Arab League was founded on 22 March 1945. The Charter of the Arab League endorsed the principle of an Arab homeland whilst respecting the individual sovereignty of its member states.
Today, Arabs primarily inhabit the 22 member states of the Arab League. The Arab world stretches around 13 million km , from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Horn of Africa and the Indian Ocean in the southeast. People of non-Arab ethnicities associated with non-Arabic languages also live in these countries, sometimes as a majority. These include Somalis, Kurds, Berbers, the Afar people, Nubians and others. Beyond the boundaries of the League of Arab States, Arabs can also be found in the global diaspora. The ties that bind Arabs are ethnic, linguistic, cultural, historical, identical, nationalist, geographical and political. The Arabs have their own customs, language, architecture, art, literature, music, dance, media, cuisine, dress, society, sports and mythology.
Arabs are a diverse group in terms of religious affiliations and practices. In the pre-Islamic era, most Arabs followed polytheistic religions. Some tribes had adopted Christianity or Judaism and a few individuals, the hanifs, apparently observed another form of monotheism. Today, about 93% of Arabs are adherents of Islam and there are sizable Christian minorities. Arab Muslims primarily belong to the Sunni, Shiite and Ibadi denominations. Arab Christians generally follow one of the Eastern Christian Churches, such as those within the Oriental Orthodox churches, Eastern Catholic churches, or Eastern Protestant churches. There also exist small numbers of Arab Jews still living in Arab countries and a much larger population of Jews descended from Arab Jewish communities living in Israel and various Western countries, who may or may not consider themselves Arab today. Christian minorities in Arab-majority states may also not consider themselves Arab, such as Copts and Assyrians. Other smaller minority religions also exist, such as the Druze, Alawites, Yazidism, Zoroastrianism and the Baháʼí Faith. Although Alawites, Druze and most Christian minorities do not identify as Arab.
Like every large culture group in history, Arabs have greatly influenced and contributed to diverse fields, notably the arts and architecture, language, philosophy, mythology, ethics, literature, politics, business, music, dance, cinema, medicine, science and technology in ancient and modern history.
Can a Muslim be an Arab and not a Muslim?
Can a Muslim be an Arab and not a Muslim?
One can be an Arab and not a Muslim and vice versa. One can be Arab by birth but not necessarily a Muslim, someone not born an Arab can become a Muslim but not the other way round.
www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-b…
Not all Arabs are followers of the Islam religion. They are a diverse group of people that are affiliated with different religious groups. All Muslims, on the contrary, follow the Islam religion. In addition to that, Arabic is the Arab’s first language, while Muslims may use any language in the world,...
difference.guru/difference-between-an-ara…
Arab is an ethno-linguistic category, identifying people who speak the Arabic language as their mother tongue (or, in the case of immigrants, for example, whose parents or grandparents spoke Arabic as their native language).
teachmideast.org/articles/arab-middle-eas…
“Muslim” refers to anyone who is a follower of the religion of Islam, which has existed since the 7th century AD. It centers on belief in one AND ONLY ONE God, Allah, and his Prophets and Messengers (including the ones from Judaism and Christianity), the last one being Mohamed.
www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-b…
https://www.arabamerica.com/not-all-arabs-are-muslims-and-not-all-muslims-are-arabs
Перевести · 23.09.2020 · In addition to this, only ~20% of Muslims actually live in the Middle East. Along with this it would be important to inform students that Muslims do use Arabic for their prayers because the Quran is written in Arabic, but that does not necessarily mean they speak Arabic …
https://difference.guru/difference-between-an-arab-and-a-muslim
Перевести · 13.11.2017 · Arab. Muslim. A term used to refer to the group of people who speak Arabic as their first language. A term used to refer to a follower of the Islam religion. Member of the Semitic people of the Arabian Peninsula. Do not belong to an ethnicity. Not all Arabs follow the Islam religion. All Muslims follow the Islam …
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-Arab-and-Muslim
Перевести · An Arab is a member of the Semitic race originally from the Arabian peninsula and surrounding territories who speaks Arabic and who inhabits much of the Middle East and northern Africa irrespective of the religion he believes in whereas a Muslim is a believer or adherent of Islam …
Quite simple. “Muslim” refers to anyone who is a follower of the religion of Islam, which has existed since the 7th century AD. It centers on belie...
One is religious, the other is ethnic. A muslim is a person who accepts the five pillars of the religion Islam. 1. Profession of faith. 2. Proper...
Arab : The person who is in the middle east or Arabian peninsula or gulf countries. Whoose lineage is from the tribes of Arabs. We can say Arabic s...
Just to augment Quora User's excellent answer here are some statistics: * Approximately 92% of Arabs are Muslims (according to: http://www.hf.ui...
Arab is an ethnic group. Muslim is a follower of a religion (Islam). There are 400+ million Arabs. Almost 95% of them are Muslims with significant...
An Arab is a member of the Semitic race originally from the Arabian peninsula and surrounding territories who speaks Arabic and who inhabits much o...
Arabs are people who speak Arabic (or had recent ancestors who spoke Arabic; cf. Italian-Americans). They’re a linguistic group, whose language is...
As others have written and explained in an orderly fashion, Arabs are an ethnicity that originate from Arabian Peninsula and incurred rapid growth...
Wow give me one similarity between the two. You can be both an Arab and a Muslim, you can be one of these and not the other or you could be neithe...
Arabs are a nation, they are Semites who have continuously inhabited the Arabian Peninsula for thousands of years. All inhabitants of the Arabian P...
https://www.islamicfinder.org/islamic-date-converter
Перевести · 11.03.2021 · The Hijri Year started when the Prophet (PBUH) migrated from Makkah to Madinah. Hijrah is also known as Hejira or Hijra means migration/emigration. The Prophet (PBUH) made the Hijrah as the Muslims were badly persecuted in Mecca and the Muslims …
https://www.islamicfinder.org/islamic-calendar
Перевести · The Islamic calendar consists of 12 months similar to the Gregorian calendar. However, it consists of 354-355 days unlike the 365-366 days in the regular calendar. The Islamic New Year starts …
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Many Americans have a hard time distinguishing between the terms Arab, Middle Eastern, and Muslim. Here we break down the various terms to help you distinguish between these three categories.
Arab is an ethno-linguistic category, identifying people who speak the Arabic language as their mother tongue (or, in the case of immigrants, for example, whose parents or grandparents spoke Arabic as their native language). Arabic is a Semitic language, closely related to Hebrew and Aramaic. While Arabs speak the same language, there is enormous ethnic diversity among the spoken dialects.
There are 26 countries or territories in western Asia and Africa where Arabic is the official or one of the official languages of the state: Algeria, Bahrain, Chad (with French), Comoros (with French and Shikomor), Djibouti (with French), Egypt, Eritrea (with Tigrignan), Iraq (with Kurdish), Israel (with Hebrew), Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia (with Somali), Syria, Sudan, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates, Western Sahara, and Yemen. Alternately, Arab typically applies to the 22 member states of the League of Arab States; these members include the above with exception of Chad, Eritrea, Israel, and the Western Sahara.
In each of these countries there may be different ethnic groups whose mother tongue is not Arabic. Members of these groups may also speak Arabic, but they might not identify themselves as Arabs. For example, in both Chad and Iraq, members of non-Arab ethnic groups use Arabic as a lingua franca to communicate. Also, in many Arab countries, before the founding of the state of Israel, there were active Arabic-speaking Jewish communities in such places as Morocco and Iraq; most of these populations moved to Israel after its founding in 1948 but maintain aspects of their Arab ancestry.
There are also minorities of Arabs in many other countries, such as Iran, Turkey, France, and the United States.
To answer “Who is Middle Eastern?” we must ask ourselves “What is the Middle East?” The Middle East itself is not a fixed term. It was originally coined in the early twentieth century to designate the area between the British colony of India and the Near East (the Balkans and western part of the Ottoman Empire). Of course, the term itself incorporates a European perspective, since the Middle East is only “east” relative to western Europe; had the Chinese had the power to impose their perspective in our maps, the region might have been known as the Midwest!
The “Middle East” is a term describing a region, or a geographical area sharing certain characteristics as opposed to areas like West Asia or North Africa, which define a relatively clear geographical location by reference to broadly accepted continental borders. This certainly complicates deciding who could be classified as “Middle Eastern”.
Depending on how we define those characteristics, the borders of the Middle East can change. For example, we might describe the Middle East geographically as a hot and arid region in western Asia between the Mediterranean in the west and the Indian subcontinent in the east; or we might describe it historically as a predominantly Muslim area sharing a common cultural heritage based on Arabic; or we might describe it strategically from a geopolitical and economic perspective, with consideration for its large reserves of oil.
Each definition has problems and might lead to a different map of the “Middle East.” For example, Turkey, Israel and Iran are not Arabic-speaking countries, yet most maps would include them in the Middle East. The Arabic-speaking countries of North Africa, including Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco, are not in Asia. Most current maps leave them out of the Middle East, except for Egypt, despite a long shared history and many cultural similarities with other Arab countries. Yet the same maps often include Iran, Afghanistan and sometimes even Pakistan – countries with different langua
3d Porn Long
Latex Anal Video
24video Net Mother And Son Porn
Massage Pillow
Loli Moans
Muslims - Wikipedia
Common Confusions About Arabs and Muslims
Arabs - Wikipedia
Not All Arabs Are Muslims and Not All Muslims Are Arabs
Arab vs Muslim - Difference
Hijri to Gregorian Date Converter - Islamic Date Converter ...
Islamic Calendar 2021 - Hijri 1442 to Gregorian Calendar ...
Arabic Muslim













.jpg)