20. The Mughal Empire
Ancient-History.
Learning Objectives
Students will acquire knowledge about
1. Political History of the Mughal Empire.
2. Babur and his achievements.
3. Humayuns’ difficulties and the Sur interregnum.
4. Akbar and his achievements – Religious policy.
5. Jahangir and Shah Jahan.
6. Aurangazeb and his religious policy.
7. Causes for the decline of the Mughal empire.
Political History
Babur (1526-1530)
Babur was the founder of the Mughal Empire in India. His original name was Zahiruddin Muhammad. He was related to Timur from his father’s side and to Chengiz Khan through his mother. Babur succeeded his father Umar Shaikh Mirza as the ruler of Farghana. But he was soon defeated by his distant relative and as a result lost his kingdom. He became a wanderer for sometime till he captured Kabul from one of his uncles. Then, Babur took interest in conquering India and launched four expeditions between 1519 and 1523.

Military Conquests
On the eve of Babur’s invasion of India, there were five prominent Muslim rulers – the Sultans of Delhi, Gujarat, Malwa, Bengal and the Deccan – and two prominent Hindu rulers – Rana Sangha of Mewar and the Vijayanagar Empire. Once again by the end of 1525, Babur started from Kabul to conquer India. He occupied Lahore easily by defeating its governor, Daulat Khan Lodi. Then he proceeded against Delhi where Ibrahim Lodi was the Sultan. On 21st April 1526 the first Battle of Panipat took place between Babur and Ibrahim Lodi, who was killed in the battle. Babur’s success was due his cavalry and artillery. Babur occupied Delhi and sent his son Humayun to seize Agra. Babur proclaimed himself as “Emperor of Hindustan”.
His subsequent victories over Rana Sangha and the Afghans secured his position as the ruler of India. Rana Sangha of Mewar was a great Rajput warrior. He marched against Babur and in the Battle of Khanua (near Agra) held in 1527 Babur won a decisive victory over him. Babur assumed the title Ghazi.
In 1528, Babur captured Chanderi from another Rajput ruler Medini Rai. In the next year, Babur defeated the Afghans in the Battle of Gogra in Bihar. By these victories, Babur consolidated his power in India. Babur died at Agra in 1530 at the age of forty seven.
Estimate of Babur
Babur was a great statesman and a man of solid achievements. He was also a great scholar in Arabic and Persian languages. Turki was his mother tongue. He wrote his memoirs, Tuzuk-i-Baburi in Turki language. It provides a vivid account of India. He frankly confesses his own failures without suppressing any facts. He was also a naturalist and described the flora and fauna of India.
Humayun (1530-1540)
Humayun was the eldest son of Babur. Humayun means “fortune” but he remained the most unfortunate ruler of the Mughal Empire. Humayun had three brothers, Kamran, Askari and Hindal. Humayun divided the empire among his brothers but this proved to be a great blunder on his part. Kamran was given Kabul and Kandahar. Sambhal and Alwar were given to Askari and Hindal.

When Humayun was busy with fighting the Afghans in the east, he got the news that Bahadur Shah of Gujarat was advancing towards Delhi. Therefore, he hastily concluded a treaty with the Afghan leader Sher Khan (later Sher Shah) and proceeded towards Gujarat.
Humayun captured Gujarat from Bahadur Shah and appointed Askari as its governor. But soon Bahadur Shah recovered Gujarat from Askari who fled from there. In the meantime Sher Khan became powerful in the east. Humayun marched against him and in the Battle of Chausa, held in 1539, Sher Khan destroyed the Mughal army and Humayun escaped from there. Humayun reached Agra to negotiate with his brothers. But as they were not cooperative, Humayun was forced to fight with Sher Khan alone in the Battle of Bilgram in 1540. This battle was also known as Battle of Kanauj. Humayun was thoroughly defeated by Sher Khan. After losing his kingdom, Humayun became an exile for the next fifteen years.
Sur Interregnum (1540-1555)
The founder of the Sur dynasty was Sher Shah, whose original name was Farid. He was the son of Hasan Khan, a jagirdar of Sasaram in Bihar. Later, Farid served under the Afghan ruler of Bihar, who gave him the title Sher Khan for his bravery. We have already seen how he defeated Humayun at the Battle of Chausa and became the ruler of Delhi in 1540.
Sher Shah Sur (1540-1545)
Sher Shah waged extensive wars with the Rajputs and expanded his empire. His conquests include Punjab, Malwa, Sind, Multan and Bundelkhand. His empire consisted of the whole of North India except Assam, Nepal, Kashmir and Gujarat.

Sher Shah’s Administration
Although his rule lasted for five years, he organized a brilliant administrative system. The central government consisted of several departments. The king was assisted by four important ministers:
1. Diwan –i- Wizarat – also called as Wazir - in charge of Revenue and Finance.
2. Diwan-i-Ariz – in charge of Army.
3. Diwan-i-Rasalat- Foreign Minister.
4. Diwan-i-Insha- Minister for Communications.
Sher Shah’s empire was divided into forty seven sarkars. Chief Shiqdar (law and order) and Chief Munsif (judge) were the two officers in charge of the administration in each sarkar. Each sarkar was divided into several parganas. Shiqdar (military officer), Amin (land revenue), Fotedar (treasurer) Karkuns (accountants) were in charge of the administration of each pargana. There were also many administrative units called iqtas. SHER SHAH SUR
The land revenue administration was well organized under Sher Shah. Land survey was carefully done. All cultivable lands were classified into three classes – good, middle and bad. The state’s share was one third of the average produce and it was paid in cash or crop. His revenue reforms increased the revenue of the state. Sher Shah introduced new silver coins called “Dam” and they were in circulation till 1835.
Sher Shah had also improved the communications by laying four important highways. They were: 1. Sonargaon to Sind 2. Agra to Burhampur 3. Jodhpur to Chittor and 4. Lahore to Multan. Rest houses were built on the highways for the convenience of the travelers. Police was efficiently reorganized and crime was less during his regime.
The military administration was also efficiently reorganized and Sher Shah borrowed many ideas like the branding of horses from Alauddin Khalji.
Estimate of Sher Shah
Sher Shah remained a pious Muslim and generally tolerant towards other religions. He employed Hindus in important offices. He was also a patron of art and architecture. He built a new city on the banks of the river Yamuna near Delhi. Now the old fort called Purana Qila and its mosque is alone surviving. He also built a Mausoleum at Sasaram, which is considered as one of the master pieces of Indian architecture. Sher Shah also patronized the learned men. Malik Muhammad Jayasi wrote the famous Hindi work Padmavat during his reign.
After Sher Shah’s death in 1545 his successors ruled till 1555 when Humayun reconquered India.
Humayun (1555-1556)
When Humayun left India in 1540, he married Hamida Banu Begum on his way to Sind. When they stayed in Amorkot, a Hindu kingdom ruled by Rana Prasad, Akbar was born in 1542. Humayun then proceeded to Iran and sought help from its ruler. He later defeated his brothers, Kamran and Askari. In the meantime the Sur dynasty in India was declining rapidly. In 1555, Humayun defeated the Afghans and recovered the Mughal throne. After six months, he died in 1556 due to his fall from the staircase of his library. Although Humayun was not a good General and warrior, he was kind and generous. He was also learned and a student of mathematics, astronomy and astrology. He also loved painting and wrote poetry in Persian language.
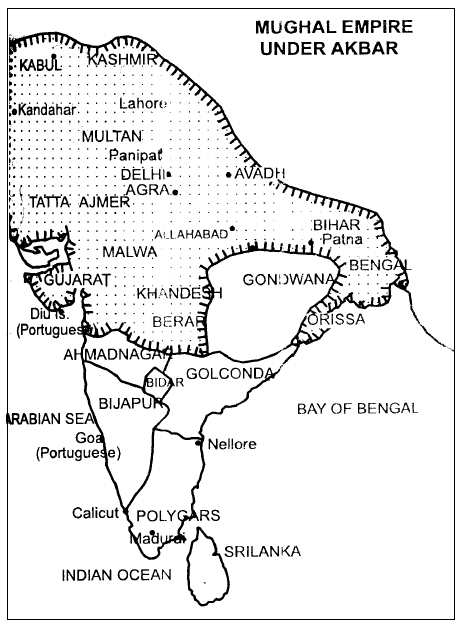
Akbar (1556-1605)
Akbar was one of the greatest monarchs of India. He succeeded the throne after his father Humayun’s death. But his position was dangerous because Delhi was seized by the Afghans. Their commander-in-Chief, Hemu, was in charge of it. In the second Battle of Panipat in 1556, Hemu was almost on the point of victory. But an arrow pierced his eye and he became unconscious. His army fled and the fortune favoured Akbar. The Mughal victory was decisive.

During the first five years of Akbar’s reign, Bairam Khan acted as his regent. He consolidated the Mughal empire. After five years he was removed by Akbar due to court intrigues and sent to Mecca. But on his way Bairam was killed by an Afghan.
Akbar’s military conquests were extensive. He conquered northern India from Agra to Gujarat and then from Agra to Bengal. He strengthened the northwest frontier. Later, he went to the Deccan.
Relations with Rajputs
The Rajput policy of Akbar was notable. He married the Rajput princess, the daughter of Raja Bharamal. It was a turning point in the history of Mughals. Rajputs served the Mughals for four generations. Many of them rose to the positions of military generals. Raja Bhagawan Das and Raja Man Singh were given senior positions in the administration by Akbar. One by one, all Rajput states submitted to Akbar.
But the Ranas of Mewar continued to defy despite several defeats. In the Battle of Haldighati, Rana Pratap Singh was severely defeated by the Mughal army led by Man Singh in 1576. Following the defeat of Mewar, most of the leading Rajput rulers had accepted Akbar’s suzerainty.
Akbar’s Rajput policy was combined with a broad religious toleration. He abolished the pilgrim tax and later the jiziya. The Rajput policy of Akbar proved to be beneficial to the Mughal state as well as to the Rajputs. The alliance secured to the Mughals the services of the bravest warriors. On the other hand it ensured peace in Rajasthan and a number of Rajputs who joined the Mughal service rose to important positions.
Religious Policy
Akbar rose to fame in the pages of history due to his religious policy. Various factors were responsible for his religious ideas. The most important among them were his early contacts with the sufi saints, the teachings of his tutor Abdul Latif, his marriage with Rajput women, his association with intellectual giants like Shaikh Mubarak and his two illustrious sons – Abul Faizi and Abul Fazl – and his ambition to establish an empire in Hindustan.
In the beginning of his life, Akbar was a pious Muslim. Soon after marrying Jodh Bai of Amber, he abolished the pilgrim tax and in 1562, he abolished jiziya. He allowed his Hindu wives to worship their own gods. Later, he became a skeptical Muslim. In 1575, he ordered for the construction of Ibadat Khana (House of worship) at his new capital Fatepur Sikri. Akbar invited learned scholars from all religions like Hinduism, Jainism, Christianity and Zoroastrianism. He disliked the interference of the Muslim Ulemas in political matters. In 1579, he issued the “Infallibility Decree” by which he asserted his religious powers.
In 1582, he promulgated a new religion called Din Ilahi or Divine Faith. It believes in one God. It contained good points of all religions. Its basis was rational. It upholds no dogma. It was aimed at bridging the gulf that separated different religions. However, his new faith proved to be a failure. It fizzled out after his death. Even during his life time, it had only fifteen followers including Birbal. Akbar did not compel anyone to his new faith.
Land Revenue Administration
Akbar made some experiments in the land revenue administration with the help of Raja Todar Mal. The land revenue system of Akbar was called Zabti or Bandobast system. It was further improved by Raja Todar Mal. It was known as Dahsala System which was completed in 1580. By this system, Todar Mal introduced a uniform system of land measurement. The revenue was fixed on the average yield of land assessed on the basis of past ten years. The land was also divided into four categories – Polaj (cultivated every year), Parauti (once in two years), Chachar (once in three or four years) and Banjar (once in five or more years). Payment of revenue was made generally in cash.
Mansabdari System
Akbar introduced the Mansabdari system in his administration. Under this system every officer was assigned a rank (mansab). The lowest rank was 10 and the highest was 5000 for the nobles. Princes of royal blood received even higher ranks. The ranks were divided into two – zat and sawar. Zat means personal and it fixed the personal status of a person. Sawar rank indicated the number of cavalrymen of a person who was required to maintain. Every sawar had to maintain at least two horses. The mansab rank was not hereditary. All appointments and promotions as well as dismissals were directly made by the emperor.
Jahangir (1605-1627)
When Akbar died, Prince Salim succeeded with the title Jahangir (Conqueror of World) in 1605. Jahangir’s rule witnessed a spate of rebellions. His son Khusrau revolted but was defeated and imprisoned. One of his supporters, Guru Arjun, the fifth Sikh Guru, was beheaded.

Nur Jahan
In 1611, Jahangir married Mehrunnisa who was known as Nur Jahan (Light of World). Her father Itimaduddauala was a respectable person. He was given the post of chief diwan. Other members of her family also benefited from this alliance. Nur Jahan’s elder brother Asaf Khan was appointed as Khan-i-Saman, a post reserved for the nobles. In 1612, Asaf Khan’s daughter, Arjumand Banu Begum (later known as Mumtaj), married Jahangir’s third son, prince Khurram (later Shah Jahan).
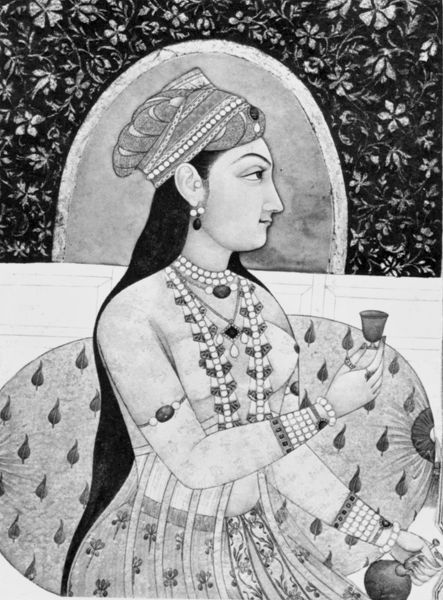

It was believed by some historians that Nur Jahan formed a group of “junta” and this led to two factions in the Mughal court. This drove Shah Jahan into rebellion against his father in 1622, since he felt that Jahangir was completely under Nur Jahan’s influence. However, this view is not accepted by some other historians. Till Jahangir became weak due to ill health, he only took important political decisions. It is revealed from his autobiography.
However, it is clear that Nur Jahan dominated the royal household and set new fashions based on Persian traditions. She encouraged Persian art and culture in the court. She was a constant companion of Jahangir and even joined him in his hunting.
The rise of Shah Jahan was due to his personal ambitions. He rose in revolt against his father who ordered him to go to Kandahar. This rebellion distracted the activities of the empire for four years. After Jahangir’s death in 1627, Shah Jahan reached Agra with the support of the nobles and the army. Nur Jahan was given a pension and lived a retired life till her death eighteen years later.
Shah Jahan (1627-1658)
Shah Jahan launched a prolonged campaign in the northwest frontier to recover Kandahar and other ancestral lands. The Mughal army lost more than five thousand lives during the successive invasions between 1639 and 1647. Then Shah Jahan realized the futility of his ambition and stopped fighting.
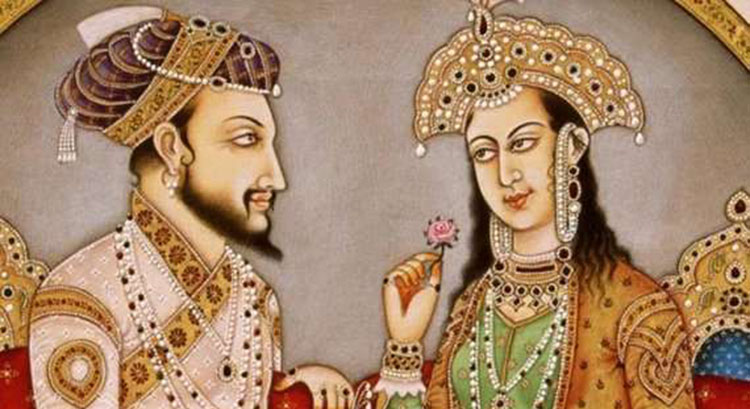

MUMTAJ – A PAINTING
His Deccan policy was more successful. He defeated the forces of Ahmadnagar and annexed it. Both Bijapur and Golkonda signed a treaty with the emperor. Shah Jahan carved four Mughal provinces in the Deccan – Khandesh, Berar, Telungana and Daulatabad. They were put under the control of his son Aurangazeb.
War of Succession
The last years of Shah Jahan’s reign were clouded by a bitter war of succession among his four sons – Dara Shikoh (crown prince), Shuja (governor of Bengal), Aurangazeb (governor of Deccan) and Murad Baksh (governor of Malwa and Gujarat). Towards the end of 1657, Shah Jahan fell ill at Delhi for some time but later recovered. But the princes started fighting for the Mughal throne.
Aurangazeb emerged victorious in this struggle. He entered the Agra fort after defeating Dara. He forced Shah Jahan to surrender. Shah Jahan was confined to the female apartments in the Agra fort and strictly put under vigil. But he was not ill-treated. Shah Jahan lived for eight long years lovingly nursed by his daughter Jahanara. He died in 1666 and buried beside his wife’s grave in the Taj Mahal.
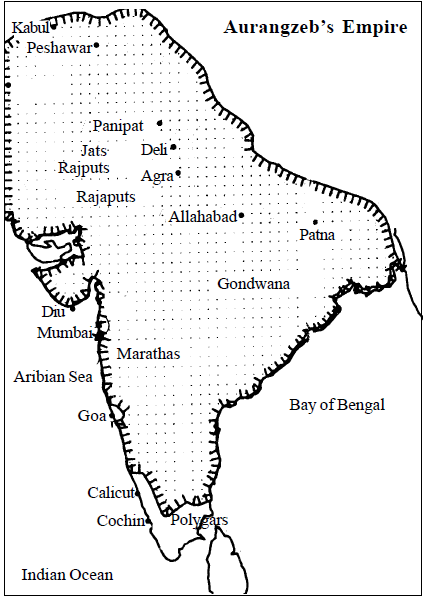
Aurangazeb (1658-1707)
Aurangazeb was one of the ablest of the Mughal kings. He assumed the title Alamgir, World Conqueror. His military campaigns in his first ten years of reign were a great success. He suppressed the minor revolts. But he faced serious difficulties in the latter part of his reign. The Jats and Satnamis and also the Sikhs revolted against him. These revolts were induced by his harsh religious policy.
Deccan Policy
The Deccan policy of the Mughals started from the reign of Akbar, who conquered Khandesh and Berar. Jahangir fought against Malik Amber of Ahmadnagar. During the Shah Jahan’s reign, Aurangazeb, as governor of Deccan, followed an aggressive Deccan policy. When he became the Mughal emperor, for the first twenty five years, he concentrated on the northwest frontier. At that time, the Maratha ruler, Sivaji carved out an independent Maratha kingdom in the territories of north and south Konkan.
To contain the spread of the Marathas, Aurangazeb decided to invade Bijapur and Golkonda. He defeated Sikandar Shah of Bijapur and annexed his kingdom. Then, he proceeded against Golkonda and eliminated the Kutb Shahi dynasty. It was also annexed by him. In fact, the destruction of the Deccan kingdoms was a political blunder on the part of Aurangazeb. The barrier between the Mughals and the Marathas was removed and there ensued a direct confrontation between them. Also, his Deccan campaigns exhausted the Mughal treasury. According to J.N. Sarkar, the Deccan ulcer ruined Aurangazeb.
Religious Policy
Aurangazeb was a staunch and orthodox Muslim in his personal life. His ideal was to transform India into an Islamic state. He created a separate department to enforce moral codes under a high-powered officer called Muhtasib. Drinking was prohibited. Cultivation and use of bhang and other drugs were banned. Aurangazeb forbade music in the Mughal court. He discontinued the practice of Jarokhadarshan. He also discontinued the celebration of Dasarah and royal astronomers and astrologers were also dismissed from service.
Initially Aurangazeb banned the construction of new Hindu temples and repair of old temples. Then he began a policy of destroying Hindu temples. The celebrated temples at Mathura and Benares were reduced to ruins. In 1679, he reimposed jiziya and pilgrim tax. He was also not tolerant of other Muslim sects. The celebration of Muharram was stopped. His invasions against the Deccan sultanates were partly due to his hatred of the Shia faith.
He was also against the Sikhs and he executed the ninth Sikh Guru Tej Bahadur. This had resulted in the transformation of Sikhs into a warring community.
His religious policy was responsible for turning the Rajputs, the Marathas and Sikhs into the enemies of Mughal empire. It had also resulted in the rebellions of the Jats of Mathura and the Satnamis of Mewar. Therefore, Aurangazeb was held responsible for the decline of the Mughal empire.
Personality and Character of Aurangazeb
In his private life, Aurangazeb was industrious and disciplined. He was very simple in food and dress. He earned money for his personal expenses by copying Quran and selling those copies. He did not consume wine. He was learned and proficient in Arabic and Persian languages. He was a lover of books. He was devoted to his religion and conducted prayers five times a day. He strictly observed the Ramzan fasting.
In the political field, Aurangazeb committed serious mistakes. He misunderstood the true nature of the Maratha movement and antagonized them. Also, he failed to solve the Maratha problem and left an open sore. His policy towards Shia Deccan Sultanates also proved to be a wrong policy.
His religious policy was also not successful. Aurangazeb was an orthodox Sunni Muslim. But his move to apply his religious thought rigidly in a non-Muslim society was a failure. His antagonistic policies towards non-Muslims did not help him to rally the Muslims to his side. On the other hand it had strengthened political enemies of the Mughal Empire.
Causes for the Downfall of the Mughals
The Mughal Empire declined rapidly after the death of Aurangazeb. The Mughal court became the scene of factions among the nobles. The weakness of the empire was exposed when Nadir Shah imprisoned the Mughal Emperor and looted Delhi in 1739. The causes for the downfall of the Mughal Empire were varied. To some extent, the religious and Deccan policies of Aurangazeb contributed to its decline. The weak successors and demoralization of the Mughal army also paved the way for it. The vastness of the empire became unwieldy. The financial difficulties due to continuous wars led to the decline. The neglect of the sea power by the Mughals was felt when the Europeans began to settle in India. Further, the invasions of Nadir Shah and Ahmad Shah Abdali weakened the Mughal state. Thus the decline and downfall of the Mughal Empire was due to the combination of political, social and economic factors.
Learning Outcome
After learning this lesson the students will be able to explain
1. Political History of the Mughal Empire from Babur to Aurangazeb.
2. Achievements of Babur and the difficulties of Humayun.
3. Sur interregnum – Sher Shah’s administration.
4. The reign of Akbar – his administration, Mansabdari system and religious policy.
5. Jahangir,