UNIFORM AND NON-UNIFORM MOTION
by: SNM
UNIFORM AND NON-UNIFORM MOTION
A moving body may cover equal distances in equal intervals of time or different distances in equal intervals of time. On the basis of above assumption, the motion of a body can be classified as uniform motion and non-uniform motion.
Uniform motion:
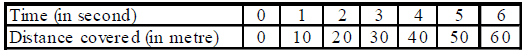
When a body covers equal distances in equal intervals of time however small may be time intervals, the body is said to describe a uniform motion.
Example of uniform motion –
(i) An aeroplane flying at a speed of 600 km/h
(ii) A train running at a speed of 120 km/h
(iii) Light energy travelling at a speed of 3 × 108 m/s
Non-uniform motion:

When a body covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, the body is said to be moving with a nonuniform motion.
Example of non-uniform motion –
(i) An aeroplane running on a runway before taking off.
(ii) A freely falling stone under the action of gravity.
(iii) An object thrown vertically upward.
(iv) When the brakes are applied to a moving car.
Velocity H The velocity of a body is the displacement of a body per unit time.

The displacement covered by a body per unit time or the speed of a body in specified direction is called the velocity.
Unit: In SI system: m/s or ms-1
In CGS system: cm/s or cms-1
Other km/h or kmh-1, km/min.
Uniform velocity
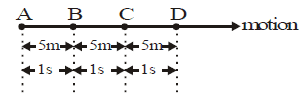
Body moving with uniform velocity
When a body covers equal displacement in equal intervals of time, the body is said to be moving with a uniform velocity.
Conditions for uniform velocity:-
(i) The body must cover equal displacement in equal intervals of time.
(ii) The direction of motion of the body should not change.
Ex. (i) A train running towards south with a speed of 120 km/h.
(ii) An aeroplane flying due north-east with a speed of 600 km/h.
Very important note :-
The direction of velocity represents the direction of motion of body.
OR
Sign of velocity represents the direction of motion of body.
Non-uniform velocity/variable velocity :
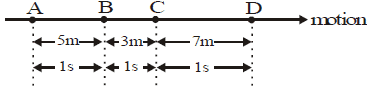
Body moving with non-uniform velocity
When a body covers unequal displacement in equal intervals of time, the body is said to be moving with variable velocity.
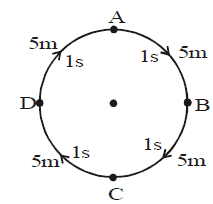
Body moving with variable velocity
When a body covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, but its direction changes, then the body is said to be moving with variable velocity.
Conditions for variable velocity:
(i) It should cover unequal displacement in equal intervals of time.
(ii) It should cover equal distances in equal intervals of time but its direction must change.
Ex. (i) A car running towards north on a busy road has a variable velocity as the displacement covered by it per unit time changes with change in the road condition.
(ii) The blades of a rotating ceiling fan, a person running around a circular track with constant speed etc. are the example of variable velocity, as the direction of the moving body changes in each case.
Average velocity:
Total displacement divided by total time is called average velocity.
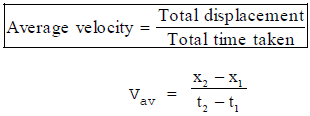
OR
The arithmetic mean of initial velocity and final velocity for a given time period, is called average velocity.

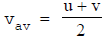
where u = initial velocity, v = final velocity
Memorize: When a body moves with constant velocity, the average velocity is equal to instantaneous velocity. The body is said to be in uniform motion.