Genius of Stephen Williams Hawking
Great Space
Stephen William Hawking was an English theoretical physicist, cosmologist, author, and Director of Research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology within the University of Cambridge.His scientific works included a collaboration with Roger Penrose on gravitational singularity theorems in the framework of general relativity and the theoretical prediction that black holes emit radiation, often called Hawking radiation. Hawking was the first to set out a theory of cosmology explained by a union of the general theory of relativity and quantum mechanics. He was a vigorous supporter of the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics.
Hawking was an Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts (FRSA), a lifetime member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, and a recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the highest civilian award in the United States. In 2002, Hawking was ranked number 25 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge between 1979 and 2009 and achieved commercial success with works of popular science in which he discusses his own theories and cosmology in general. His book A Brief History of Time appeared on the British Sunday Timesbest-seller list for a record-breaking 237 weeks.
Hawking had a rare early-onset slow-progressing form of motor neurone disease (also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis "ALS" or Lou Gehrig's disease) that gradually paralysed him over the decades. Even after the loss of his speech, he was still able to communicate through a speech-generating device, initially through use of a hand-held switch, and eventually by using a single cheek muscle. He died on 14 March 2018 at the age of 76.
Life and science
Hawking's genius, which arguably deserves a Nobel Prize, is to have brought together several different but equally fundamental fields of physical theory: gravitation, cosmology, quantum theory, thermodynamics and information theory and find a connection.
It starts with general relativity: the theory of gravitation that Albert Einstein devised in the 1910s to replace that of Isaac Newton.
Newton's view of gravity assumed that massive objects created a "field" that permeated space, rather like the field of a magnet. This field enabled one body with mass, like the Earth, to exert a force on another, like the Moon or an apple. Newton did not claim to know what this force was. It was simply a fact of nature that all objects that possess mass create it.
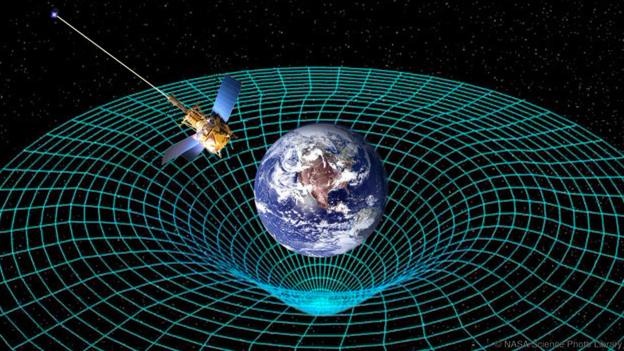
But according to Einstein's theory of general relativity, gravity is not a field in space. Instead, it is a property of space itself.
The idea is that massive bodies, such as the Sun, cause space to curve around them. This distortion of space affects the motion of anything nearby. For instance, it holds the Earth in orbit around the Sun, like a marble rolling around the rim of a bowl.
One of the predictions of Einstein's theory is that a sufficiently large object, such as a really massive star, can collapse under the pull of its own gravity in a runaway process. All the mass shrinks into an infinitesimally small point of infinite density, called a singularity.
This collapse creates a region of space so severely warped by gravity that not even light can escape from it. We call this a black hole.
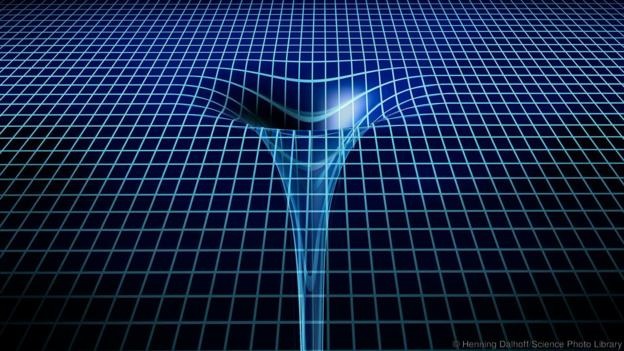
All this had been proposed in a 1939 paper by the American physicist Robert Oppenheimer – who would later help develop the atomic bomb – and his student Hartland Snyder.
It was only really at this point that Hawking's exceptional intellect began to shine through
But many physicists could not believe in something as bizarre as a singularity. So for years the idea languished, as others assumed that some process would intervene to prevent it.
It was only around 1959, when Hawking began his undergraduate studies at the University of Oxford, that physicists started to take the idea seriously. It was examined closely by John Wheeler at Princeton University in New Jersey, who allegedly gave black holes their name, Roger Penrose in the UK, and Yakov Zel'dovich in the Soviet Union.
After completing his degree in physics, Hawking started a PhD at the University of Cambridge, under the supervision of cosmologist Denis Sciama. His attention was captured by this resurgence of interest in general relativity and black holes.

It was only really at this point that Hawking's exceptional intellect began to shine through. He had just scraped a First at Oxford, and had a lot of mathematical catching-up to do. He had also recently been diagnosed with a form of motor neurone disease called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, which would ultimately leave him almost entirely paralysed.
ultimately leave him almost entirely paralysed.
Hawking's disability was severe, and even walking with crutches was very difficult for him
Under Sciama's guidance, Hawking began thinking about the Big Bang theory: the idea that the universe began as a tiny speck that subsequently expanded. Nowadays this is widely accepted, but at the time it was still up for debate.
Hawking realised that the Big Bang was rather like the collapse of a black hole in reverse.
He developed this idea with Penrose. In 1970 the two of them published a paper showing that general relativity implies that the universe must have begun as a singularity.
By this time Hawking's disability was severe, and even walking with crutches was very difficult for him. In late 1970, as he was getting laboriously into bed one night, he had a sudden realisation about black holes: one that would spark a series of discoveries about how they behave.

Hawking realised that a black hole can only increase, never decrease, in size.
This may seem obvious. Since nothing that gets too close can escape, a black hole can only ever swallow more matter and thus gain mass.
The total entropy of the universe can only increase, never decrease
A black hole's mass in turn determines its size, measured as the radius of the event horizon, the point beyond which nothing can escape. This boundary will creep inexorably outwards like the skin of an inflating balloon.
But Hawking went further. He showed that a black hole can never be split into smaller ones – even, say, through the collision of two black holes.
Then Hawking made another intuitive leap. He argued that the event horizon's ever-expanding surface area was analogous to another quantity that, according to physics, could only grow.

That quantity was entropy, which measures the amount of disorder in a system. Atoms stacked together regularly in a crystal have low entropy, while atoms drifting around randomly in a gas have high entropy.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, the total entropy of the universe can only increase, never decrease. In other words, the universe inevitably gets more disordered as it gets older. Hawking pointed out that these two rules of nature – the increasing surface area of a black hole and the increasing entropy of the universe – were oddly similar.
Most physicists – including Hawking – thought Bekenstein's proposal made no sense
When Hawking announced his result at the end of 1970, a young physicist named Jacob Bekensteinmade a bold proposal: what if this wasn't just an analogy? Bekenstein suggested that the surface area of a black hole's event horizon might be a measure of the black hole's entropy.
But that seemed wrong. If an object has entropy, it must also have a temperature. And if it has a temperature, then it must radiate energy, yet the whole point of a black hole is that nothing gets out.
For this reason, most physicists – including Hawking – thought Bekenstein's proposal made no sense. Even Bekenstein himself said that the black hole's apparent temperature couldn't be "real" since it leads to a paradox.
But when Hawking set out to prove Bekenstein wrong, he found that the young student was, as he later admitted, "basically correct". In order to show this, he had to bring together two areas of physics that nobody else had managed to unify: general relativity and quantum theory.
Quantum theory is used to describe invisibly small things, like atoms and their component particles, while general relativity is used to describe matter on the cosmic scale of stars and galaxies.
According to quantum theory, allegedly empty space is in fact far from a void
The two theories seem fundamentally incompatible. General relativity assumes that space is smooth and continuous like a sheet, whereas quantum theory insists that the world and everything in it is grainy at the smallest scales, parcelled into discrete lumps.
Physicists have struggled for decades to unify the two theories – which might then point to a "theory of everything". Such a theory is, to use an apt cliché, a holy grail of modern physics.
In his early career Hawking expressed a yearning for such a theory, but his analysis of black holes did not pretend to offer one. Instead, his quantum analysis of black holes used a sort of patchwork of the two existing theories.

According to quantum theory, allegedly empty space is in fact far from a void, because space cannot be smoothly, absolutely empty at all scales. Instead it is alive with activity.
Pairs of particles are constantly fizzing spontaneously into existence, one made of matter and the other antimatter. One of the particles has positive energy and the other negative, so overall no new energy is being created. The two then annihilate one another so quickly that they cannot be directly detected. As a result, they are called "virtual particles".
Hawking had proved himself wrong: black holes can get smaller after all
Hawking suggested that these pairs of particles could be upgraded from virtual to real, but only if they are created right next to a black hole.
There is a chance that one of the pair will be sucked inside the event horizon, leaving its partner stranded. This severed twin may then shoot out into space. If the negative-energy particle is absorbed by the black hole, the total energy of the black hole decreases, and therefore so does its mass. The other particle then carries away positive energy.
The end result is that the black hole radiates energy, now known as Hawking radiation, while gradually getting smaller. In other words, Hawking had proved himself wrong: black holes can get smaller after all. This is tantamount to saying that the black hole will slowly evaporate, and that it is not truly black at all.
What's more, that shrinkage would not necessarily be gradual and sedate.

In 1971 Hawking conceived a radical new vision of black holes. During the Big Bang, he suggested, some lumps of matter could have collapsed into miniature black holes. Each lump would weigh billions of tons, which sounds a lot but is far smaller than the Earth, and the resulting black hole would be smaller than an atom.
Because a black hole's temperature increases as its event horizon's surface area gets smaller, black holes this tiny would be hot: Hawking described them as "white hot". They would fizz with Hawking radiation, shedding mass until they eventually disappeared.
And they would not go quietly. A mini-black hole would get hotter as it got smaller, until eventually it would explode with the energy of a million one-megaton hydrogen bombs.
Hawking outlined his theory of Hawking radiation and exploding primordial mini-black holes in a paper in Nature in 1974. It was a shocking, controversial idea. Yet nowadays most physicists believe that Hawking radiation really will be generated by black holes.
So far nobody has managed to detect this radiation. That's not surprising, though: an ordinary black hole's temperature would barely be above absolute zero, so the energy it emits as Hawking radiation would be extremely tiny.
Seven years later, Hawking announced another disturbing implication of disappearing black holes. They destroy information, he said.

When particles or light rays pass inside a black hole's event horizon, they never return to the rest of the universe. Any such entity can be considered to carry information: for example, information about a particle's mass and position. This information is also locked away inside the black hole.
However, what happens to that information if the black hole evaporates? There are two possibilities: either it is somehow encoded in the Hawking radiation emitted by the black hole, or it is gone for good. Hawking claimed that it vanished.
When Hawking suggested that black holes destroy information, Susskind argued that he was plain wrong
When Hawking spoke in San Francisco in 1981 about the paradox of vanishing information in black-hole physics, the American physicist Leonard Susskinddisagreed. He was one of the few who appreciated just how disturbing it would be if information were lost from the universe.
We like to imagine that causes come before their effects, not the other way around. In principle, although generally not in practice, that means we could trace and reconstruct the history of any particle in the universe based on the information about its current state.
But that reconstruction from effects to cause would become impossible if information is being destroyed in black holes. If information is truly being lost, the whole notion of cause and effect starts to look shaky.
So when Hawking suggested that black holes destroy information, Susskind argued that he was plain wrong.

The debate raged, in a fairly collegial manner, for decades. In 1997 it took on the form of a wager, something Hawking loves to indulge. Hawking bet John Preskill of the California Institute of Technology an encyclopaedia that information was indeed lost in black holes, while Preskill bet that it was not.
He tried to describe the Big Bang in quantum mechanical terms
At a conference in Dublin in 2004, Hawking finally conceded that Susskind was right – and that Preskill should get his encyclopaedia. But in typically stubborn fashion, he qualified that statement by claiming that the information was only returned to the universe in a corrupted form that was virtually impossible to read, and that he had proved that this was so.
Hawking spelt out his argument in a short paper the following year. It did not convince everyone that his argument was better than Susskind's.
The episode was characteristic of Hawking's style. He is bold and brilliant, but not always rigorous enough to fully persuade, and sometimes seemingly driven by an intuition that can turn out to be quite wrong – as when he bet against experimental detection of the Higgs particle.

The melange of general relativity, quantum theory, thermodynamics and information theory in Hawking's work on black holes is innovative and remarkable. Nothing else he has done has equalled it.
The very concept of an "origin" in time vanishes into the quantum foam
In the 1980s he tried to describe the Big Bang in quantum mechanical terms. Working with James Hartle, he developed a simple quantum equation that supposedly describes the entire universe in its early stages. But it does so in such general terms that, for many physicists, it doesn't say anything very meaningful.
The one thing the equation does suggest, however, is that it is futile to ask about the ultimate origin of the universe.
When the universe was still extremely tiny, less than a billionth of a yoctometre across, quantum theory implies that the distinction between space and time was extremely fuzzy. That means the early universe did not have meaningful boundaries in time or space, even though it was still self-contained. The very concept of an "origin" in time vanishes into the quantum foam.
This is the model explained in Hawking's best-selling A Brief History of Time (1988), which secured his status as a global celebrity. The idea is still debated.
Inspiring people both through his deep insights into the most mysterious corners of the cosmos and his ability to succeed in spite of a disease that had been expected to take his life at an early age, Hawking became an inspiration to people the world over, appearing in several TV shows. Twice married and divorced, Hawking was father to three children—two sons and a daughter—by his first wife, Jane Hawking.
At his 75th birthday party in Cambridge last year, Hawking urged people to “look up at the stars and not down at your feet” and to explore the wonders of the world around them. “Be curious,” he said, according to a University of Cambridge statement, “and however difficult life may seem, there is always something you can do, and succeed at. It matters that you don’t just give up.”
Sources: BBC,Wikipedia,Nature,Sciencemag.
That's the book(Must Read)

More Hawking's books:
The Grand Design (Rating 4.0 - 977 Reviews, Bestseller, Must Read)
The Illustrated Brief History of Time, Updated and Expanded Edition (Rating 4,5 - 2100 Reviews,1996)
George's Secret Key to the Universe (Rating 4,5 - 177 Reviews, 2009)
The Universe in a Nutshell (Rating 4,5 - 2123 Reviews, 2001, Bestseller, Must Read)
Legendary shows:
The Theory of Everything - Classic, must see.
Into the Universe With Stephen Hawking - One of the most successful educational course about space and our universe.
