CHEMISTRY
PSC Company Corporation Group
*OUR TELIGRAM GROUP LINK* : https://t.me/psccompanycorporation
Introduction

Father of Chemistry
Ans : Robert Boyle
The author of the book 'Sceptical Chymist' is
Ans : Robert Boyle
Father of Modern Chemistry
Ans : Antoine Lavoisier
Father of Indian Chemistry
Ans : P.C.Roy
Father of Organic Chemistry
Ans : Friedrich Wohler
Ancient Chemistry is known as
Ans : Alchemy
Ancient Chemists were known as
Ans : Alchemists
The scientist known as the father of Sodapop
Ans : Joseph Priestly
International year of chemistry
Ans : 2011
New methods used in chemistry which aim to reduce pollution are called
Ans : Green Chemistry
The term Green Chemistry was coined by
Ans : Paul.T.Anastas
STATES OF MATTER
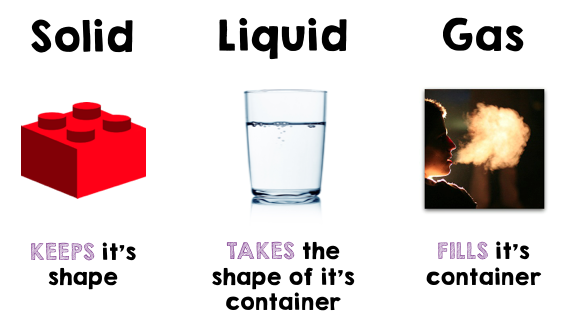
There are seven stable physical states
1) Solid
2) Liquid
3) Gas
4) Plasma
5) Bose- Einstein condensate (Super atom)
6) Fermionic condensate
7) Super Fluidity
■DUAL NATURE OF MATTER
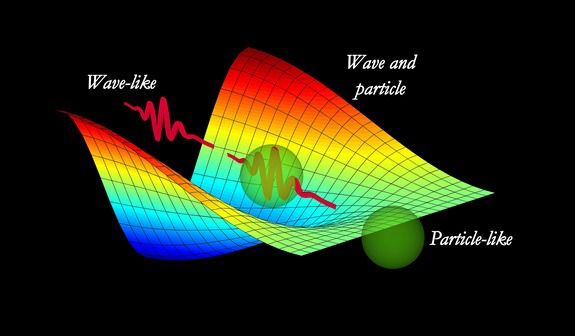
The concept dual nature of Matter was put forward by
Ans : Louis de-Broglie
The construction of electron microscope was based on
Ans : Dual Nature of Matter
The dual nature of electrons was
Ans : I.H.Germer
ATOM

Basic unit of Chemistry
Ans : Atom
Smallest units of a matter
Ans : Atom
Atom was derived from a greek word
Ans : 'Atomos' (means indivisible)
Atom was discovered by
Ans : John Dalton
Law of Multiple Proportion was put forward by
Ans : John Dalton
The term 'atom' was coined by
Ans : Ostwald
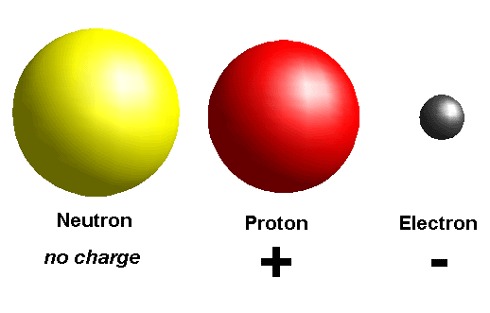
The fundamental particles of an atom
Ans : Proton, Electron and Neutron
The central part of an atom
Ans : Nucleus
The sub atomic particles of Nucleus
Ans : Protons and Neutrons
Heaviest sub atomic particle
Ans : Neutron
Lightest sub atomic particle
Ans : Electron
Moving particle of an atom
Ans : Electron
The charge of an electron is
Ans : Negative
Protons and Neutrons are collectively known as
Ans : Nucleons
Chemical property of a substance is determined by
Ans : Electrons
The smallest atom
Ans : Helium (He)
The simplest atom
Ans : Hydrogen (H)
Biggest known atom
Ans : Francium (Fr)
The unit of measuring mass of an atom
Ans : Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
1 atomic mass unit is equal to
Ans : 1.6605 xlO’27 Kg
The element used to find amu
Ans : Carbon-12
ELECTRONS
Electron is discovered by
Ans : JJ.Thomson
The name Electron was proposed by
Ans : Stoney
Charge of an electron
Ans : 1.6 x 10-19C (determined by Millikan)
Mass of electron
Ans : 9.1 x 10_31kg
Dual nature of electron
Ans : Louis-de-broglie
PROTON
Proton was discovered by
Ans : Ernest Rutherford
The identity card of an element
Ans : Proton
The mass of a proton is
Ans : 1.672 x 10^-27 kg
The theory of Proton was presented by
Ans : William Prout
NEUTRON

Neutron was discovered by
Ans : James Chadwick in 1932
The heaviest fundamental particle of an atom
Ans : Neutron
The least stable particle
Ans : Neutron
Neutrons are bound very tightly
Chargeless particle of an atom
Ans : Neutron
The atom without neutron
Ans : Protium (Isotope of Hydrogen)
Atomic number - It is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic number is denoted by the alphabet
Ans : Z
Mass number - The total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom
Mass number is denoted by
Ans : A
Anti particle of the neutron with the same mass of neutron
Ans : Anti neutron
Anti particle of the proton with the same mass of proton
Ans : Anti proton
Nuclear particle with the mass of an electron but opposite charge
Ans : Positron
Atomic Theory
Ans : John Dalton
Uncertainty Principle
Ans : Werner Heisenberg
Structure of Atom
Ans : Niels Bohr
Plum Pudding Model
Ans : J.J. Thomson
Wave Mechanics Model
Ans : Max Planck
Electron (-ve charge)
Ans : J.J. Thomson
Proton (ve charge)
Ans : Ernest Rutherford
Neutron (No charge)
Ans : James Chadwick
Nucleus (ve charge)
Ans : Ernest Rutherford
Positron (ve charge)
Ans : Carl Anderson
Antineutron (No charge)
Ans : Bruce Cork
The combining capacity of one atom to another
Ans : Valency
Atom is bigger than its nucleus
Ans : 10^5 times
Electrons move in a circular path called
Ans : Orbit
The maximum number of elements in an orbit is
Ans : 2
The orbit followed by a moving electrons around the nucleus of an atom
Ans : Shell
The maximum number of electrons in a shell
Ans : 2n2 (n = Number of shell)
MOLECULE

Smallest particle of a substance having all its properties
Ans : Molecule
The term molecule was coined by
Ans : Avogadro
The number of molecules obtained in 1 mole of gas is called
Ans : Avogadro Number
Avagadro Number
Ans : 6.023 xl023/mol
International mole day
Ans : October 23
The bricks of Universe
Ans : Molecules
The SI Unit of the amount of substance
Ans : Mole
A molecule made up of only one kind of atom is called
Ans : Monoatomic molecule
A molecule made up of two kinds of atom is called
Ans : Diatomic molecule
ELEMENTS

Substance which is composed of similar kind of atoms is called
Ans : Elements
The scientist who proved that the elements are made up of atoms
Ans : John Dalton
The term 'elements' was coined by
Ans : Robert Boyle
The first scientist who gave a definition to element is
Ans : Robert Boyle
The scientist who gave symbols for elements on the basis of their names
Ans : JohnJ.Berzelius
The scientist who classified elements into Metals and Non-metals
Ans : Lavoisier
Elements are classified into
Ans : Metals, non-metals and metalloids
Metals: Elements that conduct electricity and heat which tends to lose electrons
Non-Metals : Elements that do not conduct electricity and heat which tends to accept electrons.
Metalloids: Elements showing properties of both metals and non-metals
The international association which gives names of elements
Ans : International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC)
The headquarters of IUPAC
Ans : Zurich (Switzerland)
The most abundant element in the universe
Ans : Hydrogen
The second most abundant element in the universe
Ans : Helium
The only radio active element in liquid form
Ans : Francium
The only radio active element in gaseous form
Ans : Radon
The most electro positive stable element
Ans : Cesium
COMPOUND

The combination of two or more elements is called
Ans : Compounds
The separation of a compound into its elements by chemical means is called
Ans : Analysis
The formation of a compound by the union of elements is called
Ans : Synthesis
Examples: Water, Steam, Salt etc.
The recently discovered chemical compound for the treatment of cancer
Ans : Cisplatin
The element which forms largest number of compounds
Ans : Carbon
The second element which forms largest number of compounds
Ans : Hydrogen
COMPOUNDS AND ITS USES

Silver Iodide
Ans : For artificial rain
Formaldehyde
Ans : Preservation of dead bodies
Sodium citrate
Ans : Anti coagulant in blood bank
Sodium Benzoate
Ans : For preservation of grains and food
Silver Bromide
Ans : Manufacturing of photo films
Freon
Ans : Used in refrigerator as coolant
Sodium Peroxide
Ans : Air purifier in submarines
Carbon dioxide
Ans : Used in Fire extinguisher
MIXTURES

Two or more substances (elements or compounds or both) that do not combine chemically during the mixing
Ans : Mixtures
The two kinds of mixtures are :
Ans : Heterogeneous mixture and Homogeneous mixture
Heterogeneous mixture
Ans : Having more than one phase
Eg: Concrete, Wood
Homogeneous mixture
Ans : Having same proportions of its compounds through out a given sample. Two or more components are so evenly distributed in Homogeneous mixture
Eg: Quartz, Glass, Air
COLLOID AND EMULSION

A mixture of two faces of the matter is called
Ans : Colloid
Eg : Emulsion, Aerosols, Fog, Milk
A colloidal solution formed between two liquids is called
Ans : Emulsion
A colloid formed between gas particles and liquid or solid particles
Ans : Foam
Colloid which contains particles of liquid or solid dispersed in gas
Ans : Aerosol
ISOTOPES
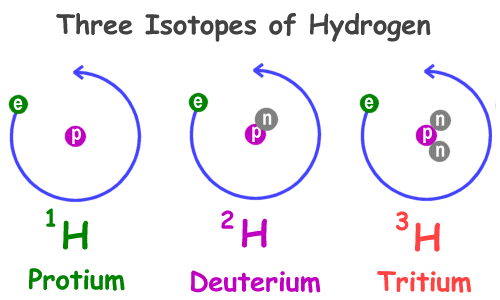
Atoms of the same element having same atomic number and different mass number are known as
Ans : Isotopes
Isotope was discovered by
Ans : Frederick Soddy
ISOTOPE AND ITS USAGE

Carbon 14
Ans : Used to determine the age of fossils
Cobalt 60
Ans : Used for the treatment of cancer
Phosphorous 32
Ans : Used for the treatment of skin cancer
Oxygen 15, Iodine - 131
Ans : Used as medicine
Isotopes differ in the number of
Ans : Neutrons
The isotopes of hydrogen are
Ans : Protium, Deuterium, Tritium
ISOBARS
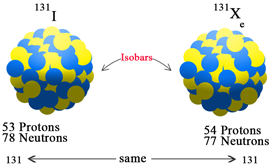
Elements having same mass number and different atomic number are known as
Ans : Isobars
Eg : Calcium - 40 (20 Ca^40), Argon - 40 (18Ar^40)
The term Isobars was suggested by
Ans : Alfred Walter Stewart
ISOTONES
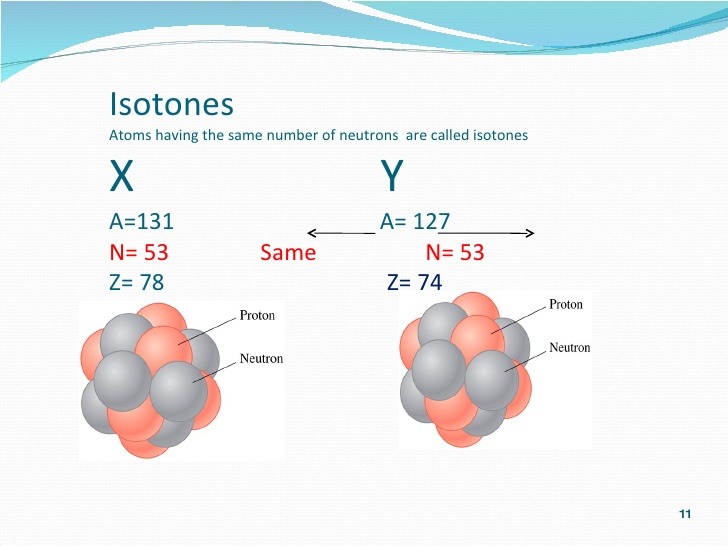
Atoms of elements- having same number of neutrons are called
Ans : Isotones
eg : Helium (2He^4) and Tritium (1H^3) (both contain 2 neutrons)
The term Isotones was formed by
Ans : K.Guggenheimer
ISOMERS
Compounds with same molecular formula but different structures are known as
Ans : Isomers
Eg: Glucose (C^6H^12O^6),Fructose (C^6H^12O^6)
ALLOTROPES
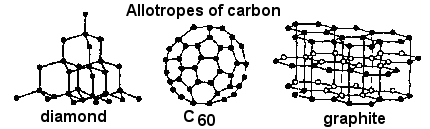
Different forms of the same element with different physical appearances are known as
Ans : Allotropes
Eg: Diamond, Graphite and Charcoal
are the allotropes of Carbon
The allotrope of Oxygen
Ans : Ozone
PERIODIC TABLE
An arrangement of elements with similar properties placed together is called
Ans : Periodic Table
Mendeleev's periodic table was based on
Ans : increasing order of atomic mass
Moseley's periodic table was based on the
Ans : atomic number of elements
The modern periodic table is based on
Ans : atomic number
Modern periodic table contains
Ans : 7 horizontal rows and 18 vertical columns
The periodic table was discovered by
Ans : Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev
Modern periodic table was discovered by
Ans : Henry Moseley
Periodic laws were put forward by
Ans : Mendeleev
Modern periodic laws were put forward by
Ans : Moseley
The scientist who classified elements based on Atomic Values is
Ans : Lothar Meyer
The rows are called
Ans : Periods
Columns are called
Ans : Groups
The left side of the periodic table denotes
Ans : Metals
The right side of the periodic table denotes
Ans : Non-metals
ELEMENTS SCIENTISTS

Hydrogen - Henry Cavendish
Oxygen - Joseph Priestly
Selenium - Berzelius
Thorium - Berzelius
Calcium - Humphry Davy
Sodium - Humphry Davy
Potassium - Humphry Davy
Boron - Humphry Davy
Barium - Humphry Davy
Uranium - Martin Klaproth
Radium - Madam Curie
Nitrogen - Daniel Rutherford
Fluorine - Henri Moissan
Iodine - Bernard Courtois
Chlorine - Carl Wilhelm Scheele
BHC - Michael Faraday
Methane - Alexander Volta
Titanium - William Gregor
Aluminium - Hans Orsted
Nitrous Oxide - Joseph Priestly
DDT - Paul Muller

Most abundant element on earth's crust - Oxygen
Most abundant metal in earth's crust - Aluminium
Most abundant metalloid in earth's crust - Silicon
Most abundant element in atmosphere - Nitrogen
Most abundant element in the universe - Hydrogen
Most abundant element in human body - Oxygen
Most abundant gas in atmosphere - Nitrogen
Most abundant element in sea water - Chlorine
Most abundant element in moon's surface - Titanium
Most abundant metal present in human body and bones - Calcium
Most abundant metal compound in bones - Calcium phosphate
Most abundant compound on earth's surface - Water (H2O)
Most abundant compound in sea water - Sodium Chloride
Second most abundant compound in sea water - Magnesium Chloride
Most chemically reactive element - Fluorine
Second most chemically reactive element - Chlorine
The lightest and simplest element - Hydrogen
The lightest metal - Lithium
The rarest element in the earth - Astatine
The heaviest element - Osmium
The heaviest gaseous element - Radon
First man made element - Technetium
Most stable element - Lead
The periodic table is divided into 4 main blocks
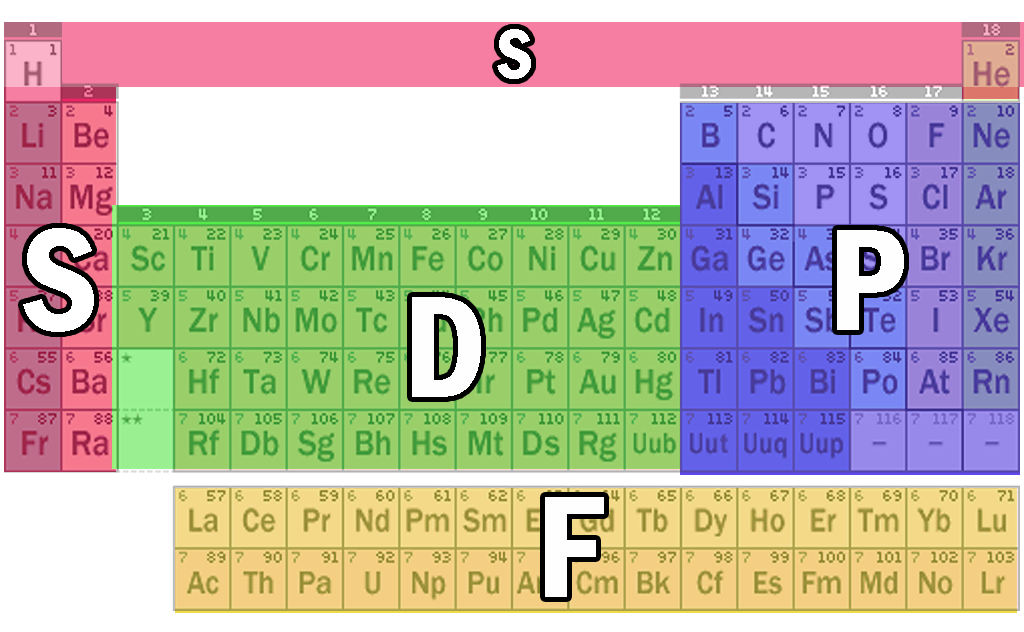
S block - elements of group 1 and 2
P block - elements of group 13 to 18
D block - elements of group 3 to 12
F block - Lanthanides and Actinides
The shortest period of the periodic table
Ans : First period
The longest period of the periodic table
Ans : Sixth period
Elements with atomic number 57-71 are known as
Ans : Lanthanides (rare earths)
Elements with atomic number 89-103 are known as
Ans : Actinides (radio active rare earths)
Total number of elements in periodic table
Ans : 118
The number of naturally occurring elements
Ans : 92
CLASSIFICATION OF GROUPS
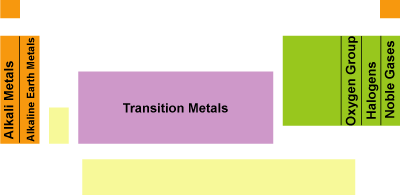
1st group -Alkali metals
2nd group- Alkaline earth metals
3-12 group -Transition elements
13thgroup -Boron family
14thgroup -Carbon family
15thgroup - Nitrogen family
16thgroup - Oxygen family
17thgroup - Halogen
18thgroup - Noble gas
The first artificial element
Ans : Technetium (Z = 43)
Man made elements are known as
Ans : Transuranics
CHARACTERISTICS OF PERIODIC TABLE
Features Top to bottom Left to right
Atomic size increases decreases
Ionization Energy decreases increases
Electron affinity decreases increases
Ionization potential decreases increases
CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
Metals and non-metals
Ans : Lavoisier
Triads
Ans : Dobereiner
Law of octaves
Ans : John Newland
Based on atomic weight
Ans : Mendeleev
Based on atomic number
Ans : Moseley
Element present in 1,2 and 13-18 groups are known as
Ans : Representative elements
All transitive elements are
Ans : Metals
Transitive elements form
Ans : Coloured compounds
ELEMENTS WITH SPECIAL NAMES

Name of earth - Tellurium (52)
Name of Moon - Selenium (34)
Name of Sun - Helium (2)
Name of Asteroid - Palladium (46)
Honour of women - Curium (96), Meitnerium (109)
Name of Ceres - Cerium(58)
Name of Uranus - Uranium (92)
Name of Neptune - Neptunium (93)
Name of Pluto - Plutonium (94)
ROOM TEMPERATURE CASES

The liquid metal at room temperature
Ans : Mercury
The liquid non-metal at room temperature
Ans : Bromine
Two elements which are liquids at room temperature
Ans : Bromine, Mercury
ELECTRONEGATIVITY
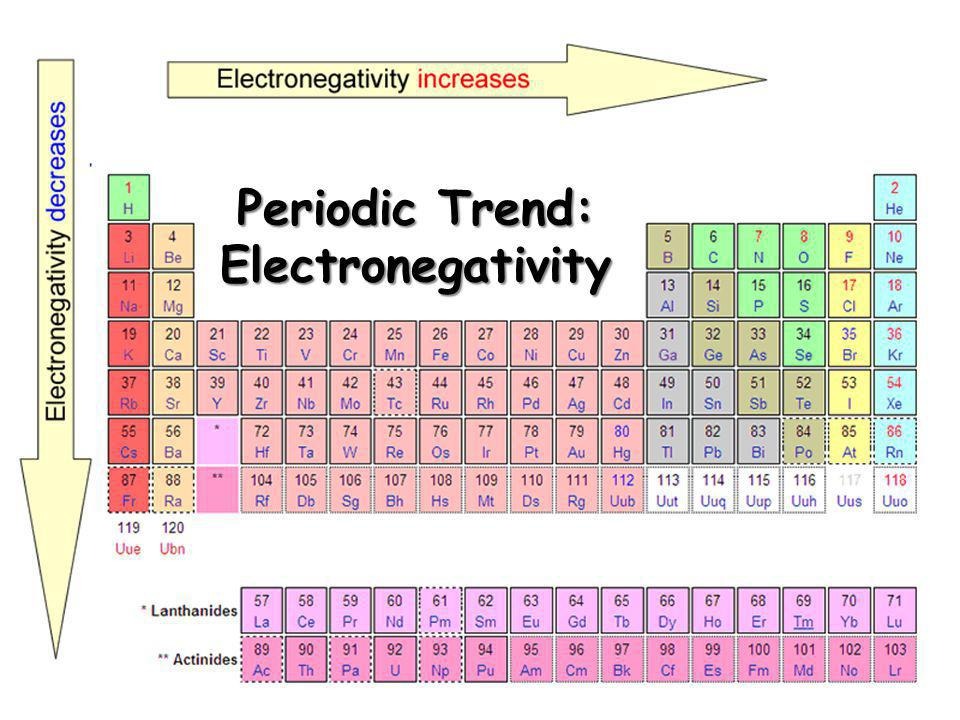
The ability of an atom to accept the electrons during molecular bond formulation is known as
Ans : Electro negativity
Electronegativity was discovered by
Ans : Linus Pauling
Electronegativity scale was invented by
Ans : Linus Pauling
The element which has most electronegativity
Ans : Fluorine
The elements which have least electronegativity
Ans : Francium, Caesium
CAESIUM

The metal used in atomic clocks
The metal which shows least expansion
Most electro positive stable element
Element having least electro negativity
ELEMENT SYMBOL LATIN NAME
Iron Fe Ferrum
Gold Au Aurum
Silver Ag Argentum
Copper Cu Cuprum
Antimony Sb Stibium
Mercury Hg Hydrargyrum
Sodium Na Natrium
Tungsten W Wolfram
Tin Sn Stannum
Potassium K Kalium
Lead Pb Plumbum
ATOMIC NO. ELEMENTS SYMBOLS
113 Nihonium Nh
115 Moscovium Mc
117 Tennessine Ts
118 Oganesson Og
TYPES OF REACTIONS
Two types of reactions are
Ans : Physical and Chemical reactions
PHYSICAL REACTION
A reaction in which no new substance is produced is called
Ans : Physical reaction It can be reversed
eg : Freezing, Melting
*OUR TELIGRAM GROUP LINK* : https://t.me/psccompanycorporation
