BIOLOGY 🔬 🌱
PSC Company Corporation Group
PART 1️⃣
INTRODUCTION
OUR TELIGRAM GROUP LINK 📲 https://t.me/psccompanycorporation
Father of Biology
Ans : Aristotle
The term Biology was first coined by
Ans : Lamarck
Father of Zoology
Ans : Aristotle
The living beings were classified into two (plants and animals) by
Ans : Aristotle
The animals were classified into animal with red blood and without red blood by
Ans : Aristotle

The famous book of Aristotle
Ans : History of Animals
Father of botany
Ans : Theophrastus
The famous book of Theophrastus
Ans : Historia plantum
The branch of biology which deals with the study of origin of life
Ans : Abiogenesis
The life originated from
Ans : Water
The first successful experiment based on the origin of life was done by
Ans : A.I. Oparin (1932)
First life is a microbes having the capacity of
Ans : Photosynthesis
The basic Chemical unit of life
Ans : Amino acids
Amino acids were first synthesized in a laboratory by
Ans : Stanley Miller and Harold Urey
Study of life in outer space
Ans : Exobiology
The basic unit of life
Ans : Cell
The cell is synthesized of chemicals such as carbohydrates, protein, lipid, nucleic acid etc.
The components of carbohydrates
Ans : Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Father of modern Botany
Ans : Carl Linnaeus
Father of Indian Botany
Ans : William Rosburgh
Scientist who discovered that the body of animal is made up of cell
Ans : Theodor Schwann
Scientist who discovered that the body of plant is made up of cell
Ans : M.J. Schleiden
Scientist who discovered that new cells are formed by the division of cell
Ans : Rudolph Virchow
The components of proteins are
Ans : Amino acids
Nucleic acids are responsible for
Ans : Heredity
CELL

The word cell is from the latin word.
Ans : Cellula
All living organisms are made up of
Ans : Cell
Study of cell - Cytology
Study of tissue - Histology
The physical unit of life
Ans : Protoplasm
Who invented the cell
Ans : Robert Hook in 1665
Cell theory was proposed by
Ans : M.J. Schleiden and Theodor Schwann (1839)

Scientist who observed cork cells under a microscope
Ans : Robert Hook
Plant cell was discovered by
Ans : Robert Hook
The term protoplasm was coined by
Ans:E. Purkinje
Scientist who called protoplasm as the physical basis of life
Ans:T.H. Huxley
Largest cell
Ans : Ostrich's egg
Smallest cell
Ans : Mycoplasma

Organisms known as pleuro pneumonia like organism (PPLO)
Ans : Mycoplasma
Smallest cell in the human body
Ans : Sperm
Largest cell in human body
Ans : Ovum
Longest cell in human body
Ans : Neuron
Power house of a cell
Ans : Mitochondria
Brain of the cell
Ans : Nucleus
Kitchen of the cell
Ans : Chloroplast
Energy Currency of the cell
Ans : ATP
Suicidal bag
Ans : Lysosomes
Traffic Police of the cell
Ans : Golgibodies

Skeletal system of the cell
Ans : Endoplasmic reticulum
The cell having most life span in human body
Ans : RBC
Cytoplasm and Nucleus are included in
Ans : Protoplasm
The cell organelle known as protein factory
Ans : Ribosome
The organelle in the site of protein synthesis
Ans : Ribosome
Ribosome has its own
Ans : RNA
Two types of acids present in cell
Ans : DNA and RNA

The basic unit of chromosome
Ans : DNA
The functional unit of DNA
Ans : Genes
Function of DNA
Ans : Transmission of hereditary traits
Function of RNA
Ans : Protein synthesis
Each chromosome has
Ans : A pair of DNA
DNA sugar is called
Ans : Deoxyribose
The nitrogen bases in DNA
Ans : Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine
The RNA sugar
Ans : Ribose
The nitrogen bases in RNA
Ans : Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine and Guanine
The double helical model of DNA was discovered by
Ans : James Watson and Francis Crick
The enzyme present in lysosome
Ans : Hydrolytic enzyme
Lysosome was discovered by
Ans : Christion de Duve (1955)
Compounds enter the cell through
Ans : Endoplasmic reticulum
The cell organelle which is the sites of energy transfer in living cell
Ans : Mitochondria

The functions of mitochondria
Ans : Cellular respiration, ATP production
The stage of cellular respiration which does not need oxygen
Ans : Glycolysis
The term Mitochondria was coined by
Ans : Carl Benda (1898)
Name the process in which the main product is energy
Ans : Cellular respiration
In mitochondria the energy is formed in the form of
Ans:ATP molecules
Which molecule is known as the energy currency
Ans : ATP molecule
ATP
Ans : Adenosine Triphosphate
The cell that lacks mitochondria and nucleus
Ans : RBC
Number of ATP molecule that will get from one molecule of glucose
Ans : 38ATP
The elements in the component of ATP
Ans : Nitrogen and phosphorus
Kerb's cycle is related to
Ans : Cellular respiration
Cell respiration was discovered by
Ans : Adolf Krebs
The whole process of a cell is controlled by
Ans : Nucleus
The cell without nucleus
Ans : Prokaryotic cell
The cell with nucleus
Ans : Eukaryotic cell
Nucleus was discovered by
Ans : Robert Brown
Name the process in which lysosome digest its own cell organelles
Ans : Autoplagy
A network like structure inside the nucleus is called
Ans : Chromatin Reticulum
The structure of cell is first explained in the book of
Micrographia
The living thing which do not obey cell theory.
Ans : Virus
The scientist first studied about all structure and cell reaction
Ans : Theodor Schwaan
Schwaan cell are seen in
Ans : Nerve cell
In plants, boundary of cell is made up of cellulose called
Ans : Cell wall

Outer most covering of plant cell is made up of
Ans : Cell wall
Cell wall is made up of
Ans : Cellulose
The hardest and undigestable sugar
Ans : Cellulose
Outermost covering of animal cell is made up of
Ans : Cell membrane
Cotton is the example of
Ans : Pure cellulose
The group of cells is known as
Ans : Tissue
HUMAN BODY

The base of life is
Ans : Amino acids
The largest cell in human body is
Ans : Neuron
Life originated from
Ans : Water
Theory of evolution was proposed by
Ans : Charles Darwin
The largest cell in human body
Ans : Ovum
The smallest cell in human body
Ans : Sperm
The main function of sweating is to regulate the
Ans : Body temperature
Normal temperature of human body
Ans : 36.9°C (98.4°F)
The temperature of human body in
Ans : Kelvin scale - 310K
The most abundant mineral in the human body
Ans : Calcium
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Central Nervous System consists of
Ans : Brain and Spinal cord
The whole nervous system controlled and co-ordinated by
Ans : Central Nervous System
The basic unit of nervous system is
Ans : Neuron
The speciality of neurons from other cell is that they lack the capability of
Ans : Cell division
The speed of impulses through neurons to brain is
Ans : 0.5 -100 m/s
The voltage difference (Resting membrane potential) of nerve fibre
Ans : 70 mV
Parts of Neuron
Ans : Axon, Dendron and Synaptic knob
The long fibre of neuron
Ans : Axon

Axon is covered by
Ans : Myelin Sheath
Myelin sheath is made up of
Ans : Fat molecules
Synaptic knob is seen at the top of
Ans : Axon
Group of axons which are covered by connective tissue known as
Ans : Nerves
Nerves are of three types
Ans : Sensory nerves, Motor nerves and Mixed nerves
The nerves that conduct impulses from sensory organs to brain or spinal cord is called
Ans : Sensory nerves
Mixed nerves are formed by
Ans : Sensory nerves and motor nerves

The axonite passes an impulse into another neuron through a junction called
Ans : Synapse
The transmitter substances which are present in the synapse are usually in the form of
Ans : Acetylcholine
Colour of the myelin sheath
Ans : White colour
The group of nerve cells which lack the myelin sheath are called
Ans : Grey matter
The group of nerve cell with myelin sheath are called
Ans : White matter
11th cranial nerve is an example of
Ans : Motor nerves
Vagus (cranial nerve), spinal nerve etc are examples of
Ans : Mixed nerves
Optic nerve is an example of
Ans : Sensory nerves
The disease that occurs due to the loss of neuron in the brain
Ans : Alzheimer's disease
The loss of motor neuron in the body
Ans : Parkinson's disease
BRAIN

Brain is enclosed and protected in
Ans : Cranium
Average weight of an adult human brain
Ans : 1.4 kg (1400 gm)
Brain is covered and protected by a three layered membrane known as
Ans : Meninges
Meningitis is affected to
Ans : Meninges
The diagnosis of bacterial meningitis is done by culture of
Ans : CSF sample
Vasopressin and oxytocin are produced by
Ans : Hypothalamus
It also controls the hormone production of
Ans : Pituitary gland
ADH (Vasopressin) is the hormone which regulates
Ans : Water content in the body
Key hormone for child birth
Ans : Oxytocin
Oxytocin also maintains the normal level of
Ans : Blood particles
The clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spine
Ans : Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
The fluid protects against the mechanical injury and external shock
Ans : Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
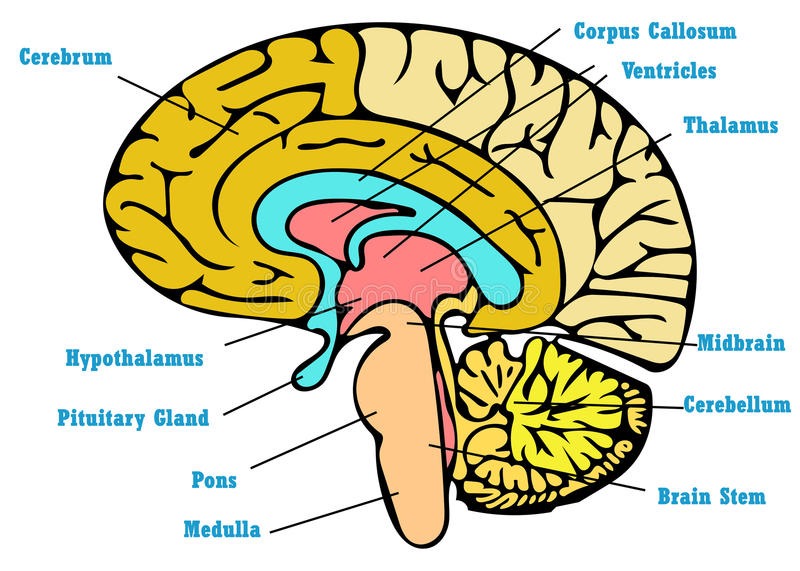
Brain can be divided into three parts
Ans : Cerebrum, Cerebellum and Medulla oblongata
CEREBRUM

The largest part of the brain
Ans : Cerebrum
The surface of the cerebrum is closely packed with cell body of
Ans : Neurons
The nerve band which separates the right and left hemispheres of the brain is called
Ans : Corpus callosum
The special nerve for speech language in the brain
Ans : Broca's area
The part of the cerebrum which is known as sensory speech area (motor speech area)
Ans : Broca's area
The seat of intelligence in brain
Ans : Cerebrum
The part of the cerebrum associated with the ability of recognise and understand language
Ans : Wernickers area
The part of brain which controls thoughts, emotion, will power, memory, consciousness, imagination, experience, recognisation, reasoning, laughing
Ans : Cerebrum
All voluntary actions are controlled by
Ans : Cerebrum
CEREBELLUM

Second largest part of the brain
Ans : Cerebellum
Cerebellum is seen just below the
Ans : Cerebrum
Cerebellum controls
Ans : Muscular movements
Equilibrium, Orientation and Balance of the body are controlled by
Ans : Cerebellum
Cerebellum is also known as
Ans : Little brain
Alcohol affects the
Ans : Cerebellum
MEDULLA OBLONGATA

The posterior most part of the brain
Ans : Medulla Oblongata
Medulla Oblongata seems like a rod and attached to the
Ans : Cerebellum
Involuntary actions like respiration, heart beat, contraction of blood vessels etc. are controlled by
Ans : Medulla Oblongata
The control centers of sneezing, coughing vomiting etc are also present in
Ans : Medulla Oblongata
The part of brain in which an injury causes a sudden death
Ans : Medulla Oblongata
THALAMUS

Thalamus is seen inside the
Ans : Brain
The centre of retransmission of impulses from cerebrum to cerebellum
Ans : Thalamus
Pain killers works on
Ans : Thalamus
HYPOTHALAMUS

Hypothalamus is seen just below the
Ans : Thalamus
Temperature regulation, hunger, thirst, emotional reactions etc are controlled by
Ans : Hypothalamus
Thermo regulatory centre of the human body
Ans : Hypothalamus
Part of the brain that helps to maintain the normal constitution of blood
Ans : Hypothalamus
SPINAL CORD

Spinal cord extends from medulla oblongata to posterior most part of
Ans : Vertebral column
Length of Spinal cord
Ans : 45 cm
Spinal cord is also covered with
Ans : Meninges
Spinal cord is situated in the neural canal of
Ans : Vertebral column
The site of reflex actions
Ans : Spinal Cord
CRANIAL NERVES

The nerves arising from the different part of brain is called
Ans : Cranial nerves
Number of cranial nerves
Ans : 12 pairs
Number of spinal nerves
Ans : 31 pairs
The longest cranial nerve in human body
Ans : Vagus nerve
SENSORY ORGANS

Environmental changes are detected through our
Ans : Sense organs
The human sense organs contain receptors that relay information through sensory neurons to the appropriate places within the
Ans : Nervous system
Eyes help to see the objects
Eyes are situated inside a body cavity of the skull called
Ans : Orbits
Study of eye and eye diseases
Ans : Ophthalmology
There are three layers present in the eye ball
Ans : Sclera, Choroid, Retina
The transparent front portion of sclera is known as
Ans : Cornea
The middle layer of eye, nourishes oxygen and food
Ans : Choroid
Behind the cornea the front portion of choroid, hangs like a vertical curtain called
Ans : Iris
The opening seen at the centre of iris is called
Ans : Pupil
The convex lens is present just behind the
Ans : Pupil
The innermost layer of eye where the image is formed
Ans : Retina
The space between lens and cornea is called
Ans : Aqueous chamber
Aqueous chamber is filled with
Ans : Aqueous humour
Aqueous humour supplies oxygen and nutrition for
Ans : Lens and cornea

The space between lens and retina is called
Ans : Vitreous chamber
Vitreous chamber is filled with
Vitreous humour
Vitreous humour helps to maintain the shape of
Ans : Eyeball
The 'safe guards of eye'
Ans : Eyelids
Yellow spot (fovea) is seen in
Ans : Retina
The area of keenest vision and the region is characterised by the presence of cones only
Ans : Yellow spot
Outer layer of eye - Sclera
Middle layer of eye - Choroid
Inner layer of eye - Retina
The cells responsible for dim light vision
Ans : Rods cells
The pigment present in rod cells
Ans : Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin is called
Ans : Visual purple
The compound obtained from vitamin A help to synthesize Rhodopsin
Ans : Retinin
The poor vision in Dim light is caused due to the deficiency of
Ans : Vitamin A
The poor vision in Dim light is known as
Ans : Night Blindness
Cone cells help to percept the colours and cone cells contain a pigment called
Ans : Photospin
Cells responsible for bright light vision and colour vision
Ans : Cone Cells
The enzyme present in tears are
Ans : Lysozymes
If the distant object is looked at fixedly, a clear image is formed in
Ans : Yellow spot
The right distance which enable the proper vision is
Ans : 25cm
The metal responsible for brightness of eye
Ans : Zinc
The metal seen in tear is
Ans : Zinc
The lens present in eye is
Ans : Biconvex lens
The lachrymal glands produce
Ans : Tears
EYE DISORDER

The disease caused by a reduction in the elasticity of lens, with age is called
Ans : Presbyopia
The lens becomes either partially or completely opaque with age
Ans : Cataract
The condition of not seeing distant objects clearly since the image is formed in front of the retina
Ans : Short-sight
Short- sight is otherwise known as
Ans : Myopia (Near- sightedness)
The defect of short- sight is corrected by using
Ans : Bi concave lens
The condition of not seeing near objects clearly since the image is formed behind the retina
Ans : Long-Sight
Long-sight is otherwise known as
Ans : Hypermetropia
The defect of long- sight is corrected by using
Ans : Bi convex lens
The condition of curvature of cornea become irregular and the image is not clearly formed
Ans : Astigmatism
The defect of Astigmatism is corrected by using
Ans : Cylindrical lens
The condition in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object
Ans : Crossed eye / Strabismus /Squint Eye
Squint eye is otherwise known as
Ans : Crossed eye / Strabismus
The defect of squint eye is corrected by
Ans : Eye surgery
The condition due to the increase of j pressure in the eye ball
Ans : Glaucoma
Pain in eyes and seeing halos around light are due to
Ans : Glaucoma
Inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid
Ans : Conjunctivitis (pink eye)
Disable to distinguish the colours is known as
Ans : Colour Blindness
A person who suffers colour blindness cannot distinguish
Ans : Red and Green
Colour blindess is also known as
Ans : Daltonism
Colour blindness was discovered by
Ans : John Dalton
The procedure of replacing abnormal corneal tissue with a healthy cornea is known as
Ans : Keratoplasty
The newly discovered layer in human cornea is
Ans : Dua's layer
Dua's layer is discovered by the Indian Scientist
Ans : Harminder Singh Dua
The abnormal protrusion of the eyeball or eyeballs is called
Ans : Exophthalmos
The visual activity can be measured using an eye chart called
Ans : Snellen chart
The retention of a visual image for a second after the removal of the object is called
Persistence of vision The instrument used to examine the inner eye
Ophthalmoscope
The first eye transplant surgery was done by
Edward Konard Sim (1905)
EAR

The organ of hearing and equilibrium
Ans : Ear
Each ear consists of three parts
Ans : External ear, middle ear and inner ear
The external or outer ear consists Of
Ans : Pinna, auditory canal and tympanic membrane
The narrow cavity middle ear consists of network of three bones
Ans : Malleus, incus and stapes
The minimum sound frequency for a human can hear
Ans : 20Hz
A normal person hears sound frequencies from
Ans : 20Hz to 20,000 Hz
Hammer like bone in the middle year
Ans : Malleus
Anvil like bone in the middle ear
Ans : Incus
Horse shoe shaped (stirrup) bone in ear
Ans : Stapes
The smallest bone in human body
Ans : Stapes
The narrow tube which connects the pharynx to middle ear cavity is called
Ans : Eustachian tube
The narrow tube which helps to maintain the air pressure of ear cavity
Ans : Eustachian tube
The membrane which separates middle ear from inner ear is called
Ans : Oval window
Inner part of the inner ear
Ans : Vestibule, cochlea and semi circular canals
The calcium carbonate particles present in Vestibules are called
Ans : Otoliths
The fluid filled in the inner ear are
Ans : Perilymph and Endolymph
The equilibrium of the body is maintained by
Ans : Vertibules and semi circular canals
The instrument used for examining the outer ear drum
Ans : Otoscope
The part of ear which has a shape of small snail shell
Ans : Cochlea
The part of ear which helps hearing
Ans : Cochlea
TONGUE

The taste sensation is possible through
Ans : Taste buds
The small projections on the surface of tongue are called
Ans : Papillae
The nerve that is related to the movement of tongue is called
Ans : Hypoglossal Nerve
The nerve related to taste, facial expression etc
Ans : Facial Nerve
Taste buds at the tip of the tongue are sensitive to
Ans : Salt and Sweet taste
Taste buds at the both side of the tongue are sensitive to
Ans : Sour taste
Taste buds at the back of the tongue are sensitive to
Ans : Bitter taste
The disease affecting the tongue is called
Ans : Red Beef Tongue
Substance which evokes sour taste
Ans : H ions
Substance which evokes salt taste
Ans : Na ions
SKIN

The study of skin is
Ans : Dermatology
The largest sensory organ in the body
Ans : Skin
Largest organ in the body
Ans : Skin
The sense of touch is great at the tips of
Ans : Fingers and toes
Skin weighs about
Ans : 5.5 Kg
Immunity, water balance, temperature regulation etc are functions of the
Ans : Skin
The outer layer of skin is called
Ans : Epidermis
The inner layer of skin is called
Ans : Dermis
Through respiration we obtain
Ans : Oxygen
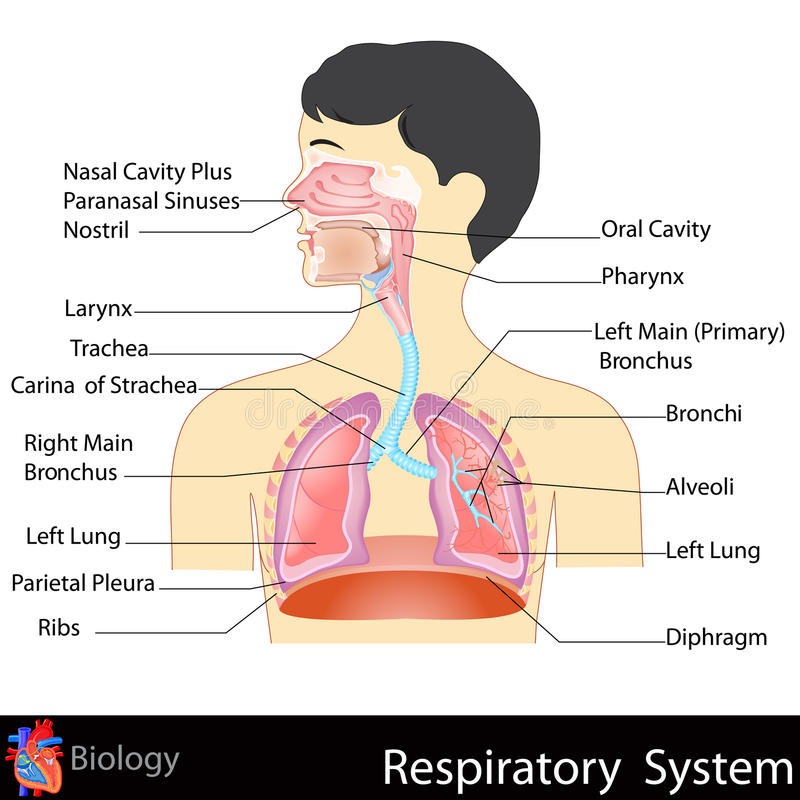
The respiratory system extends from nostrils to
Ans : Lungs
The arrangement to prevent the food particles entering the trachea during respiration is called
Ans : Epiglottis
The wall of the trachea is made up of
Ans : 'C' shaped cartilaginous rings
Lungs are situated in
Ans: Thorax
The organ without muscles
Ans: Lungs
These airsacs are known as alveoli (Singular: alveolus)Haemoglobin in RBC transport
Ans : Oxygen
The air that is expired and inspired during a normal respiration is called
Ans : Tidal air
The volume of air inspired and expired during normal respiration is called
Ans : Tidal volume (500ml)
The condition in which a person is not able to respire normally and won't get enough oxygen is called
Ans : Asphyxia
Lungs volume can be measured using
Ans : Spirometer
Pneumonia, Bronchitis, Emphysema, SARS, Silicosis, Tuberculosis, Asthma etc are diseases which affect the
Ans : Lungs
The amount of oxygen in expired air
Ans : 16%
The amount of oxygen is inspired air
Ans: 21%
The amount of C02 in inspired air
Ans : 5%
The amount C02 in expired air
Ans: 0.03%
CELLULAR RESPIRATION

The reactions takes place in the cell to liberate energy is called
Ans : Cellular respiration
Mitochondria was discovered by
Ans : Richard Altman (1886)
Powerhouse of the cell
Ans : Mitochondria
Mitochondria converts oxygen and nutrients into
Ans : Energy
In Mitochondria energy is stored in the form of
Ans : ATP
Kreb's cycle takes place in
Ans : Mitochondria
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM

The food we will eat pass through
Ans : Alimentary canal The organ which prevents the
The organ which prevents the entering of food in naso pharynx
Ans : Uvula
The pigment gives colour to skin
Ans : Melanin
The deficiency of melanin leads to a disease called
Ans : Albinism
The fluid gives softness to the skin and hair
Ans : Sebum
Sebaceous glands are the excretory glands
Eczema, Psoriasis, Melanoma, vitiligo etc are diseases that affected the
Ans : Skin
The disease in which the patches of epidermis detaches from the skin
Ans : Psoriasis
The average days takes to replace total old skin in human
Ans : 30 days
Warts is caused by
Ans : Virus
NOSE

The organ for both respiration and sense of smell
Ans : Nose
The condition in which smell cannot be recognized
Ans : Anosmia
The nerve which related to olfactory is known as
Ans : Olfactory nerve
The condition of bleeding from nose
Ans : Epistaxis
Snakes, lizards etc can detect smell through their
Ans : Tongues
The part of the brain which helps in olfactor is
Ans : Cerebrum
The ability of olfaction is high in
Ans : Sharks
In land the ability of olfaction is high in
Ans : Dog
ANIMALS AND THEIR WEIGHT OF BRAIN

Sperm whale- 7800g
Elephant - 5000g
Dolphin - 1700g
Human - 1400g
Horse - 530g
Cow - 500g
Chimpanzee- 420g
Dog - 72g
Cat - 30g
Rabbit - 12g
Owl - 2.2g
Rat - 2g
Frog - O.1g
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Energy for the life activities are obtained from
Ans : Food
The element which helps to release energy from food particles
Ans : Oxygen
The masticated food moves to stomach through
Ans : Oesophagus
The fluid which helps to break down lipid to smaller particles
Ans : Bile
Bile is secreted in
Ans : Liver
Digestive enzyme of starch
Ans : Amylase
Digestive enzyme of protein
Ans : Pepsin
Digestive enzyme of fat
Ans : Lipase
The enzyme present in saliva
Ans : Ptyalin
The enzyme which destroys the micro organisms in the food particles
Ans : Lysosyme
The protein which cannot digest by Pepsin
Ans : Keratin
The pigments present in bile
Ans : Bilirubin and biliverdin
The largest organ inside the human body
Ans : Small intestine
The water absorption takes place in
Ans : Large intestine
The nutrients in the digested food are absorbed from
Ans : Small intestine
Enzyme which converts starch to maltose
Ans : Ptyalin
The hormone secreted by stomach
Ans : Gastrin
KIDNEY

Study of Kidney
Ans : Nephrology
The bean shaped organ in human body
Ans : Kidneys
The major excretory organ in human body Pair of
Ans : Kidney
Name the tube that carries the wire from kidney to urinary bladder
Ans : Ureter
The organ which purify the blood and the waste materials excreted through urine
Ans : Kidneys
The organ situated behind the abdomen, are on each side of vertebral column
Ans : Kidneys
Each kidney weighs about
Ans : 150 g
1100 ml of blood pass through the kidney per
Ans : Minute
The micro sieves inside the kidney
Ans : Nephrons
The cup shaped part of a nephron
Ans : Bowman's capsule
The capillaries of the Bowman's capsule
Ans : Glomerulus
The organ affected by the poison of viper
Ans : Kidney
The 96% of urine is
Ans : Water
2% of urine is composed of
Ans : Urea and salt
The pale yellow colour of urine is the presence of a pigment known as
Ans : Urochrome
About 1.5 litre of unire is secreted by an adult man in
Ans : 24 hours
The hormone helps the kidney to reabsorb the water
Ans : Anti Diuretic Hormone
Diabetes insipidus is the disease caused by the deficiency of
Ans : ADH (vasopressin)
The disease caused by the inflammation of nephron
Ans : Nephritis
Nephritis is also known as
Ans : Bright's Disease
Surgical removal of kidney is called
Ans : Nephrectomy First transplanted organ Kidney
First kidney transplantation was done by
Ans : Dr.R.H.Laler (1950)
The element which causes kidney diseases
Ans : Cadmium
The type of pain caused by kidney stones when it blocks the urinary tract
Ans : Renal colic
Chemically kidney stone is
Ans : Calcium Oxalate
Renal artery is the blood vessel that carries blood to
Ans : Kidney
The blood vessel which carries blood filtered by the kidney
Ans : Renal vein
The process of removal of urea from the blood by equipments when both kidneys failed to remove urea
Ans : Dialysis
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM

Circulatory system include
Ans : Blood, blood vessels and heart
Blood Circulation was discovered by
Ans : William Harvey
The insect which has open circulatory system
Ans : Cockroach
Phylum Arthropods possess open circulatory system
Cockroach is the living being having most number of
Ans : Chambers in heart
Number of chambers in the heart of a cockroach
Ans : 13
The blood of cockroach is colourless due to the absence of
Ans : Haemoglobin
Closed type circulatory system is present in
Ans : Earth worm
The living being which has the smallest heart
Ans : Earthworm
In earthworm the heart is known as
Ans : Lateral hearts
Human being possess
Ans : Closed circulatory system
The important parts of human circulatory system are
Ans : Blood, blood vessels and heart
The blood capillaries were identified by
Ans : Marcello Malpighi
The instrument used to measure the blood pressure
Ans : Sphygmomanometer
The process of formation of blood cells
Ans : Haemopoiesis
The blood cells without nucleus
Ans : RBC and platelets
OUR TELIGRAM GROUP LINK 📲 https://t.me/psccompanycorporation
