Answers
Kither1. Construction management is a professional service that uses specialized, project management techniques to oversee the planning, design, and construction of a project, from its beginning to its end.
2. A Project Manager is a person who has the overall responsibility for the successful initiation, planning, design, execution, monitoring, controlling and closure of a project.
3. Financial Soundness, Technical Ability, Management Capability, Health and Safety and Reputation are some of the Bid Selection Methods.
4. Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring, Controlling and Closing are the principles and processes of Project Management.
5. An Event is a specific instant of time, which makes the start or end of an activity.
6. An Activity is the actual performance of the task and It is the work required to complete a specific task.
7. Estimating project time and cost, Planning and organizing resources, providing direction these are the uses of CPM.
8. Critical activities are the project tasks that must start and finish on time to ensure that the project ends on schedule. Non critical activies can be delayed for specific time interval and it won't affect project completion schedule.
9. Critical path is the path of activities that can't be delayed and that must start and finish on time.
10. The amount of time the scheduled activity can be delayed or extended from its early start start without delaying the project finish is called Float. A formula to calculate total float is LS (Late Start) – ES (Early Start) or LF (Late, Finish) – EF (Early Finish)
11. Plan Schedule Management.
Define Activities.
Sequence Activities
Estimate Activity Resources.
Estimate Activity Durations.
Develop Schedule.
These are the steps involved in scheduling process.
12.
- Finish-to-Start (FS): The successor activity cannot start unless the predecessor activity finishes.
- Start-to-Start (SS): The successor activity cannot start unless the predecessor activity starts.
- Start-to-Finish (SF): The successor activity cannot finish unless the predecessor activity starts.
- Finish-to-Finish (FF): The successor activity cannot finish unless the predecessor activity finishes.
13.
Gantt charts are useful for planning and scheduling projects. They help you assess how long a project should take, determine the resources needed, and plan the order in which you'll complete tasks. They're also helpful for managing the dependencies between tasks.
14.
Primavera P6 Project Layout Files are a valuable feature for mirroring reports on different projects in P6. It is possible to save or export and store P6 Project Layout Files in the windows operating system. These PLF files can then be imported and opened to produce a similar screen report on a different project.
15. Duration Percent Complete
Physical Percent Complete
Units Percent Complete
are the types of percentage complete.
16. Project > Maintain Baseline > Add
Project > Assign Baseline > Select > Close
Right Click Ghantt chart > Mark Project Baseline > Close.
17. Cost accounting is defined as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail.
19. By WPS & Docs option we can Add documents related to the particular activity.
PART B
2. EPS: The Enterprise Project Structure (EPS) is a hierarchy used to organize projects.
• The EPS is made of roots and nodes • Each root in the EPS can be sub-divided into many nodes • Nodes represent different levels within the structure • E.g., nodes can represent divisions within your company, departments, project groups, and site locations • All projects must be included in a node • Each node can contain an unlimited no. of projects • Projects always represent the lowest level of hierarchy • Placement of a project in the hierarchy determines the summary level in which it is included.
OPS: The Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS) is a hierarchy used to organize responsibilities.
• The OBS is made of roots and nodes • Each root in the OBS can be sub-divided into many nodes • Nodes represent different levels within the structure • E.g., nodes can represent subordinates within your company, departments, project groups, and site locations • All responsible persons must be included in a node • Each node can contain an unlimited no. of responsible persons
WBS: The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical arrangement of the products and services produced during, and by, a project. It enables you to divide a project into meaningful and logical pieces for the purpose of planning and control.
• Each project has a unique WBS hierarchy • The root level of the WBS is equal to the Project ID and Project Name • Elements within the WBS have parent/child relationship, which means that you can rollup and summarize information from the lower levels.
3.
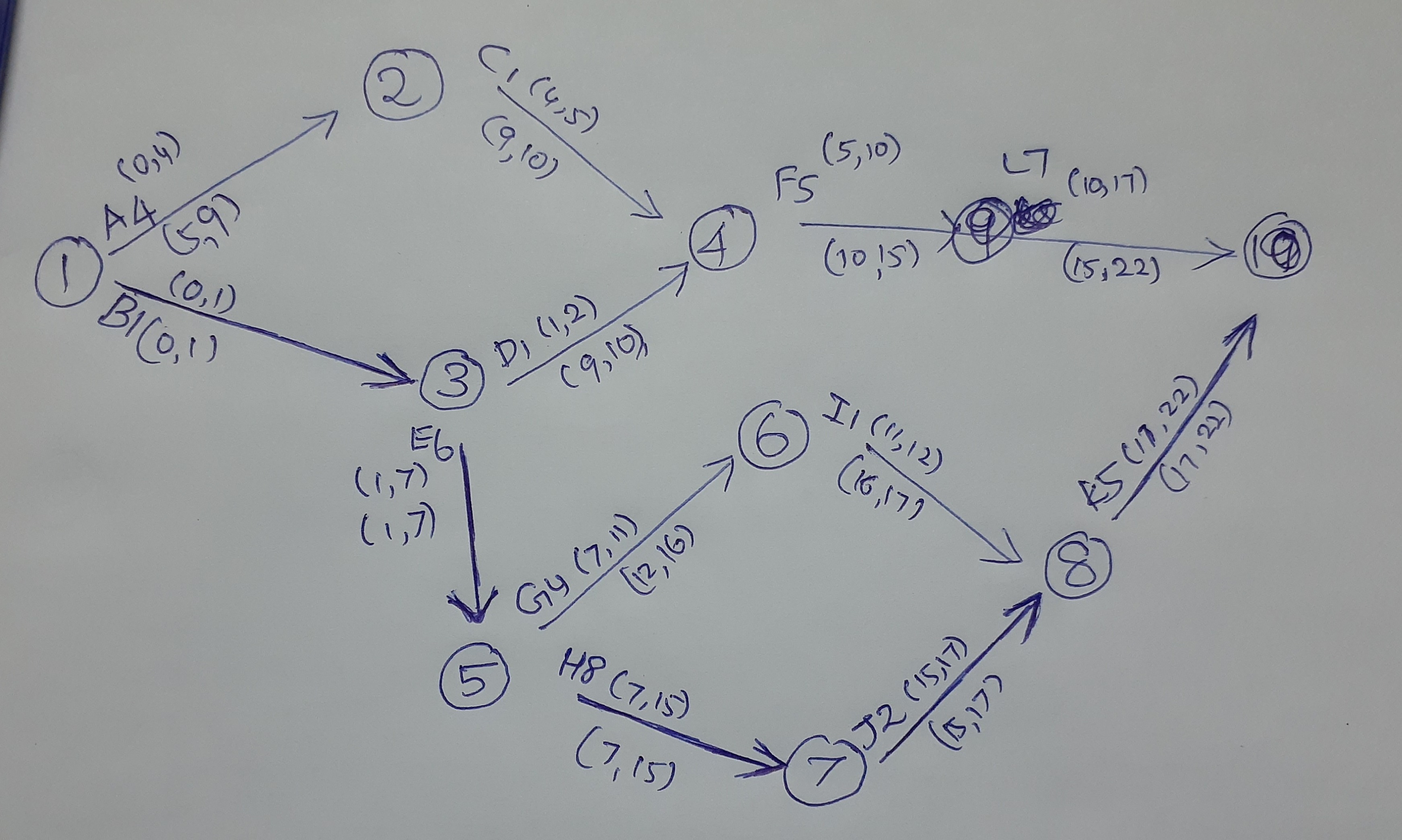
Activity(ES,EF)(LS,LF)
A(0,4)(5,9)
B(0,1)(0,1)
C(4,5)(9,10)
D(1,2)(9,10)
E(1,7)(1,7)
F(5,10)(10,15)
G(7,11)(12,16)
H(7,15)(7,15)
I(11,12)(16,17)
J(15,17)(15,17)
K(17,22)(17,22)
L(10,17)(15,22)
4. Activity Codes:
• Activity Codes enable you to classify and categorize activities according to you organizational and project needs.
• You can use activity codes to view and roll-up activities in the Activity Table; build reports in the Report Wizard or Report Editor; organize a layout by grouping activities into specific categories; and select and summarize activities.
• Examples include Phase, Area, Site, and Division.
• Activity codes can be defined at three levels • Global Level – Available to all activities in the database • Create an unlimited no. of global-level activity codes • Organize activities within a project or across the project structure • EPS Level – Available to all activities within the EPS node and its children • Create an unlimited no. of EPS-level activity codes • Organize activities within a project or across a portion of the EPS • Project Level – Available to activities only in the project in which code is defined • Create upto 500 activity codes per project • Filter and organize activities based on unique, project-specific requirements