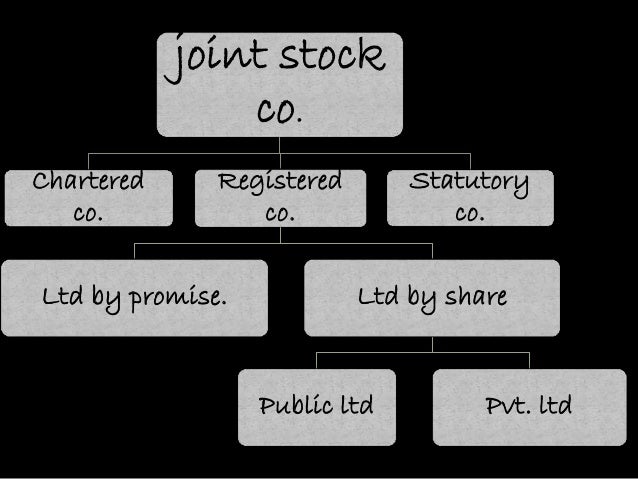
Public Joint Stock Company

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
РекламаИнтернет-магазин yoox.com. Скидки до -80%! Доставка по всей стране · пн-вс 10:00-22:00
РекламаРеально низкие цены! 10 лет на рынке! Доставка и самовывоз! Более 5000 продуктов! · Москва · пн-пт 10:00-18:00, сб 12:00-15:00
Продавец: vitfit.ru. ОГРНИП: 309774633000300
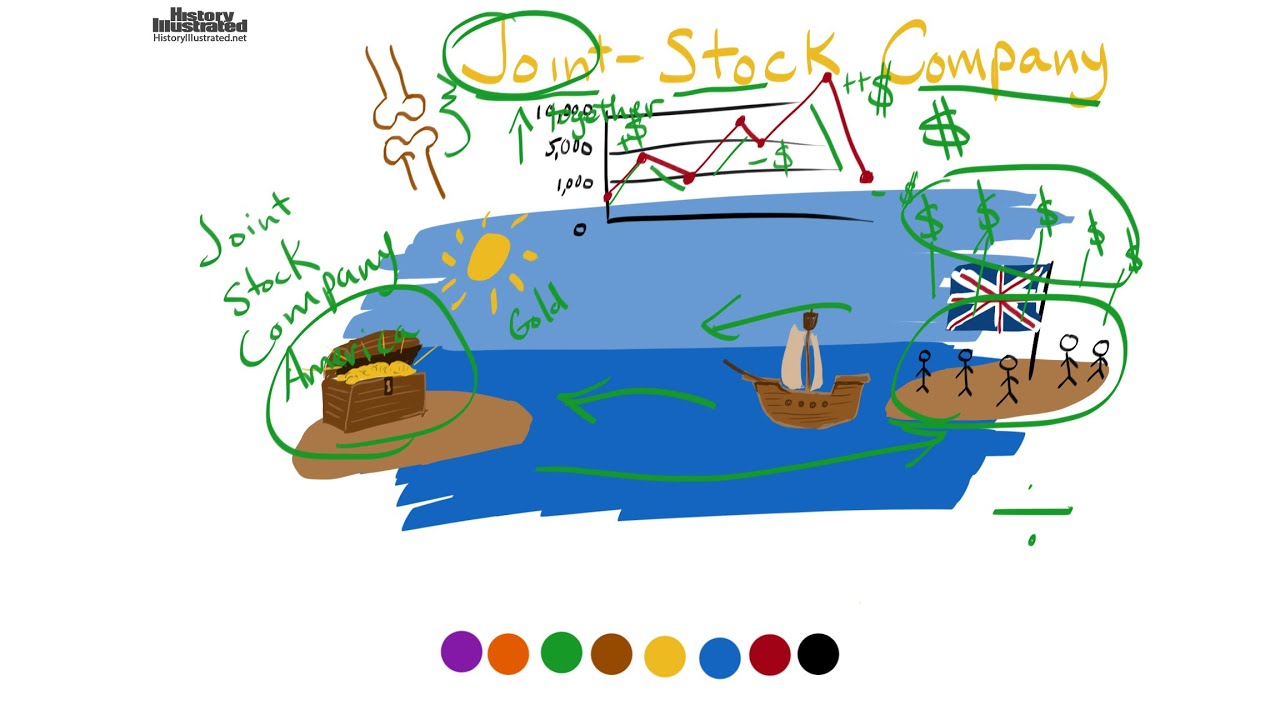
A public joint stock company is a method to allow thousands or millions of people to jointly own a business. The most important feature is limited liability. The most important function of a public joint stock company is that the investor can only lose their initial investment.
bizfluent.com/facts-5801561-public-joint-st…
What is a public joint stock company in UAE?
What is a public joint stock company in UAE?
Public Joint Stock Company (PJSC) is defined as an organization whose capital is divided into negotiable shares of equal value and a partner therein shall be liable only to the extent of his share in the capital of the company, in accordance with the UAE Federal Commercial Companies Law (the ‘Law”).
mimolegal.com/en/uae-onshore-public-joi…
What are the features of a public joint stock company?
What are the features of a public joint stock company?
A public joint stock company is a method to allow thousands or millions of people to jointly own a business. The most important feature is limited liability. Limited Liability. The most important function of a public joint stock company is that the investor can only lose their initial investment.
bizfluent.com/facts-5801561-public-joint-…
Is the New York Stock Exchange a joint stock company?
Is the New York Stock Exchange a joint stock company?
Public joint stock companies are the way that the vast majority of the economy is organized. Everything you see about the New York Stock Exchange and every reference to stocks rising or falling is about people trading shares of public joint stock companies.
bizfluent.com/facts-5801561-public-joint-…
What did the Joint Stock Company Act 1844 do?
What did the Joint Stock Company Act 1844 do?
Consequently, registration and incorporation of companies, without specific legislation, was introduced by the Joint Stock Companies Act 1844. Initially, companies incorporated under this Act did not have limited liability, but it became common for companies to include a limited liability clause in their internal rules.
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joint-stock_comp…
https://bizfluent.com/facts-5801561-public-joint-stock-company-.html
Перевести · 26.09.2017 · A public joint stock company is a method to allow thousands or millions of people to jointly own a business. The most important feature is limited …
mimolegal.com/en/uae-onshore-public-joint-stock-company
Перевести · Public Joint Stock Company (PJSC) is defined as an organization whose capital is divided into negotiable shares of equal value and a partner therein shall be …
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joint-stock_company
Ориентировочное время чтения: 10 мин
Australia
In Australia corporations are registered and regulated by the Commonwealth Government through the Australian Securities and Investments Commission. Corporations law has been largely codified in the Corporations Act 2001.
Brazil
In Brazilthere are many different types of lega…
Australia
In Australia corporations are registered and regulated by the Commonwealth Government through the Australian Securities and Investments Commission. Corporations law has been largely codified in the Corporations Act 2001.
Brazil
In Brazil there are many different types of legal entities (sociedades), but the two most common ones commercially speaking are (i) sociedade limitada, identified by "Ltda." or "Limitada" after the company's name, equivalent to the British limited liability company, and (ii) sociedade anônima or companhia, identified by "SA" or "Companhia" in the company's name, equivalent to the British public limited company. The "Ltda." is mainly governed by the new Civil Code, enacted in 2002, and the "SA", by Law 6.404, dated December 15, 1976, as amended.
Bulgaria
In Bulgaria, a joint-stock company is called a aktsionerno druzhestvo or AD (Bulgarian: Акционерно дружество or АД)
Canada
In Canada both the federal government and the provinces have corporate statutes, and thus a corporation may be incorporated either provincially or federally. Many older corporations in Canada stem from Acts of Parliament passed before the introduction of general corporation law. The oldest corporation in Canada is the Hudson's Bay Company; though its business has always been based in Canada, its Royal Charter was issued in England by King Charles II in 1670, and became a Canadian charter by amendment in 1970 when it moved its corporate headquarters from London to Canada. Federally recognized corporations are regulated by the Canada Business Corporations Act.
Chile
The Chilean form of joint-stock company is called sociedad por acciones (often abbreviated "SpA"). They were created in 2007 by Law N° 20.190, and they are the most recent variety of societary types, as they represent a simplified form of corporation – originally conceived for venture capital companies.
Czech Republic and Slovakia
The Czech form of the public limited company is called akciová společnost (a.s.) and its private counterpart is called společnost s ručením omezeným (s.r.o.). Their Slovak equivalents are called akciová spoločnosť (a.s.) and spoločnosť s ručením obmedzeným (s.r.o.).
German-speaking countries
Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Liechtenstein recognize two forms of company limited by shares: the Aktiengesellschaft (AG), analogous to public limited companies (or corporations in US/Can) in the English-speaking world, and the Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (GmbH), similar to the modern private limited company.
Italy
Italy recognizes three types of company limited by shares: the public limited company (società per azioni, or S.p.A.), the private limited company (società a responsabilità limitata, or S.r.l.), and the publicly traded partnership (società in accomandita per azioni, or S.a.p.a.). The latter is a hybrid of the limited partnership and public limited company, having two categories of shareholders, some with and some without limited liability, and is rarely used in practice.
Japan
In Japan, both the state and local public entities under the Local Autonomy Act (now 47 prefectures, made in the 19th century and municipalities) are considered to be corporations (法人, hōjin). Non-profit corporations may be established under the Civil Code.
The term "company" (会社, kaisha) or (企業 kigyō) is used to refer to business corporations. The predominant form is the Kabushiki gaisha (株式会社), used by public corporations as well as smaller enterprises. Mochibun kaisha (持分会社), a form for smaller enterprises, are becoming increasingly common. Between 2002 and 2008, the intermediary corporation (中間法人, chūkan hōjin) existed to bridge the gap between for-profit companies and non-governmental and non-profit organizations.
Norway
In Norway, a joint-stock company is called an aksjeselskap, abbreviated AS. A special and by far less common form of joint-stock companies, intended for companies with a large number of shareholders, is the publicly traded joint-stock companies, called allmennaksjeselskap and abbreviated ASA. A joint-stock company must be incorporated, has an independent legal personality and limited liability, and is required to have a certain capital upon incorporation. Ordinary joint-stock companies must have a minimum capital of NOK 30,000 upon incorporation, which was reduced from 100,000 in 2012. Publicly traded joint-stock companies must have a minimum capital of NOK 1 million.
Romania
In Romania, a joint-stock company is called "societate pe acțiuni". According to Law 31/1991 there are two types of joint-stock companies: "societatea pe acțiuni" and "societate în comandită pe acţiuni".
Russia
See: Open joint-stock company (OJSC).
Spain
In Spain there are two types of companies with limited liability: (i) "S.L.", or Sociedad Limitada (a private limited company), and (ii) "S.A.", or Sociedad Anónima (similar to a public limited company).
Ukraine
There exist several types of joint stock companies (Ukrainian: Акціонерне Товариство, Aktsionerne Tovarystvo) in Ukraine. Due to specifics of the Soviet economy, all enterprises in the Soviet republic as the rest of the Soviet Union were state owned and private entrepreneurship was strictly prohibited and criminally prosecuted. Following the Gorbachev initiated broad spectrum reforms (perestroika), there was introduced a term of khozraschet and permission for organization of public economic entities called cooperatives.
Following dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine's economy along with the rest former Soviet republics was further reformed to more liberal. Along with private entrepreneurship, many state owned companies were privatized, primarily by the former party's apparatchiks which gave a rise of another term "Red directors". Many companies started to be sold at open market and commercialized. Those companies were transformed in joint-stock companies by selling their shares for mutual cooperation and investment.
As in the rest former Soviet republics (predominantly Russia) in Ukraine were created following commercial companies:
• National Joint-stock company
• Open Joint-stock company
• Closed Joint-stock company
In 2009 further reforms were introduced and open joint-stock companies were forced to be restructured as public joint-stock company (Ukrainian: Публічне Акціонерне Товариство, Publichne Aktsionerne Tovarystvo) or private joint-stock company (Ukrainian: Приватне Акціонерне Товариство, Pryvatne Aktsionerne Tovarystvo).
Minimum amount of share capital is 1250 minimum wages (as of 1 January 2017 4,000,000 UAH or 148,000 USD).
Ukraine National Securities and Stock Market Commission is the main stock market state authority.
United Kingdom
Most companies are regulated by the Companies Act 2006. The most common type of company is the private limited company ("Limited" or "Ltd"). Private limited companies can either be limited by shares or by guarantee. Other corporate forms include the public limited company ("plc") and the private unlimited company.
Some corporations, both public and private sector, are formed by Royal Charter or Act of Parliament.
A special type of corporation is a corporation sole, which is an office held by an individual natural person (the incumbent), but which has a continuing legal entity separate from that person.
United States
Several types of conventional corporations exist in the United States. Generically, any business entity that is recognized as distinct from the people who own it (i.e., is not a sole proprietorship or a partnership) is a corporation. This generic label includes entities that are known by such legal labels as ‘association’, ‘organization’ and ‘limited liability company’, as well as corporations proper.
Only a company that has been formally incorporated according to the laws of a particular state is called ‘corporation’. A corporation was defined in the Dartmouth College case of 1819, in which Chief Justice Marshall of the United States Supreme Court stated that " A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible, and existing only in contemplation of the law". A corporation is a legal entity, distinct and separate from the individuals who create and operate it. As a legal entity the corporation can acquire, own, and dispose of property in its own name like buildings, land and equipment. It can also incur liabilities and enter into contracts like franchising and leasing. American corporations can be either profit-making companies or non-profit entities. Tax-exempt non-profit corporations are often called "501(c)3 corporation", after the section of the Internal Revenue Code that addresses the tax exemption for many of them.
In some states, such as Colorado, a corporation may represent itself pro se in courts of law in some situations
The federal government can only create corporate entities pursuant to relevant powers in the U.S. Constitution. Thus, virtually all corporations in the U.S. are incorporated under the laws of a particular state. A major exception to the federal non-participation in the incorporation of private businesses is in banking; under the National Bank Act, banks may receive charters from the federal government as "national banks", subjecting them to the regulation of the federal Office of the Comptroller of the Currency rather than state banking regulators.
All states have some kind of "general corporation law" (California, Delaware, Kansas, Nevada and Ohio actually use that exact name) which authorizes the formation of private corporations without having to obtain a charter for each one from the state legislature (as was formerly the case in the 19th century). Many states have separate, self-contained laws authorizing the formation and operation of certain specific types of corporations that are wholly independent of the state general corporation law. For example, in California, nonprofit corporations are incorporated under the Nonprofit Corporation Law, and in Illinois, insurers are incorporated under the Illinois Insurance Code.
Corporations are created by filing the requisite documents with a particular state government. The process is called "incorporation", referring to the abstract concept of clothing the entity with a "veil" of artificial personhood (embodying, or "corporating" it, ‘corpus’ being the Latin word for ‘body’). Only certain corporations, including banks, are chartered. Others simply file their articles of incorporation with the state government as part of a registration process.
Once incorporated, a corporation has artificial personhood everywhere it may operate, until such time as the corporation may be dissolved. A corporation that operates in one state while being incorporated in another is a "foreign corporation". This label also applies to corporations incorporated outside of the United States. Foreign corporations must usually register with the secretary of state's office in each state to lawfully conduct business in that state.
A corporation is legally a citizen of the state (or other jurisdiction) in which it is incorporated (except when circumstances direct the corporation be classified as a citizen of the state in which it has its head office, or the state in which it does the majority of its business). Corporate business law differs dramatically from state to state. Many prospective corporations choose to incorporate in a state whose laws are most favorable to its business interests. Many large corporations are incorporated in Delaware, for example, without being physically located there because that state has very favorable corporate tax and disclosure laws.
Companies set up for privacy or asset protection often incorporate in Nevada, which does not require disclosure of share ownership. Many states, particularly smaller ones, have modeled their corporate statutes after the Model Business Corporation Act, one of many model sets of law prepared and published by the American Bar Association.
As juristic persons, corporations have certain rights that attach to natural persons. The vast majority of them attach to corporations under state law, especially the law of the state in which the company is incorporated – since the corporations very existence is predicated on the laws of that state. A few rights also attach by federal constitutional and statutory law, but they are few and far between compared to the rights of natural persons. For example, a corporation has the personal right to bring a lawsuit (as well as the capacity to be sued) and, like a natural person, a corporation can be libeled.
Harvard College, an undergraduate school of Harvard University, formally the President and Fellows of Harvard College (also known as the Harvard Corporation), is the oldest corporation in the western hemisphere. Founded in 1636, the second of Harvard's two governing boards was incorporated by the Great and General Court of Massachusetts in 1650. Significantly, Massachusetts itself was a corporate colony at that time – owned and operated by the Massachusetts Bay Company (until it lost its charter in 1684) - so Harvard College is a corporation created by a corporation.
Many nations have modeled their own corporate laws on American business law. Corporate law in Saudi Arabia, for example, follows the model of New York State corporate law. In addition to typical corporations in the United States, the federal government, in 1971 passed the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA), which authorized the creation of 12 regional native corporations for Alaska Natives and over 200 village corporations that were entitled to a settlement of land and cash. In addition to the 12 regional corporations, the legislation permitted a 13th regional corporation without a land settlement for those Alaska Natives living out of the State of Alaska at the time of passage of ANCSA.
Closely held corporations and publicly traded corporations
https://www.linguee.ru/английский-русский/перевод/public+joint...
Примеры перевода, содержащие „Public Joint Stock Company“ – Русско-английский словарь и система поиска по миллионам русских переводов.
Рекламапоставщиков. Разумная цена. Бесплатная доставка · Москва
РекламаКупить технику Apple и аксессуары в фирменном магазине компании.
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Comstock Images/Comstock/Getty Images
A public joint stock company is a method to allow thousands or millions of people to jointly own a business. The most important feature is limited liability.
The most important function of a public joint stock company is that the investor can only lose their initial investment. Their liability is limited so that if the business fails they do not then have to pay more to cover any debts.
The stock of the company is the machines, plants, patents and so on and this is owned jointly. Each investor owns a small part of the whole. Any profits are divided out according to what share of the company each owns.
Public refers to ownership of a share of the company being open to the public. This most often means that it is traded on a stock exchange and anyone willing to pay the price on the day can become a part owner of the company.
Public joint stock companies are the way that the vast majority of the economy is organized. Everything you see about the New York Stock Exchange and every reference to stocks rising or falling is about people trading shares of public joint stock companies.
The combination of limited liability and widespread ownership is w
Google Hairy Pussy
Big Hairy Pussy Old Granny
Perky Black Tits
Sleeping Ass Fucking
Overwatch Custom Game
What Is a Public Joint Stock Company? | Bizfluent
Public Joint Stock Company | Mimo Legal Consulting
Joint-stock company - Wikipedia
Public Joint Stock Company - Русский перевод – Словарь Ling…
Public Joint Stock Company