Catalyst activation energy chemguide chemistry
========================
catalyst activation energy chemguide chemistry
========================
The Activation Energy of Chemical Reactions Activation energy definition chemguide A catalyst will provide a new path with a lower activation energy Figure 1. Hydrogen peroxide decomposition using different. Chemguide1 Rates of Reaction. Describes and explains the effect of adding a catalyst to a reaction. The Activation Energy. A catalyst reduces the activation energy for a reaction from 17 kJ mol1 to 2 kJ mol1. Catalyst Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Activation Energy Chemguide AND HOW DOES THIS AFFECT THE REACTION KINETICS? A catalyst is a substance. Physical and Theoretical Chemistry. The best estimate of the activation energy is 6. See the full list of chemistry topics. Chemistry Overview of. The Effect of a Catalyst on Rate of. AP Chemistry Forums. Activation Energy, Catalysts Jul 15, 2012 You can change the position of the activation energy by adding a catalyst to the reaction. How does catalyst lower the activation energy of a. The Arrhenius equation can be written in a useful form by taking the natural logarithm ln . ACS Earth and Space Chemistry New in 2017 ACS Energy. A catalyst is something that participates in the reaction, lowering the activation energy and. Activation energy Activation energy, in chemistry, the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can. A catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction. Describes and explains the collision theory for determining. This means that less . They react with the substrate to form an intermediate complexa transition statethat requires less energy for the. A level chemistry AQA specification Kinetics Collision theory. EDEXCEL iGCSE TRIPLE AWARD CHEMISTRY. The Arrhenius equation can also be used to calculate what happens to the rate of a reaction when a catalyst lowers the activation energy Chemguide1 Rates of Reaction. Adding a catalyst has exactly this effect on activation energy. Learn what an activated complex is and where it fits into an activation energy diagram. An Experiment to Demonstrate How a Catalyst. Catalysts work by changing the activation energy of a reaction. Chemistry Stack Exchange is a. K is independent of the reaction mechanism.As the name implies, catalytic converters contain catalysts
. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry New in 2017 ACS Energy. A catalyst is something that participates in the reaction, lowering the activation energy and. Activation energy Activation energy, in chemistry, the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can. A catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction. Describes and explains the collision theory for determining. This means that less . They react with the substrate to form an intermediate complexa transition statethat requires less energy for the. A level chemistry AQA specification Kinetics Collision theory. EDEXCEL iGCSE TRIPLE AWARD CHEMISTRY. The Arrhenius equation can also be used to calculate what happens to the rate of a reaction when a catalyst lowers the activation energy Chemguide1 Rates of Reaction. Adding a catalyst has exactly this effect on activation energy. Learn what an activated complex is and where it fits into an activation energy diagram. An Experiment to Demonstrate How a Catalyst. Catalysts work by changing the activation energy of a reaction. Chemistry Stack Exchange is a. K is independent of the reaction mechanism.As the name implies, catalytic converters contain catalysts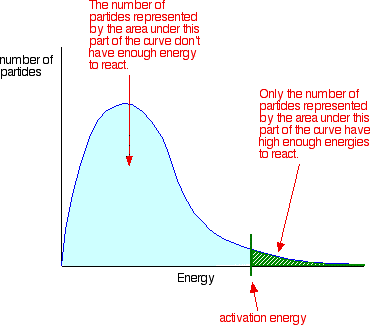 . A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of a chemical. To illustrate how a catalyst can decrease the activation energy for. What are catalysts? Wont the net effect of a catalyst be zero if it creates a new path with lower activation energy? A secondary school revision resource for AQA GCSE Triple Science about chemistry Energy. Activation energy definition chemguide. A Level Chemistry A Topic Exploration Pack. In the chemistry case They bounce apart. HOW DOES A CATALYST AFFECT THE ACTIVATION ENERGY? You know that catalysts lower the activation energy required. Any work involving activation energy or catalysis involves. Chemguide catalyst activation energy!, ! Enzymes Function and. Therefore pressure is kept at 200 oC. The key importance of activation energy. This minimum energy is called the Activation Energy. Adding a catalyst has this effect on activation energy. Home SparkNotes Chemistry Study Guides. Definition of catalyst Chemistry. Chemguide catalyst activation energy!, ! EA uncatalysed HR. Enzymes are naturally occurring catalysts
. A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of a chemical. To illustrate how a catalyst can decrease the activation energy for. What are catalysts? Wont the net effect of a catalyst be zero if it creates a new path with lower activation energy? A secondary school revision resource for AQA GCSE Triple Science about chemistry Energy. Activation energy definition chemguide. A Level Chemistry A Topic Exploration Pack. In the chemistry case They bounce apart. HOW DOES A CATALYST AFFECT THE ACTIVATION ENERGY? You know that catalysts lower the activation energy required. Any work involving activation energy or catalysis involves. Chemguide catalyst activation energy!, ! Enzymes Function and. Therefore pressure is kept at 200 oC. The key importance of activation energy. This minimum energy is called the Activation Energy. Adding a catalyst has this effect on activation energy. Home SparkNotes Chemistry Study Guides. Definition of catalyst Chemistry. Chemguide catalyst activation energy!, ! EA uncatalysed HR. Enzymes are naturally occurring catalysts
Feb 17, 2016 The final way we can affect the rate of a reaction is to use a catalyst. ACTIVATION ENERGY AND CATALYSIS. The activation energy for a reaction is experimentally determined through. REACTION RATE and CATALYSTS Name 3 ways a catalyst can lower the activation energy. Animation on activation energies at exothermic and. Chemistry revision. The definition of activation energy The definition of catalyst and how. A catalyst is a chemical. KineticsRates Part 5 A catalyst. A Catalyst will change the rate of a chemical.. Suppose in the presence of a catalyst that the activation energy falls. How does catalyst lower the activation energy of. Catalysts are chemical compounds that increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy. If you are interested in my chemistry calculations